前言
开心一刻
过年女婿来岳父家走亲戚,当时小舅子主就问:姐夫,你什么时候能给我姐幸福,让我姐好好享受生活的美好。你们这辈子不准备买一套大点的房子吗?姐夫说:现在没钱啊!不过我有一个美丽可爱的女儿,等长大后找个有钱的老公嫁了,那时我就能和你姐一起住大房子了。岳父不乐意的说了一句:当初我也是这么认为的,可惜未能如愿。
路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索!
github:https://github.com/youzhibing
码云(gitee):https://gitee.com/youzhibing
ServletContext
ServletContext介绍
定义了servlet与其servlet容器通信的一些列方法,例如,获取文件的MIME类型,分派请求或写入日志文件。
Servlet的运行模式是一个典型的“握手型的交互式”运行模式。所谓“握手型的交互式”就是两个模块为了交换数据通常都会准备一个交易场景,这个场景一直跟随这个交易过程直到这个交易完成为止。这个交易场景的初始化是根据这次交易对象指定的参数来定制的,这些制定参数通常就是一个配置类。所以对号入座,交易场景由ServletContext来描述,而定制的参数集合由ServletConfig来描述。而ServletRequest和ServletResponse就是要交互的具体对象,它们通常都作为运输工具来传递交互结果。ServletContext,即servlet上下文,用于存放web应用信息;每个Java虚拟机每个Web项目只有一个ServletContext,它是由Web服务器创建,代表当前web应用。
Servlet 3.0规范之前
我们采用2.5来看下源码
maven依赖
javax.servlet servlet-api 2.5 provided
源码
/* * The contents of this file are subject to the terms * of the Common Development and Distribution License * (the "License"). You may not use this file except * in compliance with the License. * * You can obtain a copy of the license at * glassfish/bootstrap/legal/CDDLv1.0.txt or * https://glassfish.dev.java.net/public/CDDLv1.0.html. * See the License for the specific language governing * permissions and limitations under the License. * * When distributing Covered Code, include this CDDL * HEADER in each file and include the License file at * glassfish/bootstrap/legal/CDDLv1.0.txt. If applicable, * add the following below this CDDL HEADER, with the * fields enclosed by brackets "[]" replaced with your * own identifying information: Portions Copyright [yyyy] * [name of copyright owner] * * Copyright 2005 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved. * * Portions Copyright Apache Software Foundation. */ package javax.servlet; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.Set; /** * * Defines a set of methods that a servlet uses to communicate with its * servlet container, for example, to get the MIME type of a file, dispatch * requests, or write to a log file. * *There is one context per "web application" per Java Virtual Machine. (A * "web application" is a collection of servlets and content installed under a * specific subset of the server's URL namespace such as
/catalog* and possibly installed via a.warfile.) * *In the case of a web * application marked "distributed" in its deployment descriptor, there will * be one context instance for each virtual machine. In this situation, the * context cannot be used as a location to share global information (because * the information won't be truly global). Use an external resource like * a database instead. * *
The
@link ServletConfig} object, which the Web server provides the * servlet when the servlet is initialized. * * @author Various * * @see Servlet#getServletConfig * @see ServletConfig#getServletContext * */ public interface ServletContext { /** * Returns the context path of the web application. * *ServletContextobject is contained within * the {The context path is the portion of the request URI that is used * to select the context of the request. The context path always comes * first in a request URI. The path starts with a "/" character but does * not end with a "/" character. For servlets in the default (root) * context, this method returns "". * *
It is possible that a servlet container may match a context by * more than one context path. In such cases the * {
@link javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest#getContextPath()} * will return the actual context path used by the request and it may * differ from the path returned by this method. * The context path returned by this method should be considered as the * prime or preferred context path of the application. * * @return The context path of the web application, or "" for the * default (root) context * * @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest#getContextPath() * * @since Servlet 2.5 */ public String getContextPath(); /** * Returns aServletContextobject that * corresponds to a specified URL on the server. * *This method allows servlets to gain * access to the context for various parts of the server, and as * needed obtain {
@link RequestDispatcher} objects from the context. * The given path must be begin with "/", is interpreted relative * to the server's document root and is matched against the context roots of * other web applications hosted on this container. * *In a security conscious environment, the servlet container may * return
@param uripath anullfor a given URL. * *Stringspecifying the context path of * another web application in the container. * @return theServletContextobject that * corresponds to the named URL, or null if either none exists or the container wishes to restrict * this access. * * @see RequestDispatcher * */ public ServletContext getContext(String uripath); /** * Returns the major version of the Java Servlet API that this * servlet container supports. All implementations that comply * with Version 2.5 must have this method * return the integer 2. * * @return 2 * */ public int getMajorVersion(); /** * Returns the minor version of the Servlet API that this * servlet container supports. All implementations that comply * with Version 2.5 must have this method * return the integer 5. * * @return 5 * */ public int getMinorVersion(); /** * Returns the MIME type of the specified file, ornullif * the MIME type is not known. The MIME type is determined * by the configuration of the servlet container, and may be specified * in a web application deployment descriptor. Common MIME * types are"text/html"and"image/gif". * * * @param file aStringspecifying the name * of a file * * @return aStringspecifying the file's MIME type * */ public String getMimeType(String file); /** * Returns a directory-like listing of all the paths to resources within the web application whose longest sub-path * matches the supplied path argument. Paths indicating subdirectory paths end with a '/'. The returned paths are all * relative to the root of the web application and have a leading '/'. For example, for a web application * containing
* /welcome.html
* /catalog/index.html
* /catalog/products.html
* /catalog/offers/books.html
* /catalog/offers/music.html
* /customer/login.jsp
* /WEB-INF/web.xml
* /WEB-INF/classes/com.acme.OrderServlet.class,
* * getResourcePaths("/") returns {"/welcome.html", "/catalog/", "/customer/", "/WEB-INF/"}
* getResourcePaths("/catalog/") returns {"/catalog/index.html", "/catalog/products.html", "/catalog/offers/"}.
