TMS320C6455的EMIF外部存储器接口
DSP6455的EMIFA模块
前言:
C6455的EMIFA可以访问多种外部存储器,比如:SRAM,ROM,FLASH等等。当然,也包括FPGA。本文的重点就是介绍使用EMIFA接口与FPGA建立无缝连接以及和FLASH的连接。
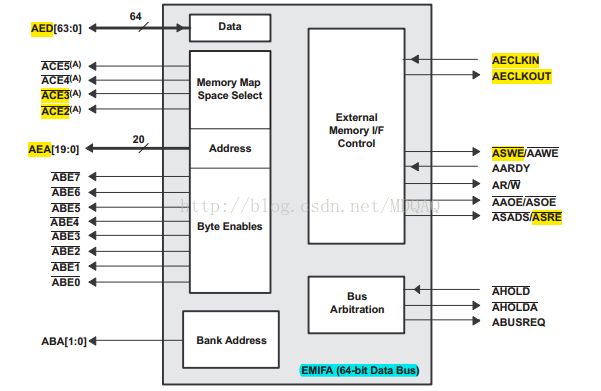
1.EMIF接口信号图
部分管脚说明:
•AED[63:0] 64位数据总线
•AEA[19:0] 20位地址总线(Optional)
•ACE2 片选信号(低有效)
•ACE3 片选信号(低有效)
•AECLKOUT 时钟信号
•ASWE 写使能(低有效)
•ASRE 读使能(低有效)
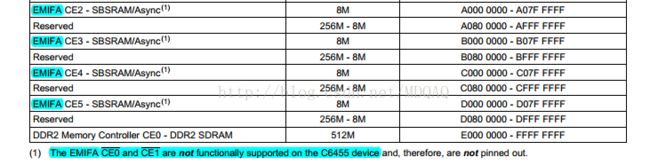
2.EMIF片选信号及映射情况
从图中可以看出:
•EMIFA共支持4个外部存储器,例如把CE2分配给FPGA,CE3分配给FLASH。
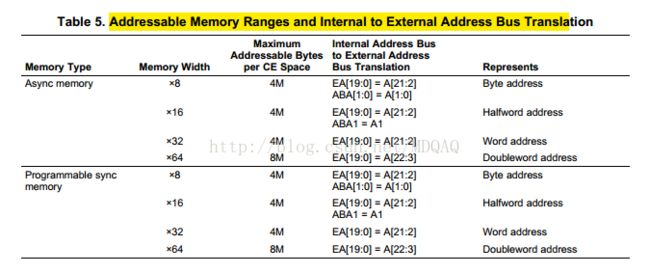
•每个外部存储器的寻址空间大小是8MB。FPGA20根地址线即2的20次方,也就是1MB,此外由于数据总线是64位的,故对应的寻址空间是8MB(但是在这里FLASH我们配置的是8位内存位宽,所以此处是4M寻址空间)
在读取FPGA内部RAM数据时告诉EDMA要读取的数据的基地址是0xA0000000,以及读取的数据的长度即可。
在读取FLASH数据时告诉EDMA要读取的数据的基地址是0xB0000000,以及读取的数据的长度即可。
3.EMIF与 FPGA和FLASH连接原理图
EMIF:
FPGA:
FLASH:
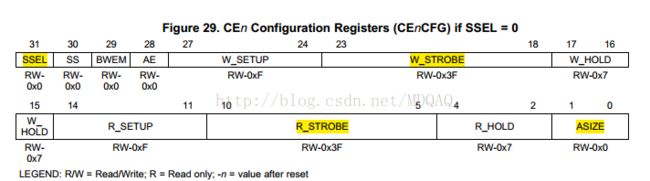
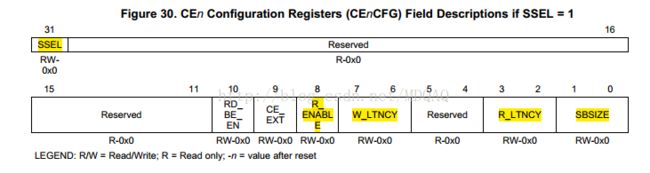
4.配置EMIFA的寄存器
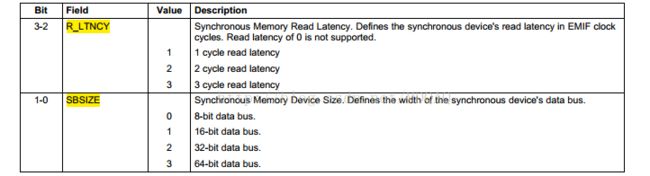
主要配置寄存器是CEnCFG。该寄存器有两套完全不同的配置,分别对应于同步存储器模式和异步存储器模式。由于FPGA内部RAM工作于同步模式,故我们来看一下同步模式下该寄存器的配置。FLASH则是采用异步模式。
(1)异步模式的外部存储器(高亮部分)FLASH配置
(2)同步模式的外部存储器(高亮部分)FPGA配置
5.代码编写
配置EMIFA模块时,主要的步骤如下:
(1) 使能设备EMIFA模块
(2) 配置CEnCFG寄存器
(3) 初始化EMIFA模块
#define EMIFA_BASE_ADDR (0x70000000)
#define EMIFA_MIDR (*(int*)(EMIFA_BASE_ADDR + 0x00000000))
#define EMIFA_STAT (*(int*)(EMIFA_BASE_ADDR + 0x00000004))
#define EMIFA_BPRIO (*(int*)(EMIFA_BASE_ADDR + 0x00000020))
#define EMIFA_CE2CFG (*(int*)(EMIFA_BASE_ADDR + 0x00000080))
#define EMIFA_CE3CFG (*(int*)(EMIFA_BASE_ADDR + 0x00000084))
#define EMIFA_CE4CFG (*(int*)(EMIFA_BASE_ADDR + 0x00000088))
#define EMIFA_CE5CFG (*(int*)(EMIFA_BASE_ADDR + 0x0000008C))
#define EMIFA_AWCC (*(int*)(EMIFA_BASE_ADDR + 0x000000A0))
void init_emif(void)
{
/* Enable the async EMIF and the DDR2 Memory Controller */
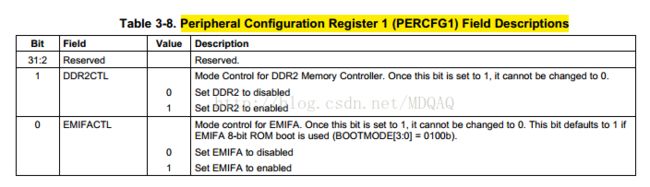
*(int *)(0x02AC002C) = 0x00000003; // PERCFG1 = 0x02AC002C
/* Configure async EMIF */
//EMIFA_CE2CFG = 0x80240122; /* 32-bit sync, 10 cycle read/write strobe for fpga A0000000 - A07FFFFF */
EMIFA_CE2CFG = 0x8000000A; /* 32-bit sync, write latency 0 read latency 2 */
EMIFA_CE3CFG = 0x00240120; /* 8-bit async, 10 cycle read/write strobe for norflash */
//EMIFA_CE4CFG = 0x00240122; /* 32-bit async, 10 cycle read/write strobe for fpga*/
//EMIFA_CE4CFG = 0x00240121; /* 16-bit Async, read/write strobe for fpga*/
//EMIFA_CE5CFG = 0x80240122; /* 32-bit async, 10 cycle read/write strobe */
EMIFA_BPRIO = 0x000000FE; /* Enable priority based starvation control SPRU971A sec. 7.2 */
EMIFA_AWCC = 0x000002FF; //TA 2 clock,
}代码说明:
FPGA:
#define EMIF_FPGA_BASE_ADDR 0xA0000000
void WriteFpga(Uint32 addr,Uint32 data)
{
*((Uint32*) (EMIF_FPGA_BASE_ADDR + addr)) = data;
}
Uint32 ReadFpga(Uint32 addr)
{
Uint32 reData = 0;
reData = *((Uint32*) (EMIF_FPGA_BASE_ADDR + addr));
return reData;
}
Uint32 emif_test(Uint32 addr, Uint8 *data, Uint32 len)
{
int num;
Uint32 readData;
Uint32 startData = 0x11111111;
Uint32 writeData;
for(num = 0; num < 256 / 4; num++)
{
writeData = startData + num;
WriteFpga(num * 4, writeData);
readData =ReadFpga(num * 4);
if(readData != writeData)
{
printf("write = %X read = %X\n", writeData, readData);
}
}
printf("emif test OK! \n");
return 0;
}FLASH:
#define FLASH_BASE 0xB0000000
#define FLASH_RESET 0xF0
#define FLASH_CMD_AA 0xAA
#define FLASH_CMD_55 0x55
#define FLASH_PROGRAM 0xA0
#define FLASH_PROGRAM_BUFFER 0x29
#define FLASH_ERASE 0x80
#define FLASH_ERASE_CHIP 0x10
#define FLASH_ERASE_SECTOR 0x30
#define FLASH_ERASE_SUSPEND 0xB0
#define FLASH_ERASE_RESUME 0x10
int norflash_erase( Uint32 start, Uint32 length )
{
Uint16 i;
Uint8 *pdata;
Uint32 sector_base,end;
end = start + length - 1; // Calculate end of rang
/* Walk through each sector, erase any sectors within range */
sector_base = FLASH_BASE;
for (i = 0; i < FLASH_SECTORS; i++)
{
if ( ( ( sector_base >= start ) || ( sector_end[i] >= start ) ) &&
( ( sector_base <= end ) || ( sector_end[i] <= end ) ) )
{
/* Start sector erase sequence */
FLASH_CTL555 = FLASH_CMD_AA;
FLASH_CTL2AA = FLASH_CMD_55 ;
FLASH_CTL555 = FLASH_ERASE;
FLASH_CTL555 = FLASH_CMD_AA;
FLASH_CTL2AA = FLASH_CMD_55 ;
/* Start erase at sector address */
pdata = (Uint8 *)sector_base;
*pdata = FLASH_ERASE_SECTOR;
/* Wait for erase to complete */
while (1)
if (*pdata & 0x80)
break;
/* Put back in read mode */
*((Uint8 *)FLASH_BASE) = FLASH_RESET;
}
/* Advance to next sector */
sector_base = sector_end[i] + 1;
}
*((Uint8 *)FLASH_BASE) = FLASH_RESET;
return 0;
}
int norflash_write( Uint8* src, Uint32 dst, Uint32 length )
{
Uint32 i;
Uint8* psrc8;
Uint8* pdst8;
volatile Uint8* addr8 = ( Uint8* )FLASH_BASE;
/*
* Align to 8 or 8 bits
*/
psrc8 = ( Uint8* )src;
pdst8 = ( Uint8* )dst;
for ( i = 0 ; i < length ; i ++ )
{
/* Program one 8-bit word */
FLASH_CTL555 = FLASH_CMD_AA;
FLASH_CTL2AA = FLASH_CMD_55;
FLASH_CTL555 = FLASH_PROGRAM;
*pdst8 = *psrc8;
/* Wait for programming to complete */
// Wait for operation to complete
while(1)
if (*pdst8 == *psrc8)
break;
pdst8++;
psrc8++;
}
*addr8 = FLASH_RESET;
return 0;
}
int norflash_read( Uint32 src, Uint8* dst, Uint32 length )
{
Uint32 i;
Uint8* psrc8 = ( Uint8* )src;
Uint8* pdst8 = ( Uint8* )dst;
/*
* Set to Read Mode
*/
FLASH_BASE_PTR8 = FLASH_RESET;
/*
* Read Data to Buffer
*/
for ( i = 0 ; i < length ; i ++ )
*pdst8++ = *psrc8++;
return 0;
}
int norflash_test(Uint32 dstAddr, Uint32 length, Uint8 start)
{
int retVal;
Uint32 num;
Uint32 wLen;
Uint8 data;
Uint8 *testData = NULL;
testData = (Uint8*)malloc(1024);
if(testData == NULL)
{
printf("malloc is error!\n");
return -1;
}
for(num = 0; num < 1024; num++)
{
testData[num] = start + num;
}
norflash_erase(dstAddr, length);
while(length > 0)
{
wLen = length > 1024 ? 1024 : length;
length -= wLen;
retVal = norflash_write(testData, dstAddr, wLen);
if(retVal != 0)
{
printf("nor flash write is error!\n");
return -1;
}
memset(testData, 0, wLen);
retVal = norflash_read(dstAddr, testData, wLen);
if(retVal != 0)
{
printf("nor flash write is error!\n");
return -1;
}
for(num = 0; num < wLen; num++)
{
data = start + num;
if(testData[num] != data)
{
printf("nor flash test is error!\n");
return -1;
}
}
dstAddr += wLen;
}
printf("nor flash test is ok!\n");
return 0;
}
FLASH代码说明:
参看:http://blog.csdn.net/mdqaq/article/details/53606900