适合新手——MySQL中基于SQL语言增删改查等基础的练习大汇总
前言
这是我听老师讲课做的笔记,考试要看的。 这是视频地址
作者:RodmaChen
关注我的csdn博客,更多Linux笔记知识还在更新
本人只在csdn写博客
配套这篇文章解释更香哇!MySQL中SQL数据库基础知识大汇总出炉了
SQL语言四种结构的练习
- 一. DDL——数据库、表、视图等的建立、删除
- 二. DML——添加、删除和修改数据表中的记录
- 三. DCL——数据库对象的权限管理和事务管理
- 3.1 用户管理——user
- 3.2 权限管理
- 3.3 禁止root用户远程登录
- 3.4 忘记用户密码的解决
- 四. DQL——查询数据表中的记录
- 4.1 select简单查询
- 4.2 where条件查询
- 4.2.1 in的用法
- 4.2.2 like用法
- 4.3 函数
- 4.3.1 聚合函数
- 4.3.2 case when判断条件语句
- 4.4 查询结果排序与分页
- 4.4.1 order by 排序
- 4.4.2 limit 分页查询
- 4.5 数据的分组和筛选
- 4.5.1 group by——分组
- 4.5.2 having——筛选各组数据
- 4.5.3 group_concat——显示统计数量列表
- 4.6 去除重复数据——distinct
- 4.7 表连接(内连接、外连接、自连接)
- 4.7.1 内连接
- 4.7.2 左连接
- 4.7.3 自连接
- 4.8 子查询EXISTS和IN的使用
- 小知识
一. DDL——数据库、表、视图等的建立、删除
接下来如何创建表结构
- 设置id主键:
id int not null auto_increment primary key(auto_increment顺序增加) - 设置名字:
name varchar(30) - 设置电话:
phone varchar(20)
create table contacts(
ip int not null auto_increment primary key ,
name varchar(30) ,
phone varchar(20) );
添加字段sex,类型为varchar(1)
alter table contacts add sex varchar(1);
修改字段sex的类型为tinyint
alter table contacts modify sex tinyint;
删除字段sex
alter table contacts drop column sex;
删除contacts表
drop table contacts;
二. DML——添加、删除和修改数据表中的记录
测试:
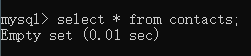
- 查看:select * from contacts;
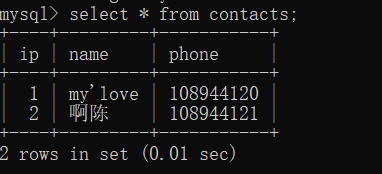
- 插入:
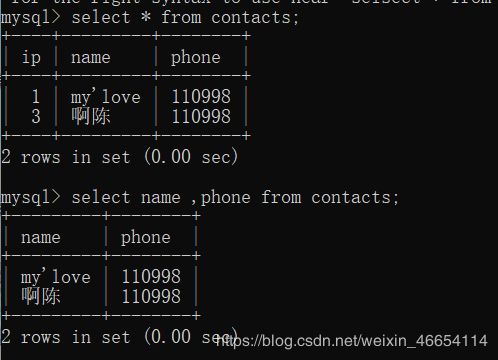
insert into contacts (name, phone) values ("my'love",'108944120');
insert into contacts(name,phone ) value ('啊陈','108944121');
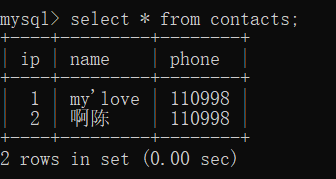
更新
update contacts set phone='110998'
update contacts set phone='110998' where name='啊陈';
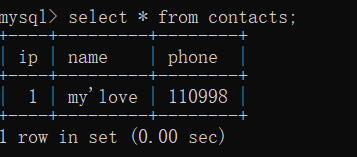
删除
delete from contacts where name='啊陈';
三. DCL——数据库对象的权限管理和事务管理
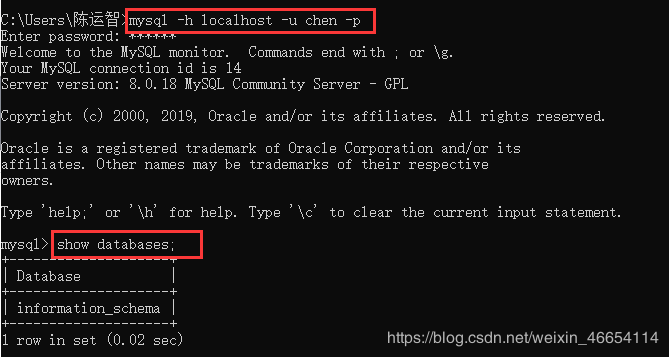
3.1 用户管理——user
\G格式化输入
用户名和密码对了主机不对也不能连
create user 'chen'@'%' identified by '123456';
create user 'yun'@'192.168.0.1' identified by '123456';
mysql> drop user 'chen'@'%';
mysql> drop user 'yun'@'192.168.0.1';
alter user '用户名'@'主机名' identified by '新密码';
3.2 权限管理
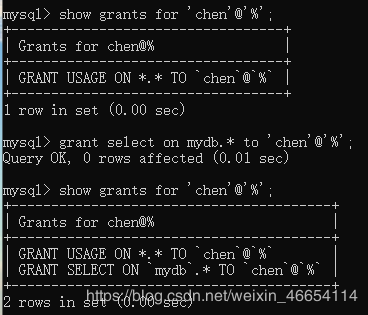
给用户赋予了mydb所有表权限
//只有登录的权限
mysql> flush privileges;
