python基础学习(九)——堡垒机案例
笔者是一个痴迷于挖掘数据中的价值的学习人,希望在平日的工作学习中,挖掘数据的价值,找寻数据的秘密,笔者认为,数据的价值不仅仅只体现在企业中,个人也可以体会到数据的魅力,用技术力量探索行为密码,让大数据助跑每一个人,欢迎直筒们关注我的公众号,大家一起讨论数据中的那些有趣的事情。
我的公众号为:livandata
![]()
开发堡垒机之前,先来学习Python的paramiko模块,该模块机遇SSH用于连接远程服务器并执行相关操作。
Ssh:
Ssh: #!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ UTF-8 _*_
import paramiko
transport= paramiko.Transport(('192.168.120.128', 22))
transport.connect(username='livan', password='123456789')
sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(transport)
#将localhost.py上传至服务器 /tmp/test_from_win:此为文件名
sftp.put('livan_test', '/tmp/test_from_win')
#将remove_path 下载到本地 local_path
#sftp.get('remove_path', 'local_path')
transport.close()Sftp:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ UTF-8 _*_
import paramiko
transport= paramiko.Transport(('192.168.120.128', 22))
transport.connect(username='livan', password='123456789')
sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(transport)
#将localhost.py上传至服务器/tmp/test_from_win:此为文件名
sftp.put('livan_test', '/tmp/test_from_win')
#将remove_path 下载到本地 local_path
#sftp.get('remove_path', 'local_path')
transport.close()
SSHClient
用于连接远程服务器并执行基本命令
基于用户名密码连接:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
import paramiko
# 创建SSH对象 ssh = paramiko.SSHClient() # 允许连接不在know_hosts文件中的主机 ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy()) # 连接服务器 ssh.connect(hostname='c1.salt.com', port=22, username='wupeiqi', password='123')
# 执行命令 stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df') # 获取命令结果 result = stdout.read()
# 关闭连接 ssh.close() |
import paramiko
transport =paramiko.Transport(('hostname', 22))
transport.connect(username='wupeiqi', password='123')
ssh =paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh._transport =transport
stdin, stdout,stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')
print stdout.read()
transport.close()
Ssh密钥:
RSA-非对称密钥验证。
公钥:public key;
私钥:private key;
10.0.0.31(私钥)——(连接)——》10.0.0.41(公钥)
公钥是给别人的,私钥自己保留。
顾先生成一对密钥:
Ssh-keygen:生产公钥、私钥,密钥对。
第一个为私钥信息:id_rsa
第二个为公钥信息:id_rsa.pub
然后到root/.ssh/id_rsa下进入id_rsa,会看到私钥的加密算法;
Id_rsa.pub:看到公钥的加密算法。
在Linux中以固定的用户名登录,/home/livan/scripts/.ssh/authorized_keys,进入此文件,将刚才的公钥信息存入其中,则下次登录不需要再输入密码。
如果从livan登录其他的信息:可以通过命令传递公钥:
Ssh-copy-id
Ssh-copy-id -i
Ssh-copy-id -i [email protected]
Ssh-copy-id “-p52113 [email protected]”
然后再登录root即可:
Ssh [email protected] -p52113
Ssh的密钥传输:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ UTF-8 _*_
import paramiko
private_key = paramiko.RSAKey._from_private_key_file('/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa')
#创建ssh对象
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
#允许连接不在know_hosts文件中的主机:
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
#连接服务器
ssh.connect(hostname='hostname', port=22, username='livan', pkey=private_key)
#执行命令
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')
#获取命名结果:
res, err = stdout.read(), stderr.read()
result = res if res else err
print(result.decode())
#关闭
ssh.close()
基于公钥密钥连接:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
import paramiko
private_key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file ('/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa')
# 创建SSH对象 ssh = paramiko.SSHClient() # 允许连接不在know_hosts文件中的主机 ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy()) # 连接服务器 ssh.connect(hostname='c1.salt.com', port=22, username='wupeiqi', key=private_key)
# 执行命令 stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df') # 获取命令结果 result = stdout.read()
# 关闭连接 ssh.close() |
import paramiko
private_key =paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file('/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa')
transport =paramiko.Transport(('hostname', 22))
transport.connect(username='wupeiqi', pkey=private_key)
