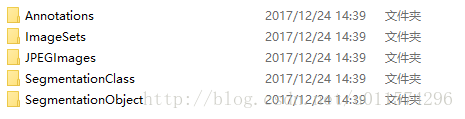yolov3目标识别在工业检测中的应用
本篇博客记录了一个深度学习在工业领域的应用项目。功能是检测视野范围内的零件总数,如果数量少于设定的标准数量,则报警,如果放置了不同型号的零件,同样需要报警。常规方法是用传统的图像处理的模板匹配,但使用halcon和opencv的模板匹配效果都不好,于是尝试用深度学习目标检测。
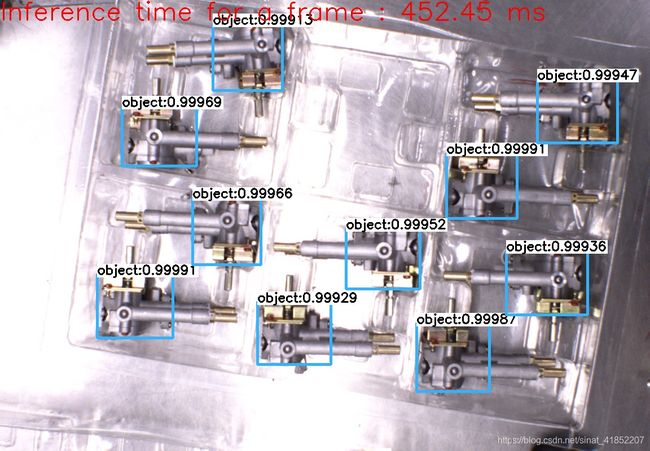
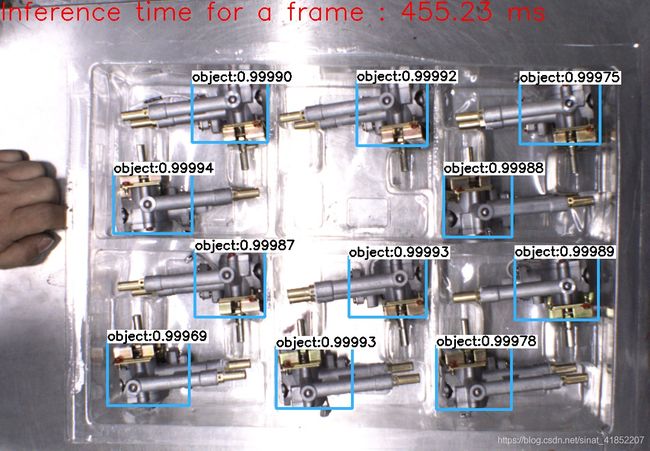
效果如下图所示:识别率超过99%(可以获取到目标的个数,类别,概率,矩形框位置,可以适应一定的光照、角度、大小变化)
目录:
1.安装darknet yolov3环境
2.采集并制作数据集,用yolov3训练
3.在opencv3.4版本使用训练好的模型、
4.在vs里编写软件
正文:
1.yolov3环境搭建参考另一篇博客https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_41852207/article/details/90906309
我的编译环境是yolov3 win10 cuda8.0 vs2017
2.采集并制作数据集,用yolov3训练
2.1 如何制作数据集和一些工程经验
参考:数据集构造流程https://blog.csdn.net/u011574296/article/details/78953681
第一步:了解voc数据集,建好空文件夹
1)JPEGImages文件夹
文件夹里包含了训练图片和测试图片,混放在一起
2)Annatations文件夹
文件夹存放的是xml格式的标签文件,每个xml文件都对应于JPEGImages文件夹的一张图片,同名
3)ImageSets文件夹
Action存放的是人的动作,我们暂时不用;Layout存放的人体部位的数据。我们暂时不用
Main存放的是图像物体识别的数据,分为20类,当然我们自己制作就不一定了, Main里面有test.txt , train.txt, val.txt ,trainval.txt.这四个文件我们后面会生成
Segmentation存放的是可用于分割的数据
4)其他的文件夹不解释了,分割XXX等用的
现在就仿照这个文件夹格式,自己建好空文件夹就行。
第二步:搞定JPEGSImages文件夹
1)把你的图片放到JPEGSImages里面,在VOC2007里面,人家的图片文件名都是000001.jpg类似这样的,我们也统一格式,把我们的图片名字重命名成这样的,如果你的文件太多怎么办,请看另一篇文章http://blog.csdn.net/gaohuazhao/article/details/60324715 能批量重命名文件
第三步:搞定Annatations文件夹
网上很多教程,但是我觉得都很麻烦,可以下载精灵标注助手,手动标注,会自动生成图片信息的xml文件
1)一张张的慢慢画框。。。。。。。。。大约过了几个小时,好继续下一步
2)保存的路径就是我们的Annatations文件夹,别保存别的地方去了,,,
第四步:搞定ImageSets文件夹中的Main文件夹中的四个文件(这四个txt文档是干嘛的,看名字就知道,就是分分多少图片作为训练,多少图片作为测试)
trianval是train和val的总和
直接上一个代码给你:
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/gaohuazhao/article/details/60871886
用这个python脚本生成四个txt文件(随机分配训练集、验证集、测试集),于ImageSets/Main中。
经验总结:由于工业中采集的图片非常单一,零件总是位于同一背景下,数据的单一使得训练的模型容易过于简化,很容易误识别。举个例子就是如果训练猫的时候,总是将猫放到绿色的草地上,模型可能认为草地上只要有一坨东西,就是猫。这样训练的结果可能是,放一只狗到草地上,模型可能也会认为是猫。所以训练的时候,训练集一定不能太单一,训练图片中除了零件,还要改变零件所在的背景,比如添加一些干扰物体,这样训练的模型误识别率才会降低。
2.2 使用yolov3训练自己的数据集,并测试
这部分见这篇博客:https://mp.csdn.net/postedit
我用了300张左右的图片训练,总共迭代2万次,batchsize为8。在迭代1万次左右后已经收敛的差不多了,2万次迭代后,loss值收敛到0.2左右。
如果难以收敛,考虑(1)有没有过多脏数据(标注错误的数据)(2)尝试降低学习率。
如果训练收敛了,但实际测试的时候,有误识别,考虑在训练的时候增加干扰物,在物体周边增加多种不相关物体。
如果训练收敛了,但实际测试的时候有漏识别,考虑(1)增加训练图片数量,训练集应该包含一些光照、角度、位置的变化,增强泛化性能。(2)训练的时候,loss曲线是否收敛的不够接近0。我的loss最终为0.2左右,如果太大,说明不够收敛,需要在训练到瓶颈的时候减小学习率。
3 在opencv中调用训练好的模型,进行目标识别
把里面的路径改成自己的就可以
//在debug模式下没有优化,要在release下运行 速度快
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace dnn;
vector classes;
vector getOutputsNames(Net&net);
void drawPred(int classId, float conf, int left, int top, int right, int bottom, Mat& frame);
void postprocess(Mat& frame, const vector& outs, float confThreshold, float nmsThreshold);
int main()
{
string names_file = "D:/software_engineer/darknet/darknet/cfg/voc.name";
String model_def = "D:/software_engineer/darknet/darknet/cfg/yolov3.cfg";
String weights = "D:/software_engineer/darknet/darknet/backup/yolov3_last.weights";