*@param path the partial path used to match the resources, * which must start with a / *@return a Set containing the directory listing, or null if there are no resources in the web application whose path * begins with the supplied path. * @since Servlet 2.3 */ public Set getResourcePaths(String path); /** * Returns a URL to the resource that is mapped to a specified * path. The path must begin with a "/" and is interpreted * as relative to the current context root. * *This method allows the servlet container to make a resource * available to servlets from any source. Resources * can be located on a local or remote * file system, in a database, or in a
.warfile. * *The servlet container must implement the URL handlers * and
URLConnectionobjects that are necessary * to access the resource. * *This method returns
null* if no resource is mapped to the pathname. * *Some containers may allow writing to the URL returned by * this method using the methods of the URL class. * *
The resource content is returned directly, so be aware that * requesting a
.jsppage returns the JSP source code. * Use aRequestDispatcherinstead to include results of * an execution. * *This method has a different purpose than *
@param path ajava.lang.Class.getResource, * which looks up resources based on a class loader. This * method does not use class loaders. * *Stringspecifying * the path to the resource * * @return the resource located at the named path, * ornullif there is no resource * at that path * * @exception MalformedURLException if the pathname is not given in * the correct form * */ public URL getResource(String path) throws MalformedURLException; /** * Returns the resource located at the named path as * anInputStreamobject. * *The data in the
InputStreamcan be * of any type or length. The path must be specified according * to the rules given ingetResource. * This method returnsnullif no resource exists at * the specified path. * *Meta-information such as content length and content type * that is available via
getResource* method is lost when using this method. * *The servlet container must implement the URL handlers * and
URLConnectionobjects necessary to access * the resource. * *This method is different from *
@param path ajava.lang.Class.getResourceAsStream, * which uses a class loader. This method allows servlet containers * to make a resource available * to a servlet from any location, without using a class loader. * * *Stringspecifying the path * to the resource * * @return theInputStreamreturned to the * servlet, ornullif no resource * exists at the specified path * * */ public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String path); /** * * Returns a {@link RequestDispatcher} object that acts * as a wrapper for the resource located at the given path. * ARequestDispatcherobject can be used to forward * a request to the resource or to include the resource in a response. * The resource can be dynamic or static. * *The pathname must begin with a "/" and is interpreted as relative * to the current context root. Use
@param path agetContextto obtain * aRequestDispatcherfor resources in foreign contexts. * This method returnsnullif theServletContext* cannot return aRequestDispatcher. * *Stringspecifying the pathname * to the resource * * @return aRequestDispatcherobject * that acts as a wrapper for the resource * at the specified path, ornullif * theServletContextcannot return * aRequestDispatcher* * @see RequestDispatcher * @see ServletContext#getContext * */ public RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path); /** * Returns a {@link RequestDispatcher} object that acts * as a wrapper for the named servlet. * *Servlets (and JSP pages also) may be given names via server * administration or via a web application deployment descriptor. * A servlet instance can determine its name using * {
@link ServletConfig#getServletName}. * *This method returns
@param name anullif the *ServletContext* cannot return aRequestDispatcherfor any reason. * *Stringspecifying the name * of a servlet to wrap * * @return aRequestDispatcherobject * that acts as a wrapper for the named servlet, * ornullif theServletContext* cannot return aRequestDispatcher* * @see RequestDispatcher * @see ServletContext#getContext * @see ServletConfig#getServletName * */ public RequestDispatcher getNamedDispatcher(String name); /** * * @deprecated As of Java Servlet API 2.1, with no direct replacement. * *This method was originally defined to retrieve a servlet * from a
ServletContext. In this version, this method * always returnsnulland remains only to preserve * binary compatibility. This method will be permanently removed * in a future version of the Java Servlet API. * *In lieu of this method, servlets can share information using the *
*/ public Servlet getServlet(String name) throws ServletException; /** * * @deprecated As of Java Servlet API 2.0, with no replacement. * *ServletContextclass and can perform shared business logic * by invoking methods on common non-servlet classes. *This method was originally defined to return an
*/ public Enumeration getServlets(); /** * @deprecated As of Java Servlet API 2.1, with no replacement. * *Enumeration* of all the servlets known to this servlet context. In this * version, this method always returns an empty enumeration and * remains only to preserve binary compatibility. This method * will be permanently removed in a future version of the Java * Servlet API. *This method was originally defined to return an *
*/ public Enumeration getServletNames(); /** * * Writes the specified message to a servlet log file, usually * an event log. The name and type of the servlet log file is * specific to the servlet container. * * * @param msg aEnumeration* of all the servlet names known to this context. In this version, * this method always returns an emptyEnumerationand * remains only to preserve binary compatibility. This method will * be permanently removed in a future version of the Java Servlet API. *Stringspecifying the * message to be written to the log file * */ public void log(String msg); /** * @deprecated As of Java Servlet API 2.1, use * {@link #log(String message, Throwable throwable)} * instead. * *This method was originally defined to write an * exception's stack trace and an explanatory error message * to the servlet log file. *
*/ public void log(Exception exception, String msg); /** * Writes an explanatory message and a stack trace * for a givenThrowableexception * to the servlet log file. The name and type of the servlet log * file is specific to the servlet container, usually an event log. * * * @param message aStringthat * describes the error or exception * * @param throwable theThrowableerror * or exception * */ public void log(String message, Throwable throwable); /** * Returns aStringcontaining the real path * for a given virtual path. For example, the path "/index.html" * returns the absolute file path on the server's filesystem would be * served by a request for "http://host/contextPath/index.html", * where contextPath is the context path of this ServletContext.. * *The real path returned will be in a form * appropriate to the computer and operating system on * which the servlet container is running, including the * proper path separators. This method returns
@param path anull* if the servlet container cannot translate the virtual path * to a real path for any reason (such as when the content is * being made available from a.wararchive). * * *Stringspecifying a virtual path * * * @return aStringspecifying the real path, * or null if the translation cannot be performed * * */ public String getRealPath(String path); /** * Returns the name and version of the servlet container on which * the servlet is running. * *The form of the returned string is * servername/versionnumber. * For example, the JavaServer Web Development Kit may return the string *
JavaServer Web Dev Kit/1.0. * *The servlet container may return other optional information * after the primary string in parentheses, for example, *
@return aJavaServer Web Dev Kit/1.0 (JDK 1.1.6; Windows NT 4.0 x86). * * *Stringcontaining at least the * servlet container name and version number * */ public String getServerInfo(); /** * Returns aStringcontaining the value of the named * context-wide initialization parameter, ornullif the * parameter does not exist. * *This method can make available configuration information useful * to an entire "web application". For example, it can provide a * webmaster's email address or the name of a system that holds * critical data. * *
@param name aStringcontaining the name of the * parameter whose value is requested * * @return aStringcontaining at least the * servlet container name and version number * * @see ServletConfig#getInitParameter */ public String getInitParameter(String name); /** * Returns the names of the context's initialization parameters as an *EnumerationofStringobjects, or an * emptyEnumerationif the context has no initialization * parameters. * * @return anEnumerationofString* objects containing the names of the context's * initialization parameters * * @see ServletConfig#getInitParameter */ public Enumeration getInitParameterNames(); /** * Returns the servlet container attribute with the given name, * ornullif there is no attribute by that name. * An attribute allows a servlet container to give the * servlet additional information not * already provided by this interface. See your * server documentation for information about its attributes. * A list of supported attributes can be retrieved using *getAttributeNames. * *The attribute is returned as a
@param name ajava.lang.Object* or some subclass. * Attribute names should follow the same convention as package * names. The Java Servlet API specification reserves names * matchingjava.*,javax.*, * andsun.*. * * *Stringspecifying the name * of the attribute * * @return anObjectcontaining the value * of the attribute, ornull* if no attribute exists matching the given * name * * @see ServletContext#getAttributeNames * */ public Object getAttribute(String name); /** * Returns anEnumerationcontaining the * attribute names available * within this servlet context. Use the * {@link #getAttribute} method with an attribute name * to get the value of an attribute. * * @return anEnumerationof attribute * names * * @see #getAttribute * */ public Enumeration getAttributeNames(); /** * * Binds an object to a given attribute name in this servlet context. If * the name specified is already used for an attribute, this * method will replace the attribute with the new to the new attribute. *If listeners are configured on the
