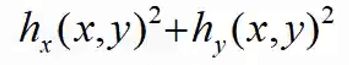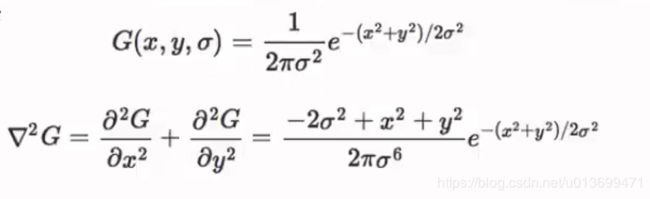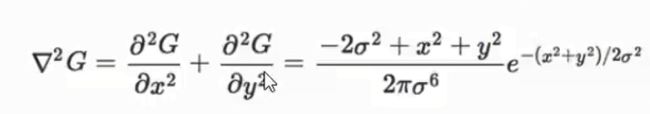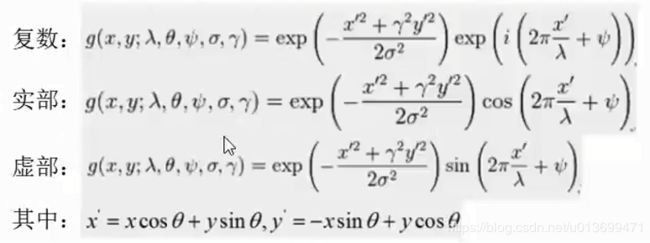计算机视觉的深度学习实战四:图像特征提取
计算机视觉的深度学习实战四:图像特征提取
综述:
- 颜色特征
- 量化颜色直方图、聚类颜色直方图
- 几何特征
- Edge,Corner,Blob
- 基于关键点的特征描述子
- SIFT、SURF、ORB
- 其他特征提取:(LBP、Gabor)
- 代码实践
一、颜色特征
1、量化颜色直方图
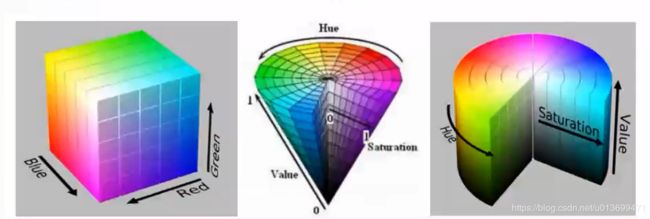
- 适用颜色空间:RGB、HSV等颜色空间
- 操作
- 颜色空间量化,单元(bin)由单元中心代表
- 统计落在量化单元上的像素数量
2、聚类颜色直方图
- 适用颜色空间:Lab等颜色空间
- 操作:
- lab空间是用数字化的方法来描述人的视觉感应。
- Lab颜色空间中:
- L分量用于表示像素的亮度,取值范围是[1,100],表示从纯黑到纯白;
- a表示从品红色到深绿色的范围,取值范围是[127,-128];
- b表示从黄色到蓝色的范围,取值范围是[127,-128].
3、
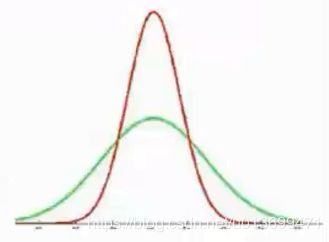
- 设想两幅图像的颜色直方图几乎相同,只是互相错开了一个bin,这时如果采用L1距离或者欧拉距离计算两者的相似度,会得到很小的相似度值。
- 为了克服这个缺陷,需要考虑到相似但不相同的颜色之间的相似度:
- 一种方法是采用二次式距离;
- 另一种方法是对颜色直方图事先进行平滑过滤,即每个bin中的像素对于相邻的几个bin也有贡献。
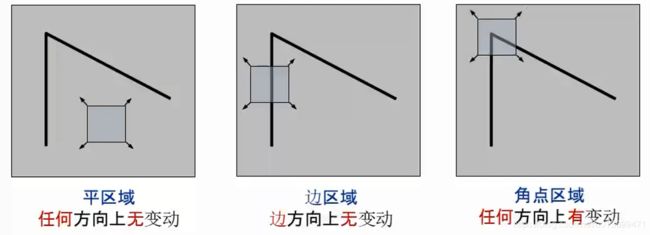
二、几何特征
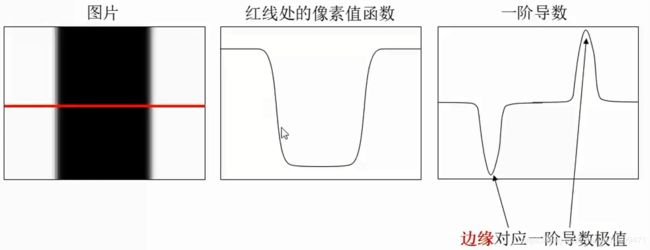
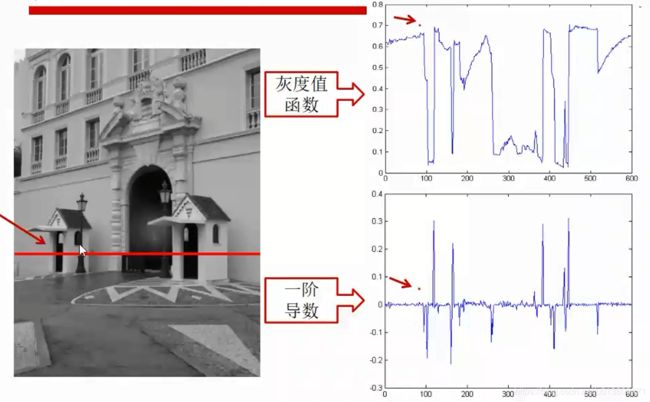
1、边缘(Edge)
- 像素明显变化的区域
- 具有丰富的语义信息
- 用于
- 物体识别
- 几何、视角变换
