HIT 软件构造2019春 Lab2
update: 3/13/2019 未考虑checkRep,RI,AF
update:3/17/2019 改一下MyExp继承RuntimeException
update:3/23/2019 修改P1 poet题目理解,更新poem的stream写法
update:3/24/2019 Edge Immutable条件
Trick:
使用Collection.stream处理满足map-filter-reduce的序列。
DEF:
关于checkRep,RI,AF
QA:
如何检查输入合法?
自定义类继承RuntimeException,如果继承自Exception则需要明确对抛出的Exception进行声明,这里选择RuntimeException,与直接继承Exception相比不需要显示抛出(函数声明throws...),同时也不强制使用try catch捕获(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException是一个例子),可以直接在catch中打印错误信息。
MyExp示例:
package P3;
public class MyExp extends RuntimeException {
//错误信息
private String expMsg="MyException";
public MyExp(String msg) {
this.expMsg = msg;
}
public String getExpMsg() {
return expMsg;
}
public void setExpMsg(String expMsg) {
this.expMsg = expMsg;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return this.expMsg+"\t 请重新输入";
}
//实现assertTrue的断言功能,如果cond为假则抛出异常,使用该函数进行输入合法判断
public static void assertTrue(boolean cond,String msg) throws MyExp {
if(!cond) throw new MyExp(msg);
}
}
捕获:
![]()
//"输入位置需合法" 为需要打印的错误提示信息
打印:
//在game.getPieceAtCord中使用了MyExp.assertTrue,如果想要捕获错误打印错误,需要try catch
实验报告:
Poetic Walks
分别新建两个类ConcreteEdgesGraph,ConcreteVerticesGraph 实现Graph接口。
Graph接口要求实现add(添加新节点),set(添加新边),remove(移除节点),vertices(获得所有的节点集合),sources(target)获得以target为目标节点的边的起始节点,targes(source)获得以source为起始节点的边的目标节点。
Poet:给定一组单词(文件输入),对于两个相邻的单词a和b,认为存在一条由a到b的有向边,通过Graph接口构造有向图。再给定一由单词组成的句子,如果句子中两个相邻单词之间在Graph图中有一个中间单词则将中间单词插入到两单词之间(如果有多个则插入权重最大的那个)。
-
-
- Get the code and prepare Git repository
-
自 https://github.com/rainywang/Spring2019_HITCS_SC_Lab2/tree/master/P1 获得实验代码。
Git init
Git remote add origin [email protected]:ComputerScienceHIT/Lab2-1170300825.git
在远程仓库新建Master分支
Git pull origin master
Git add .
Git commit -m “init”
Git push origin master
--git已经初始化
-
-
- Problem 1: Test Graph
- Problem 1: Test Graph
-
如果需要测试,默认ConcreteEdgesGraph implements Graph
Public Graph
return new ConcreteEdgesGraph();
}
此时可以运行GraphStaticTest进行测试。
-
-
- Problem 2: Implement Graph
- Implement ConcreteEdgesGraph
- Problem 2: Implement Graph
-
- 实现(generic) Edge
类
| 域 |
声明 |
| Private L source |
起始节点 |
| Private L target |
目标节点 |
| Private int weight |
边的权值 |
| 接口 |
说明 |
| Getter (Immutable木有setter) |
三个域的getter |
| judgeVertex |
便利函数,判断一个节点是否为这条边的端点之一 |
| @Override equas |
比较函数 |
| @Override hashCode |
生成hash值 |
- 实现ConcreteEdgesGraph类
| 函数 |
实现思路 |
| add(L vertex) |
调用List.add,其返回结果为boolean且满足spec定义。 |
| set(L source,L target,int weight) |
检查输入满足weight>=0。当weight>0时,如果当前没有该edge,则直接添加,返回值为0,如果已经有该edge,则记录旧值,修改为新值。如果weight==0,当删除的边不存在时返回0,当存在时,删除该节点,该边,如果此时两端点之中没有边与之相连了则删除节点。 |
| remove(L vertex) |
检查输入满足vertex存在vertices中,当存在时,删除该节点,同时删除所有与之相连的边,此时检查vertices中是否有点 没有连边,如果有则删除。 |
| Set |
返回vertices |
| Sources(L target) |
在edges中寻找所有目标点是target的初始节点(加权),符合Map-filter-reduce的处理流程,Stream写法:
|
| Targets(L source) |
符合Map-filter-reduce的处理流程,Stream写法:
|
-
-
-
- Implement ConcreteVerticesGraph
-
-
一、实现(generic) Vertex
| 域 |
声明 |
| Private L label |
Label |
| Private Map |
所有以label为目标节点的边,<起始节点lable,边的权重>. |
| Private Map |
所有以label为其实节点的边,<目标节点label,边的权重> |
| 接口 |
说明 |
| Getter and Setter |
三个域的getter and setter |
| setSource(L source,int weight) |
检查输入满足source!=null,weight>=0。当weight==0时,调用this.removeSource,当weight>0时,调用Map.put修改source并且记录初始值。 |
| removeSource(L source) |
检查输入满足source!=null,调用sources.remove,并返回旧值(不存在则返回0)。 |
| setTarget(L target,int weight) |