ServletContextthe * container notifies them accordingly. ** If a null value is passed, the effect is the same as calling *
removeAttribute(). * *Attribute names should follow the same convention as package * names. The Java Servlet API specification reserves names * matching
@param name ajava.*,javax.*, and *sun.*. * * *Stringspecifying the name * of the attribute * * @param object anObjectrepresenting the * attribute to be bound * * * */ public void setAttribute(String name, Object object); /** * Removes the attribute with the given name from * the servlet context. After removal, subsequent calls to * {@link #getAttribute} to retrieve the attribute's value * will returnnull. *If listeners are configured on the
@param name aServletContextthe * container notifies them accordingly. * * *Stringspecifying the name * of the attribute to be removed * */ public void removeAttribute(String name); /** * Returns the name of this web application corresponding to this ServletContext as specified in the deployment * descriptor for this web application by the display-name element. * * * @return The name of the web application or null if no name has been declared in the deployment descriptor. * @since Servlet 2.3 */ public String getServletContextName(); }
定义了 一些列的方法,具体就不看了,有兴趣的可以详细看下
Servlet 3.0+ 规范
我们采用4.0.1来看下源码
maven依赖
javax.servlet javax.servlet-api 4.0.1 provided
源码
/* * Copyright (c) 1997-2018 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. * Copyright 2004 The Apache Software Foundation * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package javax.servlet; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.EnumSet; import java.util.EventListener; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import javax.servlet.descriptor.JspConfigDescriptor; /** * Defines a set of methods that a servlet uses to communicate with its * servlet container, for example, to get the MIME type of a file, * dispatch requests, or write to a log file. * ** * getResourcePaths("/") would return * {"/welcome.html", "/catalog/", "/customer/", "/WEB-INF/"}, * and getResourcePaths("/catalog/") would return * {"/catalog/index.html", "/catalog/products.html", * "/catalog/offers/", "/catalog/moreOffers/"}. * * @param path the partial path used to match the resources, * which must start with a / * @return a Set containing the directory listing, or null if there * are no resources in the web application whose path * begins with the supplied path. * * @since Servlet 2.3 */ public SetThere is one context per "web application" per Java Virtual Machine. (A * "web application" is a collection of servlets and content installed under a * specific subset of the server's URL namespace such as
/catalog* and possibly installed via a.warfile.) * *In the case of a web * application marked "distributed" in its deployment descriptor, there will * be one context instance for each virtual machine. In this situation, the * context cannot be used as a location to share global information (because * the information won't be truly global). Use an external resource like * a database instead. * *
The
@link ServletConfig} object, which the Web server provides the * servlet when the servlet is initialized. * * @author Various * * @see Servlet#getServletConfig * @see ServletConfig#getServletContext */ public interface ServletContext { /** * The name of the ServletContext attribute which stores * the private temporary directory (of type java.io.File) * provided by the servlet container for the ServletContext */ public static final String TEMPDIR = "javax.servlet.context.tempdir"; /** * The name of theServletContextobject is contained within * the {ServletContextattribute whose value * (of typejava.util.List<java.lang.String>) contains * the list of names of JAR files inWEB-INF/libordered by * their web fragment names (with possible exclusions if *<absolute-ordering>without any *<others/>is being used), or null if no * absolute or relative ordering has been specified */ public static final String ORDERED_LIBS = "javax.servlet.context.orderedLibs"; /** * Returns the context path of the web application. * *The context path is the portion of the request URI that is used * to select the context of the request. The context path always comes * first in a request URI. If this context is the "root" context * rooted at the base of the Web server's URL name space, this path * will be an empty string. Otherwise, if the context is not rooted at * the root of the server's name space, the path starts with a / * character but does not end with a / character. * *
It is possible that a servlet container may match a context by * more than one context path. In such cases the * {
@link javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest#getContextPath()} * will return the actual context path used by the request and it may * differ from the path returned by this method. * The context path returned by this method should be considered as the * prime or preferred context path of the application. * * @return The context path of the web application, or "" for the * root context * * @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest#getContextPath() * * @since Servlet 2.5 */ public String getContextPath(); /** * Returns aServletContextobject that * corresponds to a specified URL on the server. * *This method allows servlets to gain * access to the context for various parts of the server, and as * needed obtain {
@link RequestDispatcher} objects from the context. * The given path must be begin with /, is interpreted relative * to the server's document root and is matched against the context * roots of other web applications hosted on this container. * *In a security conscious environment, the servlet container may * return
@param uripath anullfor a given URL. * *Stringspecifying the context path of * another web application in the container. * @return theServletContextobject that * corresponds to the named URL, or null if either none exists or the container wishes to restrict * this access. * * @see RequestDispatcher */ public ServletContext getContext(String uripath); /** * Returns the major version of the Servlet API that this * servlet container supports. All implementations that comply * with Version 4.0 must have this method return the integer 4. * * @return 4 */ public int getMajorVersion(); /** * Returns the minor version of the Servlet API that this * servlet container supports. All implementations that comply * with Version 4.0 must have this method return the integer 0. * * @return 0 */ public int getMinorVersion(); /** * Gets the major version of the Servlet specification that the * application represented by this ServletContext is based on. * *The value returned may be different from {
@link #getMajorVersion}, * which returns the major version of the Servlet specification * supported by the Servlet container. * * @return the major version of the Servlet specification that the * application represented by this ServletContext is based on * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xmlorweb-fragment.xml, nor annotated * with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener} * * @since Servlet 3.0 */ public int getEffectiveMajorVersion(); /** * Gets the minor version of the Servlet specification that the * application represented by this ServletContext is based on. * *The value returned may be different from {
@link #getMinorVersion}, * which returns the minor version of the Servlet specification * supported by the Servlet container. * * @return the minor version of the Servlet specification that the * application represented by this ServletContext is based on * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xmlorweb-fragment.xml, nor annotated * with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener} * * @since Servlet 3.0 */ public int getEffectiveMinorVersion(); /** * Returns the MIME type of the specified file, ornullif * the MIME type is not known. The MIME type is determined * by the configuration of the servlet container, and may be specified * in a web application deployment descriptor. Common MIME * types includetext/htmlandimage/gif. * * @param file aStringspecifying the name of a file * * @return aStringspecifying the file's MIME type */ public String getMimeType(String file); /** * Returns a directory-like listing of all the paths to resources * within the web application whose longest sub-path matches the * supplied path argument. * *Paths indicating subdirectory paths end with a /. * *
The returned paths are all relative to the root of the web * application, or relative to the /META-INF/resources * directory of a JAR file inside the web application's * /WEB-INF/lib directory, and have a leading /. * *
The returned set is not backed by the {
@code ServletContext} object, * so changes in the returned set are not reflected in the * {@code ServletContext} object, and vice-versa. * *For example, for a web application containing: * *
{@code * /welcome.html * /catalog/index.html * /catalog/products.html * /catalog/offers/books.html * /catalog/offers/music.html * /customer/login.jsp * /WEB-INF/web.xml * /WEB-INF/classes/com.acme.OrderServlet.class * /WEB-INF/lib/catalog.jar!/META-INF/resources/catalog/moreOffers/books.html * }
The path must begin with a / and is interpreted * as relative to the current context root, * or relative to the /META-INF/resources directory * of a JAR file inside the web application's /WEB-INF/lib * directory. * This method will first search the document root of the * web application for the requested resource, before searching * any of the JAR files inside /WEB-INF/lib. * The order in which the JAR files inside /WEB-INF/lib * are searched is undefined. * *
This method allows the servlet container to make a resource
* available to servlets from any source. Resources
* can be located on a local or remote
* file system, in a database, or in a .war file.
*
*
The servlet container must implement the URL handlers
* and URLConnection objects that are necessary
* to access the resource.
