Mybatis笔记
文章目录
- Mybatis笔记
- 入门创建与简单CURD
- SqlSession的创建
- 使用XML构建SqlSessionFactory
- 不使用XML构建SqlSessionFactory
- 使用SqlSessionFactory获取SqlSession
- 作用域和生命周期和命名空间
- 作用域和生命周期
- 命名空间namespace
- 简单的CURD
- 准备工作
- 做CURD需改动的内容
- Map和模糊查询
- 配置
- 环境配置
- 配置读取
- 别名
- 映射器配置
- 解决属性名和字段名不一致的问题
- 日志工厂
- Log4j使用步骤
- 分页
- 使用Limit分页
- RowBounds分页
- 使用注解开发
- 面向接口编程
- Lombok
- 复杂查询环境搭建
- 多对一
- 按照查询嵌套
- 结果嵌套处理
- 一对多处理
- 动态SQL
- 代码总结
Mybatis笔记
入门创建与简单CURD
SqlSession的创建
mybatis的maven依赖包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatisartifactId>
<version>x.x.xversion>
dependency>
概念理解:
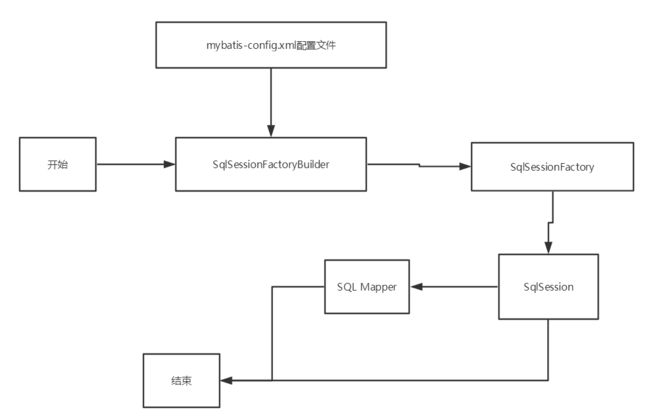
每个基于MyBatis的应用都是以一个SqlSeesionFactory的实例为核心的,该实例可用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder获得,这个SSFB可以通过XML配置文件或预先配置的Configuration实例构建。
使用XML构建SqlSessionFactory
方法流程:
- 先完成xml配置文件的创建
- 获取xml文件路径,用资源获取输入流
- 用输入流获得SqlSessionFactory
xml配置文件:
xml配置文件包含核心设置,包括数据库连接实例、决定事务作用域和控制方式的事务管理器,先给个简单示例:
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/example/BlogMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
configuration>
mapper中包含一组映射器,这些映射器包含了SQL代码和映射定义信息。
使用类路径下的资源文件进行配置并获取SqlSessionFactory:
这三行还是比较固定的
// 文件路径
String resource = "org/mybatis/example/mybatis-config.xml";
// 利用资源获得输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 根据输入流获取SSF
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
不使用XML构建SqlSessionFactory
方法流程:
使用java代码写的,具体没看懂,然而因为要用一些高级映射,所以还是会用到xml
获取代码:
DataSource dataSource = BlogDataSourceFactory.getBlogDataSource();
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = new JdbcTransactionFactory();
Environment environment = new Environment("development", transactionFactory, dataSource);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(environment);
configuration.addMapper(BlogMapper.class);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(configuration);
使用SqlSessionFactory获取SqlSession
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()
作用域和生命周期和命名空间
作用域和生命周期
注意:使用依赖注入可以直接忽略生命周期(这块和Spring挂钩)。
| 类 | 生命周期 | 最佳作用域 |
|---|---|---|
| SqlSessionFactoryBuilder | 这个类可以实例化、使用、丢弃,一旦创建了SqlSessionFactory就不需要这个东西了 | 最好是作为一个局部变量,方法作用域 |
| SqlSessionFactory | 一旦被创建就一直运行,没有任何理由丢弃或重建另一个实例,也不应重复创建多次 | 应用作用域 |
| SqlSession | 每个线程都有自己的SqlSession实例,SqlSession实例不是线程安全的,不可共享 | 请求或方法作用域,不可放在静态域中,不可放在托管域中,使用应立刻关闭,关闭应放到finally中 |
| 映射器实例 | 在调用他们的方法中被获取,使用完毕后即可丢弃,不需要显示地关闭 | 方法作用域 |
官方建议:
方法作用域就是放在try里面那样子。
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
// 你的应用逻辑代码
}
命名空间namespace
作用:
- 用名字来将不同语句隔离,同时实现接口绑定,即使暂时不用,也要遵守
- 将命名空间放在何是的java包命名空间中,代码更整洁
两种命名规则:
- 全限命名,如
com.mypackage.MyMapper.selectAllThings - 短命名,如
selectAllThings。如果全局唯一可以如此,如果不唯一,则要用全名。
简单的CURD
方法流程:
- 先创建一个接口类,该类中的方法相当于被Sql实现
- 用xml文件将mapper和接口绑定,xml文件中通过"id"来绑定对应的方法
- 调用sqlSession.getMapper(接口类.class)方法会获取的一个接口类的实例
- 使用该实例可调用接口的方法,来实现Sql的功能
准备工作
父工程maven配置文件:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itgroupId>
<artifactId>Mybatis_learnartifactId>
<packaging>pompackaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<modules>
<module>mybatis-01module>
modules>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.47version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatisartifactId>
<version>3.5.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resourcesdirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.propertiesinclude>
<include>**/*.xmlinclude>
includes>
<filtering>falsefiltering>
resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/javadirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.propertiesinclude>
<include>**/*.xmlinclude>
includes>
<filtering>falsefiltering>
resource>
resources>
build>
project>
工具类:
public class utils {
public static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static {
try{
// 文件路径
String resource = "config.xml";
// 利用资源获得输入流, 这里有个异常
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 根据输入流获取SSF
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (Exception o){
o.printStackTrace();
}
}
public SqlSession geSS(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
数据库记录对应的实体类:
该类和数据库记录相对应, 类中的私有成员变量名应和数据库中的相同。
当从数据库中取出数据的时候,就用该类接受。
// 实体类
public class User {
// 名字和数据库里的一样
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name, String pwd) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", pwd='" + pwd + '\'' +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
}
核心配置文件:
管理事务、数据库连接、映射相关内容。
注意的点:
- 数据库url中useSSL是加密相关,设为false就没有验证了
- and功能要使用特殊符号:
& - mapper中用resource的话,路径必须是
/
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=false&userUnicode=true&characterEncoding=gbk"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="1234"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="it/dao/BlogMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
configuration>
资源过滤:
maven默认只能读取resources中的xml,使用下面的build,可以将检索范围扩大。
注意:
- filter是使用项目属性或系统属性代替文件属性。如果系统是utf-8,而文件是gbk,设置true的话可能乱码
- 该内容放在父工程中,会对所有的子工程生效
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resourcesdirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.propertiesinclude>
<include>**/*.xmlinclude>
includes>
<filtering>truefiltering>
resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/javadirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.propertiesinclude>
<include>**/*.xmlinclude>
includes>
<filtering>truefiltering>
resource>
resources>
build>
做CURD需改动的内容
流程:
- 编写接口类
- 修改对应mapper.xml中的内容进行绑定
- 测试,注意提交事务
接口类:
需要实现的Sql功能的方法都在这里
// 得是个接口,参数和返回类型要和sql语句匹配
public interface BlogMapper {
// 注释和xml不可共存
// @Select("SELECT * FROM mybatis.user where id = #{id}")
User getUser(int id);
// insert, 参数为对应class
int doInsert(User user);
// update,参数为对应class
int doUpdate(User user);
// delete, 参数随意
int doDelete(int id);
// map用法,key为String类型,value为Object类型
User getUserMap(Map<String, Object> map);
// 模糊查询
List<User> getUserMH(String string);
}
配置文件绑定
namespace和接口的绑定、接口类中的方法和xml中的SQL语句的绑定。
注意:
- namespace中的包名要和接口一样
- id对应namespace绑定的接口类的方法名,要一致
- resultType是返回值的类型,如果返回的是
List,那么这里也要是E - paramterType是参数的类型,只有一个基本数据类型的情况,可以直接在SQL中获取,可不写;如果是多参数的话,用map或者注解好一些
<mapper namespace="it.dao.BlogMapper">
<select id="getUser" resultType="it.User">
select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id}
select>
<insert id="doInsert" parameterType="it.User">
insert into mybatis.user(id, Name, pwd) value (#{id}, #{name}, #{pwd});
insert>
<update id="doUpdate" parameterType="it.User">
update mybatis.user set Name=#{name}, pwd=#{pwd} where id=#{id};
update>
<delete id="doDelete" parameterType="int">
delete from mybatis.user where id=#{id};
delete>
<select id="getUserMap" parameterType="map" resultType="it.User">
select * from mybatis.user where id=#{iddd};
select>
<select id="getUserMH" resultType="it.User">
select * from mybatis.user where name like #{value};
select>
mapper>
测试类:
public class dot {
public static void main(String[] args) {
utils g = new utils();
