1、按系列罗列Linux的发行版,并描述不同发行版之间的联系与区别?
1、Debian:(纯正的社区方式,免费开源)
Ubuntu:主要针对于桌面系统和服务器系统,基于Debian开发。
Linux Mint:主要针对于用户个人桌面系统,提供更有效,更爽快的用户体验。
2、slackware (商业版的Linunx)
suse:主要针对商业的服务器和桌面系统,基于slackware开发
SLES(SUSE Linux Enterprise Server(SLES):企业版的linux服务器,唯一与微软Windows兼容的linux操作系统
OpenSUSE:由SUSE二次开发,针对于个人桌面系统开发,提供开源。
3、Redhat(早期开源免费,后期被红帽收购)
Fedora: 是Redhat是针对个人用户发行的linux系统,每隔大概6个月发行新版本。
Centos:是基于Redhat企业级的linux发行版本,基于Redhat linux enterprice server 开发。新版本每隔两年发行新版本,每个版本每隔6个月更新,以支持新的设备硬件。
4、其他发行版本
Gentoo:定制版linux,几乎可以为任何程序和需求作出优化和定制。Gentoo的哲学是:自由和选择。
Kali:主要用于测试和***使用。
主要联系和区别:
联系:都是基础linux内核开发的系统,都需要遵循GNU的GPL协定和LGPL协定。所有发行都有自己的版本号:主版本号、次版本号、发行号、修正号
区别:不同发行版采用不同版本的内核、库、程序组成。主要区别:包管理器的不同,debianx系列采用的是DPKG包管理系统,apt(aptitude)是它主要前端包管理工具。openSUSE、Fedora、centOS、使用的是RPM包管理系统、yum、dnf是它的主要前端包管理工具。
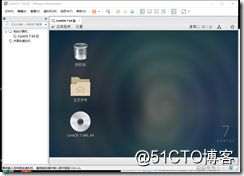
2、安装Centos7.6操作系统,创建一个自己名字的用户名,并可以正常登录,将主要步骤截图。
1、创建虚拟机
2、安装光盘:
3:登录
3、配置环境变量,实现执行history的时候可以看到执行命令的时间。
一、临时生效方式:在终端下运行:$HISTTIMEFORMAT=”%F%T”
二、永久生效方式:在开机启动运行脚本目录中创建一个脚本
reboot 重启生效
4、总结Linux哲学思想。
(1)一切皆文件:把几乎所有的资源抽象为文件形式:包括硬件设备,甚至通信接口等:
open(),close(),read(),write(),delete(),create()
(2)由众多单一功能的程序组成,每个程序只做一件事,并且做好。
(3)尽量避免和用户交互
目标:易于以编程的方式实现自动化任务
(4)使用文本文件保存配置信息。
5、总结Linux常用命令使用格式,并用实例说明。例如echo、screen、date、ifconfig、export等命令
echo:回显一行文本,主要用法:
echo –n:回显不会换行:
echo –e: enable interpretation of backslash escapes 可以解释反斜杠与逃逸符:\t \b等
screen:
语法: screen [ -options ] [ cmd [ args ] ]
screen -r [[pid.]tty[.host]]
命令行参数: -A
Adapt the sizes of all windows to the size of the current terminal.(将所有的窗口调整为终端的大小)
-d|-D [pid.tty.host]
does not start screen, but detaches the elsewhere running screen session.(分离在别处运行的会话)

-h num
Specifies the history scrollback buffer to be num lines high.(指明历史缓冲区行数)
-m causes screen to ignore the $STY environment variable. With "screen -m" creation of a new session is enforced,(忽略$STY(screen会话)环境变量,强制创建一个新的会话)
-r sessionowner/[pid.tty.host]
resumes a detached screen session.(恢复离线的会话)
-R attempts to resume the first detached screen session it finds. If successful, all other command-line options are ignored. If no detached session exists, starts a new session using the specified options, just as if -R had not been specified.(先恢复离线,若没有离线则创建新的会话)
-ls [match]
-list [match]
does not start screen, but prints a list of pid.tty.host strings identifying your screen sessions(显示目前所有的screen作业)
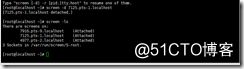
-wipe [match]
does the same as "screen -ls", but removes destroyed sessions instead of marking them as -S sessionname
When creating a new session, this option can be used to specify a meaningful name for the session.)
-x Attach to a not detached screen session. (Multi display mode). (恢复之前离线的screen作业)
-S sessionname
When creating a new session, this option can be used to specify a meaningful name for the session.( 当创建一个新的会话,给它定义一个名字)
date:
date:显示时间 date [OPTION]... [+FORMAT] format:
格式符:
+%S: 从1970年1月1号(Unix元年)到现在经过的秒数
设定日期:date [-u|--utc|--universal] [MMDDhhmm[[CC]YY][.ss]]
date 101008082013.08
ifconfig:网口配置
-a display all interfaces which are currently available, even if down(显示所有接口,即使他是关闭的)
-s display a short list (like netstat -i)(显示简要的信息)
export:设置以及输出shell变量属性
Marks each NAME for automatic export to the environment of subsequently executed commands. If VALUE is supplied, assign VALUE before exporting(自动标识每个名字给输出随后执行命令的环境,如果值被支持,则在输出前指定值)
Options:
语法:export [-fnp][变量名称]=[变量设置值]:
-f refer to shell functions(代表[变量名称]为shell函数)
-n remove the export property from each NAME(从每个变量删除输出属性)
-p display a list of all exported variables and functions(显示所有shell 环境变量和函数)