Android Dimension转换算法原理分析
Android Dimension
参考:Android Dimension转换算法原理分析
Dimension 简述
在Android中,我们可以在values文件夹中定义各种资源,其中有一种就是dimension(values/dimen.xml)
dimension是一个包含单位(dp、dip、sp、pt、px、mm、in)的尺寸,可以用于定义视图的宽度、字号等。
定义dimen
<resources>
<dimen name="text_size">22spdimen>
resources>在xml布局获取dimen
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:textSize="@dimen/text_size"/>在Java代码中获取dimen
float textSize = context.getResources().getDimension(R.dimen.text_size);从Java代码可以发现,无论之前在资源文件中定义的dimen是什么单位,在代码中均转换成了float类型的数值。
两个dimen值,如果数值部分相同,但单位不同,显然转换后的float值也不同。
定义一组dimen,数值部分相同,单位不同
<resources>
<dimen name="tdp">15dpdimen>
<dimen name="tdip">15dipdimen>
<dimen name="tsp">15spdimen>
<dimen name="tpt">15ptdimen>
<dimen name="tpx">15pxdimen>
<dimen name="tmm">15mmdimen>
<dimen name="tin">15indimen>
resources>在Java代码中使用getDimension与getValue方法获取这些dimen的值
public static void transDimension(Context context) {
Resources res = context.getResources();
TypedValue typedValue = new TypedValue();
//dp
res.getValue(R.dimen.tdp, typedValue, true);
System.out.println("15dp = " + res.getDimension(R.dimen.tdp) + ", data = " + Integer.toBinaryString(typedValue.data));
//dip
res.getValue(R.dimen.tdip, typedValue, true);
System.out.println("15dip = " + res.getDimension(R.dimen.tdip) + ", data = " + Integer.toBinaryString(typedValue.data));
//sp
res.getValue(R.dimen.tsp, typedValue, true);
System.out.println("15sp = " + res.getDimension(R.dimen.tsp) + ", data = " + Integer.toBinaryString(typedValue.data));
//pt
res.getValue(R.dimen.tpt, typedValue, true);
System.out.println("15pt = " + res.getDimension(R.dimen.tpt) + ", data = " + Integer.toBinaryString(typedValue.data));
//px
res.getValue(R.dimen.tpx, typedValue, true);
System.out.println("15px = " + res.getDimension(R.dimen.tpx) + ", data = " + Integer.toBinaryString(typedValue.data));
//mm
res.getValue(R.dimen.tmm, typedValue, true);
System.out.println("15mm = " + res.getDimension(R.dimen.tmm) + ", data = " + Integer.toBinaryString(typedValue.data));
//in
res.getValue(R.dimen.tin, typedValue, true);
System.out.println("15in = " + res.getDimension(R.dimen.tin) + ", data = " + Integer.toBinaryString(typedValue.data));
}打印结果
System.out: 15dp = 30.0, data = 111100000001
System.out: 15dip = 30.0, data = 111100000001
System.out: 15sp = 30.0, data = 111100000010
System.out: 15pt = 61.451466, data = 111100000011
System.out: 15px = 15.0, data = 111100000000
System.out: 15mm = 174.19313, data = 111100000101
System.out: 15in = 4424.5054, data = 111100000100从log可以看出,不同单位情况下,即使数值相同,转换成的float值也是不同。
从data值中,我们发现,对于不同的单位,高位是相同的,代表数值,低位是不同的,代表单位。可以大胆猜想:dimen在系统中是以 数值+单位 的形式存储的
Dimension源码分析
使用Resources的getDimension获取dimension的值(R.dimon.id的值 * 单位)
/**
* Retrieve a dimensional for a particular resource ID. Unit
* conversions are based on the current {@link DisplayMetrics} associated
* with the resources.
*
* @param id The desired resource identifier, as generated by the aapt
* tool. This integer encodes the package, type, and resource
* entry. The value 0 is an invalid identifier.
*
* @return Resource dimension value multiplied by the appropriate (R.dimon.id的值 * 单位)
* metric.
*
* @throws NotFoundException Throws NotFoundException if the given ID does not exist.
