SpringCloud之Ribbon实战使用及源码实现
SpringCloud之Ribbon实战使用及源码实现
一、Ribbon概述
Ribbon与负载均衡
负载均衡(Load Balance),即利用特定方式将流量分摊到多个操作单元上的一种手段,它对系统吞吐量与系统处理能力有着质的提升,毫不夸张地说,当今极少有企业没有用到负载均衡器或是负载均衡策略的。我们提到负载均衡,往往第一个想到的就是Nginx,或许还会想到LVS,这些大家都不陌生,且不管它们的使用方式,工作在什么层次,本质还是对于流量的疏导。
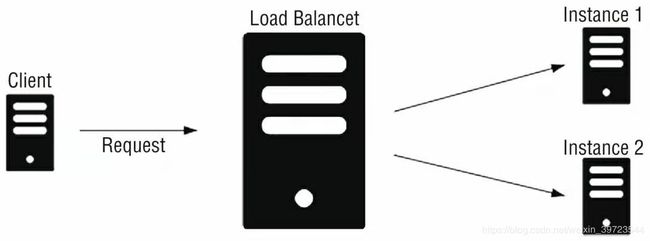
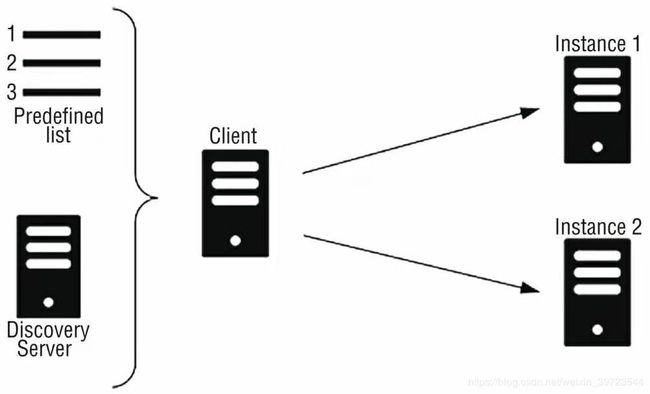
业界对于负载均衡有不少分类,最常见的有软负载与硬负载,代表产品是Nginx与F5;还有一组分类方式笔者认为最能体现出Ribbon与传统负载均衡的差别,那就是集中式负载均衡与进程内负载均衡。集中式负载均衡指位于因特网与服务提供者之间,并负责把网络请求转发到各个提供单位,这时候Nginx与F5就可以划为一类了,也可以称为服务端负载均衡,其原理如下图所示;进程内负载均衡是指从一个实例库选取一个实例进行流量导入,在微服务的范畴内,实例库一般是存储在Eureka、Consul、Zookeeper、etcd这样的注册中心,而此时的负载均衡器就是类似Ribbon的IPC(Inter-Process Communication,进程间通信)组件,因此,进程内负载均衡也叫作客户端负载均衡,其原理如下二图所示。
F5是四层负载均衡,Nginx是七层负载均衡。而我们所探讨的Ribbon之类则属于进程内的负载均衡。感兴趣的同学可以深入了解>了负载均衡的技术。
Spring Cloud官方是这样描述Ribbon的:
Ribbon is a client-side load balancer that gives you a lot of control over thebehavior of HTTP and TCP clients.
