一步一步教你构建一个MPU6050(I2C类)驱动(三)
首先我们要控制MPU6050,实质上就是读写它里面寄存器的值。i2c的数据通信帧的组成在前面已经讲过了这里就不在展开,我们先来看看内核中已经帮我们封装好的,构建一个数据帧的API:
/**
* i2c_master_send - issue a single I2C message in master transmit mode
* @client: Handle to slave device
* @buf: Data that will be written to the slave
* @count: How many bytes to write, must be less than 64k since msg.len is u16
*
* Returns negative errno, or else the number of bytes written.
*/
int i2c_master_send(const struct i2c_client *client, const char *buf, int count)
{
int ret;
struct i2c_adapter *adap = client->adapter;
struct i2c_msg msg;
msg.addr = client->addr;
msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN;
msg.len = count;
msg.buf = (char *)buf;
ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1);
/*
* If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg transmitted), return #bytes
* transmitted, else error code.
*/
return (ret == 1) ? count : ret;
}
/**
* i2c_master_recv - issue a single I2C message in master receive mode
* @client: Handle to slave device
* @buf: Where to store data read from slave
* @count: How many bytes to read, must be less than 64k since msg.len is u16
*
* Returns negative errno, or else the number of bytes read.
*/
int i2c_master_recv(const struct i2c_client *client, char *buf, int count)
{
struct i2c_adapter *adap = client->adapter;
struct i2c_msg msg;
int ret;
msg.addr = client->addr;
msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN;
msg.flags |= I2C_M_RD;
msg.len = count;
msg.buf = buf;
ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1);
/*
* If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg received), return #bytes received,
* else error code.
*/
return (ret == 1) ? count : ret;
}一个是发送数据的 i2c_master_send ,一个是接受数据的 i2c_master_recv 。
以 i2c_master_send 为例子我们来分析一下这个函数是怎么实现的。
该函数的形参分别是什么在函数前面的注释就已经有了,我们来看看它的函数体,前面的
int ret;
struct i2c_adapter *adap = client->adapter;
struct i2c_msg msg;
msg.addr = client->addr;
msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN;
msg.len = count;
msg.buf = (char *)buf;这部分的内容就是将形参导入的数据填充到 i2c_msg 这个结构体中,那我们又来展开看看这个结构体是干什么用的:
/**
* struct i2c_msg - an I2C transaction segment beginning with START
*
* @addr: Slave address, either seven or ten bits. When this is a ten
* bit address, I2C_M_TEN must be set in @flags and the adapter
* must support I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR.
* @flags: I2C_M_RD is handled by all adapters. No other flags may be
* provided unless the adapter exported the relevant I2C_FUNC_*
* flags through i2c_check_functionality().
* @len: Number of data bytes in @buf being read from or written to the
* I2C slave address. For read transactions where I2C_M_RECV_LEN
* is set, the caller guarantees that this buffer can hold up to
* 32 bytes in addition to the initial length byte sent by the
* slave (plus, if used, the SMBus PEC); and this value will be
* incremented by the number of block data bytes received.
* @buf: The buffer into which data is read, or from which it's written.
。。。。
*/
struct i2c_msg {
__u16 addr; /* slave address */
__u16 flags;
#define I2C_M_TEN 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */
#define I2C_M_RD 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */
#define I2C_M_STOP 0x8000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000 /* if I2C_FUNC_NOSTART */
#define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_RECV_LEN 0x0400 /* length will be first received byte */
__u16 len; /* msg length */
__u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */
};由注释这里就得知到了,这个结构体其实就是我们说的i2c的数据帧,i2c的通信其实就是在传输这个 i2c_msg 结构体。
那我们继续回到 i2c_master_send 中,该函数接下来调用了 i2c_transfer 这个函数,展开:
/**
* i2c_transfer - execute a single or combined I2C message
* @adap: Handle to I2C bus
* @msgs: One or more messages to execute before STOP is issued to
* terminate the operation; each message begins with a START.
* @num: Number of messages to be executed.
*
* Returns negative errno, else the number of messages executed.
*
* Note that there is no requirement that each message be sent to
* the same slave address, although that is the most common model.