//给用户赋予了mydb所有表权限
mysql> grant select on mydb.* to 'chen'@'%';
//在查看发现有了select只读权限了
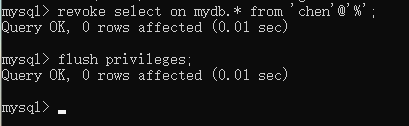
//删除
mysql> revoke select on mydb.* from 'chen'@'%';
//刷新权限
mysql> flush privileges;
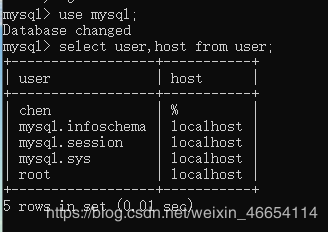
3.3 禁止root用户远程登录
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> select user,host from user;
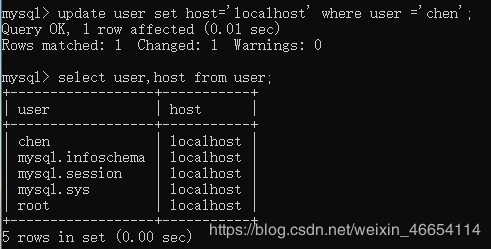
如果出现user不是root,host不是localhost的情况root用户就能远程登录
%如何机器都能远程登录
改为只能 本机连
update user set host='localhost' where user ='chen';
mysql> select user,host from user;
3.4 忘记用户密码的解决
停掉服务
不能关闭窗口
//停止服务
net stop mysql80
//关闭权限验证
mysqld --defaults-file="C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\my.ini" --console --skip-grant-tables --shared-memory
![]()
重新开一个窗口
![]()
//使用数据表
mysql> use mysql;
//查看数据表
mysql> show tables;
//user里面包含用户,查看用户
mysql> select user,host from user;
![]()
////刷新权限
flush privileges;
//更改root用户密码
alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by '123456';
![]()
//重新启动服务
C:\WINDOWS\system32>net start mysql80
//登录进去就行
C:\WINDOWS\system32>mysql -u root -p
![]()
四. DQL——查询数据表中的记录
4.1 select简单查询
mysql> select * from contacts;
mysql> select name ,phone from contacts;
mysql> select name , phone from contacts where name="my'love";
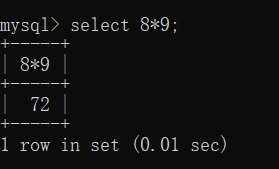
也可以当成计算器使用
4.2 where条件查询
create table employee( id int not null auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(30) comment '姓名',
sex varchar(1) comment '性别',
salary int comment '薪资(元)' );
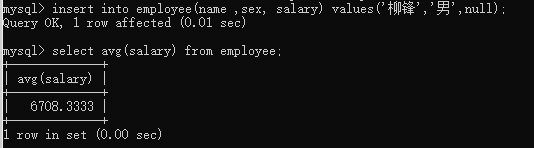
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('张三', '男', 5500);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('李洁', '女', 4500);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('李小梅', '女', 4200);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('欧阳辉', '男', 7500);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('李芳', '女', 8500);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('张江', '男', 6800);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('李四', '男', 12000);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('王五', '男', 3500);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('马小龙', '男', 6000);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('龙五', '男', 8000);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('冯小芳', '女', 10000);