ssh =paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh._transport =transport
stdin, stdout,stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')
transport.close()
import paramiko
from io import StringIO
key_str = """-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATEKEY-----
MIIEpQIBAAKCAQEAq7gLsqYArAFco02/55IgNg0r7NXOtEM3qXpb/dabJ5Uyky/8
NEHhFiQ7deHIRIuTW5Zb0kD6h6EBbVlUMBmwJrC2oSzySLU1w+ZNfH0PE6W6fans
H80whhuc/YgP+fjiO+VR/gFcqib8Rll5UfYzf5H8uuOnDeIXGCVgyHQSmt8if1+e
7hn1MVO1Lrm9Fco8ABI7dyv8/ZEwoSfh2C9rGYgA58LT1FkBRkOePbHD43xNfAYC
tfLvz6LErMnwdOW4sNMEWWAWv1fsTB35PAm5CazfKzmam9n5IQXhmUNcNvmaZtvP
c4f4g59mdsaWNtNaY96UjOfx83Om86gmdkKcnwIDAQABAoIBAQCnDBGFJuv8aA7A
ZkBLe+GN815JtOyye7lIS1n2I7En3oImoUWNaJEYwwJ8+LmjxMwDCtAkR0XwbvY+
c+nsKPEtkjb3sAu6I148RmwWsGncSRqUaJrljOypaW9dS+GO4Ujjz3/lw1lrxSUh
IqVc0E7kyRW8kP3QCaNBwArYteHreZFFp6XmtKMtXaEA3saJYILxaaXlYkoRi4k8
S2/K8aw3ZMR4tDCOfB4o47JaeiA/e185RK3A+mLn9xTDhTdZqTQpv17/YRPcgmwz
zu30fhVXQT/SuI0sO+bzCO4YGoEwoBX718AWhdLJFoFq1B7k2ZEzXTAtjEXQEWm6
01ndU/jhAasdfasdasdfasdfa3eraszxqwefasdfadasdffsFIfAsjQb4HdkmHuC
OeJrJOd+CYvdEeqJJNnF6AbHyYHIECkj0Qq1kEfLOEsqzd5nDbtkKBte6M1trbjl
HtJ2Yb8w6o/q/6Sbj7wf/cW3LIYEdeVCjScozVcQ9R83ea05J+QOAr4nAoGBAMaq
UzLJfLNWZ5Qosmir2oHStFlZpxspax/ln7DlWLW4wPB4YJalSVovF2Buo8hr8X65
lnPiE41M+G0Z7icEXiFyDBFDCtzx0x/RmaBokLathrFtI81UCx4gQPLaSVNMlvQA
539GsubSrO4LpHRNGg/weZ6EqQOXvHvkUkm2bDDJAoGATytFNxen6GtC0ZT3SRQM
WYfasdf3xbtuykmnluiofasd2sfmjnljkt7khghmghdasSDFGQfgaFoKfaawoYeH
C2XasVUsVviBn8kPSLSVBPX4JUfQmA6h8HsajeVahxN1U9e0nYJ0sYDQFUMTS2t8
RT57+WK/0ONwTWHdu+KnaJECgYEAid/ta8LQC3p82iNAZkpWlGDSD2yb/8rH8NQg
9tjEryFwrbMtfX9qn+8srx06B796U3OjifstjJQNmVI0qNlsJpQK8fPwVxRxbJS/
pMbNICrf3sUa4sZgDOFfkeuSlgACh4cVIozDXlR59Z8Y3CoiW0uObEgvMDIfenAj
98pl3ZkCgYEAj/UCSni0dwX4pnKNPm6LUgiS7QvIgM3H9piyt8aipQuzBi5LUKWw
DlQC4Zb73nHgdREtQYYXTu7p27Bl0Gizz1sW2eSgxFU8eTh+ucfVwOXKAXKU5SeI
+MbuBfUYQ4if2N/BXn47+/ecf3A4KgB37Le5SbLDddwCNxGlBzbpBa0=
-----END RSAPRIVATE KEY-----"""
private_key =paramiko.RSAKey(file_obj=StringIO(key_str))
transport =paramiko.Transport(('10.0.1.40', 22))
transport.connect(username='wupeiqi', pkey=private_key)
ssh =paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh._transport =transport
stdin, stdout,stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')
result = stdout.read()
transport.close()
print(result)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ UTF-8 _*_
import paramiko
private_key = paramiko.RSAKey._from_private_key_file('/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa')
#创建ssh对象
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
#允许连接不在know_hosts文件中的主机:
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
#连接服务器
ssh.connect(hostname='hostname', port=22, username='livan', pkey=private_key)
#执行命令
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')
#获取命名结果:
res, err = stdout.read(), stderr.read()
result = res if res else err
print(result.decode())
#关闭
ssh.close()
SFTPClient
用于连接远程服务器并执行上传下载
基于用户名密码上传下载
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
import paramiko
transport = paramiko.Transport(('hostname',22)) transport.connect(username='wupeiqi',password='123')
sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(transport) # 将location.py 上传至服务器 /tmp/test.py sftp.put('/tmp/location.py', '/tmp/test.py') # 将remove_path 下载到本地 local_path sftp.get('remove_path', 'local_path')
transport.close() |
基于公钥密钥上传下载
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
import paramiko
private_key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file ('/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa')
transport = paramiko.Transport(('hostname', 22)) transport.connect(username='wupeiqi', pkey=private_key )
sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(transport) # 将location.py 上传至服务器 /tmp/test.py sftp.put('/tmp/location.py', '/tmp/test.py') # 将remove_path 下载到本地 local_path sftp.get('remove_path', 'local_path')
transport.close() |
#!/usr/bin/envpython
# -*- coding:utf-8-*-
import paramiko
import uuid
class Haproxy(object):
def__init__(self):
self.host = '172.16.103.191'
self.port = 22
self.username = 'wupeiqi'
self.pwd = '123'
self.__k =None
def create_file(self):
file_name = str(uuid.uuid4())
with open(file_name,'w') as f:
f.write('sb')
returnfile_name
def run(self):
self.connect()
self.upload()
self.rename()
self.close()
def connect(self):
transport =paramiko.Transport((self.host,self.port))
transport.connect(username=self.username,password=self.pwd)
self.__transport =transport
def close(self):
self.__transport.close()
def upload(self):
# 连接,上传
file_name = self.create_file()
sftp =paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(self.__transport)
# 将location.py上传至服务器 /tmp/test.py
sftp.put(file_name, '/home/wupeiqi/tttttttttttt.py')
def rename(self):
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh._transport = self.__transport
# 执行命令
stdin, stdout, stderr =ssh.exec_command('mv/home/wupeiqi/tttttttttttt.py /home/wupeiqi/ooooooooo.py')
# 获取命令结果
result = stdout.read()
ha = Haproxy()
ha.run()
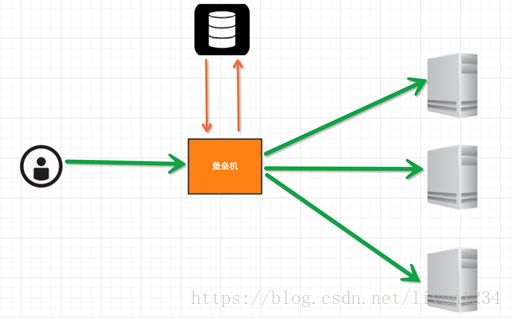
堡垒机的实现
实现思路:
堡垒机执行流程:
1. 管理员为用户在服务器上创建账号(将公钥放置服务器,或者使用用户名密码)
2. 用户登陆堡垒机,输入堡垒机用户名密码,现实当前用户管理的服务器列表
3. 用户选择服务器,并自动登陆
4. 执行操作并同时将用户操作记录
注:配置.brashrc实现ssh登陆后自动执行脚本,如:/usr/bin/python /home/wupeiqi/menu.py
实现过程
步骤一,实现用户登陆
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
import getpass
user = raw_input('username:') pwd = getpass.getpass('password') if user == 'alex' and pwd == '123': print '登陆成功' else: print '登陆失败' |
步骤二,根据用户获取相关服务器列表
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
dic = { 'alex': [ '172.16.103.189', 'c10.puppet.com', 'c11.puppet.com', ], 'eric': [ 'c100.puppet.com', ] }
host_list = dic['alex']
print 'please select:' for index, item in enumerate(host_list, 1): print index, item
inp = raw_input('your select (No):') inp = int(inp) hostname = host_list[inp-1] port = 22 |
步骤三,根据用户名、私钥登陆服务器
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
tran = paramiko.Transport((hostname, port,)) tran.start_client() default_path = os.path.join(os.environ['HOME'], '.ssh', 'id_rsa') key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(default_path) tran.auth_publickey('wupeiqi', key)
# 打开一个通道 chan = tran.open_session() # 获取一个终端 chan.get_pty() # 激活器 chan.invoke_shell()
######### # 利用sys.stdin,肆意妄为执行操作 # 用户在终端输入内容,并将内容发送至远程服务器 # 远程服务器执行命令,并将结果返回 # 用户终端显示内容 #########
chan.close() tran.close() |
while True:
# 监视用户输入和服务器返回数据
# sys.stdin 处理用户输入
# chan 是之前创建的通道,用于接收服务器返回信息
readable, writeable, error = select.select([chan,sys.stdin, ],[],[],1)
if chan inreadable:
try:
x = chan.recv(1024)
iflen(x) == 0:
print'\r\n*** EOF\r\n',
break
sys.stdout.write(x)
sys.stdout.flush()
exceptsocket.timeout:
pass
if sys.stdin inreadable:
inp = sys.stdin.readline()
chan.sendall(inp)
# 获取原tty属性
oldtty =termios.tcgetattr(sys.stdin)
try:
# 为tty设置新属性
# 默认当前tty设备属性:
# 输入一行回车,执行
# CTRL+C 进程退出,遇到特殊字符,特殊处理。
# 这是为原始模式,不认识所有特殊符号
# 放置特殊字符应用在当前终端,如此设置,将所有的用户输入均发送到远程服务器
tty.setraw(sys.stdin.fileno())
chan.settimeout(0.0)
while True:
# 监视 用户输入 和 远程服务器返回数据(socket)
# 阻塞,直到句柄可读
r, w, e = select.select([chan,sys.stdin], [], [], 1)
if chan in r:
try:
x = chan.recv(1024)
iflen(x) == 0:
print'\r\n*** EOF\r\n',
break
sys.stdout.write(x)
sys.stdout.flush()
exceptsocket.timeout:
pass
ifsys.stdin in r:
x = sys.stdin.read(1)
iflen(x) == 0:
break
chan.send(x)
finally:
# 重新设置终端属性
termios.tcsetattr(sys.stdin,termios.TCSADRAIN, oldtty)
def windows_shell(chan):
import threading
sys.stdout.write("Line-buffered terminal emulation. Press F6 or ^Z tosend EOF.\r\n\r\n")