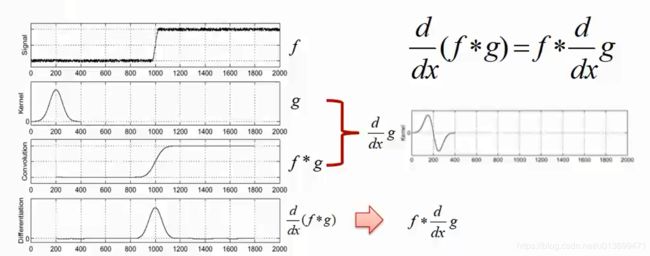
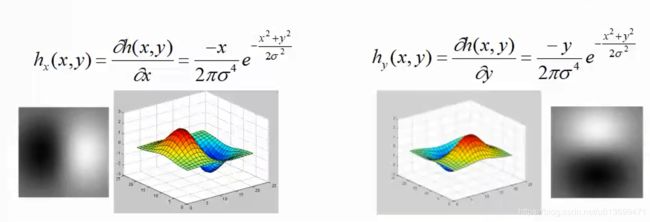
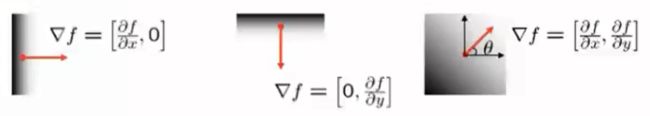
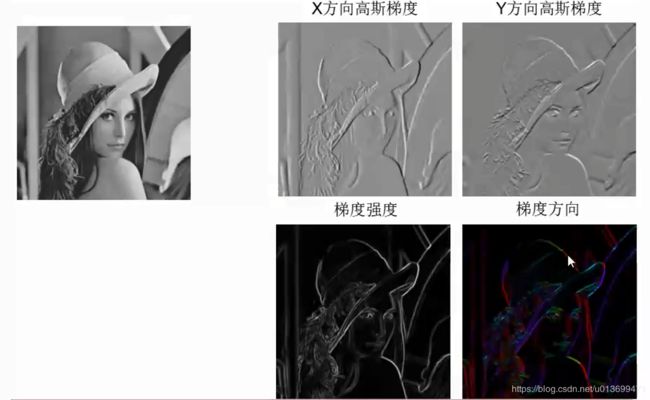
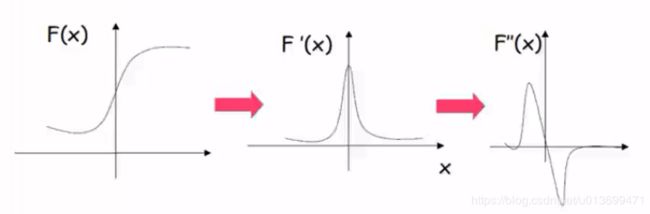
边缘提取:
- 先高斯(高斯平滑)去噪,再用一阶导数获取极值
- 导数对噪声敏感
三、基于特征点的特征描述子
- 从不同的距离,不同的方向、角度,不同的光照条件下观察一个物体时,物体的大小,形状,敏感都会有所不同。但我们依然可以判断它是同一物体。
- 理想的特征描述子应该具备这些性质。即,在大小、方向、明暗不同的图像中,同一特征点应具有足够相似的描述子,称之为描述子的可复现性。
1、几何特征:特征点/关键点
兴趣点/关键点(Interest point/Key point)
- 图片配准/拼接
- 运动跟踪
- 物体识别
- 机器人导航
- 3D重建
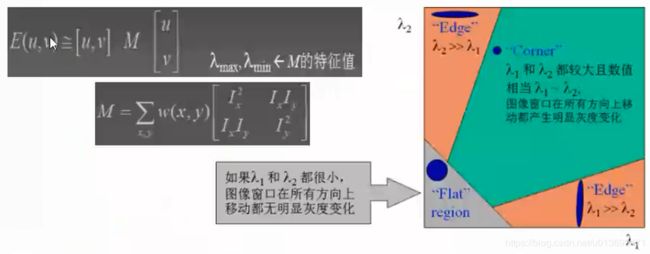
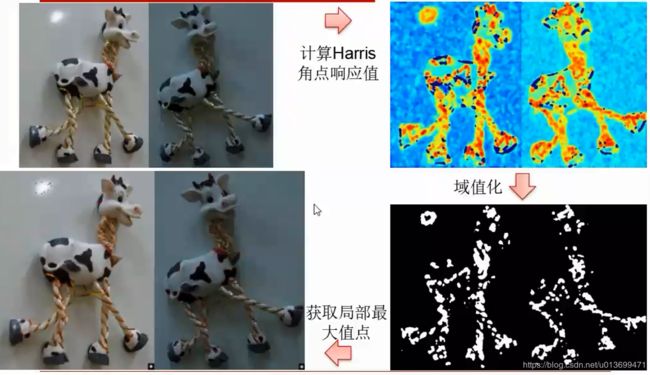
2、几何特征:Harris角点
Harris角点(Corner)
判断Harris角点:
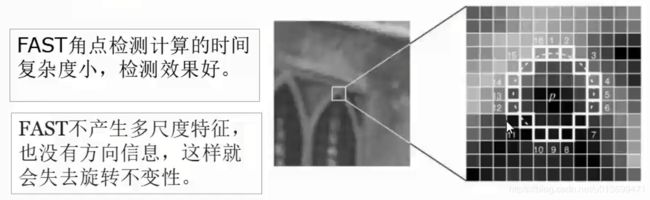
3、FAST角点检测
-
FAST角点检测是一种快速角点特征检测算法。
-
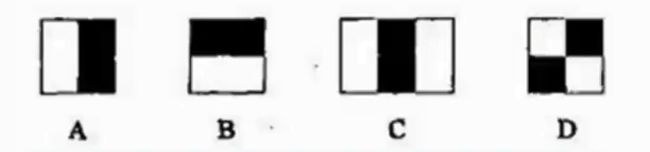
FAST角点定义为:若某像素点与其周围领域内足够多的像素点处于不同的区域,则该像素点可能为角点,也就是某些属性与众不同。
-
FAST特征点检测是对兴趣点所在圆周上的16个像素点进行判断,若判断后的当前中心像素点为暗或亮,将决定其是否为角点。
-
确定一个阈值t,观察某像素点为中心的一个半径等于3像素的离散化的圆,这个圆的边界上有16个像素。
-
如果在这个大小为16个像素的圆上有N(12)个连续的像素点,他们的像素值要么都比
I p + t I_p+t Ip+t
大,要么都比
I p − t I_p-t Ip−t
小,则p他就是一个角点。
4、几何特征:斑点