检查输入满足target!=null,weight>=0,当weight=0时,调用this.removeTarget,当weight>0时,调用targets.put并返回旧值(不存在则返回0)。 |
| removeTarget(L target) |
检查满足target!=null。调用targets.remove(),返回旧值。 |
| remove(final L vertex) |
调用removeSource和removeTarget |
- 实现ConcreteVertices类
| 函数 |
实现思路 |
| add(L vertex) |
检查输入满足vertex!=null。调用vertices.add,并返回结果 |
| set(L source,L target,int weight) |
检查输入满足weight>=0。如果source或者target不存在与vertices中则新建Vertex加入到vertices中,调用sourceVertex.setTarget,targetVertex.setSource。检查删除没有连边的节点。 |
| remove(L vertex) |
检查输入满足vertex!=null。如果输入节点不存在则返回false,否则,遍历vertices中的每一个节点调用v.remove在targes和sources中删除该节点,在vertices中删除该节点,检查删除没有连边的节点。 |
| Set |
符合Map-filter-reduce的处理流程,Stream写法:
|
| Sources(L target) |
如果没有target则返回空集合,否则调用targetVertex.getSources(getter) |
| Targets(L source) |
如果没有source则返回空集合,否则调用targetVertex.getTargets(getter) |
-
-
- Problem 3: Implement generic Graph
- Make the implementations generic
- Problem 3: Implement generic Graph
-
将类声明修改为:
将类的内部函数参数、返回值、域修改为L。
-
-
-
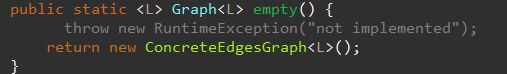
- Implement Graph.empty()
-
-
修改Graph.empty为:
-
-
- Problem 4: Poetic walks
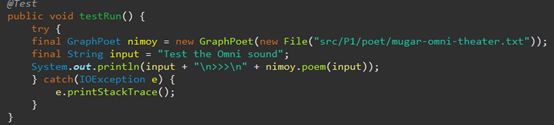
- Test GraphPoet
- Problem 4: Poetic walks
-
配置文件为:new File(“src/P1/poet/mugar-omni-theater.txt”)
测试代码如下:
-
-
-
- Implement GraphPoet
-
-
| 域 |
说明 |
| Private final Graph |
配置文件生成的Graph |
| Private final List |
文集包含的单词 |
- extractWordsFromFile(File corpus)
读取corpus配置文件,并从中提取中所有的单词。
使用split进行字符串分割
- Graph
generateAffinityGraph
根据单词序列构造一个Graph,按照题目中对于图的定义,我们将前后两个相邻的单词之间添加一条从前向后的有向边。
- public String poem(String input)
首先将input切割为单词序列inputWords,对于每两个相邻的节点v1和v2,如果v1.targets()与v2.sources()存在交集,则说明两个单词之间可以添加一个bridge,自交集中选择去权重最大的一个添加到两单词之间。
//stream+lambda 使用实例:
public String poem(String input) {
// 匹配任何空格
String[] inputWords = input.split("\\s");
StringBuilder poem = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < inputWords.length; i++) {
poem.append(inputWords[i]+" ");
if (i + 1 >= inputWords.length) {
break;
}
// 获得i的出边
Map word1Targets =
affinityGraph.targets(inputWords[i].toLowerCase());
// 获得i+1的入边
Map word2Sources =
affinityGraph.sources(inputWords[i+1].toLowerCase());
Set probableBridges = word1Targets.keySet();
// stream流程:取交集 ->根据权值进行排序->toList
List sortedBridges = probableBridges.stream()
.filter(possibleBridge -> word2Sources.containsKey(possibleBridge))
.sorted((String s1,String s2)->
{return word1Targets.get(s2)+word2Sources.get(s2)-
word1Targets.get(s1)-word2Sources.get(s1);})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if(!sortedBridges.isEmpty()) {
poem.append(sortedBridges.get(0)+" ");
}
}
checkRep();
return poem.toString().trim();
} -
-
-
- Graph poetry slam
-
-
Main函数实现如下:
-
-
- Before you’re done
-
项目的目录结构树状示意图:
Re-implement the Social Network in Lab1
继承P1中ConcreteEdgesGraph
-
-
- FriendshipGraph类
-
| 函数 |
实现思路 |
| addVertex(Person newPerson) |
调用父类接口this.add(newPerson) |
| addEdge(Person pa,Person pb) |
调用父类接口this.set(pa,pb,1) |
| getDistance(Person stPerson,Person edPerson) |
使用BFS算法求得图中stPerson与edPerson之间的最短距离,BFS中需要遍历邻居节点,这时候只需要调用父类接口this.targets(topPerson)就可以获得topPerson的所有邻居节点。 |
-
-
- Person类
-
| 域 |
作用 |
| Private String nameString |
记录人名 |
| Private static Set |
记录所有出现过的人名,在构造方法中如果出现重名情况则抛出SamNameException (extends Exception) |
-
-
- 客户端main()
-
测试代码如下:
-
-
- 测试用例
-
测试普通操作:包括addVertex,addEdge,包括重名情况
测试getDistance:测试不能达到目的地、有多条路径达到目的地的情况。
-
-
- 提交至Git仓库
-
Git add .