Ribbon是一个客户端负载均衡器,它赋予了应用一些支配HTTP与TCP行为的能力,可以得知,这里的客户端负载均衡(许多人称之为后端负载均衡)也是进程内负载均衡的一种。它在Spring Cloud生态内是一个不可缺少的组件,少了它,服务便不能横向扩展,这显然是有违云原生12要素的。此外,Feign与Zuul中已经默认集成了Ribbon,在我们的服务之间凡是涉及调用的,都可以集成它并应用,从而使我们的调用链具备良好的伸缩性。
入门案例
在了解了其基本概念之后,来一个快速的入门的案例,来使我们快速了解Ribbon的作用。案例中使用的Spring Cloud的版本号是Finchley,对应的Spring Boot的版本是2.0.3。
1.父工程
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.gyoomigroupId>
<artifactId>ribbon-parentartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<modules>
<module>eureka-servermodule>
<module>client-amodule>
<module>ribbon-load-balancermodule>
modules>
<packaging>pompackaging>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.0.3.RELEASEversion>
parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>Finchley.RELEASEversion>
<type>pomtype>
<scope>importscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
dependencyManagement>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestonesid>
<name>Spring Milestonesname>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/libs-milestoneurl>
<snapshots>
<enabled>falseenabled>
snapshots>
repository>
repositories>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>ribbon-parentartifactId>
<groupId>com.gyoomigroupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<artifactId>client-aartifactId>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
application.yml
server:
port: 7070
spring:
application:
name: client-a
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.host:127.0.0.1}:${eureka.port:8888}/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class ClientAApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ClientAApplication.class, args);
}
}
测试类(提供一个接口进行测试)
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/add")
public String add(Integer a, Integer b, HttpServletRequest request){
return " From Port: "+ request.getServerPort() + ", Result: " + (a + b);
}
}
结构如下:
3.创建eureka注册服务中心
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>ribbon-parentartifactId>
<groupId>com.gyoomigroupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<artifactId>eureka-serverartifactId>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-serverartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
application.yml
server:
port: 8888
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
registerWithEureka: false
fetchRegistry: false
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
4.负载均衡测试入口项目
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>ribbon-parentartifactId>
<groupId>com.gyoomigroupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<artifactId>ribbon-load-balancerartifactId>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbonartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
application.yml
spring:
application:
name: ribbon-load-balancer
server:
port: 7777
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.host:127.0.0.1}:${eureka.port:8888}/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class RibbonLoadbalancerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RibbonLoadbalancerApplication.class, args);