斑点(Blob)
局部特征:SIFT(尺度不变特征变换)Scale-invariant feature transform
- 基于尺度空间不变的特征
- SIFT特征计算步骤
- 在DoG尺度空间中获取极值点,即关键点
- LoG尺度空间和DoG(差分高斯)尺度空间
- 对关键点处理
- 位置插值(获得精确的关键点)
- 去除边缘点
- 关键点的方向估计
- 关键点描述子的生成
- 区域坐标旋转
- 计算采样区域的直方图
- 在DoG尺度空间中获取极值点,即关键点
- 特点:
- 具有良好的不变性
- 旋转、尺度缩放、平移、亮度变化、
- 对视角变化、仿射变换和噪声也有一定程度的稳定性
- 独特性好,信息量丰富
- 适用于在海量特征数据库中进行快速、准确的匹配
- 多量性
- 即使少数物体也可以产生大量的SIFT特征
- 计算快
- 经优化的SIFT匹配算法甚至可以达到实时性
- 可扩展性,可以很方便的与其他形式的特征向量进行联合。
- 具有良好的不变性
- 尺度空间:
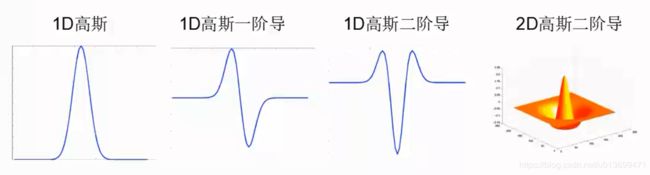
- 高斯金字塔就是在传统金字塔的基础上,对每一层用不同的参数σ做高斯模糊,是的每一层金字塔有多张高斯模糊图像,这样一组图像是一个octave。


- SIFT-计算高斯差分(DoG)空间
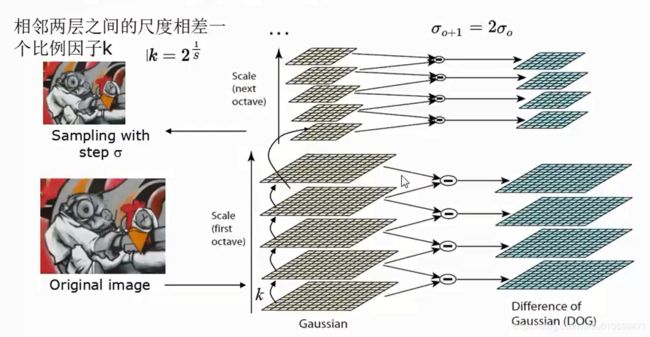

- SIFt-DoG空间极值点就是“关键点”
- 通过拟合三维二次函数来精确确定关键点的位置和尺度
- 离散空间的极值点并不是真正的极值点,上图显示了二维函数离散空间得到的极值点与连续空间极值点的差别。利用已知的离散空间点插值得到的连续空间极值点的方法叫做子像素插值。
- 同时去除低对比度的关键点和不稳定的边缘相应点(因为DoG算子会产生较强的边缘响应),以增强匹配稳定性、提高抗噪声能力。
- DoG算子会产生较强的边缘响应,需要剔除不稳定的边缘相应点。获取特征点处的Hessian矩阵,主曲率通过一个2×2的Hessian矩阵H求出
SIFT-特征点方向估计
- 在尺度上计算梯度直方图
- 8方向以特征点为中心、以3×1.5σ为半径
- 活取最高值方向为关键点主方向
- 为了匹配的稳定性,将超过最高值80%的方向称为辅方向

- 为了保证特征矢量具有旋转不变性,需要以特征点为中心,将特征点附近邻域内的图像旋转一个方向角θ