*
*
This method returns null
* if no resource is mapped to the pathname.
*
*
Some containers may allow writing to the URL returned by * this method using the methods of the URL class. * *
The resource content is returned directly, so be aware that
* requesting a .jsp page returns the JSP source code.
* Use a RequestDispatcher instead to include results of
* an execution.
*
*
This method has a different purpose than
* java.lang.Class.getResource,
* which looks up resources based on a class loader. This
* method does not use class loaders.
*
*
String specifying
* the path to the resource
*
* @return the resource located at the named path,
* or null if there is no resource at that path
*
* @exception MalformedURLException if the pathname is not given in
* the correct form
*/
public URL getResource(String path) throws MalformedURLException;
/**
* Returns the resource located at the named path as
* an InputStream object.
*
* The data in the InputStream can be
* of any type or length. The path must be specified according
* to the rules given in getResource.
* This method returns null if no resource exists at
* the specified path.
*
*
Meta-information such as content length and content type
* that is available via getResource
* method is lost when using this method.
*
*
The servlet container must implement the URL handlers
* and URLConnection objects necessary to access
* the resource.
*
*
This method is different from
* java.lang.Class.getResourceAsStream,
* which uses a class loader. This method allows servlet containers
* to make a resource available
* to a servlet from any location, without using a class loader.
*
*
*
String specifying the path
* to the resource
*
* @return the InputStream returned to the
* servlet, or null if no resource
* exists at the specified path
*/
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String path);
/**
*
* Returns a {@link RequestDispatcher} object that acts
* as a wrapper for the resource located at the given path.
* A RequestDispatcher object can be used to forward
* a request to the resource or to include the resource in a response.
* The resource can be dynamic or static.
*
* The pathname must begin with a / and is interpreted as
* relative to the current context root. Use getContext
* to obtain a RequestDispatcher for resources in foreign
* contexts.
*
*
This method returns null if the
* ServletContext cannot return a
* RequestDispatcher.
*
*
String specifying the pathname
* to the resource
*
* @return a RequestDispatcher object
* that acts as a wrapper for the resource
* at the specified path, or null if
* the ServletContext cannot return
* a RequestDispatcher
*
* @see RequestDispatcher
* @see ServletContext#getContext
*/
public RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path);
/**
* Returns a {@link RequestDispatcher} object that acts
* as a wrapper for the named servlet.
*
* Servlets (and JSP pages also) may be given names via server * administration or via a web application deployment descriptor. * A servlet instance can determine its name using * {
@link ServletConfig#getServletName}. * *This method returns null if the
* ServletContext
* cannot return a RequestDispatcher for any reason.
*
*
String specifying the name
* of a servlet to wrap
*
* @return a RequestDispatcher object
* that acts as a wrapper for the named servlet,
* or null if the ServletContext
* cannot return a RequestDispatcher
*
* @see RequestDispatcher
* @see ServletContext#getContext
* @see ServletConfig#getServletName
*/
public RequestDispatcher getNamedDispatcher(String name);
/**
* @deprecated As of Java Servlet API 2.1, with no direct replacement.
*
* This method was originally defined to retrieve a servlet
* from a ServletContext. In this version, this method
* always returns null and remains only to preserve
* binary compatibility. This method will be permanently removed
* in a future version of the Java Servlet API.
*
*
In lieu of this method, servlets can share information using the
* ServletContext class and can perform shared business logic
* by invoking methods on common non-servlet classes.
*
*
This method was originally defined to return an
* Enumeration of all the servlets known to this servlet
* context.
* In this version, this method always returns an empty enumeration and
* remains only to preserve binary compatibility. This method
* will be permanently removed in a future version of the Java
* Servlet API.
*
*
Enumeration of {@code javax.servlet.Servlet Servlet}
*/
@Deprecated
public EnumerationThis method was originally defined to return an
* Enumeration
* of all the servlet names known to this context. In this version,
* this method always returns an empty Enumeration and
* remains only to preserve binary compatibility. This method will
* be permanently removed in a future version of the Java Servlet API.
*
*
Enumeration of {@code javax.servlet.Servlet Servlet} names
*/
@Deprecated
public EnumerationString specifying the
* message to be written to the log file
*/
public void log(String msg);
/**
* @deprecated As of Java Servlet API 2.1, use
* {@link #log(String message, Throwable throwable)}
* instead.
*
* This method was originally defined to write an * exception's stack trace and an explanatory error message * to the servlet log file. * *
@param exception theException error
* @param msg a String that describes the exception
*/
@Deprecated
public void log(Exception exception, String msg);
/**
* Writes an explanatory message and a stack trace
* for a given Throwable exception
* to the servlet log file. The name and type of the servlet log
* file is specific to the servlet container, usually an event log.
*
* @param message a String that
* describes the error or exception
*
* @param throwable the Throwable error
* or exception
*/
public void log(String message, Throwable throwable);
/**
* Gets the real path corresponding to the given
* virtual path.
*
* For example, if path is equal to /index.html, * this method will return the absolute file path on the server's * filesystem to which a request of the form * http://<host>:<port>/<contextPath>/index.html * would be mapped, where <contextPath> corresponds to the * context path of this ServletContext. * *
The real path returned will be in a form * appropriate to the computer and operating system on * which the servlet container is running, including the * proper path separators. * *
Resources inside the /META-INF/resources * directories of JAR files bundled in the application's * /WEB-INF/lib directory must be considered only if the * container has unpacked them from their containing JAR file, in * which case the path to the unpacked location must be returned. * *
This method returns null if the servlet container
* is unable to translate the given virtual path to a
* real path.
*
*
The form of the returned string is
* servername/versionnumber.
* For example, the JavaServer Web Development Kit may return the string
* JavaServer Web Dev Kit/1.0.
*
*
The servlet container may return other optional information
* after the primary string in parentheses, for example,
* JavaServer Web Dev Kit/1.0 (JDK 1.1.6; Windows NT 4.0 x86).
*
*
*
String containing at least the
* servlet container name and version number
*/
public String getServerInfo();
/**
* Returns a String containing the value of the named
* context-wide initialization parameter, or null if
* the parameter does not exist.
*
* This method can make available configuration information useful * to an entire web application. For example, it can provide a * webmaster's email address or the name of a system that holds * critical data. * *
@param name aString containing the name of the
* parameter whose value is requested
*
* @return a String containing the value of the
* context's initialization parameter, or null if the
* context's initialization parameter does not exist.
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the argument {@code name} is
* {@code null}
*
* @see ServletConfig#getInitParameter
*/
public String getInitParameter(String name);
/**
* Returns the names of the context's initialization parameters as an
* Enumeration of String objects, or an
* empty Enumeration if the context has no initialization
* parameters.
*
* @return an Enumeration of String
* objects containing the names of the context's
* initialization parameters
*
* @see ServletConfig#getInitParameter
*/
public Enumerationweb.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public boolean setInitParameter(String name, String value);
/**
* Returns the servlet container attribute with the given name, or
* null if there is no attribute by that name.
*
* An attribute allows a servlet container to give the
* servlet additional information not
* already provided by this interface. See your
* server documentation for information about its attributes.
* A list of supported attributes can be retrieved using
* getAttributeNames.
*
*
The attribute is returned as a java.lang.Object
* or some subclass.
*
*
Attribute names should follow the same convention as package
* names. The Java Servlet API specification reserves names
* matching java.*, javax.*,
* and sun.*.