}
// 这里使用具有负载均衡功能的restTemplate进发送Http请求
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
测试入口类
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/add")
public String add(Integer a, Integer b) {
String result = restTemplate
.getForObject("http://CLIENT-A/add?a=" + a + "&b=" + b, String.class);
System.out.println(result);
return result;
}
}
测试并查看效果
- 先启动Eureka-Server工程
- 再启动Ribbon-Load-Banlance工程
- 再然后,先以7070端口启动一个Clinet-a服务;然后再议7075端口启动一个一模一样的服务。
然后使用Rest测试工具,请求http://127.0.0.1:7777/add?a=100&b=999这个Url.我们会发现,返回的结果是From Port: 7070, Result: 1099, From Port: 7075, Result: 1099交替出现。
至此快速入门案例结束。源代码连接在这里源码。
二、Ribbon的实战
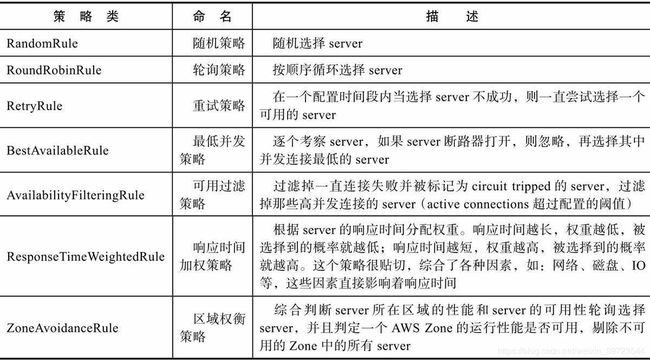
谈到Ribbon,就会谈到负载均衡,而谈到负载均衡,就会衍生出多种负载均衡策略。我们熟知的Nginx有一些非常实用的负载均衡策略,比如:轮询(Round Robin)、权重(Weight)、ip_hash等,丰富的策略能够让我们在构建应用时有充分的余地,可以根据业务场景选择最合适的策略。在Ribbon中,也有丰富的负载均衡策略可供选择,一共有7种,如下图所示。
2.1 全局策略设置
使用Ribbon的时候想要全局更改负载均衡策略,需要加一个配置类,如下代码所示。
@Configuration
public class TestConfiguration {
@Bean
public IRule ribbonRule() {
return new RandomRule();
}
}
就这样一个简单的配置,加上之后凡是通过Ribbon的请求都会按照配置的规则来进行,需要注意,代码在后续内容会有改动,读者如想测试可以还原。7种自带负载均衡策略,使用只需在这里新建出来即可,后续章节可以这样配置,也可以使用自实现策略。
2.2 基于配置文件的策略设置
其实Ribbon提供注解的配置的方式,但是这种方式强耦合于代码中,所以就不推荐大家使用,感兴趣的同学可以去了解下。实际开发中非常推荐配置文件来对源服务负载策略进行配置,其基本语法是client-a服务使用随机策略。
client-a:
ribbon:
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule
使用HTTP发起请求,免不了要经历极端环境,此时对调用进行时限控制以及时限之后的重试尤为重要。注意,F版中Ribbon的重试机制是默认开启的,需要添加对于超时时间与重试策略的配置,如下代码所示。
client-a:
ribbon:
ConnectTimeout: 30000
ReadTimeout: 30000
MaxAutoRetries: 1 #对第一次请求的服务的重试次数
MaxAutoRetriesNextServer: 1 #要重试的下一个服务的最大数量(不包括第一个服务)
OkToRetryOnAllOperations: true
2.3 Ribbon的饥饿加载
Ribbon在进行客户端负载均衡的时候并不是在启动时就加载上下文,而是在实际请求的时候才去创建,因此这个特性往往会让我们的第一次调用显得颇为疲软乏力,严重的时候会引起调用超时。所以我们可以通过指定Ribbon具体的客户端的名称来开启饥饿加载,即在启动的时候便加载所有配置项的应用程序上下文,如下代码所示。
ribbon:
eager-load:
enabled: true
clients: client-a, client-b, client-c
2.4 利用配置文件自定义Ribbon客户端
Ribbon在1.2.0版本之后,就可以使用配置文件来定制Ribbon客户端了,其实质也就是使用配置文件来指定一些默认加载类,从而更改Ribbon客户端的行为方式,并且使用这种方式优先级最高,优先级高于使用注解@RibbonClient指定的配置和源码中加载的相关Bean。我们可以通过下图中给出的配置来设置。
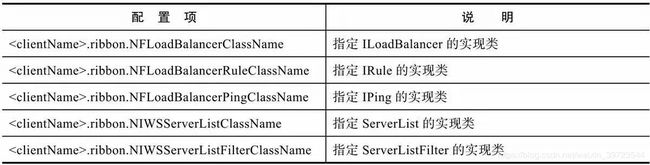
可以使用Ribbon自带实现类,也可以自实现。下面是一个对client源服务的相关定制示例:
client:
ribbon:
NIWSServerListClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.ConfigurationBasedServerList
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.WeightedResponseTimeRule
2.5 Ribbon脱离Eureka的使用
在默认情况下,Ribbon客户端会从Eureka注册中心读取服务注册信息列表,来达到一种动态负载均衡的功能。但是有一种情况下则不会推荐这种方式,即如果Eureka是一个供很多人使用的公共注册中心(比如社区公益Eureka,地址:http://eureka.springcloud.cn),此时极易产生服务侵入性问题,所以就不要从Eureka中读取服务列表了,而应该在Ribbon客户端自行指定源服务地址,让Ribbon脱离Eureka来使用。
为了达到这一目的,首先需要在Ribbon中禁用Eureka的功能:
ribbon:
eureka:
enabled: false
然后对源服务设定地址列表:
client:
ribbon:
listOfServers: http://localhost:7070,http://localhost:7071
三、Ribbon的进阶
3.1 核心工作原理
我们已经了解了Ribbon的一些使用方式,现在让我们来看一看它的核心功能是如何被实现的,关于这部分内容,我会着重讲解官方文档中提到的那些上层接口,以及Ribbon从启动到负载均衡器选择服务实例的过程。
官方文档中提到了Ribbon中的核心接口,它们共同定义了Ribbon的行为特性,如下图所示。
