winpcap介绍
【winpcap 驱动简介】
winpcap(windows packet capture)是 windows平台下一个免费,公共的网络访问系统。开发winpcap这个项目的目的在于为 win32应用程序提供访问网络底层的能力。它提供了以下的各项功能:1> 捕获原始数据报,包括在共享网络上各主机发送/接收的以及相互之间交换的数据报;
2> 在数据报发往应用程序之前,按照自定义的规则将某些特殊的数据报过滤掉;
3> 在网络上发送原始的数据报;
4> 收集网络通信过程中的统计信息。
winpcap的主要功能在于独立于主机协议(如TCP-IP)而发送和接收原始数据报。也就是说,winpcap不能阻塞,过滤或控制其他应用程序数据报的发收,它仅仅只是监听共享网络上传送的数据报。因此,它不能用于 QoS调度程序或 个人防火墙。目前,winpcap开发的主要对象是 windows NT/2000/XP,这主要是因为在使用winpcap的用户中只有一小部分是仅使用 windows 95/98/Me,并且M$也已经放弃了对 win9x的开发。因此本文相关的程序T-ARP也是面向NT/2000/XP用户的。其实winpcap中的面向9x系统的概念和NT系统的非常相似,只是在某些实现上有点差异,比如说9x只支持 ANSI编码,而NT系统则提倡使用 Unicode编码。有个软件叫 sniffer pro.可以作网管软件用,有很多功能,可监视网络运行情况,每台网内机器的数据流量,实时反映每台机器所访问IP以及它们之间的数据流通情况,可以抓包,可对过滤器进行设置,以便只抓取想要的包,比如 POP3包, smtp包,ftp包等,并可从中找到邮箱用户名和密码,还有 ftp用户名和密码.它还可以在使用交换机的网络上监听,不过要在交换机上装它的一个软件.还有一个简单的监听软件叫 Passwordsniffer,可截获邮箱用户名和密码,还有ftp用户名和密码,它只能用在用HUB网络上著名软件 tcpdump及 ids snort都是基于 libpcap编写的,此外 Nmap扫描器也是基于libpcap来捕获目标主机返回的数据包的。
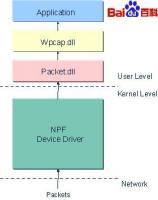
winpcap提供给用户两个不同级别的编程接口:一个基于libpcap的wpcap.dll,另一个是较底层的packet.dll。对于一般的要与unix平台上libpcap兼容的开发来说,使用pacap.dll是当然的选择。
编辑本段【Winpcap的内部结构】
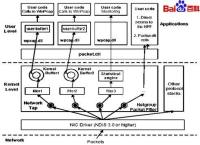
Winpcap是针对Win32平台上的抓包和网络分析的一个架构。它包括一个核心态的包过滤器,一个底层的动态链接库(packet.dll)和一个高层的不以来于系统的库(wpcap.dll)。
为什么使用“architecture”而不是“library”呢?因为抓包是一个要求与网络适配器(网卡)和操作系统交互的底层机制,而且与网络的实施也有密切关系,所以仅用“library”不能充分表达Winpcap的作用。
下图表明了Winpcap的各个组成部分:
首先,抓包系统必须绕过操作系统的协议栈来访问在网络上传输的原始数据包(raw packet),这就要求一部分运行在操作系统核心内部,直接与网络接口驱动交互。这个部分是系统依赖(system dependent)的,在Winpcap的解决方案里它被认为是一个设备驱动,称作NPF(Netgroup Packet Filter)。Winpcap开发小组针对Windows95,Windows98,WindowsME,Windows NT 4,Windows2000和WindowsXP提供了不同版本的驱动。这些驱动不仅提供了基本的特性(例如抓包和injection),还有更高级的特性(例如可编程的过滤器系统和监视引擎)。前者可以被用来约束一个抓包会话只针对网络通信中的一个子集(例如,仅仅捕获特殊主机产生的ftp通信的数据包),后者提供了一个强大而简单的统计网络通信量的机制(例如,获得网络负载或两个主机间的数据交换量)。
其次,抓包系统必须有用户级的程序接口,通过这些接口,用户程序可以利用内核驱动提供的高级特性。Winpcap提供了两个不同的库:packet.dll和wpcap.dll。前者提供了一个底层API,伴随着一个独立于Microsoft操作系统的编程接口,这些API可以直接用来访问驱动的函数;后者导出了一组更强大的与libpcap一致的高层抓包函数库(capture primitives)。这些函数使得数据包的捕获以一种与网络硬件和操作系统无关的方式进行。
〖NPF驱动〗
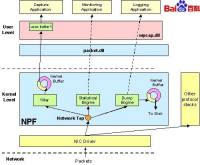
网络数据包过滤器(Netgroup Packet Filter,NPF)是Winpcap的核心部分,它是Winpcap完成困难工作的组件。它处理网络上传输的数据包,并且对用户级提供可捕获(capture)、发送(injection)和分析性能(analysis capabilities)。
〖NPF和NDIS〗
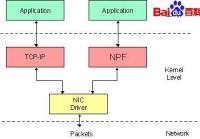
NDIS(Network Driver Interface Specification)是一个定义网络适配器(或者说成是管理网络适配器的驱动程序)与协议驱动(例如TCP/IP的实现)之间通信的规范。NDIS最主要的目的是作为一个允许协议驱动发送和接收网络( LAN或 WAN)上的数据包而不必关心特定的适配器或特定的Win32操作系统的封装。