insert into employee(name, sex, salary) values('马小花', '女', 4000);
select * from employee where sex = '男' and salary >= 10000;
select * from employee where sex = '男' or salary >= 10000;
select * from employee where sex = '男' and salary <= 4000 or salary >=10000;
4.2.1 in的用法
select * from employee where id=1 or id =2 or id =3;
select * from employee where id in(1,2,3,4);
4.2.2 like用法
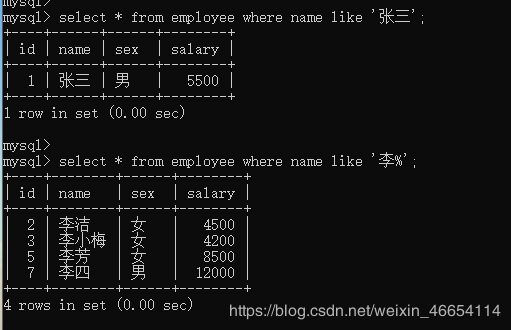
select * from employee where name like '张三';
select * from employee where name like '李%';
4.3 函数
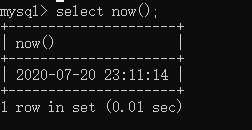
mysql> select now();
4.3.1 聚合函数
mysql> select count(*) from employee;
mysql> select count(*) from employee where sex ='男';
mysql> select count(*) from employee where sex ='女';
mysql> select sum(salary) from employee;
mysql> select avg(salary) from employee;
mysql> select max(salary) from employee;
mysql> select min(salary) from employee;
为什么会忽略空值,十三个员工平均值不变,会跳过这个员工
4.3.2 case when判断条件语句
select
id,
name,
case sex
when '男' then 'A'
when '女' then 'M'
else ''
end as sex,
salary
from employee;
4.4 查询结果排序与分页
按某数值排序,从高到低,从大到小等等
4.4.1 order by 排序
实例:
薪资排序:salary,降序后面加desc
mysql> select * from employee order by salary;
按照sex性别排序后薪资salary排序
select * from employee order by sex ,salary desc;
4.4.2 limit 分页查询
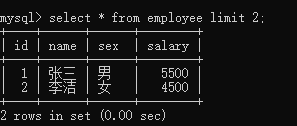
获取记录:
mysql> select * from employee limit 2;
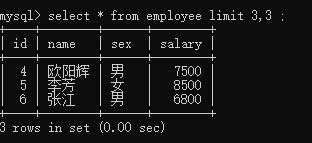
分页:
mysql> select * from employee limit 3,3 ;
4.5 数据的分组和筛选
4.5.1 group by——分组
4.5 数据的分组和筛选
4.5.1 group by——分组
select sex ,count(*) from employee group by sex;
select sex ,sum(salary) from employee group by sex;
4.5.2 having——筛选各组数据
having小于等于五的用法
mysql> select sex , count(*) from employee group by sex having count(*)<=5;
4.5.3 group_concat——显示统计数量列表
mysql> select sex ,count(*) ,group_concat(name) from
employee group by sex;
select sex,count(*) , group_concat(name order by name desc) from employee group by sex;