SqlSession sqlSession = g.geSS();
// 方法一
// 获取映射器
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
// 调用映射器方法
User user = mapper.getUser(1);
System.out.println(user.toString());
int jojo = mapper.doUpdate(new User(1, "jojo", "1234"));
System.out.println(jojo);
mapper.doDelete(2);
mapper.doInsert(new User(5, "ll","123"));
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
// 方法二
// User user1 = sqlSession.selectOne("it.dao.BlogMapper.getUser", 2);
// System.out.println(user1.toString());
// sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testMap(){
utils g = new utils();
SqlSession sqlSession = g.geSS();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
// 此处要定义一个map
Map<String, Object> map =new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("iddd",1);
User userMap = mapper.getUserMap(map);
System.out.println(userMap.toString());
// 模糊查询
System.out.println("-------------");
List<User> list = mapper.getUserMH("%李%");
for( User use: list){
System.out.println(use.toString());
}
}
}
Map和模糊查询
这两个在上面的代码中有体现
Map:
- 当实体类、或者数据库中的表、字段较多,建议使用map;当user类不能为空的时候,如果只想改变一个,那么就很不方便,使用map可以只改变一个。
- String是key,Object是value
- Map传递参数直接在SQL取出key即可, parameterType为map,所以要制作一个map作为参数。
模糊查询:
- 测试中使用通配符作为传递参数,如`"%李%""
配置
环境配置
多个环境的必要性:尽管可以配置多个环境,但每个SqlSessionFactory实例只能选择一种环境,即每个数据库对应一个SqlSessionFactory实例。
环境配置文件:
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="..." value="..."/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
生成时指定环境:
这里的environment使用的是id属性
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, environment);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, environment, properties);
生成时不指定环境:
使用default指定的环境
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, properties);
配置读取
config.properties文件:
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=false&userUnicode=true&characterEncoding=gbk
涉及到properties部分的配置代码:
<properties resource="config.properties">
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="org.apache.ibatis.parsing.PropertyParser.enable-default-value" value="true"/>
properties>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password:1234}"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
properties读取优先级:
- 最高级:方法参数传递的
- 中级:resource读取的属性,即config.properties文件
- 最低级:properties元素内指定属性,即xml中自己设置的
注意点:
- properties不需要转义,所以url要改动。
- properties必须放在xml文件中的最上面。
别名
三种起别名方式:
- 为单个实体类单独指定
- 为整个包中的实体类起别名,默认使用类的首字母小写形式(不过测试了大写也可以)
- 在实体类上边加注释
xml中代码:
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="user" type="it.User"/>
<package name="it"/>
typeAliases>
实体类中代码:
// 实体类
@Alias("user")
public class User {}
优先级:typeAlias > 注解 > package
映射器配置
三种方式:
- 通过resource配置(推荐该方法)
- 通过类配置
- 通过包配置
注意:
- 类和包的方法都有两个限制条件:1. 配置文件和接口同名;2. 两个文件在同一目录下。
xml文件代码:
<mappers>
<mapper resource="it/dao/BlogMapper.xml"/>
<mapper class="it.dao.BlogMapper"/>
<package name="it.dao"/>
mappers>
解决属性名和字段名不一致的问题
问题描述:接受数据库数据的类中的成员变量名和数据库的字段不一样
出现问题原因:
一般情况下,MyBatis会自动创建一个ResultMap,在基于属性名映射column到实体类的属性上,没匹配就会出现null。
最简单最笨的解决方式:
就是sql的起别名:
select id, name, pwd as passowrd from user where id = #{id}
使用方法:
把ResultType换成ResultMap
两种名称:
id name pwd
id name password
结果集映射:
<!--结果集映射-->
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<!--column数据库中的字段,property实体类中的属性-->
<result column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="pwd" property="password"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="UserMap">