Git commit -m “P2 is DONE”
Git push origin master
项目的目录结构树状示意图如下:
Playing Chess
-
ADT设计/实现方案
设计了哪些ADT(接口、类),各自的rep和实现,各自的mutability/ immutability说明、AF、RI、safety from rep exposure。
必要时请使用UML class diagram(请自学)描述你设计的各ADT间的关系。
- MyExp类
自定义异常类,继承自Exception,提供的接口有:
| 接口 |
作用 |
| Public String getExpMsg |
获得expMsg |
| Public void setExpMsg |
设置expMsg |
| @Override public String toString |
根据expMsg构造错误信息 |
| Public static void assertTrue(Boolean cond,String msg) throws MyExp |
检查cond是否正确,如果为false则抛出MyExp |
之所以自定义异常类,是因为使用Assert进行断言判断不合法情况的时候,AssertError只能在Junit下捕获到,当程序运行时则不能捕获,所以需要新建异常,使用MyExp来传递错误信息并进行回显。
- Position 类
| 接口 |
作用 |
| Public int x() |
获得x |
| Public int y() |
设置y |
| Override public boolean equals(Oject that) |
判断两个Postion是否相等 |
坐标类,承载坐标信息x,y
- Piece类
| 域 |
解释 |
| pieceState |
棋子状态,0为未放置,1为已经放置,2为放置之后被拿出棋盘且不可用 |
| pName |
棋子种类名称 |
| Px,py |
棋子在棋盘中所处的坐标 |
| 接口 |
作用 |
| Getter for (pName, px, py,pieceState) |
Getter |
| Setter for (pName,pxy) |
Setter |
| Public void rmFromBoard |
将该棋子从棋盘中移出,意味着不能再放入 |
棋子类,包含棋子基本信息,提供pieceState记录棋子状态。
- Player类
| 域 |
解释 |
| Private String playerName |
玩家名称 |
| Private StringBuilder gameHistorySB |
玩家操作历史 |
| Private Set |
玩家所拥有的所有棋子 |
| 接口 |
作用 |
| Getter for (playerName,playerPieces,GameHistorySB) |
Getter
|
| Public Boolean addPiece(Piece) |
玩家添加棋子,如果玩家已有该棋子,则返回false。否则向playerPieces添加后返回true |
| Public Piece getAnyPieceByFilter(Predicate predicate) |
获取该玩家所有满足功能函数predicate要求的棋子之中的任意一个。如果没有,则返回null |
| Public Boolean isContainPiece(Piece) |
判断该玩家是否包含指定棋子 |
| Public void addHistory(String gameStep) |
向gameHistorySB中添加一步的操作 |
玩家类,注意一个玩家所拥有的棋子中包含许多相同类型名称的棋子,使用对象的引用来区别不同的对象,以下相同。
- Board类
| 域 |
解释 |
| Private int boardType |
棋盘类型,0为放在格子里,1为放在交点上 |
| Private int boardSize |
棋盘大小,指的是棋盘上行或列所有的格子数目 |
| Private Piece boardPieces[][] |
存放棋盘上对应位置所放的棋子 |
| 接口 |
作用 |
| Public Piece getPieceAtCord(px,py) throws MyExp |
获取处于(px,py)位置的棋子,如果位置不合法抛出MyExp |
| Public void setPieceAtCord(int px,int py,Piece piece) |
将棋子piece放置在棋盘的(px,py)位置处。如果位置不合法则抛出MyExp |
| Public isCordAvailable(int cx,int cy) |
判断坐标(cx,cy)是否是一个合法坐标。棋盘最终的横纵可以放置的棋子数目为boardSize+boardType |
| Public isPieceInBoard(Piece piece) |
判断棋子piece是否处于棋盘之内。 |
| Public int getNumOfPlayerPiecesInBoard(Player player) |
获得player在棋盘中的棋子数目(也可以将接口交给Player实现) |
棋盘类。提供操作棋盘上棋子的接口。
这里除了检查坐标是否合法之外不进行操作的正确性检查,将检查放到Action。
- Action类
| 域 |
解释 |
| Private Board gameBoard |
游戏中棋盘对象的引用 |
| Private Player playerA,playerB |
游戏中玩家对象AB的引用 |
//以下接口作用省略检查坐标越界的说明
//省略getter and setter的作用说明
| 接口 |
作用 |
| Public void putPiece(Player player,Piece piece,Position pos) |
将玩家player的未处于棋盘的piece棋子落到pos处。修改棋子piece位置,修改棋盘gameBoard上pos位置的棋子为piece,添加玩家历史。 |
| Public void movePiece(Player player,Position st,Position ed) |
将玩家player的已经处于棋盘上的位于st的棋子移动到空地址ed。将棋盘上st位置设置为null,ed位置设置为piece,修改piece的位置为ed。添加玩家历史 |
| Public void removePiece(Player player,Position pos) |
将用户player的位于棋盘上pos的棋子移出棋盘。调用piece.rmFromBoard,将棋盘上pos位置设置为null。添加玩家历史。 |
| Public void eatPiece(Player player,Position st.Position ed) |
使用用户player的位于棋盘st位置的棋子吃掉到对手的ed位置的棋子。调用edPiece.rmFromBoard,将棋盘ed位置设置为stPiece,将棋盘st位置设置为null,将stPiece坐标设置为ed。添加用户历史。 |
下棋动作类。
异常捕捉:对于每种下棋动作,使用MyExp.assertTrue()进行异常测试,使用try catch捕捉异常,并抛出异常。
下棋动作的操作对象为player,gameBoard,和piece。其中playerA、playerB和gameBoard对象是Game传入的引用,因为每种操作都是建立在这两类对象的基础上的。
- Game类
| 域 |
解释 |
| Private String gameType |
游戏类型 |
| Private Board gameBoard |
游戏棋盘 |
| Private Action gameAction |
游戏动作 |
| Private PlayerA,PlayerB |
游戏玩家,playerA为先手 |
//以下接口作用省略检查边界的说明
//省略getter and setter的作用说明
| 接口 |
作用 |
| Public void iniGameWithPlayerName(String paName,String pbName) |
通过传入的两个玩家的名字初始化Game中的各类对象。初始化:从gameType_config.txt文件中读取游戏配置,初始化player,添加拥有的棋子,初始化棋盘,设置大小和类型。将gameBoard,playerA,playerB的引用传入Action新建gameAction对象。 |
| Public void pubPiece throws MyExp |
调用gameAction |
| Public void movePiece throws MyExp |
调用gameAction |
| Public void removePiece throws MyExp |
调用gameAction |
| Public void eatPiece throws MyExp |
调用gameAction |
