JavaWeb基础系列(四)Session和Cookie
一、会话技术简介
1. 存储客户端的状态
由一个问题引出今天的内容,例如网站的购物系统,用户将购买的商品信息存储到哪里?因为Http协议是无状态的,也就是说每个客户访问服务器端资源时,服务器并不知道该客户端是谁,所以需要会话技术识别客户端的状态。会话技术是帮助服务器记住客户端状态(区分客户端)
2. 会话技术
从打开一个浏览器访问某个站点,到关闭这个浏览器的整个过程,成为一次会话。会话技术就是记录这次会话中客户端的状态与数据的。
会话技术分为Cookie和Session:
Cookie:数据存储在客户端本地,减少服务器端的存储的压力,安全性不好,客户端可以清除cookie
Session:将数据存储到服务器端,安全性相对好,增加服务器的压力
二、Cookie技术
Cookie技术是将用户的数据存储到客户端的技术,我们分为两方面学习:
第一,服务器端怎样将一个Cookie发送到客户端
第二,服务器端怎样接受客户端携带的Cookie
2.1、服务器端向客户端发送一个Cookie
(1)创建Cookie:
Cookie cookie = new Cookie(String cookieName,String cookieValue);
示例:
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("username","zhangsan");那么该cookie会以响应头的形式发送给客户端:
![]()
注意:Cookie中不能存储中文
(2)设置Cookie在客户端的持久化时间:
cookie.setMaxAge(int seconds); —时间秒
注意:如果不设置持久化时间,cookie会存储在浏览器的内存中,浏览器关闭 cookie信息销毁(会话级别的cookie),如果设置持久化时间,cookie信息会被持久化到浏览器的磁盘文件里。
//示例:
//设置cookie信息在浏览器的磁盘文件中存储的时间是10分钟,过期浏览器自动删除该cookie信息
cookie.setMaxAge(10*60);(3)设置Cookie的携带路径:
cookie.setPath(String path);
注意:如果不设置携带路径,那么该cookie信息会在访问产生该cookie的 web资源所在的路径都携带cookie信息
//示例:
cookie.setPath("/WEB16");
//代表访问WEB16应用中的任何资源都携带cookie
cookie.setPath("/WEB16/cookieServlet");
//代表访问WEB16中的cookieServlet时才携带cookie信息(4)向客户端发送cookie:
response.addCookie(Cookie cookie);
(5)删除客户端的cookie:
如果想删除客户端的已经存储的cookie信息,那么就使用同名同路径的持久化时间为0的cookie进行覆盖即可
2.2、服务器端怎么接受客户端携带的Cookie
(1)通过request获得所有的Cookie:
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();(2)遍历Cookie数组,通过Cookie的名称获得我们想要的Cookie
for(Cookie cookie : cookies){
if(cookie.getName().equal(cookieName)){
String cookieValue = cookie.getValue();
}
}2.3、案例:显示用户上次访问时间
@WebServlet(name = "Cookie",
urlPatterns = {"/Cookie"})
public class Cookie extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request,response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获得当前时间
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
String CurrentTime = format.format(date);
//1、创建cookie对象,记录最新的访问时间
javax.servlet.http.Cookie cookie = new javax.servlet.http.Cookie("lastAccessTime",CurrentTime);
cookie.setMaxAge(60*10);
response.addCookie(cookie);
//2、获得客户端携带的Cookie -- lastAccessTime
String lastAccessTime = null;
javax.servlet.http.Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
if( cookie != null ){
for (javax.servlet.http.Cookie coo : cookies){
if("lastAccessTime".equals(coo.getName())){
lastAccessTime = coo.getValue();
}
}
}
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
if(lastAccessTime == null){
response.getWriter().write("您是第一次访问");
}else{
response.getWriter().write("您上次的访问时间是:"+lastAccessTime);
}
}
}三、Session技术
Session技术是将数据存储在服务器端的技术,会为每个客户端都创建一块内存空间 存储客户的数据,但客户端需要每次都携带一个标识ID去服务器中寻找属于自己的内 存空间。所以说Session的实现是基于Cookie,Session需要借助于Cookie存储客户的唯一性标识JSESSIONID。

3.1、获得Session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
此方法会获得专属于当前会话的Session对象,如果服务器端没有该会话的Session对象会创建一个新的Session返回,如果已经有了属于该会话的Session直接将已有的Session返回(实质就是根据JSESSIONID判断该客户端是否在服务器上已经存在 session了)
@WebServlet(name = "Session",
urlPatterns = {"/Session"})
public class Session extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request,response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
String id = session.getId();
System.out.println(id);
}
}3.2、怎样向session中存取数据(session也是一个域对象)
Session也是存储数据的区域对象,所以session对象也具有如下三个方法:
session.setAttribute(String name,Object obj);
session.getAttribute(String name);
session.removeAttribute(String name);3.2、怎样向session中存取数据(session也是一个域对象)
创建:第一次执行request.getSession()时创建
销毁:
服务器(非正常)关闭时
session过期/失效(默认30分钟)
问题:时间的起算点 从何时开始计算30分钟?