select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id}
</select>
resultMap元素是 MyBatis 中最重要最强大的元素ResultMap的设计思想是,对于简单的语句根本不需要配置显式的结果映射,而对于复杂一点的语句只需要描述它们的关系就行了。
日志工厂
日志的作用:如果一个数据库操作,出现了异常,需要排错,就要用日志。
日志类型:
- SLF4J
- LOG4J 【掌握】
- LOG4J2
- JDK_LOGGING
- COMMONS_LOGGING
- STDOUT_LOGGING 【掌握】
- NO_LOGGING
Log4j使用步骤
1. 导入Log4j的maven:
<dependency>
<groupId>log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4jartifactId>
<version>1.2.17version>
dependency>
2. log4j.properties:
属性设置文件,放到resource中,名字乱写会报错
#将等级为DEBUG的日志信息输出到console和file这两个目的地,console和file的定义在下面的代码
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,console,file
#控制台输出的相关设置
log4j.appender.console = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.Target = System.out
log4j.appender.console.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.console.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=[%c]-%m%n
#文件输出的相关设置
log4j.appender.file = org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.file.File=./log/kuang.log
log4j.appender.file.MaxFileSize=10mb
log4j.appender.file.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=[%p][%d{yy-MM-dd}][%c]%m%n
#日志输出级别
log4j.logger.org.mybatis=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG
3. mybatis配置文件中编写settings:
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/>
settings>
4. 实例化日志对象:
参数为当前类的class
static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(dot.class);
5. 日志的级别:
public void testlog4j(){
logger.info("info");
logger.debug("debug");
logger.error("error");
}
配对问题:
好像是只要在配置文件中声明了setting,然后在这个项目里不管调用什么函数都会按照日志配置文件操作。
至于Logger加载的class有啥用,现在还不知道,可能是监控这个类的所有行为?
分页
sql分页基础知识:
// 从startIndex起,每页放pageSize个
select * from user limit startIndex, pageSize;
// 从第4个起,一直到最后,是个bug,被修复了
// select * from user limit 4, -1;
// 只有一个参数,就是从0开始到n
select * from user limit n;
使用Limit分页
步骤:
- 创建一个方法接口和SQL语句
List<User> getPage(Map<String, Integer> map);
<select id="getPage" parameterType="map" resultMap="userMap">
select * from mybatis.user limit #{startIndex}, #{pageSize}
select>
- 调用方法
public void testLimi(){
utils g = new utils();
SqlSession sqlSession = g.geSS();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
// 设置key和value
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("startIndex", 1);
map.put("pageSize", 2);
List<User> page = mapper.getPage(map);
for (User user : page){
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
sqlSession.close();
}
RowBounds分页
这个方法不需要sql
步骤:
- 接口
List<User> getUserByRowBounds();
- mapper.xml
<select id="getUserByRowBounds" resultMap="UserMap">
select * from mybatis.user
select>
- 方法
@Test
public void getUserByRowBounds(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//RowBounds实现
RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(1, 2);
//通过Java代码层面实现分页
List<User> userList = sqlSession.selectList("com.kuang.dao.UserMapper.getUserByRowBounds",null,rowBounds);
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
使用注解开发
面向接口编程
根本原因:解耦,可拓展,提高复用,分成开发中,上层不用管具体的实现,大家都遵守共同的标准,使得开发变得容易,规范性更好。
关于接口的理解:
- 定义与实现的分离
- 对于系统的抽象理解
- 有两类
- 对一个个体的抽象,可对应为一个抽象体(abstract class)
- 对一个个体某一方面的抽象,即形成一个抽象面(interface)
- 一个个体可能有多个抽象面,抽象体和抽象面是有区别的
本质:主要应用反射
底层:动态代理
使用方法:
- 定义接口类的方法
- 在核心配置文件中绑定接口,而不是xml,也没有xml
- 在接口的方法上写上注解,注意参数命名
接口:
public interface BlogMapper {
@Select("select * from mybatis.user where id=#{uid}")
public User getUser(@Param("uid") int id);
// 做不到参数map
@Insert("Insert into mybatis.user(id, name, pwd) values(#{id},#{name},#{password})")
public int doInsert(User user);
@Update("update user set name=#{name}, pwd=#{password} where id=#{id}")
public int doUpdate(User user);
@Delete("delete from user where id=#{id}")
public int doDelete(int id);
}
核心配置文件变化:
绑定一个接口类
<mappers>
<mapper class="it.dao.BlogMapper"/>
mappers>
测试类:
@Test
public void testJunit(){
utils g = new utils();
SqlSession sqlSession = g.geSS();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
System.out.println("查询:");
User user1 = mapper.getUser(1);
System.out.println(user1.toString());
mapper.doInsert(new User(7, "hhh", "111"));
mapper.doDelete(5);
mapper.doUpdate(new User(4,"hxh","22"));
}
注意:
- 可以在工具类创建的时候实现自动提交事务,
ssf.openSession(true)设置为true可自动提交。 - 方法存在多个参数时,基本类型都加
@Param("id"),sql中的参数名要和Param的一样。 - 这个注解指定名字也可以在mapper.xml中使用,相当于给参数起了别名。
Lombok
使用步骤:
- 添加插件
- 导入lombok的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.10version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
- 通过加注解来自动完成一些事情。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
// 名字和数据库里的一样
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;
}
复杂查询环境搭建
多对一
按照查询嵌套
流程:
- 先整体选择,把返回值类型改一下,改为
resultMap并自定义map。 - 定义map,
type设置为原本应该接受的类型,后面的变动的地方用association或collection来改变,javaType是想要的类型,再用一个select从另一个sql中获取信息。 - mybatis会自动估计另一个
select的参数,resultType为想要的类型。
思路:
全选出来,先选出来的结果要被接收,然后在第一次输出的结果中再去查找。
代码:
// 查询所有的学生信息和对应的老师的信息
public List<Student> getStudent();
<select id="getStudent" resultMap="StudentTeacher">
select * from mybatis.student
select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<association property="teacher" column="tid" javaType="Teacher" select="getTeacher"/>
resultMap>
<select id="getTeacher" resultType="Teacher">
select * from mybatis.teacher where id=#{tid}
select>
结果嵌套处理
流程:
- 也是要做个
resultMap,不过sql语句可以写成想要的那种 - 通过对
resultMap的修改,来让结果拟合之前的sql语句
思路:
- sql语句返回的就是想要的,但是类型并不是已有的,所以要用map来做个新的类型
- map做的新类型中的变量应大于等于sql获取的,可多不可少
- association就是把对应的属性赋值进去了。
代码:
public List<Student> getStudent2();
<select id="getStudent2" resultMap="StudentTeacher2">
select s.id sid, s.name sname, t.name tname
from mybatis.student s, mybatis.teacher t
where s.tid = t.id
select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher2" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher">
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
association>
resultMap>
一对多处理
两种方法,如果结果是集合,resultMap中应用collection。
第一种方式:
<select id="getStudentsByTeacher2" resultMap="StuTeacher">
select * from mybatis.teacher where id=#{tid}
select>
<resultMap id="StuTeacher" type="Teacher">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<collection property="students" javaType="ArrayList" ofType="Student" select="getStudents" column="id"/>
resultMap>
<select id="getStudents" resultType="Student">
select * from mybatis.student where tid=#{tid}
select>
第二种方式:
<select id="getStudentsByTeacher" resultMap="Students">
select s.name sname, s.id sid, t.name tname, t.id tid
from mybatis.student s, mybatis.teacher t
where s.tid=t.id and t.id=#{tid};
select>
<resultMap id="Students" type="Teacher">
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<result property="id" column="tid"/>
<collection property="students" ofType="Student">
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
collection>
resultMap>
小结:
- 关联 - association 【多对一】
- 集合 - collection 【一对多】
- javaType & ofType
- JavaType 用来指定实体类中属性的类型
- ofType 用来指定映射到List或者集合中的 pojo类型,泛型中的约束类型!