*
* @see #getDimensionPixelOffset
* @see #getDimensionPixelSize
*/
public float getDimension(@DimenRes int id) throws NotFoundException {
synchronized (mAccessLock) {
TypedValue value = mTmpValue;
if (value == null) {
mTmpValue = value = new TypedValue();
}
getValue(id, value, true); //获取到resource ID对应的dimension值
if (value.type == TypedValue.TYPE_DIMENSION) {
// 转换为float值,也就是对应的像素px值
return TypedValue.complexToDimension(value.data, mMetrics);
}
throw new NotFoundException(
"Resource ID #0x" + Integer.toHexString(id) + " type #0x"
+ Integer.toHexString(value.type) + " is not valid");
}
}在getDimension里先用TypedValue.getValue获取到R.dimon.id对应的int值并保存在TypedValue(前面例子中的log typedValue.data = 111100000001)
/**
* Return the raw data associated with a particular resource ID.
*
* @param id The desired resource identifier, as generated by the aapt
* tool. This integer encodes the package, type, and resource
* entry. The value 0 is an invalid identifier.
* @param outValue Object in which to place the resource data.
* @param resolveRefs If true, a resource that is a reference to another
* resource will be followed so that you receive the
* actual final resource data. If false, the TypedValue
* will be filled in with the reference itself.
*
* @throws NotFoundException Throws NotFoundException if the given ID does not exist.
*
*/
public void getValue(@AnyRes int id, TypedValue outValue, boolean resolveRefs)
throws NotFoundException {
boolean found = mAssets.getResourceValue(id, 0, outValue, resolveRefs);
if (found) {
return;
}
throw new NotFoundException("Resource ID #0x"
+ Integer.toHexString(id));
}获取到Dimension的值后,用TypedValue.complexToDimension()将其转换为float值,也就是对应的像素px值。
/**
* Converts a complex data value holding a dimension to its final floating
* point value. The given data must be structured as a
* {@link #TYPE_DIMENSION}.
*
* @param data A complex data value holding a unit, magnitude, and
* mantissa.
* @param metrics Current display metrics to use in the conversion --
* supplies display density and scaling information.
*
* @return The complex floating point value multiplied by the appropriate
* metrics depending on its unit.
*/
public static float complexToDimension(int data, DisplayMetrics metrics)
{
return applyDimension(
(data>>COMPLEX_UNIT_SHIFT)&COMPLEX_UNIT_MASK,
complexToFloat(data),
metrics);
}在complexToDimension其实就是将R.dimon.id的值拆分成单位类型和数值两部分,然后调用TypedValue.applyDimension根据单位的不同,对数值进行处理。
- 获取单位类型:取TypedValue.data低4位的值
// public static final int COMPLEX_UNIT_SHIFT = 0;
// public static final int COMPLEX_UNIT_MASK = 0xf;
(data>>COMPLEX_UNIT_SHIFT)&COMPLEX_UNIT_MASK- 获取数值部分:complexToFloatt使用该int值的9-24位 * 该int值的5-8位基数进行计算,转成float
/**
* Retrieve the base value from a complex data integer. This uses the
* {@link #COMPLEX_MANTISSA_MASK} and {@link #COMPLEX_RADIX_MASK} fields of
* the data to compute a floating point representation of the number they
* describe. The units are ignored.
*
* @param complex A complex data value.
*
* @return A floating point value corresponding to the complex data.
*/
public static float complexToFloat(int complex)
{
// public static final int COMPLEX_MANTISSA_MASK = 0xffffff;
// public static final int COMPLEX_MANTISSA_SHIFT = 8;
return (complex&(TypedValue.COMPLEX_MANTISSA_MASK
<>TypedValue.COMPLEX_RADIX_SHIFT)
& TypedValue.COMPLEX_RADIX_MASK];
} - Current display metrics:metrics,在外部可以通过context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics()获取
最后,在applyDimension中根据单位的不同,将float乘上不同的系数。
- px : 直接返回数值
- dip/dp * 屏幕系数
- sp * 缩放系数
- pt * xdpi * (1.0f/72)
- in * xdpi;
- mm * xdpi * (1.0f/25.4f)
从COMPLEX_UNIT_PX直接返回float可以看出,该方法是将数值转成像素数
/**
* Converts an unpacked complex data value holding a dimension to its final floating
* point value. The two parameters unit and value
* are as in {@link #TYPE_DIMENSION}.