- 即将原图像x轴转到与主方向相同的方向。

SIFT-计算特征点描述子
- 在旋转后的坐标上采样16×16的像素窗
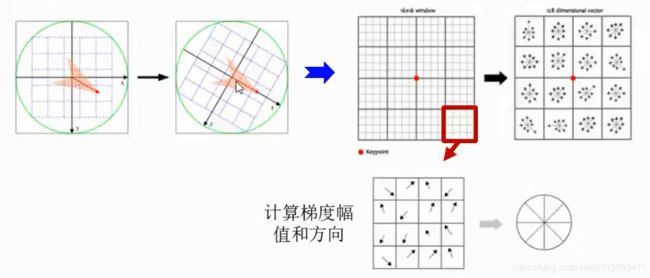
- 在旋转后的坐标上采样16×16的像素床
- 4×4网格
- 8方向直方图
- 总共128维
- SIFT的缺点是:计算太复杂,如果不借助硬件加速或专门的图像处理器很难实现。

- 改进方式:Haar-like特征:
- Haar-like特征的快速计算:积分图
5、局部特征:SURF
SURF(Speed-Up Robust Features)算子是Herbert Bay等人在2006年提出的,它是对SIFT的改进,可将速度提高三倍。
SURF只要是把SIFT中的某些运算做了简化。
- SURF把SIFT中的高斯二阶微分的模板进行了简化,使得卷积平滑操作仅需要转换成加减运算。
- 在方向确定阶段,在圆形区域计算x,y方向的haar小波响应,找到模最大的扇形方向。
- 为了找出图像中的特征点,需要对原图进行变换,变换图就是原图每个像素的Hessian矩阵行列式的近似值构成的。
- 求Hessian时要先高斯平滑,然后求二阶导数,这对于离散的像素点而言,是用模板卷积形成的,这两种操作合在一起用一个Haar模板代替就可以了。
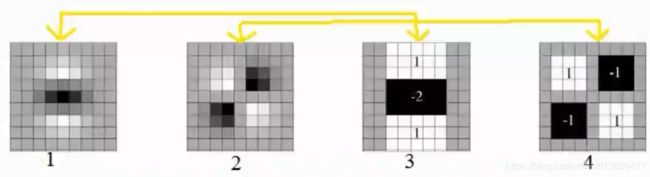
- 小造型

- 为了保证旋转不变性,在SURF中,统计特征点领域内的Haar小波特征。
- 即以特征点为中心,计算半径为6s(s为特征点所在的尺度值)的邻域内,统计60度扇形内所有点在x(水平)和y(垂直)方向的Haar小波响应总和。
- 然后60度扇形以一定间隔进行旋转,最后将最大值那个扇形的方向作为该特征点的主方向。
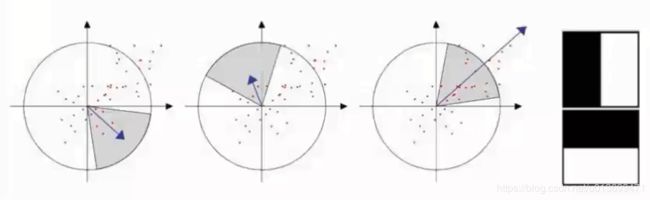
- 在特征点周围取一个正方形框,框的边长为20s(是所检测到该特征点所在的尺度)。该框的方向,就是检测出来的主方向。
- 最终,SURF的特征点特征向量的维度为64维。
- 然后把该框分为16个子区域,每个子区域统计25个像素的水平方向和垂直方向的Haar小波特征,这里的水平和垂直方向都是相对主方向而言的。
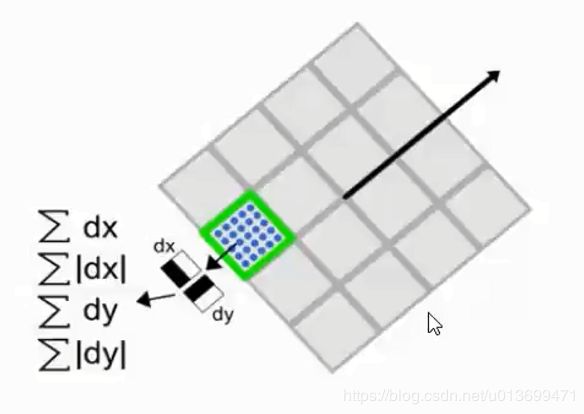