从不操作服务器端的资源开始计时
可以在工程的web.xml中进行配置:
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30session-timeout>
session-config>手动销毁session:
session.invalidate();作用范围:
默认在一次会话中,也就是说在,一次会话中任何资源公用一个session对象
面试题:浏览器关闭,session就销毁了? 不对
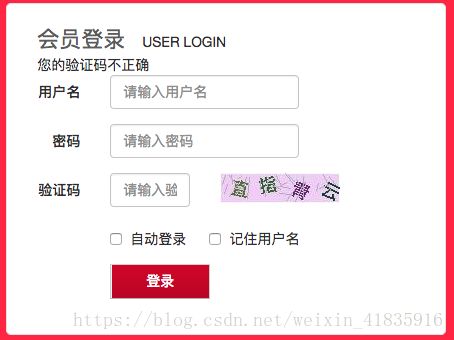
四、实现验证码校验
login.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>会员登录title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/bootstrap.min.css" type="text/css" />
<script src="js/jquery-1.11.3.min.js" type="text/javascript">script>
<script src="js/bootstrap.min.js" type="text/javascript">script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" type="text/css" />
<style>
body {
margin-top: 20px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.carousel-inner .item img {
width: 100%;
height: 300px;
}
.container .row div {
/* position:relative;
float:left; */
}
font {
color: #666;
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: normal;
padding-right: 17px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<jsp:include page="/header.jsp">jsp:include>
<div class="container"
style="width: 100%; height: 460px; background: #FF2C4C url('images/loginbg.jpg') no-repeat;">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-7">
div>
<div class="col-md-5">
<div
style="width: 440px; border: 1px solid #E7E7E7; padding: 20px 0 20px 30px; border-radius: 5px; margin-top: 60px; background: #fff;">
<font>会员登录font>USER LOGIN
<div><%=request.getAttribute("loginInfo")==null?"":request.getAttribute("loginInfo")%>div>
<form class="form-horizontal" action="/Login" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="username" class="col-sm-2 control-label">用户名label>
<div class="col-sm-6">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="username" name="username"
placeholder="请输入用户名">
div>
div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputPassword3" class="col-sm-2 control-label">密码label>
<div class="col-sm-6">
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword3" name="password"
placeholder="请输入密码">
div>
div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputPassword3" class="col-sm-2 control-label">验证码label>
<div class="col-sm-3">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="inputPassword3" name="checkCode"
placeholder="请输入验证码">
div>
<div class="col-sm-3">
<img src="/CheckImgServlet" />
div>
div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10">
<div class="checkbox">
<label> <input type="checkbox"> 自动登录
label> <label> <input
type="checkbox"> 记住用户名
label>
div>
div>
div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10">
<input type="submit" width="100" value="登录" name="submit"
style="background: url('./images/login.gif') no-repeat scroll 0 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0); height: 35px; width: 100px; color: white;">
div>
div>
form>
div>
div>
div>
div>
<jsp:include page="/footer.jsp">jsp:include>
body>
html>Servlet生成验证码:
@WebServlet(name = "CheckImgServlet",
urlPatterns = {"/CheckImgServlet"})
public class CheckImgServlet extends HttpServlet {
// 集合中保存所有成语
private List words = new ArrayList();
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
// 初始化阶段,读取new_words.txt
// web工程中读取 文件,必须使用绝对磁盘路径
String path = getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/new_words.txt");
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
words.add(line);
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 禁止缓存
// response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache");
// response.setHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");
// response.setDateHeader("Expires", -1);
int width = 120;
int height = 30;
// 步骤一 绘制一张内存中图片
