算法4第6章 网络流算法/FordFulkerson算法/增广路径算法讲解
网络流算法
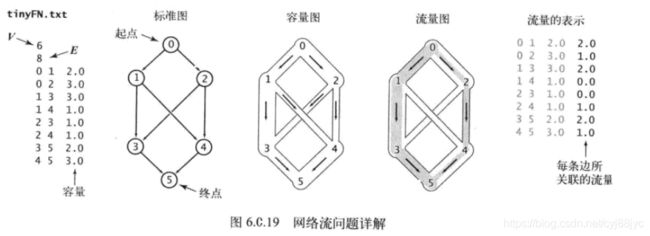
问题描述:对应下图流量图的输油网络,只有一个入口和一个出口,每条管道都有相应的容量,中间每个节点的流入量和流出量要相同,怎样设计流量网络可以使出口的流量最大。
流量图可以很自然的转换成有向图,每条边有容量限制和当前的流量,示意图如下:
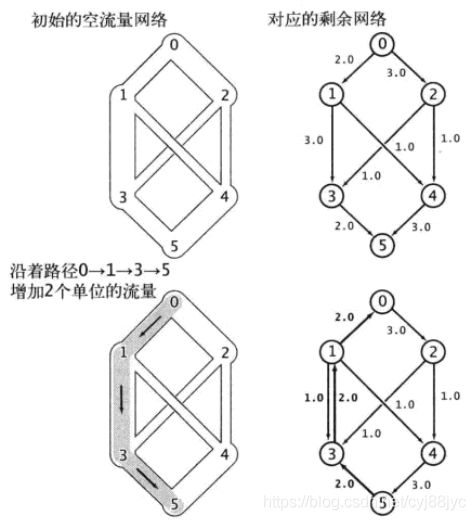
FordFulkerson算法也叫做增广路径算法可以解决最大流问题,该算法的思路是寻找一条从起点s到终点t的路径,该路径每条边的剩余流量不能为0,找出每条边剩余流量的最小值bottle,把每条边的流程增加bottle,反复此过程直到找不出这样的路径为止。这样的路径也叫做增广路径。
增广路径中边的方向也可以与流量的方向相反,这条边中的流量不能为空,正向边是流量增加bottle,方向边是流量减少bottle,如下图的0-2-3-1-4-5路径,。
增广路径中从起点指出的边和指向终点的边必然是正向的。
算法实现如下:,示意图如下:
采用广度优先搜索寻找增广路径,所以也叫做最短增广路径
public class FordFulkerson {
private static final double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-11;
private final int V; // number of vertices
private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = true iff s->v path in residual graph
private FlowEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on shortest residual s->v path
private double value; // current value of max flow
/**
* Compute a maximum flow and minimum cut in the network {@code G}
* from vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code t}.
*
* @param G the flow network
* @param s the source vertex
* @param t the sink vertex
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= s < V}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= t < V}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code s == t}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if initial flow is infeasible
*/
public FordFulkerson(FlowNetwork G, int s, int t) {
V = G.V();
validate(s);
validate(t);
if (s == t) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Source equals sink");
if (!isFeasible(G, s, t)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Initial flow is infeasible");
// while there exists an augmenting path, use it
value = excess(G, t);
while (hasAugmentingPath(G, s, t)) {
// compute bottleneck capacity
double bottle = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (int v = t; v != s; v = edgeTo[v].other(v)) {
bottle = Math.min(bottle, edgeTo[v].residualCapacityTo(v));
}
// augment flow
for (int v = t; v != s; v = edgeTo[v].other(v)) {
edgeTo[v].addResidualFlowTo(v, bottle);
}
value += bottle;
}
// check optimality conditions
assert check(G, s, t);
}
/**
* Returns the value of the maximum flow.
*
* @return the value of the maximum flow
*/
public double value() {
return value;
}
/**
* Returns true if the specified vertex is on the {@code s} side of the mincut.
*
* @param v vertex
* @return {@code true} if vertex {@code v} is on the {@code s} side of the micut;
* {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public boolean inCut(int v) {
validate(v);
return marked[v];
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException if v is outside prescibed range
private void validate(int v) {
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
}
// is there an augmenting path?
// if so, upon termination edgeTo[] will contain a parent-link representation of such a path
// this implementation finds a shortest augmenting path (fewest number of edges),
// which performs well both in theory and in practice
//广度优先搜索寻找增广路径
private boolean hasAugmentingPath(FlowNetwork G, int s, int t) {
edgeTo = new FlowEdge[G.V()];
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
// breadth-first search
Queue
queue.enqueue(s);
marked[s] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty() && !marked[t]) {
int v = queue.dequeue();
for (FlowEdge e : G.adj(v)) {
int w = e.other(v);
// if residual capacity from v to w
if (e.residualCapacityTo(w) > 0) {
if (!marked[w]) {
edgeTo[w] = e;
marked[w] = true;
queue.enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
// is there an augmenting path?