- 近似SIFT算法,实现快速版
- 先确定后选点,再找最大值
- Haar模板
- 加速三倍
- 亮度效果下效果好
- 模糊方面优于SIFT
- 尺度不变上不及SIFT
- 旋转不变上差很多

6、ORB特征描述
ORB的基本思路
- 它是对FAST角点与BRIEF特征描述子的一种结合与改进
- FAST角点检测的缺点是:
- 缺乏尺度不变性;
- 可以通告构建高斯金字塔,然后在每一层金字塔图像上检测角点,来实现尺度不变性;
- BRIEF的缺点是
- 缺乏旋转不变性;
- 需要给BRIEF加上旋转不变性
7、BRIEF
-
BRIEF需要先平滑图片,然后在特征点周围选择一个Patch,在这个Patch内通过一种选定的方法来挑选Nd个点对。
-
所有Nd个点对,都进行比较之间,我们就生成了一个Nd长的二进制串。
-
点对的生成方式(共有五种)
-
点对的位置一旦随机选定,就不能再更改
ORB对BRIEF的改进
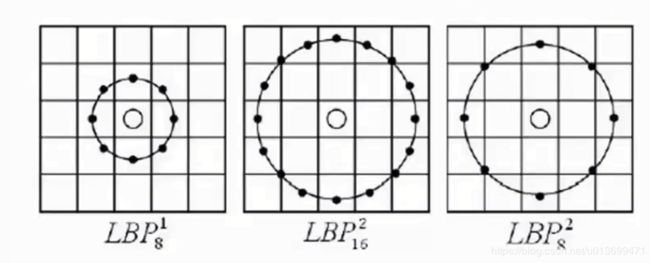
四、LBP
LBP(局部二值模式)
- 将每个像素点与周围点大小比较
- 半径为R的圆上,均匀采样P个点
- 大小量化为0或1
- 多个bit组成一个数,统计每个数的直方图
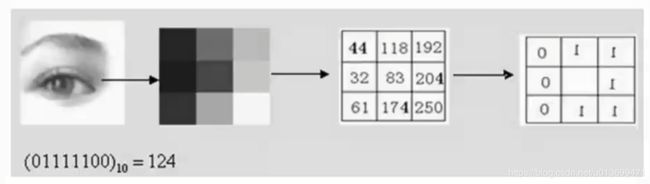
- 为解决旋转不变性的问题:将LBP周围的二进制码(如11110001)按位旋转,取二进制码最小的值为最终LBP值。
- 如:对于11110001情况,我们按位旋转,得到11100011,11000111,10001111,0001111,00111110,01111100,11111000七个不同的二进制数,最小值为00011111.
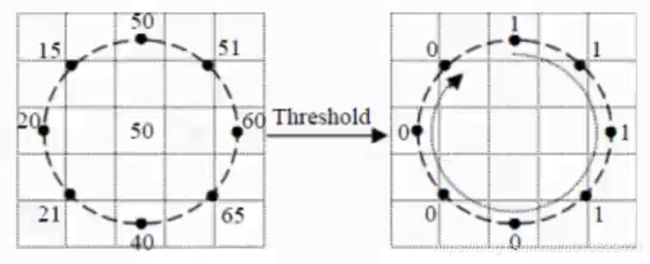
- 改进的LBP:
- LBP特征具有灰度不变性和旋转不变性等显著优点。

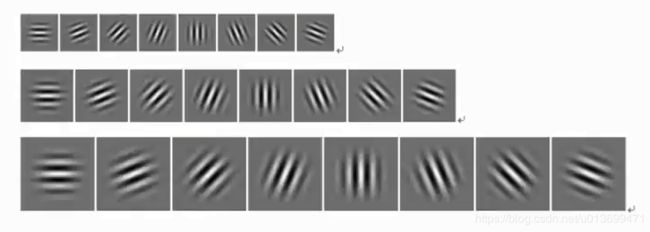
五、Gabor
- Gabor是一个用于边缘提取的线性滤波器,其频率和方向表达与人类视觉系统类似,能够提供良好的方向选择和尺度选择特性,而且对于光照变化不敏感;
- 十分适合纹理分析
- 使用一个三角函数与一个高斯函数叠加就得到了一个Gabor滤波器

Gabor滤波器组
六、代码实现
1、Haaris Corner
import numpy as np
import cv2 as cv
filename = "picture/chessboard.png"
img = cv.imread(filename)
gray = cv.cvtColor(img,cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = np.float32(gray)
dst = cv.cornerHarris(gray,2,3,0.04)
#result is dilated for marking the corners, not important
dst = cv.dilate(dst,None)
# Threshold for an optimal value, it may vary depending on the image.
img[dst>0.01*dst.max()]=[0,0,255]
cv.imshow('dst',img)
if cv.waitKey(0) & 0xff == 27:
cv.destroyAllWindows()
2、ORB
import numpy as np
import cv2 as cv
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img1 = cv.imread('picture/box.png',0) # queryImage
img2 = cv.imread('picture/box_in_scene.png',0) # trainImage
# Initiate ORB detector
orb = cv.ORB_create()
# find the keypoints and descriptors with ORB
kp1, des1 = orb.detectAndCompute(img1,None)
kp2, des2 = orb.detectAndCompute(img2,None)
# create BFMatcher object
bf = cv.BFMatcher(cv.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=True)