*/
int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
int ret;
if (adap->algo->master_xfer) {
#ifdef DEBUG
for (ret = 0; ret < num; ret++) {
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "master_xfer[%d] %c, addr=0x%02x, "
"len=%d%s\n", ret, (msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RD)
? 'R' : 'W', msgs[ret].addr, msgs[ret].len,
(msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RECV_LEN) ? "+" : "");
}
#endif
if (in_atomic() || irqs_disabled()) {
ret = i2c_trylock_adapter(adap);
if (!ret)
/* I2C activity is ongoing. */
return -EAGAIN;
} else {
i2c_lock_adapter(adap);
}
ret = __i2c_transfer(adap, msgs, num);
i2c_unlock_adapter(adap);
return ret;
} else {
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "I2C level transfers not supported\n");
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
}
}注释上写着 execute a single or combined I2C message ,其实就是实现了将上面封装好的 i2c_msg 发送到设备。(而i2c_master_recv 则是从设备接受 i2c_msg)最后就实现了i2c_master_send这个函数的 issue a single I2C message in master transmit mode 功能。
接着回到我们的MPU6050上来,先看看这个部件里常用的一些寄存器:
#define SMPLRT_DIV 0x19 //采样频率寄存器-25 典型值:0x07(125Hz)
//寄存器集合里的数据根据采样频率更新
#define CONFIG 0x1A //配置寄存器-26-典型值:0x06(5Hz)
//DLPF is disabled(DLPF_CFG=0 or 7)
#define GYRO_CONFIG 0x1B//陀螺仪配置-27,可以配置自检和满量程范围
//典型值:0x18(不自检,2000deg/s)
#define ACCEL_CONFIG 0x1C //加速度配置-28 可以配置自检和满量程范围及高通滤波频率
//典型值:0x01(不自检,2G,5Hz)
#define ACCEL_XOUT_H 0x3B //59-65,加速度计测量值 XOUT_H
#define ACCEL_XOUT_L 0x3C // XOUT_L
#define ACCEL_YOUT_H 0x3D //YOUT_H
#define ACCEL_YOUT_L 0x3E //YOUT_L
#define ACCEL_ZOUT_H 0x3F //ZOUT_H
#define ACCEL_ZOUT_L 0x40 //ZOUT_L---64
#define TEMP_OUT_H 0x41 //温度测量值--65
#define TEMP_OUT_L 0x42
#define GYRO_XOUT_H 0x43 //陀螺仪值--67,采样频率(由寄存器 25 定义)写入到这些寄存器
#define GYRO_XOUT_L 0x44
#define GYRO_YOUT_H 0x45
#define GYRO_YOUT_L 0x46
#define GYRO_ZOUT_H 0x47
#define GYRO_ZOUT_L 0x48 //陀螺仪值--72
#define PWR_MGMT_1 0x6B //电源管理 典型值:0x00(正常启用)而要对其中的寄存器进行写,我们要在一个数据帧的data区中先写入一个寄存器(地址),在写入要写入寄存器的值。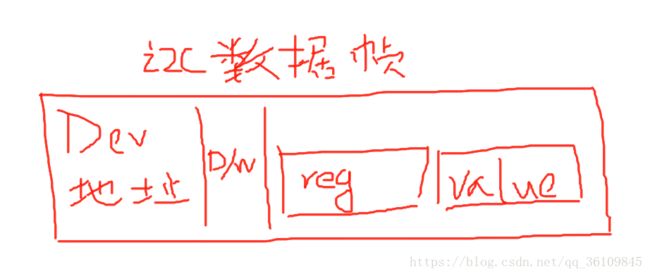
而读一个寄存器就要在一个数据帧中先读出(识别)这个寄存器,再读出相应的值。为了能更方便的读写寄存器,我们来对i2c_master_send 来做一个封装:
static int mpu6050_write_reg(struct i2c_client * client, char reg, char value)
{
char buf[2];
buf[0] = reg;
buf[1] = value;
return i2c_master_send(client, buf, 2);
}同理,写一个接受的函数:
static int mpu6050_read_reg(const struct i2c_client * client, char reg)
{
// 先写寄存器的地址, 然后在读寄存器的值
int ret;
struct i2c_adapter *adapter = client->adapter;
struct i2c_msg msg[2];
char rxbuf[1];
msg[0].addr = client->addr;
msg[0].flags = 0;
msg[0].len = 1;
msg[0].buf = ®
msg[1].addr = client->addr;
msg[1].flags = I2C_M_RD;
msg[1].len = 1;
msg[1].buf = rxbuf;
ret = i2c_transfer(adapter, msg, 2);
if(ret < 0)
{
printk("i2c_transfer read error\n");
return ret;
}
return rxbuf[0];
}
做好了读写的函数后,我们先来对MPU6050做初始化。而这个初始化就是设定MPU6050中寄存器的值,使其达到能开始正常使用的状态。
static int mpu6050_init( struct i2c_client * client)
{
//success --0 erro--1
int ret;
ret = mpu6050_write_reg(client, PWR_MGMT_1 , 0x00 );
if(ret == -1)
{
printk("--%s--error",__FUNCTION__);
return -1;
}
ret = mpu6050_write_reg(client, SMPLRT_DIV , 0x07 );
if(ret == -1)
{
printk("--%s--error",__FUNCTION__);
return -1;
}
ret = mpu6050_write_reg(client, CONFIG , 0x06 );
if(ret == -1)
{
printk("--%s--error",__FUNCTION__);
return -1;
}
ret = mpu6050_write_reg(client, GYRO_CONFIG , 0x18 );
if(ret == -1)
{
printk("--%s--error",__FUNCTION__);
return -1;
}
ret = mpu6050_write_reg(client, ACCEL_CONFIG , 0x01 );
if(ret == -1)
{
printk("--%s--error",__FUNCTION__);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}现在,我们的驱动代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include /* for struct device */
