SpringMVC实现RESTful服务
1、REST是一种架构风格,其核心是面向资源。
REST专门针对网络应用设计和开发方式,以降低开发的复杂性,提高系统的可伸缩性。REST提出设计概念和准则为:
1. 网络上的所有事物都可以被抽象为资源(resource)2. 每一个资源都有唯一的资源标识(resource identifier),对资源的操作不会改变这些标识
3. 所有的操作都是无状态的
REST简化开发,其架构遵循CRUD原则,该原则告诉我们对于资源(包括网络资源)只需要四种行为:创建,获取,更新和删除就可以完成相关的操作和处理。我们可以通过统一资源标识符(Universal Resource Identifier,URI)来识别和定位资源,并且针对这些资源而执行的操作是通过 HTTP 规范定义的。其核心操作只有GET,PUT,POST,DELETE。由于REST强制所有的操作都必须是stateless的,这就没有上下文的约束,如果做分布式,集群都不需要考虑上下文和会话保持的问题。极大的提高系统的可伸缩性。
2、模拟REST请求工具
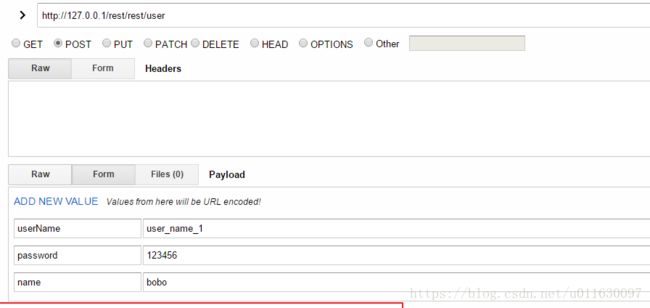
模拟rest请求可以使用工具:restclient-ui-3.5-jar-with-dependencies.jar,界面截图:
3、实现
3.1 读取查询(Retrieve) 使用 get方法请求
// 根据用户id查询用户信息
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity queryUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
try {
User user = this.userService.queryUserById(id);
if (null == user) {
// 资源不存在,响应404
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(null);
}
// 资源存在,响应200
// return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(user);
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).body(null);
} 3.2 增加(Create) 使用 post方法请求
/**
* 新增用户
*
* @param user
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity saveUser(User user) {
try {
Boolean bool = this.userService.saveUser(user);
if (bool) {
// 新增成功,响应201
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).build();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 新增失败,响应500
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).build();
} /**
* 更新用户
* @param user
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public ResponseEntity updateUser(User user) {
try {
Boolean bool = this.userService.updateUser(user);
if (bool) {
// 更新成功,响应204
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT).build();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 新增失败,响应500
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).build();
} 默认情况下,PUT请求是无法提交表单数据的,需要在web.xml中添加过滤器解决:
HttpMethodFilter
org.springframework.web.filter.HttpPutFormContentFilter
HttpMethodFilter
/*
3.4 删除(Delete) 使用DELETE方法
/**
* 删除用户
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public ResponseEntity deleteUser(@RequestParam(value = "id", defaultValue = "0") Long id) {
try {
if (id.longValue() == 0) {
// 没有传递参数,响应状态码400
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).build();
}
Boolean bool = this.userService.deleteUser(id);
if (bool) {
// 删除成功,响应204
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT).build();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 删除失败,响应500
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).build();
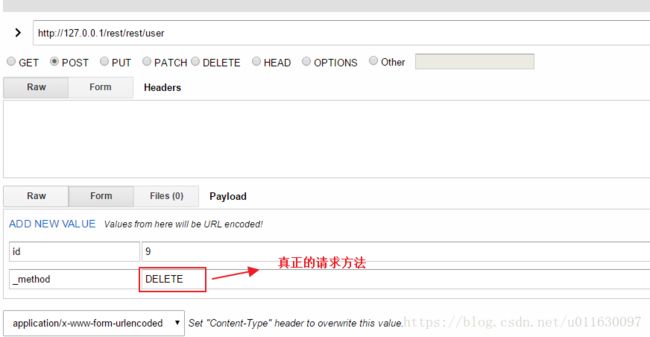
} 需要在web.xml中添加过滤器解决DELETE请求无法提交表单数据的问题:
HiddenHttpMethodFilter
org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter
HiddenHttpMethodFilter
/*
请求实例: