小白一步一步阅读vuejs源码
本篇不直接解读vuejs的双向绑定的原理,而是已读源码的视角来看vue是怎么做的。
1、下载vuejs源码
- mkdir project && cd project && git clone https://github.com/vuejs/vue.git
- npm i
2、开始一步一步读代码
- 打开package.json。看看scripts,我们先只看dev,这里有三个:full-dev,runtime-cjs-dev,esm
我们这边只看web-full-dev,这个也是我们平时引用的vuejs,其他两个是es6module和common

- 继续找到scripts/config.js,然后target:web-full-dev
// Runtime+compiler development build (Browser)
'web-full-dev': {
entry: resolve('web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js'),
dest: resolve('dist/vue.js'),
format: 'umd',
env: 'development',
alias: { he: './entity-decoder' },
banner
},
找到resolve方法,发现使用了别名alias.js
module.exports = {
vue: resolve('src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler'),
compiler: resolve('src/compiler'),
core: resolve('src/core'),
shared: resolve('src/shared'),
web: resolve('src/platforms/web'),
weex: resolve('src/platforms/weex'),
server: resolve('src/server'),
sfc: resolve('src/sfc')
}
- 至此,找到路径src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
这里挂载了$mount方法,里面主要是做了模板转换
compileToFunctions
使用了template:’#id’,el:’#id’,template:’’
的模板,编译成render方法。
import Vue from './runtime/index'
- 因为我们代码使用都是new Vue();所以我们需要找到Vue实例,继续在runtime/index
我们关注注册的$mount方法,找到dom节点,然后传递给mountComponent方法
// public mount method
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
- 这里仍然是引用core/index
初始化一些全局api,比如set,config
import Vue from './instance/index'
- 继续找到instance/index
终于找到Vue的定义了。提示需要new Vue来创建实例,然后执行Init
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
_init在initMixin里面定义的。
- 找到init.js
初始生命周期,事件,render等。
最后,执行了$mount方法。
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
……
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
- eventsMixin,注册vue的事件,消息通知的。
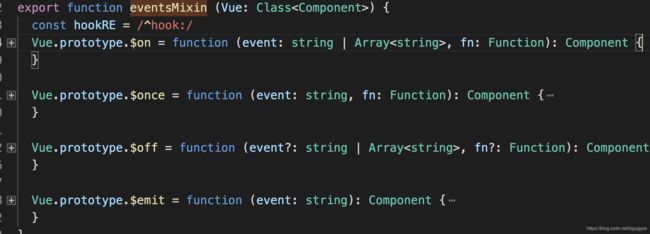
我们看下$on,由于是挂在原型上,是和实例想干,所以new Vue()页面之间是不会窜消息的,比如我司提供的共用事件消息,是挂在全局上的,消息可能会窜。
Vue.prototype.$on = function (event: string | Array, fn: Function): Component {
const vm: Component = this
if (Array.isArray(event)) {
for (let i = 0, l = event.length; i < l; i++) {
vm.$on(event[i], fn)
}
} else {
(vm._events[event] || (vm._events[event] = [])).push(fn)
// optimize hook:event cost by using a boolean flag marked at registration
// instead of a hash lookup
if (hookRE.test(event)) {
vm._hasHookEvent = true
}
}
return vm
}
callbacks.push(() => {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx)
}
})
flushCallbacks,刷新所有的nextTick的回调。
function flushCallbacks () {
pending = false
const copies = callbacks.slice(0)
callbacks.length = 0
for (let i = 0; i < copies.length; i++) {
copies[i]()
}
}
在next-tick.js里面,我们看到开始有初始化一个timerFunc,这个就是来看当前环境应该怎么去nextTick。
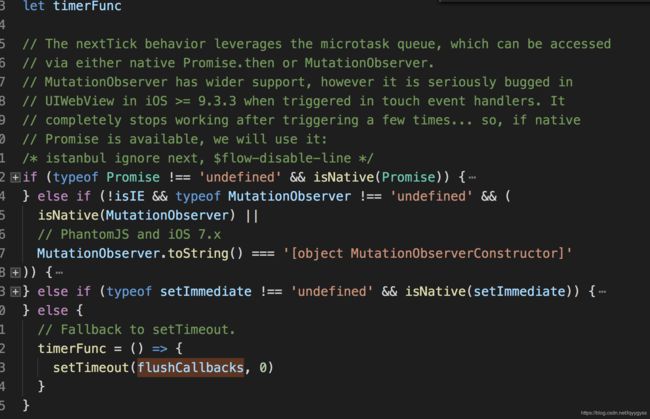
- 如果有Promise,且是原生的Promise,即当前浏览器支持的Promise,则使用Promise
我们都知道原生的Promise是微观任务,当一个eventlook宏观任务执行完成之后,会执行全部的微观任务,所以,在用户执行nexttick的时候,我们就开启一个微观promise任务,这样如果promise进入then了,则说明页面渲染这个动作完成了。
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
const p = Promise.resolve()
timerFunc = () => {
p.then(flushCallbacks)
// In problematic UIWebViews, Promise.then doesn't completely break, but
// it can get stuck in a weird state where callbacks are pushed into the
// microtask queue but the queue isn't being flushed, until the browser
// needs to do some other work, e.g. handle a timer. Therefore we can
// "force" the microtask queue to be flushed by adding an empty timer.