#include /* for completion */
#include
#include /* for struct device_node */
#include /* for swab16 */
#include
/*
做一个i2c 的驱动
*/
//MPU6050寄存器
#define SMPLRT_DIV 0x19 //采样频率寄存器-25 典型值:0x07(125Hz)
//寄存器集合里的数据根据采样频率更新
#define CONFIG 0x1A //配置寄存器-26-典型值:0x06(5Hz)
//DLPF is disabled(DLPF_CFG=0 or 7)
#define GYRO_CONFIG 0x1B//陀螺仪配置-27,可以配置自检和满量程范围
//典型值:0x18(不自检,2000deg/s)
#define ACCEL_CONFIG 0x1C //加速度配置-28
//可以配置自检和满量程范围及高通滤波频率
//典型值:0x01(不自检,2G,5Hz)
#define ACCEL_XOUT_H 0x3B //59-65,加速度计测量值 XOUT_H
#define ACCEL_XOUT_L 0x3C // XOUT_L
#define ACCEL_YOUT_H 0x3D //YOUT_H
#define ACCEL_YOUT_L 0x3E //YOUT_L
#define ACCEL_ZOUT_H 0x3F //ZOUT_H
#define ACCEL_ZOUT_L 0x40 //ZOUT_L---64
#define TEMP_OUT_H 0x41 //温度测量值--65
#define TEMP_OUT_L 0x42
#define GYRO_XOUT_H 0x43 //陀螺仪值--67,采样频率(由寄存器 25定义)写入到这些寄存器
#define GYRO_XOUT_L 0x44
#define GYRO_YOUT_H 0x45
#define GYRO_YOUT_L 0x46
#define GYRO_ZOUT_H 0x47
#define GYRO_ZOUT_L 0x48 //陀螺仪值--72
#define PWR_MGMT_1 0x6B //电源管理 典型值:0x00(正常启用
static int mpu6050_write_reg(struct i2c_client * client, char reg, char value)
{
char buf[2];
buf[0] = reg;
buf[1] = value;
return i2c_master_send(client, buf, 2);
}
static int mpu6050_read_reg(const struct i2c_client * client, char reg)
{
// 先写寄存器的地址, 然后在读寄存器的值
int ret;
struct i2c_adapter *adapter = client->adapter;
struct i2c_msg msg[2];
char rxbuf[1];
msg[0].addr = client->addr;
msg[0].flags = 0;
msg[0].len = 1;
msg[0].buf = ®
msg[1].addr = client->addr;
msg[1].flags = I2C_M_RD;
msg[1].len = 1;
msg[1].buf = rxbuf;
ret = i2c_transfer(adapter, msg, 2);
if(ret < 0)
{
printk("i2c_transfer read error\n");
return ret;
}
return rxbuf[0];
}
static int mpu6050_init( struct i2c_client * client)
{
printk("-----------%s-----------\n", __FUNCTION__);
//success --0 erro--1
int ret;
ret = mpu6050_write_reg(client, PWR_MGMT_1 , 0x00 );
if(ret == -1)
{
printk("--%s--error",__FUNCTION__);
return -1;
}
ret = mpu6050_write_reg(client, SMPLRT_DIV , 0x07 );
if(ret == -1)
{
printk("--%s--error",__FUNCTION__);
return -1;
}
ret = mpu6050_write_reg(client, CONFIG , 0x06 );
if(ret == -1)
{
printk("--%s--error",__FUNCTION__);
return -1;
}
ret = mpu6050_write_reg(client, GYRO_CONFIG , 0x18 );
if(ret == -1)
{
printk("--%s--error",__FUNCTION__);
return -1;
}
ret = mpu6050_write_reg(client, ACCEL_CONFIG , 0x01 );
if(ret == -1)
{
printk("--%s--error",__FUNCTION__);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id mpu6050_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "InvenSense,mpu6050" },
{},
};
const struct i2c_device_id mpu6050_id_table[] = {
{ "mpu6050", 0 },
{},
};
static int mpu6050_probe(struct i2c_client *client,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
printk("-----------%s-----------\n", __FUNCTION__);
if( mpu6050_init(client) != -1)
printk("mpu6050 init success!\n");
else{
printk("mpu6050 init errer");
}
return 0;
}
int mpu6050_remove(struct i2c_client *client)
{
printk("-----------%s-----------\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
struct i2c_driver mpu6050_drv =
{
.probe = mpu6050_probe,
.remove = mpu6050_remove,
.driver= {
.name = "mpu6050_drv",//sys/bus/i2c/driver
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(mpu6050_of_match),
},
.id_table = mpu6050_id_table,
};
static int __init i2cdrv_init(void)
{
printk("-----------%s-----------\n", __FUNCTION__);
return i2c_register_driver(THIS_MODULE, &mpu6050_drv);
}
static void __exit i2cdrv_exit(void)
{
printk("-----------%s-----------\n", __FUNCTION__);
i2c_del_driver(&mpu6050_drv);
}
module_init(i2cdrv_init);
module_exit(i2cdrv_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");