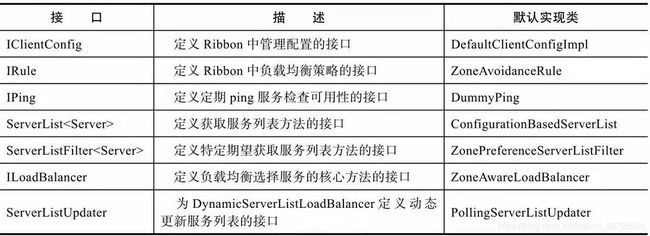
可以说,Ribbon完全是基于这些接口建立起来的,它们就是Ribbon的骨架,对它们追根溯源,可以掌握Ribbon的底层实现,关于它们的解读,这里就不详细展开了,知道每一个接口的作用之后,依靠强大的IDE,相信读者掌握它们并不是难事。其实很多读者对于Ribbon最关心的是它是如何做到使用RestTemplate达到负载均衡的,下面我们对这部分重要原理进行讲解。
在上一节中,我们知道了如何使用Ribbon来对客户端实例进行负载均衡,其基本的使用方式都需要注入一个RestTemplate的Bean,并且使用@LoadBalanced注解才能使其具备负载均衡的能力,RestTemplate在Spring中由来已久,为什么一个简单的注解就可以让它具备如此强悍的功能呢?打开其源码如下:
/**
* Annotation to mark a RestTemplate bean to be configured to use a LoadBalancerClient
* @author Spencer Gibb
*/
@Target({ ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Qualifier
public @interface LoadBalanced {
}
这里注释写得比较清楚了,这个注解是标记一个RestTemplate来使用LoadBalancerClient, LoadBalancerClient是什么?搜索发现:
它是扩展自ServiceInstanceChooser接口的,ServiceInstanceChooser内容如下:
/**
* Represents a client side load balancer
* @author Spencer Gibb
*/
public interface LoadBalancerClient extends ServiceInstanceChooser {
/**
* execute request using a ServiceInstance from the LoadBalancer for the specified
* service
* @param serviceId the service id to look up the LoadBalancer
* @param request allows implementations to execute pre and post actions such as
* incrementing metrics
* @return the result of the LoadBalancerRequest callback on the selected
* ServiceInstance
*/
<T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException;
/**
* execute request using a ServiceInstance from the LoadBalancer for the specified
* service
* @param serviceId the service id to look up the LoadBalancer
* @param serviceInstance the service to execute the request to
* @param request allows implementations to execute pre and post actions such as
* incrementing metrics
* @return the result of the LoadBalancerRequest callback on the selected
* ServiceInstance
*/
<T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException;
/**
* Create a proper URI with a real host and port for systems to utilize.
* Some systems use a URI with the logical serivce name as the host,
* such as http://myservice/path/to/service. This will replace the
* service name with the host:port from the ServiceInstance.
* @param instance
* @param original a URI with the host as a logical service name
* @return a reconstructed URI
*/
URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original);
}
❑ ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId):根据serviceId,结合负载均衡器选择一个服务实例。
❑ T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest request):使用来自LoadBalancer的ServiceInstance为指定的服务执行请求。
❑ T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequestrequest):使用来自LoadBalancer的ServiceInstance为指定的服务执行请求,是上一个方法的重载,在实现类中可以看到它们的关系,其实就是前一个方法的细节实现。
❑ URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original):使用主机ip和port构建特定的URI以供Ribbon内部使用。Ribbon使用具有逻辑服务名称的URI作为host,例如http://myservice/path/to/service。
由这些方法可以看出,这两个接口非同一般。有了这个线索,我们继续查找它在哪里被初始化,结果在同一个包下面发现了LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration,阅读发现,它正是Ribbon功能的核心配置类,其部分重要源码如下:
/**
* Auto configuration for Ribbon (client side load balancing).