NDIS支持三种类型的网络驱动:
(1) 网络接口卡 或 NIC 驱动(Network interface card or NIC drivers)。NIC驱动直接管理着网络接口卡(NIC)。NIC驱动接下边与硬件连接,从上边表现为一个接口,该接口允许高层发送数据包到网络上,处理中断,重置NIC,停止NIC,查询和设置驱动的运行特征。NIC驱动可以是小端口(miniport)或完全的NIC驱动(full NIC driver)。
Miniport驱动仅仅实现了管理NIC的必要操作,包括在NIC上发送和接收数据。对于所有最底层的NIC驱动的操作由NDIS提供,例如 同步(synchronization)。小端口(miniport)不直接调用操作系统函数,它们对于操作系统的接口是NDIS。
小端口仅仅是向上传递数据包给NDIS并且NDIS确保这些数据包被传递给正确的协议。
完全NIC驱动(Full NIC driver)完成硬件细节的操作和所有由NDIS完成的同步和查询操作。例如,完全NIC驱动维持接收到的数据的绑定信息。
(2) 中间层驱动(Intermediate drivers)中间层驱动位于高层驱动(例如协议驱动)和小端口之间。对于高层驱动,中间层驱动看起来像是小端口;对于小端口,中间层驱动看起来像协议驱动。一个中间层协议驱动可以位于另一个中间层驱动之上,尽管这种分层可能对系统性能带来负面影响。开发中间层驱动的一个关键原因是在现存的遗留协议驱动(legacy protocol driver)和小端口之间形成媒体的转化。例如,中间层驱动可以将LAN协议转换成ATM协议。中间层驱动不能与用户模式的应用程序通信,但可以与其他的NDIS驱动通信。
(3) 传输驱动或协议驱动(Transport drivers or protocol drivers)协议驱动实现了网络协议栈,例如IPX/SPX或TCP/IP,在一个或多个网络接口卡上提供它的服务。在协议驱动的上面,它为应用层客户程序服务;在它的下面,它与一个或多个NIC驱动或中间层NDIS驱动连接。
NPF是一个协议驱动。从性能方面来看,这不是最好的选择,但是它合理地独立于MAC层并且有权使用原始通信(raw traffic)。
下图表现了NPF在NDIS栈中的位置:
〖NPF结构基础〗
下图表现了伴随着NPF驱动细节的Winpcap的结构。
〖抓包〗
抓包是NPF最重要的操作。在抓包的时候,驱动使用一个网络接口监视着数据包,并将这些数据包完整无缺地投递给用户级应用程序。
抓包过程依赖于两个主要组件:
一个数据包 过滤器,它决定着是否接收进来的数据包并把数据包 拷贝给监听程序。数据包过滤器是一个有布尔输出的函数。如果 函数值是true,抓包驱动拷贝数据包给应用程序;如果是false,数据包将被丢弃。NPF数据包过滤器更复杂一些,因为它不仅决定数据包是否应该被保存,而且还得决定要保存的字节数。被NPF驱动采用的过滤系统来源于BSD Packet Filter(BPF),一个虚拟处理器可以执行伪汇编书写的用户级过滤程序。应用程序采用用户定义的过滤器并使用wpcap.dll将它们编译进BPF程序。然后,应用程序使用BIOCSETF IOCTL写入核心态的过滤器。这样,对于每一个到来的数据包该程序都将被执行,而满足条件的数据包将被接收。与传统解决方案不同,NPF不解释(interpret)过滤器,而是执行(execute)它。由于性能的原因,在使用过滤器前,NPF提供一个JIT编译器将它转化成本地的80x86函数。当一个数据包被捕获,NPF调用这个本地函数而不是调用过滤器解释器,这使得处理过程相当快。
一个循环缓冲区,用来保存数据包并且避免丢失。一个保存在 缓冲区中的数据包有一个头,它包含了一些主要的信息,例如 时间戳和 数据包的大小,但它不是协议头。此外,以队列插入的方式来保存数据包可以提高数据的存储效率。可以以组的方式将数据包从NPF缓冲区拷贝到应用程序。这样就提高了性能,因为它降低了读的次数。如果一个数据包到来的时候缓冲区已经满了,那么该数据包将被丢弃,因此就发生了 丢包。
编辑本段【Winpcap程序实例】
获得 网卡接口。在普通的 SOCKET编程中,对 双网卡编程是不行的。当主机为双网卡时,本程序可分别获得两张网卡各自的描述结构及地址,然后可以对它们分别进行操作。返回的alldevs队列首部为逻辑网卡,一般不对它进行什么操作。(一)获得 网卡 接口
#i nclude "pcap.h"
void main()
{
pcap_if_t *alldevs;
/*struct pcap_if_t{
pcap_if_t *next;
char *name;
char *description;
pcap_addr *addresses;
U_int falgs;
}
*/
pcap_if_t *d;
int i=0;
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
/* Retrieve the device list */
if (pcap_findalldevs(&alldevs, errbuf) == -1)//返回网卡列表,alldevs指向表头
{
fprintf(stderr,"Error in pcap_findalldevs: %s/n", errbuf);
exit(1);
}
/* Print the list */
for(d=alldevs;d;d=d->next)
{
printf("%d. %s", ++i, d->name);
if (d->description)
printf(" (%s)/n", d->description);
else printf(" (No description available)/n");
}
if(i==0)
{
printf("/nNo interfaces found! Make sure WinPcap is installed./n");
return;
}
/* We don't need any more the device list. Free it */
pcap_freealldevs(alldevs);
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(二)抓包
本程序俘获 局域网内 UDP报文。
#i nclude "pcap.h"
/* 4 bytes IP address */
typedef struct ip_address{
u_char byte1;
u_char byte2;
u_char byte3;
u_char byte4;
}ip_address;
/* IPv4 header */
typedef struct ip_header{
u_char ver_ihl; // Version (4 bits) + Internet header length (4 bits)
u_char tos; // Type of service
u_short tlen; // Total length
u_short identification; // Identification
u_short flags_fo; // Flags (3 bits) + Fragment offset (13 bits)
u_char ttl; // Time to live
u_char proto; // Protocol
u_short crc; // Header checksum
ip_address saddr; // Source address
ip_address daddr; // Destination address
u_int op_pad; // Option + Padding
}ip_header;
/* UDP header*/
typedef struct udp_header{
u_short sport; // Source port
u_short dport; // Destination port
u_short len; // Datagram length
u_short crc; // Checksum
}udp_header;
/* prototype of the packet handler */
void packet_handler(u_char *param, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *pkt_data);
main()
{
pcap_if_t *alldevs;
pcap_if_t *d;
int inum;
int i=0;
pcap_t *adhandle;
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
u_int netmask;
char packet_filter[] = "ip and udp";
struct bpf_program fcode;
/* Retrieve the device list */
if (pcap_findalldevs(&alldevs, errbuf) == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr,"Error in pcap_findalldevs: %s/n", errbuf);
exit(1);
}
/* Print the list */
for(d=alldevs; d; d=d->next)
{
printf("%d. %s", ++i, d->name);
if (d->description)
printf(" (%s)/n", d->description);
else
printf(" (No description available)/n");
}
if(i==0)
{
printf("/nNo interfaces found! Make sure WinPcap is installed./n");
return -1;
}
printf("Enter the interface number (1-%d):",i);
scanf("%d", &inum);
if(inum < 1 || inum > i)
{
printf("/nInterface number out of range./n");
/* Free the device list */
pcap_freealldevs(alldevs);
return -1;
}
/* Jump to the selected adapter */
for(d=alldevs, i=0; i< inum-1 ;d=d->next, i++);
/* Open the adapter */
if ( (adhandle= pcap_open_live(d->name, // name of the device
65536, // portion of the packet to capture.