def writeall(sock):
while True:
data = sock.recv(256)
ifnot data:
sys.stdout.write('\r\n*** EOF ***\r\n\r\n')
sys.stdout.flush()
break
sys.stdout.write(data)
sys.stdout.flush()
writer = threading.Thread(target=writeall,args=(chan,))
writer.start()
try:
while True:
d = sys.stdin.read(1)
ifnot d:
break
chan.send(d)
except EOFError:
# user hit ^Z or F6
pass
注:密码验证 t.auth_password(username, pw)
详见:paramiko源码demo
数据库操作
Python 操作 Mysql 模块的安装
| 1 2 3 4 5 |
linux: yum install MySQL-python
window: http://files.cnblogs.com/files/wupeiqi/py-mysql-win.zip |
SQL基本使用
1、数据库操作
| 1 2 3 |
show databases; use [databasename]; create database [name]; |
2、数据表操作
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
show tables;
create table students ( id int not null auto_increment primary key, name char(8) not null, sex char(4) not null, age tinyint unsigned not null, tel char(13) null default "-" ); |
CREATE TABLE`wb_blog` (
`id` smallint(8) unsigned NOT NULL,
`catid` smallint(5) unsigned NOT NULLDEFAULT '0',
`title` varchar(80) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`content` text NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `catename` (`catid`)
) ;
3、数据操作
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
insert into students(name,sex,age,tel) values('alex','man',18,'151515151')
delete from students where id =2;
update students set name = 'sb' where id =1;
select * from students |
4、其他
| 1 2 3 |
主键 外键 左右连接 |
Python MySQL API
一、插入数据
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
import MySQLdb
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root', passwd='1234',db='mydb')
cur = conn.cursor()
reCount = cur.execute('insert into UserInfo(Name,Address) values(%s,%s)',('alex','usa')) # reCount = cur.execute('insert into UserInfo(Name,Address) values(%(id)s, %(name)s)',{'id':12345,'name':'wupeiqi'})
conn.commit()
cur.close() conn.close()
print reCount |
import MySQLdb
conn =MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='1234',db='mydb')
cur =conn.cursor()
li =[
('alex','usa'),
('sb','usa'),
]
reCount =cur.executemany('insert intoUserInfo(Name,Address) values(%s,%s)',li)
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()
print reCount
注意:cur.lastrowid
二、删除数据
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
import MySQLdb
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root', passwd='1234',db='mydb')
cur = conn.cursor()
reCount = cur.execute('delete from UserInfo')
conn.commit()
cur.close() conn.close()
print reCount |
三、修改数据
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
import MySQLdb
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root', passwd='1234',db='mydb')
cur = conn.cursor()
reCount = cur.execute('update UserInfo set Name = %s',('alin',))
conn.commit() cur.close() conn.close()
print reCount |
四、查数据
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
# ############################## fetchone/fetchmany(num) ##############################
import MySQLdb
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root', passwd='1234',db='mydb') cur = conn.cursor()
reCount = cur.execute('select * from UserInfo')
print cur.fetchone() print cur.fetchone() cur.scroll(-1,mode='relative') print cur.fetchone() print cur.fetchone() cur.scroll(0,mode='absolute') print cur.fetchone() print cur.fetchone()
cur.close() conn.close()
print reCount
# ############################## fetchall ##############################
import MySQLdb
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root', passwd='1234',db='mydb') #cur = conn.cursor(cursorclass = MySQLdb.cursors.DictCursor) cur = conn.cursor()
reCount = cur.execute('select Name,Address from UserInfo')
nRet = cur.fetchall()
cur.close() conn.close()
print reCount print nRet for i in nRet: print i[0],i[1] |