return marked[t];
}
// return excess flow at vertex v
private double excess(FlowNetwork G, int v) {
double excess = 0.0;
for (FlowEdge e : G.adj(v)) {
if (v == e.from()) excess -= e.flow();
else excess += e.flow();
}
return excess;
}
// return excess flow at vertex v
private boolean isFeasible(FlowNetwork G, int s, int t) {
// check that capacity constraints are satisfied
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
for (FlowEdge e : G.adj(v)) {
if (e.flow() < -FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON || e.flow() > e.capacity() + FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) {
System.err.println("Edge does not satisfy capacity constraints: " + e);
return false;
}
}
}
// check that net flow into a vertex equals zero, except at source and sink
if (Math.abs(value + excess(G, s)) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) {
System.err.println("Excess at source = " + excess(G, s));
System.err.println("Max flow = " + value);
return false;
}
if (Math.abs(value - excess(G, t)) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) {
System.err.println("Excess at sink = " + excess(G, t));
System.err.println("Max flow = " + value);
return false;
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (v == s || v == t) continue;
else if (Math.abs(excess(G, v)) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) {
System.err.println("Net flow out of " + v + " doesn't equal zero");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// check optimality conditions
private boolean check(FlowNetwork G, int s, int t) {
// check that flow is feasible
if (!isFeasible(G, s, t)) {
System.err.println("Flow is infeasible");
return false;
}
// check that s is on the source side of min cut and that t is not on source side
if (!inCut(s)) {
System.err.println("source " + s + " is not on source side of min cut");
return false;
}
if (inCut(t)) {
System.err.println("sink " + t + " is on source side of min cut");
return false;
}
// check that value of min cut = value of max flow
double mincutValue = 0.0;
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
for (FlowEdge e : G.adj(v)) {
if ((v == e.from()) && inCut(e.from()) && !inCut(e.to()))
mincutValue += e.capacity();
}
}
if (Math.abs(mincutValue - value) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) {
System.err.println("Max flow value = " + value + ", min cut value = " + mincutValue);
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code FordFulkerson} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create flow network with V vertices and E edges
int V = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int E = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int s = 0, t = V-1;
FlowNetwork G = new FlowNetwork(V, E);
StdOut.println(G);
// compute maximum flow and minimum cut
FordFulkerson maxflow = new FordFulkerson(G, s, t);
StdOut.println("Max flow from " + s + " to " + t);
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
for (FlowEdge e : G.adj(v)) {
if ((v == e.from()) && e.flow() > 0)
StdOut.println(" " + e);
}
}
// print min-cut
StdOut.print("Min cut: ");
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (maxflow.inCut(v)) StdOut.print(v + " ");
}
StdOut.println();
StdOut.println("Max flow value = " + maxflow.value());
}
}
public class FlowNetwork {
private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator");
private final int V;
private int E;
private Bag
/**
* Initializes an empty flow network with {@code V} vertices and 0 edges.
* @param V the number of vertices
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code V < 0}
*/
public FlowNetwork(int V) {
if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices in a Graph must be nonnegative");
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
adj = (Bag
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
adj[v] = new Bag
}
/**
* Initializes a random flow network with {@code V} vertices and E edges.
* The capacities are integers between 0 and 99 and the flow values are zero.
* @param V the number of vertices
* @param E the number of edges
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code V < 0}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code E < 0}
*/
public FlowNetwork(int V, int E) {
this(V);
if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int v = StdRandom.uniform(V);
int w = StdRandom.uniform(V);
double capacity = StdRandom.uniform(100);
addEdge(new FlowEdge(v, w, capacity));
}
}
/**
* Initializes a flow network from an input stream.
* The format is the number of vertices V,
* followed by the number of edges E,
* followed by E pairs of vertices and edge capacities,
* with each entry separated by whitespace.
* @param in the input stream
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the endpoints of any edge are not in prescribed range
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the number of vertices or edges is negative
*/
public FlowNetwork(In in) {
this(in.readInt());
int E = in.readInt();
if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of edges must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int v = in.readInt();
int w = in.readInt();
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
double capacity = in.readDouble();
addEdge(new FlowEdge(v, w, capacity));
}
}
/**
* Returns the number of vertices in the edge-weighted graph.
* @return the number of vertices in the edge-weighted graph
*/
public int V() {
return V;
}
/**
* Returns the number of edges in the edge-weighted graph.
* @return the number of edges in the edge-weighted graph
*/
public int E() {
return E;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v) {
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
}
/**
* Adds the edge {@code e} to the network.
* @param e the edge
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless endpoints of edge are between
* {@code 0} and {@code V-1}
*/
public void addEdge(FlowEdge e) {
int v = e.from();
int w = e.to();
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
adj[v].add(e);
adj[w].add(e);
E++;
}
/**
* Returns the edges incident on vertex {@code v} (includes both edges pointing to
* and from {@code v}).
* @param v the vertex
* @return the edges incident on vertex {@code v} as an Iterable
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
public Iterable
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
// return list of all edges - excludes self loops
public Iterable
Bag
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
for (FlowEdge e : adj(v)) {
if (e.to() != v)
list.add(e);
}
return list;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of the flow network.
* This method takes time proportional to E + V.