// 65536 grants that the whole packet will be captured on all the MACs.
1, // promiscuous mode
1000, // read timeout
errbuf // error buffer
) ) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr,"/nUnable to open the adapter. %s is not supported by WinPcap/n");
/* Free the device list */
pcap_freealldevs(alldevs);
return -1;
}
/* Check the link layer. We support only Ethernet for simplicity. */
if(pcap_datalink(adhandle) != DLT_EN10MB)
{
fprintf(stderr,"/nThis program works only on Ethernet networks./n");
/* Free the device list */
pcap_freealldevs(alldevs);
return -1;
}
if(d->addresses != NULL)
/* Retrieve the mask of the first address of the interface */
netmask=((struct sockaddr_in *)(d->addresses->netmask))->sin_addr.S_un.S_addr;
else
/* If the interface is without addresses we suppose to be in a C class network */
netmask=0xffffff;
//compile the filter
if(pcap_compile(adhandle, &fcode, packet_filter, 1, netmask) <0 ){
fprintf(stderr,"/nUnable to compile the packet filter. Check the syntax./n");
/* Free the device list */
pcap_freealldevs(alldevs);
return -1;
}
//set the filter
if(pcap_setfilter(adhandle, &fcode)<0){
fprintf(stderr,"/nError setting the filter./n");
/* Free the device list */
pcap_freealldevs(alldevs);
return -1;
}
printf("/nlistening on %s.../n", d->description);
/* At this point, we don't need any more the device list. Free it */
pcap_freealldevs(alldevs);
/* start the capture */
pcap_loop(adhandle, 0, packet_handler, NULL);
return 0;
}
/* Callback function invoked by libpcap for every incoming packet */
void packet_handler(u_char *param, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *pkt_data)
{
struct tm *ltime;
char timestr[16];
ip_header *ih;
udp_header *uh;
u_int ip_len;
/* convert the timestamp to readable format */
ltime=localtime(&header->ts.tv_sec);
strftime( timestr, sizeof timestr, "%H:%M:%S", ltime);
/* print timestamp and length of the packet */
/* retireve the position of the ip header */
ih = (ip_header *) (pkt_data +
14); //length of ethernet header
/* retireve the position of the udp header */
ip_len = (ih->ver_ihl & 0xf) * 4;
uh = (udp_header *) ((u_char*)ih + ip_len);
/* convert from network byte order to host byte order */
printf("%s.%.6d len:%d ", timestr, header->ts.tv_usec, header->len);
/* print ip addresses */
printf("%d.%d.%d.%d -> %d.%d.%d.%d/n",
ih->saddr.byte1,
ih->saddr.byte2,
ih->saddr.byte3,
ih->saddr.byte4,
ih->daddr.byte1,
ih->daddr.byte2,
ih->daddr.byte3,
ih->daddr.byte4
);
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(三)发包
要在命令行下运行,给与参数:网卡描述符。或者添加代码findalldevs(),那样应很方便。
#i nclude
#i nclude
#i nclude
void usage();
void main(int argc, char **argv) {
pcap_t *fp;
char error[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
u_char packet[100];
int i;
/* Check the validity of the command line */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("usage: %s inerface", argv[0]);
return;
}
/* Open the output adapter */
if((fp = pcap_open_live(argv[1], 100, 1, 1000, error) ) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr,"/nError opening adapter: %s/n", error);
return;
}
/* Supposing to be on ethernet, set mac destination to 1:1:1:1:1:1 */
packet[0]=1;
packet[1]=1;
packet[2]=1;
packet[3]=1;
packet[4]=1;
packet[5]=1;
/* set mac source to 2:2:2:2:2:2 */
packet[6]=2;
packet[7]=2;
packet[8]=2;
packet[9]=2;
packet[10]=2;
packet[11]=2;
/* Fill the rest of the packet */
for(i=12;i<100;i++){
packet =i%256;