| Public Player getOwnerAtCord(Positon pos) throws MyExp |
获得处于pos位置的棋子的所有者,获得pos位置的棋子piece,然后调用Player.isContainPiece判断属于playerA还是playerB。 |
| Public Piece getPieceAtCord(Position pos) throws MyExp |
获取处于pos位置的棋子piece,如果没有棋子则返回null。 |
| Public int getNumOfPlayerPiecesInBoard(Player player) |
获取用户在棋盘上的所有棋子数目,调用gameBoard. getNumOfPlayerPiecesInBoard |
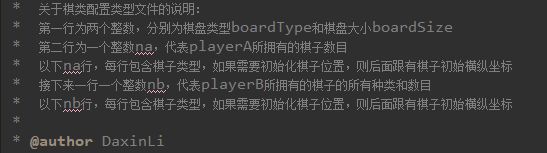
游戏配置文件规范:
游戏类。
主要功能为:读取文件配置,初始化Player,Board,Piece对象,为调用类提供下棋动作的接口。实现读取文件配置,将其他操作下放到具体对象。
-
-
- 主程序MyChessAndGoGame设计/实现方案
-
直接贴代码:
package P3;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class MyChessAndGoGame {
public Set supportGameType=new HashSet() { {
add("chess"); add("go");
}};
public Game game;
public String playerANameString,playerBNameString;
public ArrayList players = new ArrayList();
public void printMenu() {
System.out.println("1.\t将尚未在棋盘上的一颗棋子放在棋盘上的指定位置");
System.out.println("2.\t移动棋盘上的某个位置的棋子至新的位置");
System.out.println("3.\t提子(移除对手棋子)");
System.out.println("4.\t吃子(使用己方棋子吃掉对手棋子)");
System.out.println("5.\t查询某个位置的占用情况");
System.out.println("6.\t计算两个玩家分别在棋盘上的棋子总数");
System.out.println("7.\t跳过");
System.out.println("end.\t 结束操作");
}
public void gameMain() {
BufferedReader reader =null;
String[] splitItems;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while(true) {
System.out.println(String.format("输入游戏类型\t%s:",
supportGameType.stream().reduce((a,b)->a+",\t"+b)));
String strLine= reader.readLine().trim();
if(supportGameType.contains(strLine)) {
game = new Game(strLine);
break;
} else {
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入");
}
}
System.out.println("[用户A]\t请输入您的名称");
playerANameString = reader.readLine().trim();
System.out.println("[用户B]\t请输入您的名称");
playerBNameString = reader.readLine().trim();
game.iniGameWithPlayerName(playerANameString, playerBNameString);
players.add(game.getPlayerA());
players.add(game.getPlayerB());
System.out.println(String.format("%s,%s,游戏开始,请依次操作",
playerANameString,playerBNameString));
int pNI=0;
while(true) {
System.out.println();
System.out.println(String.format("->[%s]", players.get(pNI).getPlayerName()));
printMenu();
String strLine=reader.readLine().trim();
boolean exitFlag =false;
switch(strLine) {
case "1":
// 将尚未在棋盘上的一颗棋子放在棋盘上的指定位置
System.out.println("输入(pieceName,edX edY):");
strLine=reader.readLine().trim();
splitItems = strLine.split("\\s");
if(splitItems.length==3) {
try {
int px=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[1]);
int py=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[2]);
String pName=splitItems[0];
Player player=players.get(pNI);
Piece piece = player.getAnyPieceByFilter(
(p)->p.getPieceState()==0 && p.getpName().equals(pName));
if(piece==null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%s 没有未放置的 %s 棋子", player.getPlayerName(),pName));
continue;
}
game.putPiece(player,
piece,
new Position(px,py));
pNI = (pNI+1)%2;
System.out.println("[SUCCESS]");
} catch (MyExp e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
continue;
// TODO: handle exception
} catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("输入类型错误,重新输入");
continue;
}
} else {
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入");
continue;
}
break;
case "2":
// 移动棋盘上的某个位置的棋子至新的位置
System.out.println("输入(stX stY edX edY):");
strLine=reader.readLine().trim();
splitItems = strLine.split("\\s");
if(splitItems.length==4) {
try {
int stX=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[0]),
stY=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[1]),
edX=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[2]),
edY=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[3]);
Player player=players.get(pNI);
game.movePiece(player,
new Position(stX,stY), new Position(edX, edY));
pNI = (pNI+1)%2;
System.out.println("[SUCCESS]");
} catch (MyExp e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
continue;
// TODO: handle exception
} catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("输入类型错误,重新输入");
continue;
}