*
* @param unit The unit to convert from.
* @param value The value to apply the unit to.
* @param metrics Current display metrics to use in the conversion --
* supplies display density and scaling information.
*
* @return The complex floating point value multiplied by the appropriate
* metrics depending on its unit.
*/
public static float applyDimension(int unit, float value,
DisplayMetrics metrics)
{
switch (unit) {
case COMPLEX_UNIT_PX:
return value;
case COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP: //dp和dip一样
return value * metrics.density;
case COMPLEX_UNIT_SP:
return value * metrics.scaledDensity;
case COMPLEX_UNIT_PT:
return value * metrics.xdpi * (1.0f/72);
case COMPLEX_UNIT_IN:
return value * metrics.xdpi;
case COMPLEX_UNIT_MM:
return value * metrics.xdpi * (1.0f/25.4f);
}
return 0;
}至此,我们之前的猜想大致上是正确的,只是需要加上一个radix部分。即“dimension在系统中是以数值+4位radix+4位单位的形式存储的”。
枯燥的算法
为了实现将形如“10dip”的dimension转成getValue返回的int值,我们需要进行以下处理(参考com.androi.layoutlib.bridge.impl.ResourceHelper的parseFloatAttribute方法)。
首先,将dimension字符串拆成数值与单位两部分,并将数值转成浮点数。
从上文可以知道,dimension的数值部分在实际存储时,系统只提供了24位存储空间。再考虑到一个dimension是有符号的,可正可负。故最高位表示正负。因此,真正的数值只有23位进行存储。
所以,接下来,对于负数要先转成对应的正数,并乘上223加0.5(四舍五入)后转成long。(即仅保留整数和小数部分各23位)
接着,对转换后的long值进行判断。
若最低23位为0,即小数部分为0,标记radix为TypedValue.COMPLEX_RADIX_23p0,shift为23,即只保留整数部分。
若最高41位为0,即整数部分为0(java中long以8个字节存储),标记radix为TypedValue.COMPLEX_RADIX_0p23,shift为0,即只保留小数部分。
若最高33为0,即整数部分最多只有8位有效,标记radix为TypedValue.COMPLEX_RADIX_8p15,shift为8,即只保留整数部分8位,小数部分15位。
若最高25位为0,即整数部分最多只有16位有效,标记radix为TypedValue.COMPLEX_RADIX_16p7,shift为16,即只保留整数部分16位,小数部分7位。
若以上都不符合,说明小数部分不为0,整数有效部分超过16位,则标记radix为TypedValue.COMPLEX_RADIX_23p0,shift为23,即只保留整数部分。
然后,根据shift将转换后的long值进行右移,取最低24位,转为int。若原值为负数,将右移的数转成负数后再取最低24位。
最后,将最终数值左移8位,最低4-7位或上radix,0-3位或上单位。 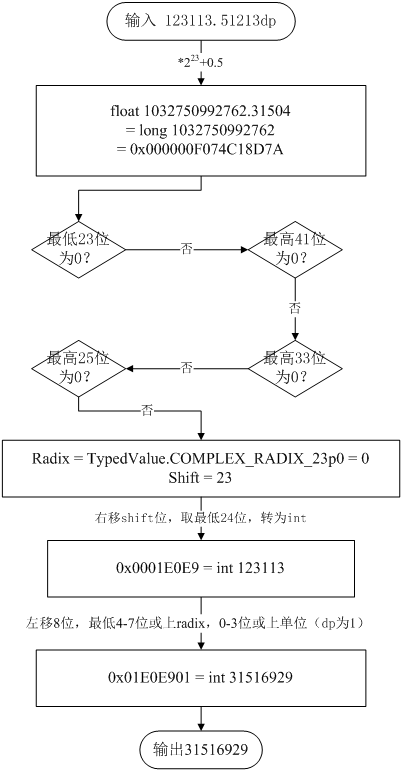
结论与应用
结论:
Dimension在系统中是通过Resource.getValue获取并以最高位(正负) + 31-9位(23位数值) + 8-5(4位radix) + 4-1 (4位单位)的32位int形式存储在TypedValue
应用:在java代码中dp转px
public static int dp2px(Context context, int dp) {
return (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, dp, context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}