*
* @author Spencer Gibb
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Will Tran
* @author Gang Li
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(RestTemplate.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(LoadBalancerRetryProperties.class)
public class LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration {
@LoadBalanced
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RestTemplate> restTemplates = Collections.emptyList();
@Bean
public SmartInitializingSingleton loadBalancedRestTemplateInitializerDeprecated(
final ObjectProvider<List<RestTemplateCustomizer>> restTemplateCustomizers) {
return () -> restTemplateCustomizers.ifAvailable(customizers -> {
for (RestTemplate restTemplate : LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.this.restTemplates) {
for (RestTemplateCustomizer customizer : customizers) {
customizer.customize(restTemplate);
}
}
});
}
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<LoadBalancerRequestTransformer> transformers = Collections.emptyList();
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public LoadBalancerRequestFactory loadBalancerRequestFactory(
LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient) {
return new LoadBalancerRequestFactory(loadBalancerClient, transformers);
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate")
static class LoadBalancerInterceptorConfig {
@Bean
public LoadBalancerInterceptor ribbonInterceptor(
LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient,
LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) {
return new LoadBalancerInterceptor(loadBalancerClient, requestFactory);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer(
final LoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) {
return restTemplate -> {
List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>(
restTemplate.getInterceptors());
list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor);
restTemplate.setInterceptors(list);
};
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(RetryTemplate.class)
public static class RetryAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public LoadBalancedRetryFactory loadBalancedRetryFactory() {
return new LoadBalancedRetryFactory() {};
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(RetryTemplate.class)
public static class RetryInterceptorAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RetryLoadBalancerInterceptor ribbonInterceptor(
LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient, LoadBalancerRetryProperties properties,
LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory,
LoadBalancedRetryFactory loadBalancedRetryFactory) {
return new RetryLoadBalancerInterceptor(loadBalancerClient, properties,
requestFactory, loadBalancedRetryFactory);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer(
final RetryLoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) {
return restTemplate -> {
List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>(
restTemplate.getInterceptors());
list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor);
restTemplate.setInterceptors(list);
};
}
}
}
从类的注解就可以看出,它配置加载的时机一是当前工程环境必须有RestTemplate的实例,二是在工程环境中必须初始化了LoadBalancerClient的实现类。整个配置类只截取了重要部分,其中,LoadBalancerRequestFactory用于创建LoadBalancerRequest供LoadBalancer-Interceptor使用,它在低版本中是没有的;LoadBalancerInterceptorConfig中则维护了Load-BalancerInterceptor与RestTemplateCustomizer的实例,它们的作用如下:
❑ LoadBalancerInterceptor:拦截每一次HTTP请求,将请求绑定进Ribbon负载均衡的生命周期。
❑ RestTemplateCustomizer:为每个RestTemplate绑定LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器。
LoadBalancerInterceptor看来已经很接近我们要找的答案了,我们截取其源码:
/**
* @author Spencer Gibb
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Ryan Baxter
* @author William Tran
*/
public class LoadBalancerInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer;
private LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory;
public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer, LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) {
this.loadBalancer = loadBalancer;
this.requestFactory = requestFactory;
}
public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer) {
// for backwards compatibility
this(loadBalancer, new LoadBalancerRequestFactory(loadBalancer));
}
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body,
final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
final URI originalUri = request.getURI();
String serviceName = originalUri.getHost();
Assert.state(serviceName != null, "Request URI does not contain a valid hostname: " + originalUri);
return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName, requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution));
}
}
原来它是利用ClientHttpRequestInterceptor来对每次HTTP请求进行拦截的,此类是Spring中维护的请求拦截器,实现它的intercept方法就可以使请求进入方法体,从而做一些处理。可以看出这里把请求拦截下来之后使用了LoadBalancerClient的execute方法来处理请求,顺便提一下,由于我们在RestTemplate中使用的URI是形如http://myservice/path/to/service的,所以这里的getHost()方法实际取到的就是服务名myservice。LoadBalancerClient接口只有一个实现类,即RibbonLoadBalancerClient,这里的execute方法体如下:
@Override
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException {
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(serviceId);
Server server = getServer(loadBalancer);
if (server == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId);
}
RibbonServer ribbonServer = new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server,
serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server));
return execute(serviceId, ribbonServer, request);
}
首先要得到一个ILoadBalancer,再使用它去得到一个Server,顾名思义,这个Server就是具体服务实例的封装了,实际上查看源码也验证了笔者的猜测,所以,getServer (loadBalancer)就是发生负载均衡过程的地方!我们再看一看它的实现:
protected Server getServer(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer) {
if (loadBalancer == null) {
return null;
}
return loadBalancer.chooseServer("default"); // TODO: better handling of key
}
运用ILoadBalancer的chooseServer方法,查看ILoadBalancer的实现类的该方法实现:
/*
* Get the alive server dedicated to key
*
* @return the dedicated server
*/
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (counter == null) {
counter = createCounter();
}
counter.increment();
if (rule == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
return rule.choose(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error choosing server for key {}", name, key, e);
return null;
}
}
}
我们发现,rule.choose(key)中的rule其实就是IRule,至此,拦截的HTTP请求与负载均衡策略得以关联起来。
参考书籍和文献
- 《重新定义SpringCloud实战》
- SpringCloud 企业级脚手架项目源码 喜欢的老铁给个星吧!!!