LeetCode第178场周赛
1365. 有多少小于当前数字的数字
给你一个数组 nums,对于其中每个元素 nums[i],请你统计数组中比它小的所有数字的数目。
换而言之,对于每个 nums[i] 你必须计算出有效的 j 的数量,其中 j 满足 j != i 且 nums[j] < nums[i] 。
以数组形式返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [8,1,2,2,3]
输出:[4,0,1,1,3]
解释:
对于 nums[0]=8 存在四个比它小的数字:(1,2,2 和 3)。
对于 nums[1]=1 不存在比它小的数字。
对于 nums[2]=2 存在一个比它小的数字:(1)。
对于 nums[3]=2 存在一个比它小的数字:(1)。
对于 nums[4]=3 存在三个比它小的数字:(1,2 和 2)。public class Solution {
//暴力
public int[] smallerNumbersThanCurrent(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
if (i == j) continue;
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) res[i]++;
}
}
return res;
}
}1366. 通过投票对团队排名
现在有一个特殊的排名系统,依据参赛团队在投票人心中的次序进行排名,每个投票者都需要按从高到低的顺序对参与排名的所有团队进行排位。
排名规则如下:
- 参赛团队的排名次序依照其所获「排位第一」的票的多少决定。如果存在多个团队并列的情况,将继续考虑其「排位第二」的票的数量。以此类推,直到不再存在并列的情况。
- 如果在考虑完所有投票情况后仍然出现并列现象,则根据团队字母的字母顺序进行排名。
给你一个字符串数组 votes 代表全体投票者给出的排位情况,请你根据上述排名规则对所有参赛团队进行排名。
请你返回能表示按排名系统 排序后 的所有团队排名的字符串。
示例 1:
输入:votes = ["ABC","ACB","ABC","ACB","ACB"]
输出:"ACB"
解释:A 队获得五票「排位第一」,没有其他队获得「排位第一」,所以 A 队排名第一。
B 队获得两票「排位第二」,三票「排位第三」。
C 队获得三票「排位第二」,两票「排位第三」。
由于 C 队「排位第二」的票数较多,所以 C 队排第二,B 队排第三。排序问题,根据不同的情况进行排序。
class Solution {
public String rankTeams(String[] votes) {
//key是参赛团队,value是该团队每个排位获得的票数
Map teamRankMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String vote : votes) {
for (int i = 0; i < vote.length(); i++) {
int[] rankArr = teamRankMap.getOrDefault(vote.charAt(i), new int[26]);
rankArr[i]++;
teamRankMap.put(vote.charAt(i), rankArr);
}
}
List> teamRankList = new ArrayList<>(teamRankMap.entrySet());
Collections.sort(teamRankList, (team1, team2) -> {
int[] ranks1 = team1.getValue();
int[] ranks2 = team2.getValue();
//根据投票排序
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (ranks1[i] != ranks2[i]) {
return ranks2[i] - ranks1[i];
}
}
//字母顺序排序
return team1.getKey() - team2.getKey();
});
//转换为字符串输出
return teamRankList.stream().map(entry -> String.valueOf(entry.getKey())).collect(Collectors.joining());
}
}
1367. 二叉树中的列表
给你一棵以 root 为根的二叉树和一个 head 为第一个节点的链表。
如果在二叉树中,存在一条一直向下的路径,且每个点的数值恰好一一对应以 head 为首的链表中每个节点的值,那么请你返回 True ,否则返回 False 。
一直向下的路径的意思是:从树中某个节点开始,一直连续向下的路径。
示例 1:
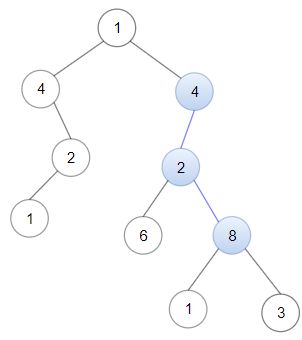
输入:head = [4,2,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3]
输出:true
解释:树中蓝色的节点构成了与链表对应的子路径。此题其实是一道SubTree的变形。
class Solution {
public boolean isSubPath(ListNode head, TreeNode root) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