select sex, count(*),group_concat(name order by name desc separator ';') from employee group by sex;
![]()
4.6 去除重复数据——distinct
数据表
create table footprint(
id int not null auto_increment primary key,
username varchar(30) comment '用户名',
city varchar(30) comment '城市',
visit_date varchar(10) comment '到访日期'
);
insert into footprint(username, city, visit_date) values('liufeng', '贵阳', '2019-12-05');
insert into footprint(username, city, visit_date) values('liufeng', '贵阳', '2020-01-15');
insert into footprint(username, city, visit_date) values('liufeng', '北京', '2018-10-10');
insert into footprint(username, city, visit_date) values('zhangsan', '上海', '2020-01-01');
insert into footprint(username, city, visit_date) values('zhangsan', '上海', '2020-02-02');
insert into footprint(username, city, visit_date) values('lisi', '拉萨', '2016-12-20');
//看用户distinct
mysql> select distinct username from footprint;
//group by也可以去重,不过它做的是分组统计的,distinct只做去重
mysql> select username from footprint group by username;
//每一个用户去过的城市
mysql> select distinct username ,city from footprint;
4.7 表连接(内连接、外连接、自连接)
多张表,表连接
主要学习内连接和左连接
drop table if exists score;//数据表
drop table if exists student;//学生表
create table student(
stu_no varchar(20) not null primary key comment '学号',
name varchar(30) comment '姓名',
address varchar(150) comment '地址'
);
insert into student(stu_no, name, address) values('2016001', '张三', '贵州贵阳');
insert into student(stu_no, name, address) values('2016002', '李芳', '陕西兴平');
insert into student(stu_no, name, address) values('2016003', '张晓燕', '江西南昌');
create table score(
id int not null auto_increment primary key,
course varchar(50) comment '科目',
stu_no varchar(20) comment '学号',
score int comment '分数',
foreign key(stu_no) references student(stu_no)
);
insert into score(course, stu_no, score) values('计算机', '2016001', 99);
insert into score(course, stu_no, score) values('离散数学', '2016001', 85);
insert into score(course, stu_no, score) values('计算机', '2016002', 78);
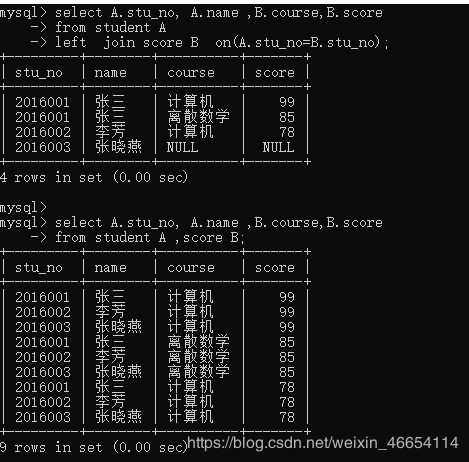
4.7.1 内连接
//内连接 join
select A.stu_no, A.name ,B.course,B.score