# Match descriptors.
matches = bf.match(des1,des2)
# Sort them in the order of their distance.
matches = sorted(matches, key = lambda x:x.distance)
# Draw first 10 matches.
img3 = cv.drawMatches(img1,kp1,img2,kp2,matches[:20],None, flags=2)
plt.imshow(img3),plt.show()
3、图片拼接
(注意原始图片不能过大,否则报错,此处500*375)
from Stitcher import Stitcher
import cv2
# 读取拼接图片
imageA = cv2.imread("image/3.png")
imageB = cv2.imread("image/4.png")
# 把图片拼接成全景图
stitcher = Stitcher()
(result, vis) = stitcher.stitch([imageA, imageB], showMatches=True)
# 显示所有图片
cv2.imshow("Image A", imageA)
cv2.imshow("Image B", imageB)
cv2.imshow("Keypoint Matches", vis)
cv2.imshow("Result", result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
import numpy as np
import cv2
class Stitcher:
#拼接函数
def stitch(self, images, ratio=0.75, reprojThresh=4.0,showMatches=False):
#获取输入图片
(imageB, imageA) = images
#检测A、B图片的SIFT关键特征点,并计算特征描述子
(kpsA, featuresA) = self.detectAndDescribe(imageA)
(kpsB, featuresB) = self.detectAndDescribe(imageB)
# 匹配两张图片的所有特征点,返回匹配结果
M = self.matchKeypoints(kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh)
# 如果返回结果为空,没有匹配成功的特征点,退出算法
if M is None:
return None
# 否则,提取匹配结果
# H是3x3视角变换矩阵
(matches, H, status) = M
# 将图片A进行视角变换,result是变换后图片
result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageA, H, (imageA.shape[1] + imageB.shape[1], imageA.shape[0]))
# 将图片B传入result图片最左端
result[0:imageB.shape[0], 0:imageB.shape[1]] = imageB
# 检测是否需要显示图片匹配
if showMatches:
# 生成匹配图片
vis = self.drawMatches(imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status)
# 返回结果
return (result, vis)
# 返回匹配结果
return result
def detectAndDescribe(self, image):
# 将彩色图片转换成灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 建立SIFT生成器
descriptor = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
# 检测SIFT特征点,并计算描述子
(kps, features) = descriptor.detectAndCompute(image, None)
# 将结果转换成NumPy数组
kps = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kps])
# 返回特征点集,及对应的描述特征
return (kps, features)
def matchKeypoints(self, kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh):
# 建立暴力匹配器
matcher = cv2.DescriptorMatcher_create("BruteForce")
# 使用KNN检测来自A、B图的SIFT特征匹配对,K=2
rawMatches = matcher.knnMatch(featuresA, featuresB, 2)
matches = []
for m in rawMatches:
# 当最近距离跟次近距离的比值小于ratio值时,保留此匹配对
if len(m) == 2 and m[0].distance < m[1].distance * ratio:
# 存储两个点在featuresA, featuresB中的索引值
matches.append((m[0].trainIdx, m[0].queryIdx))
# 当筛选后的匹配对大于4时,计算视角变换矩阵
if len(matches) > 4:
# 获取匹配对的点坐标
ptsA = np.float32([kpsA[i] for (_, i) in matches])
ptsB = np.float32([kpsB[i] for (i, _) in matches])
# 计算视角变换矩阵
(H, status) = cv2.findHomography(ptsA, ptsB, cv2.RANSAC, reprojThresh)
# 返回结果
return (matches, H, status)
# 如果匹配对小于4时,返回None
return None
def drawMatches(self, imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status):
# 初始化可视化图片,将A、B图左右连接到一起
(hA, wA) = imageA.shape[:2]
(hB, wB) = imageB.shape[:2]
vis = np.zeros((max(hA, hB), wA + wB, 3), dtype="uint8")
vis[0:hA, 0:wA] = imageA
vis[0:hB, wA:] = imageB
# 联合遍历,画出匹配对
for ((trainIdx, queryIdx), s) in zip(matches, status):
# 当点对匹配成功时,画到可视化图上
if s == 1:
# 画出匹配对
ptA = (int(kpsA[queryIdx][0]), int(kpsA[queryIdx][1]))
ptB = (int(kpsB[trainIdx][0]) + wA, int(kpsB[trainIdx][1]))
cv2.line(vis, ptA, ptB, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 返回可视化结果
return vis