* @return the number of vertices V, followed by the number of edges E,
* followed by the V adjacency lists
*/
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append(V + " " + E + NEWLINE);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
s.append(v + ": ");
for (FlowEdge e : adj[v]) {
if (e.to() != v) s.append(e + " ");
}
s.append(NEWLINE);
}
return s.toString();
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code FlowNetwork} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
FlowNetwork G = new FlowNetwork(in);
StdOut.println(G);
}
}
public class FlowEdge {
// to deal with floating-point roundoff errors
private static final double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-10;
private final int v; // from
private final int w; // to
private final double capacity; // capacity
private double flow; // flow
/**
* Initializes an edge from vertex {@code v} to vertex {@code w} with
* the given {@code capacity} and zero flow.
* @param v the tail vertex
* @param w the head vertex
* @param capacity the capacity of the edge
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if either {@code v} or {@code w}
* is a negative integer
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity < 0.0}
*/
public FlowEdge(int v, int w, double capacity) {
if (v < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex index must be a non-negative integer");
if (w < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex index must be a non-negative integer");
if (!(capacity >= 0.0)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Edge capacity must be non-negative");
this.v = v;
this.w = w;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.flow = 0.0;
}
/**
* Initializes an edge from vertex {@code v} to vertex {@code w} with
* the given {@code capacity} and {@code flow}.
* @param v the tail vertex
* @param w the head vertex
* @param capacity the capacity of the edge
* @param flow the flow on the edge
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if either {@code v} or {@code w}
* is a negative integer
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity} is negative
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code flow} is between
* {@code 0.0} and {@code capacity}.
*/
public FlowEdge(int v, int w, double capacity, double flow) {
if (v < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex index must be a non-negative integer");
if (w < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex index must be a non-negative integer");
if (!(capacity >= 0.0)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("edge capacity must be non-negative");
if (!(flow <= capacity)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("flow exceeds capacity");
if (!(flow >= 0.0)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("flow must be non-negative");
this.v = v;
this.w = w;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.flow = flow;
}
/**
* Initializes a flow edge from another flow edge.
* @param e the edge to copy
*/
public FlowEdge(FlowEdge e) {
this.v = e.v;
this.w = e.w;
this.capacity = e.capacity;
this.flow = e.flow;
}
/**
* Returns the tail vertex of the edge.
* @return the tail vertex of the edge
*/
public int from() {
return v;
}
/**
* Returns the head vertex of the edge.
* @return the head vertex of the edge
*/
public int to() {
return w;
}
/**
* Returns the capacity of the edge.
* @return the capacity of the edge
*/
public double capacity() {
return capacity;
}
/**
* Returns the flow on the edge.
* @return the flow on the edge
*/
public double flow() {
return flow;
}
/**
* Returns the endpoint of the edge that is different from the given vertex
* (unless the edge represents a self-loop in which case it returns the same vertex).
* @param vertex one endpoint of the edge
* @return the endpoint of the edge that is different from the given vertex
* (unless the edge represents a self-loop in which case it returns the same vertex)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code vertex} is not one of the endpoints
* of the edge
*/
public int other(int vertex) {
if (vertex == v) return w;
else if (vertex == w) return v;
else throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid endpoint");
}
/**
* Returns the residual capacity of the edge in the direction
* to the given {@code vertex}.
* @param vertex one endpoint of the edge
* @return the residual capacity of the edge in the direction to the given vertex
* If {@code vertex} is the tail vertex, the residual capacity equals
* {@code capacity() - flow()}; if {@code vertex} is the head vertex, the
* residual capacity equals {@code flow()}.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code vertex} is not one of the endpoints of the edge
*/
public double residualCapacityTo(int vertex) {
if (vertex == v) return flow; // backward edge
else if (vertex == w) return capacity - flow; // forward edge
else throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid endpoint");
}
/**
* Increases the flow on the edge in the direction to the given vertex.
* If {@code vertex} is the tail vertex, this increases the flow on the edge by {@code delta};
* if {@code vertex} is the head vertex, this decreases the flow on the edge by {@code delta}.
* @param vertex one endpoint of the edge
* @param delta amount by which to increase flow
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code vertex} is not one of the endpoints
* of the edge
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code delta} makes the flow on
* on the edge either negative or larger than its capacity
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code delta} is {@code NaN}
*/
public void addResidualFlowTo(int vertex, double delta) {
if (!(delta >= 0.0)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Delta must be nonnegative");
if (vertex == v) flow -= delta; // backward edge
else if (vertex == w) flow += delta; // forward edge
else throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid endpoint");
// round flow to 0 or capacity if within floating-point precision
if (Math.abs(flow) <= FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON)
flow = 0;
if (Math.abs(flow - capacity) <= FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON)
flow = capacity;
if (!(flow >= 0.0)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Flow is negative");
if (!(flow <= capacity)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Flow exceeds capacity");
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of the edge.
* @return a string representation of the edge
*/
public String toString() {
return v + "->" + w + " " + flow + "/" + capacity;
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code FlowEdge} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
FlowEdge e = new FlowEdge(12, 23, 4.56);
StdOut.println(e);
}
}