【SpringBoot2.3使用Spring Data-JPA搭建项目】
Spring的Jpa是一个非常不错的持久层框架,可以理解为就是对Hibrenate进行了封装,比起Mybatis优点在于不用关注sql语句的编写。我这案例中使用ResultFul风格来编写的。
一、搭建SpringBoot项目
导入Jpa的依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.18
全部的pom文件:
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.3.0.M3
com.cxf
demo_mall
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
demo_mall
Demo project for Spring Boot
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-freemarker
2.1.3.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.18
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.junit.vintage
junit-vintage-engine
junit
junit
org.springframework
spring-test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
spring-milestones
Spring Milestones
https://repo.spring.io/milestone
spring-milestones
Spring Milestones
https://repo.spring.io/milestone
application.yml:启动开发者模式
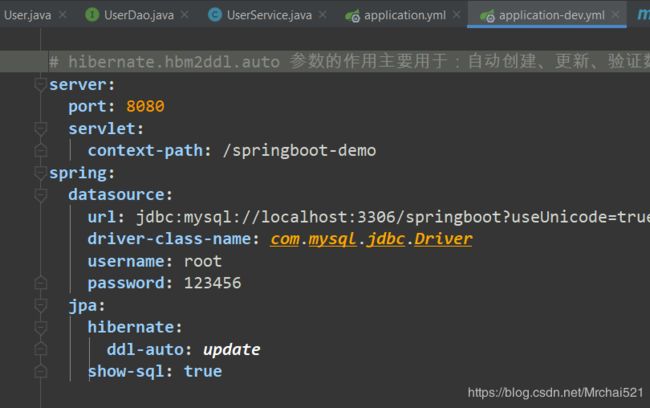
application-dev.yml
首先,我们要定义实体类,实体类对应一个数据表,其中的属性对应数据表中的字段。
User:
package com.cxf.demo_mall.api.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
/**
* @author:柴新峰
* @create:2020/4/17
*/
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String userName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String passWord;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String email;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String nickName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String regTime;
public User() {
}
public User(String userName,String passWord,String email,String nickName,String regTime) {
this.userName = userName;
this.passWord = passWord;
this.email = email;
this.nickName = nickName;
this.regTime = regTime;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getNickName() {
return nickName;
}
public void setNickName(String nickName) {
this.nickName = nickName;
}
public String getRegTime() {
return regTime;
}
public void setRegTime(String regTime) {
this.regTime = regTime;
}
}
下面是DAO层,实现用户的增删改查方法 :
package com.cxf.demo_mall.api.dao;
import com.cxf.demo_mall.api.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author:柴新峰
* @create:2020/4/19
*/
@Repository
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository {
}
在这里我们就能简单体会到Jpa的强大之处,只需要写一句userDao.findAll();就可以查到全部数据并放到user列表里,继承了JpaRepository仓库。
接下来,写UserService:
package com.cxf.demo_mall.api.service;
import com.cxf.demo_mall.api.dao.UserDao;
import com.cxf.demo_mall.api.entity.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.transaction.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author:柴新峰
* @create:2020/4/19
*/
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 添加用户
*/
public void addUser(User user){
userDao.save(user);
}
/**
* 根据id进行修改
* @param user
*/
public void updateUser(User user){
userDao.save(user);
}
/**
* 根据id进行删除
* @param id
*/
public void deleteUser(Long id){
userDao.deleteById(id);
}
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
public List listUser(){
return userDao.findAll();
}
/**
* 根据id查询一条数据
* @param id
* @return
*/
public User findById(Long id){
return userDao.findById(id).get();
}
/**
* 通过姓名查询用户集合
* @param username
* @return
*/
// public List findUserName(String username){
// return userDao.findByName(username);
// }
}
Service里面有个@Transactional是自动开始事务的注解,很方便。
完了后,到Controller类了:
package com.cxf.demo_mall.api.controller;
import com.cxf.demo_mall.api.common.CommonResult;
import com.cxf.demo_mall.api.entity.User;
import com.cxf.demo_mall.api.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author:柴新峰
* @create:2020/4/19
*/
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private CommonResult commonResult;
@PostMapping("/addUser")
public CommonResult addUser(User user) {
try {
userService.addUser(user);
return commonResult;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
commonResult.setState(500);
commonResult.setMsg("失败");
return commonResult;
}
}
/**
* 修改用户
*
* @param user
* @return
*/
@PutMapping(value = "/updateStudent")
public CommonResult updateUser(User user) {
try {
userService.updateUser(user);
return commonResult;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
commonResult.setState(500);
commonResult.setMsg("失败");
return commonResult;
}
}
/**
* 根据id删除用户
* @param id
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping("/deleteUser/{id}")
public CommonResult deleteUserById(@PathVariable(name = "id", required = true) Long id) {
try {
userService.deleteUser(id);
return commonResult;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
commonResult.setState(500);
commonResult.setMsg("失败");
return commonResult;
}
}
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/findAll")
public CommonResult listUser(){
try {
List list = userService.listUser();
commonResult.setData(list);
return commonResult;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
commonResult.setState(500);
commonResult.setMsg("查询错误");
commonResult.setData(null);
return commonResult;
}
}
/**
* 根据id查询一条数据
* @param id
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/findById/{id}")
public CommonResult findById(@PathVariable(name = "id") Long id){
try {
User user = userService.findById(id);
commonResult.setData(user);
return commonResult;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
commonResult.setState(500);
commonResult.setMsg("查询错误哦!");
commonResult.setData(null);
return commonResult;
}
}
}
抽一个全局返回对象类:
package com.cxf.demo_mall.api.common;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author:柴新峰
* @create:2020/4/19
*/
@Service
public class CommonResult {
private Integer state;
private String msg;
private Object data;
public CommonResult() {
this.state = 200;
this.msg = "成功";
}
public CommonResult(Integer state, String msg) {
this.state = state;
this.msg = msg;
}
public CommonResult(Integer state, String msg, Object data) {
this.state = state;
this.msg = msg;
this.data = data;
}
public Integer getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(Integer state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
开始启动项目:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}启动成功,数据库已经创出了表:
开始测试数据:
1)添加用户
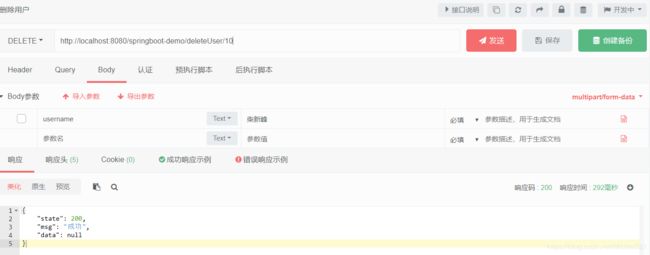
2)删除用户
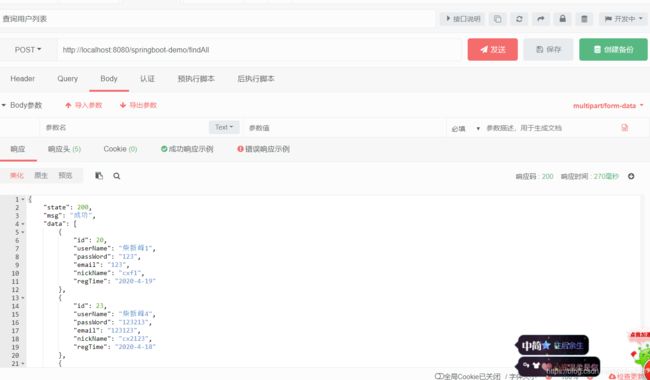
3)查询用户列表
4)根据id查询一条数据