深入学习区块链的隐私保护(四)秘密共享
秘密共享是指将秘密以适当的方式拆分,拆分后的每一个份额由不同的参与者管理,单个参与者无法恢复秘密信息,只有若干个参与者一同协作才能恢复秘密消息。秘密共享的概念最早由著名密码学家Shamir【1】和Blakley【2】于1979年分别基于拉格朗日插值法、多维空间点的性质给出了各自的方案。他们的方案由两个算法组成,秘密份额的分配算法和秘密的恢复算法。秘密份额的分配算法是将秘密分为若干子份,并将每个子份发送给不同参与者。秘密的恢复算法是指当参与者收集到足够多的子份后,可以调用该算法恢复出原始秘密。
Shamir和Blakley的方案都是基于参与者诚实的假设下进行设计的,这种假设在现实生活中无法得到满足。Chor等人于1985年提出了可验证秘密分享的概念【3】,用以解决分发者欺骗问题。可验证秘密分享在秘密分享的基础上增加了一个验证算法,即参与秘密共享的成员可以通过公开变量验证自己所拥有的子秘密的正确性。可验证秘密分享通过其验证算法是否需要参与者之间的交互分为两类:交互式的和非交互式的。交互式的可验证秘密共享方案包括【4-6】等,非交互式的可验证秘密共享方案包括【7-9】等。在可验证秘密共享中只有参与者自己可以验证自己收到的秘密份额是否正确,这使得可验证秘密共享的应用在一定程度上受到限制。因此公开可验证的秘密共享方案被提出\cite{ref14},即任何人都可以验证份额的正确性。随后,Schoenmakers【11】提出了一个构造简单、安全性和效率较高的公开可验证的秘密共享方案,该方案的安全性依赖于离散对数问题和Diffie-Hellman问题。
首先介绍经典的秘密共享方案-Shamir门限秘密共享,假设需要分享的秘密为![]() ,参与者的个数为
,参与者的个数为![]() ,当参与者收集到至少
,当参与者收集到至少![]() 个子份额后可恢复秘密,过程如下:
个子份额后可恢复秘密,过程如下:
- 秘密份额的分配算法:秘密的拥有者随机选择一个经过点
 的
的 次多项式
次多项式 ,其中
,其中 。然后,计算每个参与者
。然后,计算每个参与者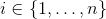 的秘密份额
的秘密份额 ,其中
,其中 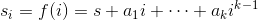 。最后,将计算的秘密份额发送给各个参与者。
。最后,将计算的秘密份额发送给各个参与者。 - 秘密的恢复算法:当参与者收集到
 个秘密份额
个秘密份额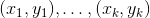 后,使用插值公式计算
后,使用插值公式计算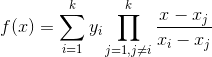 ,计算秘密
,计算秘密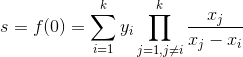 。
。
接下来介绍Schoenmakers提出的公开可验证的秘密共享方案,该秘密分享方案使用了一个非交互式证明方案![]() ,用来证明如下论据:证明者在不公开
,用来证明如下论据:证明者在不公开![]() 的前提下,证明
的前提下,证明![]() 和
和![]() 是使用同一个值
是使用同一个值![]() 生成的,即
生成的,即![]() 。
。
- 生成证据算法:证明者随机选取
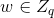 ,计算
,计算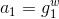 和
和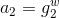 。然后计算
。然后计算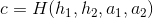 ,
,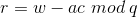 ,证据
,证据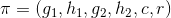 。
。 - 验证证据算法:验证者在收到
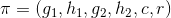 后,计算
后,计算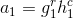 和
和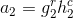 ,计算
,计算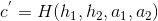 ,如果
,如果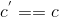 ,则验证通过,即相信证明者的论据。
,则验证通过,即相信证明者的论据。
假设![]() 表示为一个阶为
表示为一个阶为![]() 的群,其中
的群,其中![]() 为大素数。选取
为大素数。选取![]() ,
,![]() 为相互独立的生成元,即没人知道如何由
为相互独立的生成元,即没人知道如何由![]() 生成
生成![]() 。参与者的个数为
。参与者的个数为![]() ,参与者
,参与者![]() 的私钥为
的私钥为![]() ,对应的公钥为
,对应的公钥为![]() 。秘密的拥有者选取
。秘密的拥有者选取![]() ,计算秘密
,计算秘密![]() 。Schoenmakers公开可验证的秘密共享方案如下:
。Schoenmakers公开可验证的秘密共享方案如下:
- 秘密份额的分配算法:秘密的拥有者随机选择一个经过点
 的
的 次多项式
次多项式 ,其中
,其中 ,
, 。然后,计算每个参与者
。然后,计算每个参与者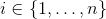 的秘密份额
的秘密份额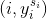 和
和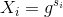 ,其中
,其中  。令
。令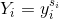 ,为每一对
,为每一对 和
和 ,调用
,调用 算法,生成公开可验证的证据
算法,生成公开可验证的证据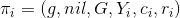 。并且发布公开的承诺
。并且发布公开的承诺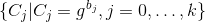 。
。 - 秘密份额的验证算法:任何人都可以通过
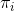 对碎片
对碎片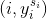 进行合法性验证,验证者计算