} else {
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入");
continue;
}
break;
case "3":
// 提子
System.out.println("输入(edX edY):");
strLine=reader.readLine().trim();
splitItems = strLine.split("\\s");
if(splitItems.length==2) {
try {
int px=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[0]);
int py=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[1]);
Player player=players.get(pNI);
game.removePiece(player,
new Position(px,py));
pNI = (pNI+1)%2;
System.out.println("[SUCCESS]");
} catch (MyExp e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
continue;
// TODO: handle exception
} catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("输入类型错误,重新输入");
continue;
}
} else {
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入");
continue;
}
break;
case "4":
// 吃子
System.out.println("输入(stX stY edX edY):");
strLine=reader.readLine().trim();
splitItems = strLine.split("\\s");
if(splitItems.length==4) {
try {
int stX=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[0]),
stY=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[1]),
edX=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[2]),
edY=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[3]);
Player player=players.get(pNI);
game.eatPiece(player,
new Position(stX,stY), new Position(edX, edY));
pNI = (pNI+1)%2;
System.out.println("[SUCCESS]");
} catch (MyExp e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
continue;
// TODO: handle exception
} catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("输入类型错误,重新输入");
continue;
}
} else {
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入");
continue;
}
break;
case "5":
// 查询某个位置的占用情况
System.out.println("输入(edX edY):");
strLine=reader.readLine().trim();
splitItems = strLine.split("\\s");
if(splitItems.length==2) {
try {
int px=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[0]);
int py=Integer.valueOf(splitItems[1]);
Piece piece =game.getPieceAtCord(new Position(px, py));
Player player=game.getOwnerAtCord(new Position(px,py));
if(player==null) {
System.out.println("该位置没有棋子");
} else {
System.out.println(String.format("该位置为 %s 的 %s 棋子",
player.getPlayerName(),piece.getpName()));
}
} catch (MyExp e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
continue;
// TODO: handle exception
} catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("输入类型错误,重新输入");
continue;
}
} else {
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入");
continue;
}
break;
case "6":
// 计算两个玩家分别在棋盘上的棋子总数
System.out.println(String.format("玩家\t%s\t在棋盘上的棋子总数为%d",
players.get(0).getPlayerName(),game.getNumOfPlayerPiecesInBoard(players.get(0))));
System.out.println(String.format("玩家\t%s\t在棋盘上的棋子总数为%d",
players.get(1).getPlayerName(),game.getNumOfPlayerPiecesInBoard(players.get(1))));
break;
case "7":
// 跳过
System.out.println("[跳过]");
pNI=(pNI+1)%2;
break;
case "end":
// 结束游戏操作
System.out.println("-------->>> END GAME <<<--------");
exitFlag = true;
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入");
break;
}
if(exitFlag) break;
}
// 询问是否查看本次比赛的走棋历史
pNI = 0;
for(pNI=0;pNI<2;pNI++) {
while(true) {
System.out.println();
System.out.println(String.format("->[%s]", players.get(pNI).getPlayerName()));
System.out.println("是否需要查看本次游戏操作历史?[yes,no]");
boolean exitFlag = true;
switch(reader.readLine().trim()) {
case "yes":
System.out.println(players.get(pNI).getGameHistoryString());
break;
case "no":
break;
default:
exitFlag = false;
break;
}
if(exitFlag) break;
}
}
System.out.println("游戏结束,再见!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyChessAndGoGame().gameMain();
}
}
-
-
- ADT和主程序的测试方案
-
测试主要针对重要ADT,测试方案如下:
- testGame(包含测试Action)
测试主要包括测试Game 的配置文件载入,Game提供的各类操作接口,如putPiece,eatPiece等。
对于操作接口的测试,设计测试用例满足题目文档中所给出的各类边界条件。
- testBoard
测试主要包括测试Board的越界情况处理以及getNumOfPlayerPiecesInBoard的函数测试。
Multi-Startup Set (MIT)
//未自定义异常捕获错误。
RepListIntervalSet:
package P4.interval;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* An implementation of IntervalSet.