if (isIOS) setTimeout(noop)
}
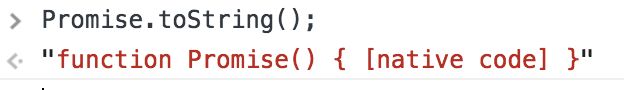
顺道看下isNative怎么做的。含有native code则为原生。
export function isNative (Ctor: any): boolean {
return typeof Ctor === 'function' && /native code/.test(Ctor.toString())
}
- 如果没有原生Promise,则使用MutationObserver:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/MutationObserver,
来监听dom的变化。如果dom的变化完成了,则回调。
创建一个MutationObserver,然后传入回调方法,创建一个文本节点,然后每次执行timerFunc的时候,修改这个文本节点的值,如果dom更新了,则回调flushCallbacks
} else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MutationObserver) ||
// PhantomJS and iOS 7.x
MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]'
)) {
// Use MutationObserver where native Promise is not available,
// e.g. PhantomJS, iOS7, Android 4.4
// (#6466 MutationObserver is unreliable in IE11)
let counter = 1
const observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks)
const textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter))
observer.observe(textNode, {
characterData: true
})
timerFunc = () => {
counter = (counter + 1) % 2
textNode.data = String(counter)
}
isUsingMicroTask = true
- 如果都没有。则直接用setTimeout了。
} else {
// Fallback to setTimeout.
timerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0)
}
}
终于知道nextTick是怎么做的了吧~
我们再回去看instance/index
- state.js看初始化的stateMixin
难怪我们能够vm.$data.xxx能获取到,原因是将dataDef挂在vm实例上,然后.xxx就是this.data的数据。
props也同理。
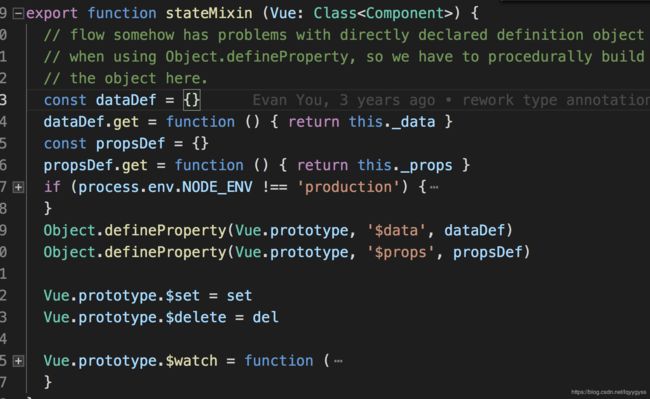
我们还注意到这里挂载了set方法。
在数据对象已经初始化完成之后,我们需要设置调用vm.set方法,才能更新页面响应。
那就顺道再看看set方法吧。
逻辑清晰易懂,如果数据已经在target上,则直接设置值即可。
如果没有__ob_,即说明该target都没有被observe,则直接设置,子元素也不做设置监听。
否则重新调用defineReactive来给target的的value来设置observe,然后再触发依赖dep的更新。
if (key in target && !(key in Object.prototype)) {
target[key] = val
return val
}
const ob = (target: any).__ob__
if (!ob) {
target[key] = val
return val
}
defineReactive(ob.value, key, val)
ob.dep.notify()
return val
- 再回过来看initState
初始化props,methods,data,compute,watch
export function initState (vm: Component) {
vm._watchers = []
const opts = vm.$options
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm)
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch)
}
}