进行合法性验证,验证者计算 ,其中
,其中 。将
。将 放入
放入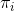 ,此时
,此时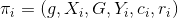 ,对
,对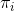 进行
进行 验证,若通过,则该碎片合法。
验证,若通过,则该碎片合法。 - 秘密份额的解密算法:参与者
 使用私钥
使用私钥 对秘密份额
对秘密份额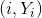 进行解密,计算
进行解密,计算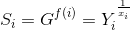 ,并且为了证明
,并且为了证明 确实是由
确实是由 生成,即需要证明参与者知道私钥
生成,即需要证明参与者知道私钥 ,并且
,并且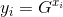 和
和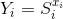 使用了该私钥。因此调用
使用了该私钥。因此调用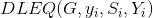 ,生成证据
,生成证据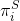 。
。 - 秘密的恢复算法:当某个参与者收集到足够多的正确秘密份额
 (正确秘密份额的判断是对证据
(正确秘密份额的判断是对证据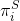 进行验证),该参与者通过如下计算恢复出秘密值
进行验证),该参与者通过如下计算恢复出秘密值 ,其中
,其中 。
。
参考文献:
【1】Shamir A. How to share a secret[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1979, 22(11): 612-613.
【2】Blakley G R. Safeguarding cryptographic keys[C]//1979 International Workshop on Managing Requirements Knowledge (MARK). IEEE, 1979: 313-318.
【3】Chor B, Goldwasser S, Micali S, et al. Verifiable secret sharing and achieving simultaneity in the presence of faults[C]//26th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (sfcs 1985). IEEE, 1985: 383-395.
【4】Ben-Or M, Goldwasser S, Wigderson A. Completeness theorems for non-cryptographic fault-tolerant distributed computation[M]//Providing Sound Foundations for Cryptography: On the Work of Shafi Goldwasser and Silvio Micali. 2019: 351-371.
【5】Chaum D, Crépeau C, Damgard I. Multiparty unconditionally secure protocols[C]//Proceedings of the twentieth annual ACM symposium on Theory of computing. 1988: 11-19.
【6】Rabin T, Ben-Or M. Verifiable secret sharing and multiparty protocols with honest majority[C]//Proceedings of the twenty-first annual ACM symposium on Theory of computing. 1989: 73-85.
【7】Feldman P. A practical scheme for non-interactive verifiable secret sharing[C]//28th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (sfcs 1987). IEEE, 1987: 427-438.
【8】Pedersen T P. Non-interactive and information-theoretic secure verifiable secret sharing[C]//Annual international cryptology conference. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1991: 129-140.
【9】Gennaro R, Rabin M O, Rabin T. Simplified VSS and fast-track multiparty computations with applications to threshold cryptography[C]//Proceedings of the seventeenth annual ACM symposium on Principles of distributed computing. 1998: 101-111.
【10】Stadler M. Publicly verifiable secret sharing[C]//International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1996: 190-199.
【11】Schoenmakers B. A simple publicly verifiable secret sharing scheme and its application to electronic voting[C]//Annual International Cryptology Conference. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1999: 148-164.