return isSub(head, root) || isSubPath(head, root.left) || isSubPath(head, root.right);
}
private boolean isSub(ListNode head, TreeNode node) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
if (head.val != node.val) {
return false;
}
return isSub(head.next, node.left) || isSub(head.next, node.right);
}
}
1368. 使网格图至少有一条有效路径的最小代价
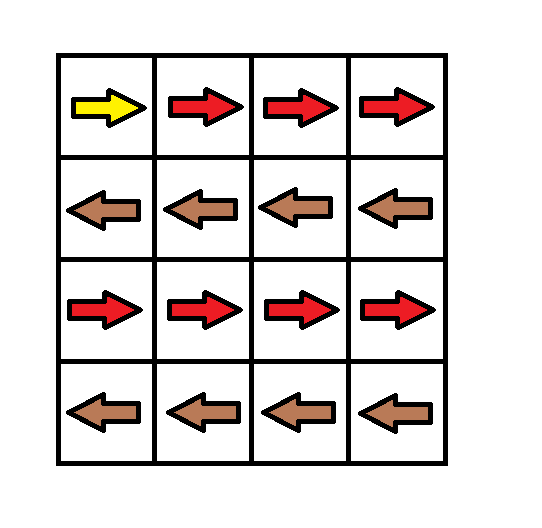
给你一个 m x n 的网格图 grid 。 grid 中每个格子都有一个数字,对应着从该格子出发下一步走的方向。 grid[i][j] 中的数字可能为以下几种情况:
- 1 ,下一步往右走,也就是你会从 grid[i][j] 走到 grid[i][j + 1]
- 2 ,下一步往左走,也就是你会从 grid[i][j] 走到 grid[i][j - 1]
- 3 ,下一步往下走,也就是你会从 grid[i][j] 走到 grid[i + 1][j]
- 4 ,下一步往上走,也就是你会从 grid[i][j] 走到 grid[i - 1][j]
注意网格图中可能会有 无效数字 ,因为它们可能指向 grid 以外的区域。
一开始,你会从最左上角的格子 (0,0) 出发。我们定义一条 有效路径 为从格子 (0,0) 出发,每一步都顺着数字对应方向走,最终在最右下角的格子 (m - 1, n - 1) 结束的路径。有效路径 不需要是最短路径 。
你可以花费 cost = 1 的代价修改一个格子中的数字,但每个格子中的数字 只能修改一次 。
请你返回让网格图至少有一条有效路径的最小代价。
示例 1:
输入:grid = [[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2],[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2]]
输出:3
解释:你将从点 (0, 0) 出发。
到达 (3, 3) 的路径为: (0, 0) --> (0, 1) --> (0, 2) --> (0, 3) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (1, 3) --> (1, 2) --> (1, 1) --> (1, 0) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (2, 0) --> (2, 1) --> (2, 2) --> (2, 3) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (3, 3)
总花费为 cost = 3.解题思路:BFS+记忆搜索
class Solution {
public int minCost(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
//由(0, 0)到其他网格的最小花费,为-1则表示待计算
int dst[][] = new int[n][m];
//用来保存待扩展的四个方向在纵轴和横轴上的增量,右-左-下-上
int d[][] = {{}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dst[i], -1);
}
//用来执行bfs的队列
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
//int数组三个参数:纵轴、横轴、当前cost
queue.offer(new int[] {0, 0, 0});
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int x = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
int q[] = queue.poll();
if (q[0] == n - 1 && q[1] == m - 1) {
continue;
}
int val = grid[q[0]][q[1]];
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++) {
int r = q[0] + d[j][0];
int c = q[1] + d[j][1];
if (r >= 0 && c >= 0 && r < n && c < m) {
int add = j == val ? 0 : 1;
if (dst[r][c] == -1 || dst[r][c] > q[2] + add) {
dst[r][c] = q[2] + add;
queue.offer(new int[] {r, c, dst[r][c]});
}
}
}
}
}
return Math.max(0, dst[n - 1][m - 1]);
}
}