*
* PS2 instructions: you MUST use the provided rep.
*/
public class RepListIntervalSet implements IntervalSet {
/**
* e.g., { "A"=[0,10), "B"=[20,30) } is represented by
* labelList = <"A", "B">
* valueList = <0, 10, 20, 30>
*/
private final List labelList = new ArrayList<>();
private final List valueList = new ArrayList<>();
// Abstraction function:
// AF(labelList,valueList)={label[i]=[valueList[2*i],valueList[2*i+1]),0<=i<=labellist.size()}
// Representation invariant:
// RI(labelList,valueList) = sizeOfLabel*2==sizeOfValue && value[2k]=start && value labels() {
return labelList.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
@Override
public boolean remove(L label) {
if(!labelList.contains(label)) {
return false;
}
int indexOfLabel=labelList.indexOf(label);
labelList.remove(indexOfLabel);
valueList.removeAll(Arrays.asList(valueList.get(2*indexOfLabel),valueList.get(2*indexOfLabel+1)));
checkRep();
return true;
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
@Override
public long start(L label) throws NoSuchElementException {
if(!labelList.contains(label))
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return valueList.get(2*labelList.indexOf(label));
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
@Override
public long end(L label) throws NoSuchElementException {
if(!labelList.contains(label))
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return valueList.get(2*labelList.indexOf(label)+1);
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("RepListIntervalSet with %d labels", labelList.size());
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
}
RepMapIntervalSet:
package P4.interval;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertDoesNotThrow;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Set;
public class RepMapIntervalSet implements IntervalSet {
/**
* e.g., { "A"=[0,10), "B"=[20,30) } is represented by
* startMap = { <"A", 0>, <"B", 20> }
* endMap = { <"A", 10>, <"B", 30> }
*/
private final Map startMap = new HashMap<>();
private final Map endMap = new HashMap<>();
// Abstraction function:
// AF(startMap,endMap)={key=[startMap[key],endMap[key]) | key in startMap.keySet()}
// Representation invariant:
// startMap.size()==endMap.size() && startMap[key]=start && value entry:startMap.entrySet()) {
L entry_key = entry.getKey();
Long entry_start= entry.getValue();
Long entry_end = endMap.get(entry_key);
if(entry_key.equals(label)) {
if(start!=entry_start || end!=entry_end) {
throw new IntervalConflictException("[Exception] label冲突:但是[start,end)不同");
} else {
insertFlag=false;
}
} else {
if(isValueAtRange(start, entry_start, entry_end)
|| isValueAtRange(entry_start, start, end)) {
throw new IntervalConflictException("[Exception] 区间冲突:包括两个重叠的区间");
}
}
}
if(insertFlag) {
startMap.put(label, start);
endMap.put(label, end);
}
checkRep();
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
@Override
public Set labels() {
return startMap.keySet();
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
@Override
public boolean remove(L label) {
if(!startMap.containsKey(label)) {
return false;
} else {
startMap.remove(label);
endMap.remove(label);
return true;
}
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
@Override
public long start(L label) throws NoSuchElementException {
if(!startMap.containsKey(label)) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return startMap.get(label);
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
@Override
public long end(L label) throws NoSuchElementException {
if(!endMap.containsKey(label)) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return endMap.get(label);
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("RepMapIntervalSet with %d labels", endMap.size());
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
}
MutiIntervalSet:
package P4.interval;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertAll;
import java.awt.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.print.attribute.HashAttributeSet;
/**
* A mutable set of labeled intervals, where each label is associated with one
* or more non-overlapping half-open intervals [start, end). Neither intervals
* with the same label nor with different labels may overlap.
*
* Labels are of immutable type L and must implement the Object contract: they are
* compared for equality using Object.equals(java.lang.Object).
*
* For example, { * "A"=[[0,10)], "B"=[[20,30)] } is a multi-interval set where
* the labels are Strings "A" and "B". We could add "A"=[10,20) to that set to obtain
* {"A"=[[0,10),[10,20)], "B"=[[20,30)] }.