from student A join score B on(A.stu_no=B.stu_no);
// inner join
select A.stu_no, A.name ,B.course,B.score
from student A inner join score B on(A.stu_no=B.stu_no);
// where
select A.stu_no, A.name ,B.course,B.score
from student A ,score B where A.stu_no=B.stu_no;
4.7.2 左连接
//左连接
select A.stu_no, A.name ,B.course,B.score
from student A
left join score B on(A.stu_no=B.stu_no);
// 交叉连接:没有按照学号进行关联(没啥用)
select A.stu_no, A.name ,B.course,B.score
from student A ,score B;
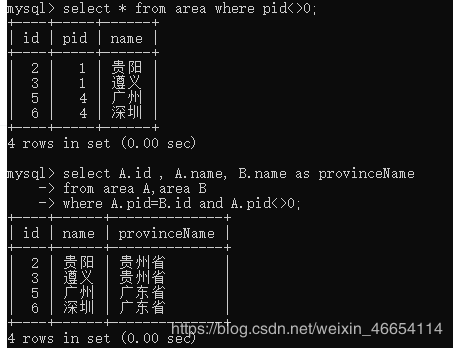
4.7.3 自连接
自连接:有层次结构的表
drop table if exists area;
drop table if exists area;
create table area(
id int not null auto_increment primary key comment '区域id',
pid int not null comment '父id(0-省份)',
name varchar(30) comment '区域名称'
);
insert into area(id, pid, name) values(1, 0, '贵州省');
insert into area(id, pid, name) values(2, 1, '贵阳');
insert into area(id, pid, name) values(3, 1, '遵义');
insert into area(id, pid, name) values(4, 0, '广东省');
insert into area(id, pid, name) values(5, 4, '广州');
insert into area(id, pid, name) values(6, 4, '深圳');
// 父类不等于0的子类
mysql> select * from area where pid<>0;
// 父类和子类的连接
mysql> select A.id , A.name, B.name as provinceName
-> from area A,area B
-> where A.pid=B.id and A.pid<>0;
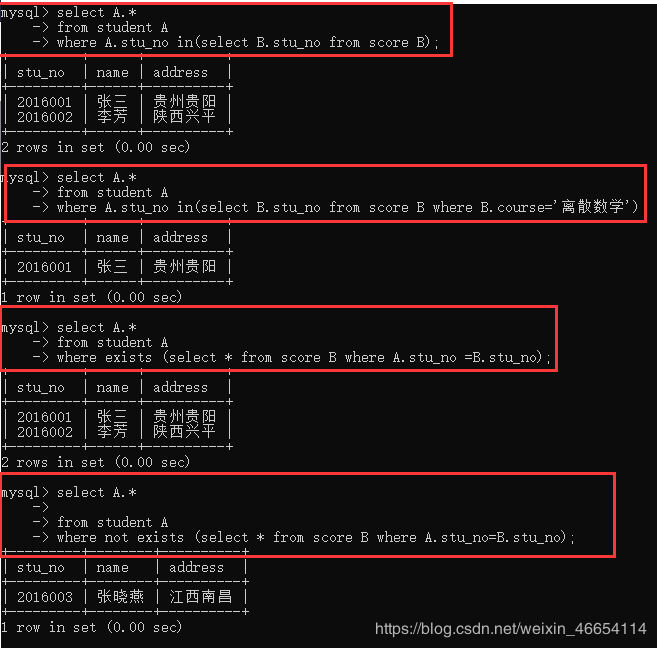
4.8 子查询EXISTS和IN的使用
子查询 in ,exists场景不一样好处不一样
![]()
以下用的数据表是上面创建的学生表和数据表
查询所有选修课程的学生
select A.*
from student A
where A.stu_no in(select B.stu_no from score B);
查询选修了离散数学的学生
select A.*
from student A
where A.stu_no in(select B.stu_no from score B where B.course='离散数学');
查询所有选修了课程的学生
select A.*
from student A
where exists (select * from score B where A.stu_no =B.stu_no);
查询所有未选修课程的学生
select A.*
from student A
where not exists (select * from score B where A.stu_no=B.stu_no);
小知识
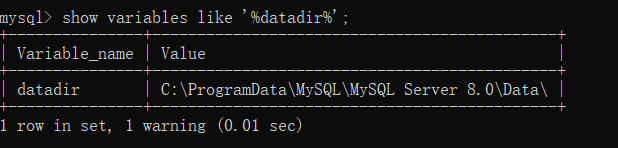
- 查看数据目录
列:
mysql> show variables like '%datadir%';
//select abs(-10);绝对值
select abs(-10);
//求字符串长度
select length("cheng");
select length("cheng") from dual;
select * from dual;
- 加密
本人博客:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46654114
本人b站求关注:https://space.bilibili.com/391105864
转载说明:跟我说明,务必注明来源,附带本人博客连接。
请给我点个赞鼓励我吧
![]()