动态SQL
比较好理解,有几个关键方法:
- where:包含方法,像是开启判断
- if:可用map来传递参数
- when与choose:就像带了break的case,满足第一个就自动停了,where 元素只会在子元素返回任何内容的情况下才插入 “WHERE” 子句。而且,若子句的开头为 “AND” 或 “OR”,where 元素也会将它们去除。
- set:update的时候用
- trim:自定义用的,好像是处理
and和or
代码总结
接口类:
public interface BlogMapper {
// 不要乱设置参数名
int InsertBlog(Blog blog);
// if查找
List<Blog> getByIf(Map<String,Object> map);
// 测试where
List<Blog> getUseWhere(Map<String,Object> map);
// 测试choose
List<Blog> getUseChoose(Map<String,Object> map);
// 测试set
int doUpdate(Map<String, Object> map);
}
<mapper namespace="it.dao.BlogMapper">
<insert id="InsertBlog" parameterType="Blog">
insert into mybatis.blog(id, title, author, create_time, views)
values (#{id}, #{title}, #{author}, #{createTime}, #{views})
insert>
<select id="getByIf" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from mybatis.blog where 1=1
<if test="author !=null ">
and author=#{author}
if>
<if test="views !=null ">
and views=#{views}
if>
select>
<select id="getUseWhere" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<if test="author !=null ">
and author=#{author}
if>
<if test="views !=null ">
and views=#{views}
if>
where>
select>
<select id="getUseChoose" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
title=#{title}
when>
<when test="author != null">
and author=#{author}
when>
<otherwise>
views=2
otherwise>
choose>
where>
select>
<update id="doUpdate" parameterType="map">
update mybatis.blog
<set>
<if test="title != null">
title=#{title},
if>
<if test="views != null">
views=#{views}
if>
set>
where author=#{author}
update>
mapper>
测试类:
@Test
public void testIf(){
utils uu = new utils();
SqlSession sqlSession = uu.geSS();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
List<Blog> byIf = mapper.getByIf(map);
System.out.println(byIf);
System.out.println("使用了条件");
map.put("author","jojo");
List<Blog> byIf2 = mapper.getByIf(map);
System.out.println(byIf2);
}
@Test
public void testWhere(){
utils uu = new utils();
SqlSession sqlSession = uu.geSS();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
List<Blog> useWhereNo = mapper.getUseWhere(map);
System.out.println(useWhereNo);
System.out.println("使用map=====================");
map.put("author","jojo");
List<Blog> useWhere = mapper.getUseWhere(map);
System.out.println(useWhere);
}
@Test
public void testChoose(){
utils uu = new utils();
SqlSession sqlSession = uu.geSS();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
System.out.println("空的,views=2的数据:");
List<Blog> choose1 = mapper.getUseChoose(map);
System.out.println(choose1);
System.out.println("title=java, author=kiruto的情况=================");
map.put("title", "java");
map.put("author", "kiruto");
List<Blog> choose2 = mapper.getUseChoose(map);
System.out.println(choose2);
}
@Test
public void testSet(){
utils uu = new utils();
SqlSession sqlSession = uu.geSS();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("author", "jojo");
map.put("title", "change");
mapper.doUpdate(map);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}