*
* PS2 instructions: this is a required ADT class. You may not change the
* specifications or add new public methods. You must use IntervalSet in your
* rep, but otherwise the implementation of this class is up to you.
*
* @param type of labels in this set, must be immutable
*/
public class MultiIntervalSet {
// 将重叠集合划分为若干个不重叠集合
private ArrayList> intervalSetList;
/**
* Create an empty multi-interval set.
*/
public MultiIntervalSet() {
this.intervalSetList = new ArrayList>();
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
/**
* Create a new multi-interval set containing the given labeled intervals.
*
* @param initial initial contents of the new set
*/
public MultiIntervalSet(IntervalSet initial) {
intervalSetList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(initial));
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
/**
* 判断value是否处于 [start,end)区间内部
*
* @param value
* @param start
* @param end
* @return 判断value是否处于 [start,end) 区间内部
*/
private boolean valueAtRange(long value,long start,long end) {
return value>=start && value itSet = intervalSetList.get(i);
if(!itSet.labels().contains(label)) {
indexOfInsertLabel = i;
}
for(L edLabel:itSet.labels()) {
Long edStart = itSet.start(edLabel);
Long edEnd = itSet.end(edLabel);
// 不论Label是否相同 检查区间是否重叠
if(valueAtRange(start, edStart, edEnd)
||valueAtRange(edStart, start, end)) {
throw new IntervalConflictException("[EXCEPTION] label不同且区间重叠");
}
if(label.equals(edLabel)
&& edStart==start &&edEnd==end) {
existEqRangeFlag = true;
}
}
}
if(!existEqRangeFlag) {
// 如果不存在 Label相同且区间相同 则可以插入
if(indexOfInsertLabel==-1) {
// 此时需要新建IntervalSet进行插入
IntervalSet newSet=IntervalSet.empty();
newSet.insert(start, end, label);
intervalSetList.add(newSet);
} else {
intervalSetList.get(indexOfInsertLabel).insert(start, end, label);
}
}
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
/**
* Remove all intervals of the given label from this set, if any.
*
* @param label label to remove
* @return true if this set contained label, and false otherwise
*/
public boolean removeAll(L label) {
boolean ansFlag = false;
for(IntervalSet itSet:intervalSetList) {
ansFlag = ansFlag | itSet.remove(label);
}
return ansFlag;
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
/**
* Get the labels in this set.
*
* @return the labels in this set
*/
public Set labels() {
Set ansSet = new HashSet<>();
for(IntervalSet itSet:intervalSetList) {
ansSet.addAll(itSet.labels());
}
return ansSet;
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
/**
* Get all the intervals in this set associated with a given label. The returned set has
* Integer labels that act as indices: label 0 is associated with the lowest interval,
* 1 the next, and so on, for all the intervals in this set that have the provided label.
*
* For example, if this set is { "A"=[[0,10),[20,30)], "B"=[[10,20)] },
* intervals("A") returns { 0=[0,10), 1=[20,30) }
* @param label the label
* @return a new interval set that associates integer indices with the in-order intervals
* of label in this set
* @throws NoSuchElementException if label is not in this set
*/
public IntervalSet intervals(L label) throws NoSuchElementException{
IntervalSet ansIntervalSet = IntervalSet.empty();
ArrayList itList = new ArrayList<>();
for(IntervalSet itSet:intervalSetList) {
if(itSet.labels().contains(label)) {
itList.add(new Turple(itSet.start(label),itSet.end(label)));
}
}
if(itList.size()==0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
itList.sort( (Object o1,Object o2)->{
Turple a = (Turple)o1;
Turple b=(Turple)o2;
if(a.getStart()b.getStart()) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
});
try {
for(int i=0;i Similarity:
package P4.startup;
import java.awt.List;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Set;
import P4.interval.IntervalConflictException;
import P4.interval.IntervalSet;
import P4.interval.MultiIntervalSet;
/**
* A [TODO mutable?] measure of similarity between multi-interval sets of
* Strings.
*
* An instance of Similarity uses a client-provided definition of label
* similarities, where 0 is least similar and 1 is most similar.
*
* Given two multi-interval sets, let min be the minimum start of any of their
* intervals, and let max be the maximum end. The similarity between the two
* sets is the ratio:
* (sum of piecewise-matching between the sets) / (max - min)
*
* The amount of piecewise-matching for any unit interval [i, i+1) is:
* 0 if neither set has a label on that interval
* 0 if only one set has a label on that interval
* otherwise, the similarity between the labels as defined for this Similarity instance
*
* For example, suppose you have multi-interval sets that use labels "happy", "sad", and "meh";
* and similarity between labels is defined as:
*
* 1 if both are "happy", both "sad", or both "meh"
* 0.5 if one is "meh" and the other is "happy" or "sad"
* 0 otherwise
*
* Then the similarity between these two sets:
* { "happy" = [[0, 1), [2,4)], "sad" = [[1,2)] }
* { "sad" = [[1, 2)], "meh" = [[2,3)], "happy" = [[3,4)] }
*
* would be: (0 + 1 + 0.5 + 1) / (4 - 0) = 0.625
*
* PS2 instructions: this is a required ADT class, and you MUST NOT weaken the
* required specifications. However you MAY strengthen the specifications and
* you MAY add additional methods.