*
*
String specifying the name
* of the attribute
*
* @return an Object containing the value of the
* attribute, or null if no attribute
* exists matching the given name.
*
* @see ServletContext#getAttributeNames
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the argument {@code name} is
* {@code null}
*
*/
public Object getAttribute(String name);
/**
* Returns an Enumeration containing the
* attribute names available within this ServletContext.
*
* Use the {
@link #getAttribute} method with an attribute name * to get the value of an attribute. * * @return anEnumeration of attribute
* names
*
* @see #getAttribute
*/
public EnumerationIf listeners are configured on the ServletContext the
* container notifies them accordingly.
*
* If a null value is passed, the effect is the same as calling
* removeAttribute().
*
*
Attribute names should follow the same convention as package
* names. The Java Servlet API specification reserves names
* matching java.*, javax.*, and
* sun.*.
*
*
String specifying the name
* of the attribute
*
* @param object an Object representing the
* attribute to be bound
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the name parameter is {@code null}
*
*/
public void setAttribute(String name, Object object);
/**
* Removes the attribute with the given name from
* this ServletContext. After removal, subsequent calls to
* {@link #getAttribute} to retrieve the attribute's value
* will return null.
*
* If listeners are configured on the ServletContext the
* container notifies them accordingly.
*
*
String specifying the name
* of the attribute to be removed
*/
public void removeAttribute(String name);
/**
* Returns the name of this web application corresponding to this
* ServletContext as specified in the deployment descriptor for this
* web application by the display-name element.
*
* @return The name of the web application or null if no name has been
* declared in the deployment descriptor.
*
* @since Servlet 2.3
*/
public String getServletContextName();
/**
* Adds the servlet with the given name and class name to this servlet
* context.
*
* The registered servlet may be further configured via the returned * {
@link ServletRegistration} object. * *The specified className will be loaded using the * classloader associated with the application represented by this * ServletContext. * *
If this ServletContext already contains a preliminary * ServletRegistration for a servlet with the given servletName, * it will be completed (by assigning the given className to it) * and returned. * *
This method introspects the class with the given className * for the {
@link javax.servlet.annotation.ServletSecurity}, * {@link javax.servlet.annotation.MultipartConfig}, * javax.annotation.security.RunAs, and * javax.annotation.security.DeclareRoles annotations. * In addition, this method supports resource injection if the * class with the given className represents a Managed Bean. * See the Java EE platform and JSR 299 specifications for additional * details about Managed Beans and resource injection. * * @param servletName the name of the servlet * @param className the fully qualified class name of the servlet * * @return a ServletRegistration object that may be used to further * configure the registered servlet, or null if this * ServletContext already contains a complete ServletRegistration for * a servlet with the given servletName * * @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already * been initialized * * @throws IllegalArgumentException ifservletName is null
* or an empty String
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public ServletRegistration.Dynamic addServlet(
String servletName, String className);
/**
* Registers the given servlet instance with this ServletContext
* under the given servletName.
*
* The registered servlet may be further configured via the returned * {
@link ServletRegistration} object. * *If this ServletContext already contains a preliminary * ServletRegistration for a servlet with the given servletName, * it will be completed (by assigning the class name of the given servlet * instance to it) and returned. * *
@param servletName the name of the servlet * @param servlet the servlet instance to register * * @return a ServletRegistration object that may be used to further * configure the given servlet, or null if this * ServletContext already contains a complete ServletRegistration for a * servlet with the given servletName or if the same servlet * instance has already been registered with this or another * ServletContext in the same container * * @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already * been initialized * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the given servlet instance
* implements {@link SingleThreadModel}, or servletName is null
* or an empty String
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public ServletRegistration.Dynamic addServlet(
String servletName, Servlet servlet);
/**
* Adds the servlet with the given name and class type to this servlet
* context.
*
* The registered servlet may be further configured via the returned * {
@link ServletRegistration} object. * *If this ServletContext already contains a preliminary * ServletRegistration for a servlet with the given servletName, * it will be completed (by assigning the name of the given * servletClass to it) and returned. * *
This method introspects the given servletClass for * the {
@link javax.servlet.annotation.ServletSecurity}, * {@link javax.servlet.annotation.MultipartConfig}, * javax.annotation.security.RunAs, and * javax.annotation.security.DeclareRoles annotations. * In addition, this method supports resource injection if the * given servletClass represents a Managed Bean. * See the Java EE platform and JSR 299 specifications for additional * details about Managed Beans and resource injection. * * @param servletName the name of the servlet * @param servletClass the class object from which the servlet will be * instantiated * * @return a ServletRegistration object that may be used to further * configure the registered servlet, or null if this * ServletContext already contains a complete ServletRegistration for * the given servletName * * @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already * been initialized * * @throws IllegalArgumentException ifservletName is null
* or an empty String
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public ServletRegistration.Dynamic addServlet(String servletName,
Class extends Servlet> servletClass);
/**
* Adds the servlet with the given jsp file to this servlet context.
*
* The registered servlet may be further configured via the returned * {
@link ServletRegistration} object. * *If this ServletContext already contains a preliminary * ServletRegistration for a servlet with the given servletName, * it will be completed (by assigning the given jspFile to it) * and returned. * *
@param servletName the name of the servlet * @param jspFile the full path to a JSP file within the web application * beginning with a `/'. * * @return a ServletRegistration object that may be used to further * configure the registered servlet, or null if this * ServletContext already contains a complete ServletRegistration for * a servlet with the given servletName * * @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already * been initialized * * @throws IllegalArgumentException ifservletName is null
* or an empty String
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 4.0
*/
public ServletRegistration.Dynamic addJspFile(
String servletName, String jspFile);
/**
* Instantiates the given Servlet class.
*
* The returned Servlet instance may be further customized before it * is registered with this ServletContext via a call to * {
@link #addServlet(String,Servlet)}. * *The given Servlet class must define a zero argument constructor, * which is used to instantiate it. * *
This method introspects the given clazz for * the following annotations: * {
@link javax.servlet.annotation.ServletSecurity}, * {@link javax.servlet.annotation.MultipartConfig}, * javax.annotation.security.RunAs, and * javax.annotation.security.DeclareRoles. * In addition, this method supports resource injection if the * given clazz represents a Managed Bean. * See the Java EE platform and JSR 299 specifications for additional * details about Managed Beans and resource injection. * * @paramweb.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @param servletName the name of a servlet
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public ServletRegistration getServletRegistration(String servletName);
/**
* Gets a (possibly empty) Map of the ServletRegistration
* objects (keyed by servlet name) corresponding to all servlets
* registered with this ServletContext.
*
* The returned Map includes the ServletRegistration objects * corresponding to all declared and annotated servlets, as well as the * ServletRegistration objects corresponding to all servlets that have * been added via one of the addServlet and addJspFile * methods. * *
If permitted, any changes to the returned Map must not affect this * ServletContext. * *
@return Map of the (complete and preliminary) ServletRegistration * objects corresponding to all servlets currently registered with this * ServletContext * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public MapThe registered filter may be further configured via the returned * {
@link FilterRegistration} object. * *The specified className will be loaded using the * classloader associated with the application represented by this * ServletContext. * *
If this ServletContext already contains a preliminary * FilterRegistration for a filter with the given filterName, * it will be completed (by assigning the given className to it) * and returned. * *
This method supports resource injection if the class with the * given className represents a Managed Bean. * See the Java EE platform and JSR 299 specifications for additional * details about Managed Beans and resource injection. * *
@param filterName the name of the filter * @param className the fully qualified class name of the filter * * @return a FilterRegistration object that may be used to further * configure the registered filter, or null if this * ServletContext already contains a complete FilterRegistration for * a filter with the given filterName * * @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already * been initialized * * @throws IllegalArgumentException iffilterName is null or
* an empty String
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public FilterRegistration.Dynamic addFilter(
String filterName, String className);
/**
* Registers the given filter instance with this ServletContext
* under the given filterName.