BufferedImage bufferedImage = new BufferedImage(width, height,
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
// 步骤二 图片绘制背景颜色 ---通过绘图对象
Graphics graphics = bufferedImage.getGraphics();// 得到画图对象 --- 画笔
// 绘制任何图形之前 都必须指定一个颜色
graphics.setColor(getRandColor(200, 250));
graphics.fillRect(0, 0, width, height);
// 步骤三 绘制边框
graphics.setColor(Color.WHITE);
graphics.drawRect(0, 0, width - 1, height - 1);
// 步骤四 四个随机数字
Graphics2D graphics2d = (Graphics2D) graphics;
// 设置输出字体
graphics2d.setFont(new Font("宋体", Font.BOLD, 18));
Random random = new Random();// 生成随机数
int index = random.nextInt(words.size());
String word = words.get(index);// 获得成语
// 定义x坐标
int x = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
// 随机颜色
graphics2d.setColor(new Color(20 + random.nextInt(110), 20 + random
.nextInt(110), 20 + random.nextInt(110)));
// 旋转 -30 --- 30度
int jiaodu = random.nextInt(60) - 30;
// 换算弧度
double theta = jiaodu * Math.PI / 180;
// 获得字母数字
char c = word.charAt(i);
// 将c 输出到图片
graphics2d.rotate(theta, x, 20);
graphics2d.drawString(String.valueOf(c), x, 20);
graphics2d.rotate(-theta, x, 20);
x += 30;
}
// 将验证码内容保存session
request.getSession().setAttribute("checkcode_session", word);
// 步骤五 绘制干扰线
graphics.setColor(getRandColor(160, 200));
int x1;
int x2;
int y1;
int y2;
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
x1 = random.nextInt(width);
x2 = random.nextInt(12);
y1 = random.nextInt(height);
y2 = random.nextInt(12);
graphics.drawLine(x1, y1, x1 + x2, x2 + y2);
}
// 将上面图片输出到浏览器 ImageIO
graphics.dispose();// 释放资源
//将图片写到response.getOutputStream()中
ImageIO.write(bufferedImage, "jpg", response.getOutputStream());
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
/**
* 取其某一范围的color
*
* @param fc
* int 范围参数1
* @param bc
* int 范围参数2
* @return Color
*/
private Color getRandColor(int fc, int bc) {
// 取其随机颜色
Random random = new Random();
if (fc > 255) {
fc = 255;
}
if (bc > 255) {
bc = 255;
}
int r = fc + random.nextInt(bc - fc);
int g = fc + random.nextInt(bc - fc);
int b = fc + random.nextInt(bc - fc);
return new Color(r, g, b);
}
} Servlet校验验证码:
@WebServlet(name = "Login",
urlPatterns = {"/Login"})
public class Login extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request,response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
//验证码校验
//获得页面输入的验证
String checkCode_client = request.getParameter("checkCode");
//获得生成图片的文字的验证码
String checkCode_session = (String) request.getSession().getAttribute("checkcode_session");
//比对页面的和生成图片的文字的验证码是否一致
if(!checkCode_session.equals(checkCode_client)){
request.setAttribute("loginInfo", "您的验证码不正确");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/login.jsp").forward(request, response);
return;
}
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
//1、获得用户名和密码
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
//2、调用一个业务方法进行该用户查询
User login1 = null;
try {
login1 = login(username,password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//3、通过user是否为null判断用户名和密码是否正确
if(login1!=null){
//用户名和密码正确
//登录成功 跳转到网站的首页
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/index.jsp");
}else
{
//用户名或密码错误
//跳回当前login.jsp
request.setAttribute("loginInfo","用户名或密码错误");
request.getRequestDispatcher("login.jsp").forward(request,response);
}
}
public User login(String username,String password) throws SQLException {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(DataSourceUtils.getDataSource());
String sql = "select * from user where username=? and password=?";
User user = runner.query(sql,new BeanHandler(User.class),username,password);
return user;
}
} Java完整博客目录如下:博客文章目录汇总
转载请标明出处,原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41835916 如果觉得本文对您有帮助,请点击顶支持一下,您的支持是我写作最大的动力,谢谢。