*/
public class Similarity {
private ArrayList simRulesArrayList;
/**
* Create a new Similarity where similarity between labels is defined in the given file.
* Each line of similarities must contain exactly three pieces, separated by one or more spaces.
* The first two pieces give a pair of strings, and the third piece gives the decimal similarity
* between them, in a format allowed by Double.valueOf(String), between 0 and 1 inclusive.
*
* Similarity between labels is symmetric, so the order of strings in the pair is irrelevant.
* A pair may not appear more than once. The similarity between all other pairs of strings is 0.
* This format cannot define non-zero similarity for strings that contain newlines or spaces,
* or for the empty string.
*
* For example, the following file defines the similarity function used in the example at the top of this class:
* happy happy 1
* sad sad 1
* meh meh 1
* meh happy 0.5
* meh sad 0.5
* @param similarities label similarity definition as described above
* @throws IOException if the similarity file cannot be found or read
*/
public Similarity(File similarities) throws IOException {
simRulesArrayList = new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(similarities));
String stringLine=reader.readLine();
while(stringLine!=null) {
String[] splitLine=stringLine.split("\\s");
// System.out.println(splitLine[0]+splitLine[1]+splitLine[2]);
simRulesArrayList.add(new Triple(splitLine[0], splitLine[1], Double.valueOf(splitLine[2])));
if(!splitLine[0].equals(splitLine[1])) {
simRulesArrayList.add(new Triple(splitLine[1], splitLine[0], Double.valueOf(splitLine[2])));
}
stringLine = reader.readLine();
}
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
/**
* 判断value是否处于 [start,end)区间内部
*
* @param value
* @param start
* @param end
* @return 判断value是否处于 [start,end) 区间内部
*/
public static boolean valueAtRange(long value,long start,long end) {
return value>=start && value=stB && edA<=edB) {
// A被B包含
return 1;
}
if(valueAtRange(stB, stA, edA) && edB>=stA && edB<=edA) {
// B被A包含
return 2;
}
// 不存在包含关系
return 0;
}
/**
* 计算两个MutilIntervalSet的交集长度
* @param itA
* @param itB
* @return 交集长度
*/
public static Double caculatePieceWiseMatching(IntervalSet itA,IntervalSet itB) {
int pa=0,pb=0;
int paLen=itA.labels().size(),pbLen=itB.labels().size();
Double matchingLenDouble = 0.0;
while(true) {
if(pa>=paLen || pb>=pbLen) {
break;
}
long startA = itA.start(pa),startB = itB.start(pb);
long endA = itA.end(pa),endB = itB.end(pb);
int containType=rangeContain(startA, endA, startB, endB);
if(containType==1) {
// A被B包含
matchingLenDouble += endA-startA;
pa++;
} else if(containType==2) {
// B被A包含
matchingLenDouble += endB-startB;
pb++;
} else {
if(valueAtRange(startA, startB, endB)) {
// 交集:startA位于B区间
matchingLenDouble += endB-startA;
pb++;
} else if(valueAtRange(startB, startA, endA)) {
// 交集:startB位于A区间
matchingLenDouble += endA-startB;
pa++;
} else {
if(startA a, MultiIntervalSet b) {
Set labelListA = a.labels();
Set labelListB = b.labels();
Double ansDouble = 0.0;
long minDouble=Long.MAX_VALUE,maxDouble=Long.MIN_VALUE;
try {
for(String label:labelListA) {
IntervalSet itSet=a.intervals(label);
for(int i=0;imaxDouble) maxDouble=ed;
}
}
for(String label:labelListB) {
IntervalSet itSet=b.intervals(label);
for(int i=0;imaxDouble) maxDouble=ed;
}
}
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(Triple triple:simRulesArrayList) {
String labelStart=triple.getStart();
String labelEnd=triple.getEnd();
Double labelValue=triple.getValue();
if(labelListA.contains(labelStart)&&labelListB.contains(labelEnd)) {
ansDouble += labelValue*caculatePieceWiseMatching(a.intervals(labelStart), b.intervals(labelEnd));
}
}
return ansDouble/(maxDouble-minDouble);
// throw new RuntimeException("not implemented");
}
}
class Triple {
private String start,end;
private Double value;
public Triple(String start,String end,Double value) {
this.setStart(start);
this.setEnd(end);
this.setValue(value);
}
public String getStart() {
return start;
}
public void setStart(String start) {
this.start = start;
}
public String getEnd() {
return end;
}
public void setEnd(String end) {
this.end = end;
}
public Double getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(Double value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
我是迷人的小尾巴
以下外链,利益相关,欢迎浏览ε≡٩(๑>₃<)۶ :
济南江鹏工贸有限公司(山东济南机械加工),济南彤昌机械科技有限公司(山东济南机械加工)