*
* The registered filter may be further configured via the returned * {
@link FilterRegistration} object. * *If this ServletContext already contains a preliminary * FilterRegistration for a filter with the given filterName, * it will be completed (by assigning the class name of the given filter * instance to it) and returned. * *
@param filterName the name of the filter * @param filter the filter instance to register * * @return a FilterRegistration object that may be used to further * configure the given filter, or null if this * ServletContext already contains a complete FilterRegistration for a * filter with the given filterName or if the same filter * instance has already been registered with this or another * ServletContext in the same container * * @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already * been initialized * * @throws IllegalArgumentException iffilterName is null or
* an empty String
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public FilterRegistration.Dynamic addFilter(
String filterName, Filter filter);
/**
* Adds the filter with the given name and class type to this servlet
* context.
*
* The registered filter may be further configured via the returned * {
@link FilterRegistration} object. * *If this ServletContext already contains a preliminary * FilterRegistration for a filter with the given filterName, * it will be completed (by assigning the name of the given * filterClass to it) and returned. * *
This method supports resource injection if the given * filterClass represents a Managed Bean. * See the Java EE platform and JSR 299 specifications for additional * details about Managed Beans and resource injection. * *
@param filterName the name of the filter * @param filterClass the class object from which the filter will be * instantiated * * @return a FilterRegistration object that may be used to further * configure the registered filter, or null if this * ServletContext already contains a complete FilterRegistration for a * filter with the given filterName * * @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already * been initialized * * @throws IllegalArgumentException iffilterName is null or
* an empty String
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public FilterRegistration.Dynamic addFilter(String filterName,
Class extends Filter> filterClass);
/**
* Instantiates the given Filter class.
*
* The returned Filter instance may be further customized before it * is registered with this ServletContext via a call to * {
@link #addFilter(String,Filter)}. * *The given Filter class must define a zero argument constructor, * which is used to instantiate it. * *
This method supports resource injection if the given * clazz represents a Managed Bean. * See the Java EE platform and JSR 299 specifications for additional * details about Managed Beans and resource injection. * *
@paramweb.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public FilterRegistration getFilterRegistration(String filterName);
/**
* Gets a (possibly empty) Map of the FilterRegistration
* objects (keyed by filter name) corresponding to all filters
* registered with this ServletContext.
*
* The returned Map includes the FilterRegistration objects * corresponding to all declared and annotated filters, as well as the * FilterRegistration objects corresponding to all filters that have * been added via one of the addFilter methods. * *
Any changes to the returned Map must not affect this * ServletContext. * *
@return Map of the (complete and preliminary) FilterRegistration * objects corresponding to all filters currently registered with this * ServletContext * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public MapRepeated invocations of this method will return the same * SessionCookieConfig instance. * *
@return the SessionCookieConfig object through which * various properties of the session tracking cookies created on * behalf of this ServletContext may be configured * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public SessionCookieConfig getSessionCookieConfig();
/**
* Sets the session tracking modes that are to become effective for this
* ServletContext.
*
* The given sessionTrackingModes replaces any * session tracking modes set by a previous invocation of this * method on this ServletContext. * *
@param sessionTrackingModes the set of session tracking modes to * become effective for this ServletContext * * @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already * been initialized * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if sessionTrackingModes
* specifies a combination of SessionTrackingMode.SSL with a
* session tracking mode other than SessionTrackingMode.SSL,
* or if sessionTrackingModes specifies a session tracking mode
* that is not supported by the servlet container
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public void setSessionTrackingModes(SetThe returned set is not backed by the {
@code ServletContext} object, * so changes in the returned set are not reflected in the * {@code ServletContext} object, and vice-versa. * * @return set of the session tracking modes supported by default for * this ServletContext * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public SetThe session tracking modes in effect are those provided to * {
@link #setSessionTrackingModes setSessionTrackingModes}. * *The returned set is not backed by the {
@code ServletContext} object, * so changes in the returned set are not reflected in the * {@code ServletContext} object, and vice-versa. * * @return set of the session tracking modes in effect for this * ServletContext * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public SetThe class with the given name will be loaded using the * classloader associated with the application represented by this * ServletContext, and must implement one or more of the following * interfaces: *
-
*
- {
If this ServletContext was passed to * {
@link ServletContainerInitializer#onStartup}, then the class with * the given name may also implement {@link ServletContextListener}, * in addition to the interfaces listed above. * *As part of this method call, the container must load the class * with the specified class name to ensure that it implements one of * the required interfaces. * *
If the class with the given name implements a listener interface * whose invocation order corresponds to the declaration order (i.e., * if it implements {
@link ServletRequestListener}, * {@link ServletContextListener}, or * {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener}), * then the new listener will be added to the end of the ordered list of * listeners of that interface. * *This method supports resource injection if the class with the * given className represents a Managed Bean. * See the Java EE platform and JSR 299 specifications for additional * details about Managed Beans and resource injection. * *
@param className the fully qualified class name of the listener * * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the class with the given name * does not implement any of the above interfaces, or if it implements * {@link ServletContextListener} and this ServletContext was not * passed to {@link ServletContainerInitializer#onStartup} * * @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already * been initialized * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public void addListener(String className);
/**
* Adds the given listener to this ServletContext.
*
* The given listener must be an instance of one or more of the * following interfaces: *
-
*
- {
If this ServletContext was passed to * {
@link ServletContainerInitializer#onStartup}, then the given * listener may also be an instance of {@link ServletContextListener}, * in addition to the interfaces listed above. * *If the given listener is an instance of a listener interface whose * invocation order corresponds to the declaration order (i.e., if it * is an instance of {
@link ServletRequestListener}, * {@link ServletContextListener}, or * {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener}), * then the listener will be added to the end of the ordered list of * listeners of that interface. * * @paramweb.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public The given listenerClass must implement one or more of the * following interfaces: *
-
*
- {
If this ServletContext was passed to * {
@link ServletContainerInitializer#onStartup}, then the given * listenerClass may also implement * {@link ServletContextListener}, in addition to the interfaces listed * above. * *If the given listenerClass implements a listener * interface whose invocation order corresponds to the declaration order * (i.e., if it implements {
@link ServletRequestListener}, * {@link ServletContextListener}, or * {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener}), * then the new listener will be added to the end of the ordered list * of listeners of that interface. * *This method supports resource injection if the given * listenerClass represents a Managed Bean. * See the Java EE platform and JSR 299 specifications for additional * details about Managed Beans and resource injection. * *
@param listenerClass the listener class to be instantiated * * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the given listenerClass * does not implement any of the above interfaces, or if it implements * {@link ServletContextListener} and this ServletContext was not passed * to {@link ServletContainerInitializer#onStartup} * * @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already * been initialized * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public void addListener(Class extends EventListener> listenerClass);
/**
* Instantiates the given EventListener class.
*
* The specified EventListener class must implement at least one of * the {
@link ServletContextListener}, * {@link ServletContextAttributeListener}, * {@link ServletRequestListener}, * {@link ServletRequestAttributeListener}, * {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionAttributeListener}, * {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionIdListener}, or * {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener} * interfaces. * *The returned EventListener instance may be further customized * before it is registered with this ServletContext via a call to * {
@link #addListener(EventListener)}. * *The given EventListener class must define a zero argument * constructor, which is used to instantiate it. * *
This method supports resource injection if the given * clazz represents a Managed Bean. * See the Java EE platform and JSR 299 specifications for additional * details about Managed Beans and resource injection. * *
@paramweb.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified EventListener class
* does not implement any of the
* {@link ServletContextListener},
* {@link ServletContextAttributeListener},
* {@link ServletRequestListener},
* {@link ServletRequestAttributeListener},
* {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionAttributeListener},
* {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionIdListener}, or
* {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener}
* interfaces.
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public <jsp-config> related configuration
* that was aggregated from the web.xml and
* web-fragment.xml descriptor files of the web application
* represented by this ServletContext.
*
* @return the <jsp-config> related configuration
* that was aggregated from the web.xml and
* web-fragment.xml descriptor files of the web application
* represented by this ServletContext, or null if no such configuration
* exists
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @see javax.servlet.descriptor.JspConfigDescriptor
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public JspConfigDescriptor getJspConfigDescriptor();
/**
* Gets the class loader of the web application represented by this
* ServletContext.
*
* If a security manager exists, and the caller's class loader
* is not the same as, or an ancestor of the requested class loader,
* then the security manager's checkPermission method is
* called with a RuntimePermission("getClassLoader")
* permission to check whether access to the requested class loader
* should be granted.
*
*
web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @throws SecurityException if a security manager denies access to
* the requested class loader
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public ClassLoader getClassLoader();
/**
* Declares role names that are tested using isUserInRole.
*
* Roles that are implicitly declared as a result of their use within * the {
@link ServletRegistration.Dynamic#setServletSecurity * setServletSecurity} or {@link ServletRegistration.Dynamic#setRunAsRole * setRunAsRole} methods of the {@link ServletRegistration} interface need * not be declared. * * @param roleNames the role names being declared * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was * passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method * of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in *web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if any of the argument roleNames is
* null or the empty string
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if the ServletContext has already
* been initialized
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public void declareRoles(String... roleNames);
/**
* Returns the configuration name of the logical host on which the
* ServletContext is deployed.
*
* Servlet containers may support multiple logical hosts. This method must
* return the same name for all the servlet contexts deployed on a logical
* host, and the name returned by this method must be distinct, stable per
* logical host, and suitable for use in associating server configuration
* information with the logical host. The returned value is NOT expected
* or required to be equivalent to a network address or hostname of the
* logical host.
*
* @return a String containing the configuration name of the
* logical host on which the servlet context is deployed.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 3.1
*/
public String getVirtualServerName();
/**
* Gets the session timeout in minutes that are supported by default for
* this ServletContext.
*
* @return the session timeout in minutes that are supported by default for
* this ServletContext
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 4.0
*/
public int getSessionTimeout();
/**
* Sets the session timeout in minutes for this ServletContext.
*
* @param sessionTimeout session timeout in minutes
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already
* been initialized
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 4.0
*/
public void setSessionTimeout(int sessionTimeout);
/**
* Gets the request character encoding that are supported by default for
* this ServletContext. This method returns null if no request
* encoding character encoding has been specified in deployment descriptor
* or container specific configuration (for all web applications in the
* container).
*
* @return the request character encoding that are supported by default for
* this ServletContext
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 4.0
*/
public String getRequestCharacterEncoding();
/**
* Sets the request character encoding for this ServletContext.
*
* @param encoding request character encoding
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already
* been initialized
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 4.0
*/
public void setRequestCharacterEncoding(String encoding);
/**
* Gets the response character encoding that are supported by default for
* this ServletContext. This method returns null if no response
* encoding character encoding has been specified in deployment descriptor
* or container specific configuration (for all web applications in the
* container).
*
* @return the request character encoding that are supported by default for
* this ServletContext
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 4.0
*/
public String getResponseCharacterEncoding();
/**
* Sets the response character encoding for this ServletContext.
*
* @param encoding response character encoding
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if this ServletContext has already
* been initialized
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this ServletContext was
* passed to the {@link ServletContextListener#contextInitialized} method
* of a {@link ServletContextListener} that was neither declared in
* web.xml or web-fragment.xml, nor annotated
* with {@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}
*
* @since Servlet 4.0
*/
public void setResponseCharacterEncoding(String encoding);
}
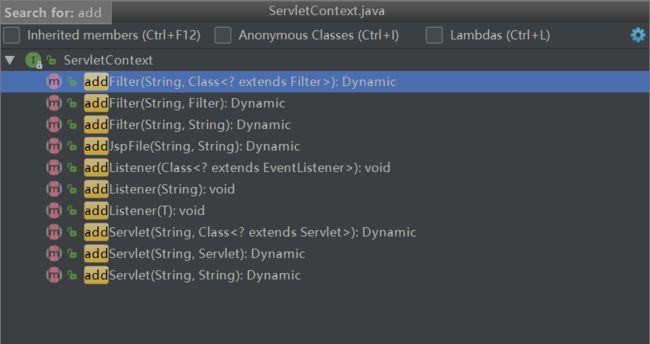
从3.0新增的方法,方法描述上都有标明@since Servlet 3.0,大家可以去细看下3.0具体新增了哪些方法。新增的add系列方法如下
也就是说可以通过ServletContext向servlet容器添加Filter、Listener和Servlet了。
补充
3.0之前和3.0之后,maven依赖的artifactId是不同的,大家需要注意一下;
servlet 3.0是一个大的版本变动,相比之前增加了比较多的特性,本文就涉及到其中一个特性:支持无web.xml配置(新的注解支持)
servlet 3.0及之后,Filter、Servlet和Listener支持注解配置(3.0之前都是配置在web.xml中)
Filter注册
springboot实现
实现Filter接口实现我们自己的Filter,这个与web.xml时期一样
package com.lee.register.filter; import javax.servlet.*; import java.io.IOException; public class MyFilter implements Filter { @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { System.out.println("myfilter init..."); } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { System.out.println("过滤处理"); chain.doFilter(request, response); } @Override public void destroy() { System.out.println("myfilter destroy..."); } }
利用FilterRegistrationBean将我们自定义的Filter注册到容器
package com.lee.register.config; import com.lee.register.filter.MyFilter; import com.lee.register.listener.MyListener; import com.lee.register.servlet.MyServlet; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletListenerRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.util.Arrays; @Configuration public class MyConfig { @Bean public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener() { ServletListenerRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(new MyListener()); return registrationBean; } @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter() { FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean(new MyFilter()); filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/hello","/myServlet")); return filterRegistrationBean; } @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet() { ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet()); registrationBean.setUrlMappings(Arrays.asList("/myServlet")); registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1); return registrationBean; } }
工程详情请点:spring-boot-filter;FilterRegistrationBean的作用与在web.xml中配置Filter类似,只是底层用了servlet3.0的新特性
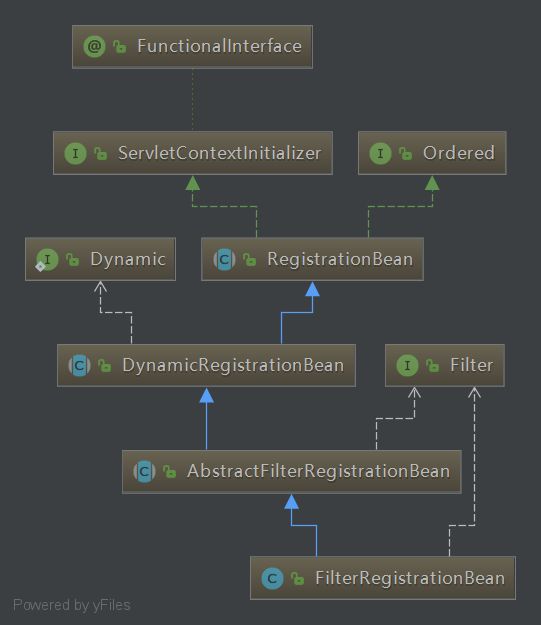
源码分析
我们知道servlet3.0+,可以通过ServeltContext来注册Filter(当然还包括Servlet、Listener)到Servlet容器;至于注册到Servlet容器后,容器容器如何处理Filter就不是本文的范畴了。我们姑且这样认为:通过ServletContext注册Filter到容器,那么Filter就能起到过滤作用了。那么问题来了,springboot是如何将Filter注册到容器的?
FilterRegistrationBean的源码
/* * Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot.web.servlet; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import org.springframework.util.Assert; /** * A {@link ServletContextInitializer} to register {@link Filter}s in a Servlet 3.0+ * container. Similar to the {@link ServletContext#addFilter(String, Filter) registration} * features provided by {@link ServletContext} but with a Spring Bean friendly design. ** The {
@link #setFilter(Filter) Filter} must be specified before calling * {@link #onStartup(ServletContext)}. Registrations can be associated with * {@link #setUrlPatterns URL patterns} and/or servlets (either by {@link #setServletNames * name} or via a {@link #setServletRegistrationBeans ServletRegistrationBean}s. When no * URL pattern or servlets are specified the filter will be associated to '/*'. The filter * name will be deduced if not specified. * * @paramthe type of { @link Filter} to register * @author Phillip Webb * @since 1.4.0 * @see ServletContextInitializer * @see ServletContext#addFilter(String, Filter) * @see DelegatingFilterProxyRegistrationBean */ public class FilterRegistrationBeanextends Filter> extends AbstractFilterRegistrationBean { /** * Filters that wrap the servlet request should be ordered less than or equal to this. */ public static final int REQUEST_WRAPPER_FILTER_MAX_ORDER = AbstractFilterRegistrationBean.REQUEST_WRAPPER_FILTER_MAX_ORDER; private T filter; /** * Create a new {@link FilterRegistrationBean} instance. */ public FilterRegistrationBean() { } /** * Create a new {@link FilterRegistrationBean} instance to be registered with the * specified {@link ServletRegistrationBean}s. * @param filter the filter to register * @param servletRegistrationBeans associate {@link ServletRegistrationBean}s */ public FilterRegistrationBean(T filter, ServletRegistrationBean... servletRegistrationBeans) { super(servletRegistrationBeans); Assert.notNull(filter, "Filter must not be null"); this.filter = filter; } @Override public T getFilter() { return this.filter; } /** * Set the filter to be registered. * @param filter the filter */ public void setFilter(T filter) { Assert.notNull(filter, "Filter must not be null"); this.filter = filter; } }
FilterRegistrationBean的类描述:一个用于向Servlet 3.0+容器注册Filter的ServletContextInitializer,类似于ServletContext提供的ServletContext#addFilter(String,Filter)注册功能,但具有Spring Bean特性的友好设计。相当于对ServletContext#addFilter进行了spring bean的友好性适配,本质还是ServletContext#addFilter。
我们来看看ServletContextInitializer,感觉和ServeltContext有很大的关系,源码如下
/* * Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot.web.servlet; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer; import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer; /** * Interface used to configure a Servlet 3.0+ {@link ServletContext context} * programmatically. Unlike {@link WebApplicationInitializer}, classes that implement this * interface (and do not implement {@link WebApplicationInitializer}) will not be * detected by {@link SpringServletContainerInitializer} and hence will not be * automatically bootstrapped by the Servlet container. ** This interface is primarily designed to allow {
@link ServletContextInitializer}s to be * managed by Spring and not the Servlet container. ** For configuration examples see {
@link WebApplicationInitializer}. * * @author Phillip Webb * @since 1.4.0 * @see WebApplicationInitializer */ @FunctionalInterface public interface ServletContextInitializer { /** * Configure the given {@link ServletContext} with any servlets, filters, listeners * context-params and attributes necessary for initialization. * @param servletContext the {@code ServletContext} to initialize * @throws ServletException if any call against the given {@code ServletContext} * throws a {@code ServletException} */ void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException; }
ServletContextInitializer允许我们以编程方式配置Servlet 3.0+ ServletContext上下文,并且SpringServletContainerInitializer不会检测到实现此接口的类(类没有实现WebApplicationInitializer),因此不会被Servlet容器自动引导;ServletContextInitializer的设计目的是由spring管理,而不是Servlet容器。ServletContextInitializer就一个方法:onStartup,我们顺着FilterRegistrationBean的类图来看看onStartup的实现
我们发现,最终还是调用ServletContext的addFilter方法将Filter注册到Servlet容器。问题又来了,ServletContextInitializer的onStartup又是在哪里被调用的呢?
springboot的启动过程中肯定在哪个地方对ServletContextInitializer的onStartup进行了调用,我们接着往下看,我们从ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java的createWebServer方法开始(Springboot启动开始到createWebServer的过程就省了)
先去spring的beanFactory中获取ServletContextInitializer的全部实例,并将其放入到ServletContextInitializerBeans的initializers中,然后遍历initializers,调用每个ServletContextInitializer的onStartup方法(有人感觉这里有点多余,其实你把initializers想成缓存就好理解了,肯定还有其他地方会用到initializers)。
至此也就通了,spring将@Bean修饰的RegistrationBean注册到beanFactory,然后从beanFactory中获取全部的ServletContextInitializer,遍历它们并调用他们的onStartup方法将RegistrationBean中的bean注册到servlet容器;但是有一点@Bean注解是如何将bean注册到beanFactory的本文没有涉及,会放到springboot启动系列篇中,敬请期待。
总结
1、ServletContext是request与response交互的平台,也是我们的web应用与servlet容器沟通的桥梁;就从本文来说,Filter、Servlet、Listener的注册都是通过ServletContext来实现的
2、Servlet3.0+有很多新特性,包括Filter、Servlet、Listener的注册,不再只是通过web.xml实现了。而springboot也只是对ServletContext的add系列方法进行了拓展,使得具有spring的友好性,而FilterRegistrationBean就是具体的实现之一。
3、springboot启动过程中,调用ServletContextInitializer类型的实例的onStartup方法,完成指定bean到servlet容器的注册;指定bean就是指我们自定义的Filter、Servlet、Listener,而不是RegistrationBean类型的实例。
参考
《深入分析Java Web技术内幕》