int in_w, in_h;
double thresh = 0.5;//阈值
double nms_thresh = 0.25;
in_w = in_h = 416;
//read names
ifstream ifs(names_file.c_str());
string line;
while (getline(ifs, line))
classes.push_back(line);
//init model
Net net1 = readNetFromDarknet(model_def, weights);
net1.setPreferableBackend(DNN_BACKEND_DEFAULT);
net1.setPreferableTarget(DNN_TARGET_CPU);
Net net2 = readNetFromDarknet(model_def, weights);
net2.setPreferableBackend(DNN_BACKEND_DEFAULT);
net2.setPreferableTarget(DNN_TARGET_CPU);
//read image and forward
Mat inputImg, blob;
inputImg = imread("D:/测试3/1.jpg");//待检图片
if (inputImg.empty())
{
cout << "can't find image" << endl;
waitKey(0);
}
//capture >> inputImg;
blobFromImage(inputImg, blob, 1 / 255.0, Size(in_w, in_h), Scalar(), true, false);
vector mat_blob;
imagesFromBlob(blob, mat_blob);
//Sets the input to the network
net1.setInput(blob);
// Runs the forward pass to get output of the output layers
vector outs;
net1.forward(outs, getOutputsNames(net1));
postprocess(inputImg, outs, thresh, nms_thresh);
vector layersTimes;
double freq = getTickFrequency() / 1000;
double t = net1.getPerfProfile(layersTimes) / freq;
string label = format("Inference time for a frame : %.2f ms", t);
putText(inputImg, label, Point(0, 15), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255));
namedWindow("res", WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("res", inputImg);
waitKey(0);
}
vector getOutputsNames(Net&net)
{
static vector names;
if (names.empty())
{
//Get the indices of the output layers, i.e. the layers with unconnected outputs
vector outLayers = net.getUnconnectedOutLayers();
//get the names of all the layers in the network
vector layersNames = net.getLayerNames();
// Get the names of the output layers in names
names.resize(outLayers.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < outLayers.size(); ++i)
names[i] = layersNames[outLayers[i] - 1];
}
return names;
}
void drawPred(int classId, float conf, int left, int top, int right, int bottom, Mat& frame)
{
//Draw a rectangle displaying the bounding box
rectangle(frame, Point(left, top), Point(right, bottom), Scalar(255, 178, 50), 3);
//Get the label for the class name and its confidence
string label = format("%.5f", conf);
if (!classes.empty())
{
CV_Assert(classId < (int)classes.size());
label = classes[classId] + ":" + label;
}
//Display the label at the top of the bounding box
int baseLine;
Size labelSize = getTextSize(label, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
top = max(top, labelSize.height);
rectangle(frame, Point(left, top - round(1.5*labelSize.height)), Point(left + round(1.5*labelSize.width), top + baseLine), Scalar(255, 255, 255), FILLED);
putText(frame, label, Point(left, top), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, Scalar(0, 0, 0), 1);
}
void postprocess(Mat& frame, const vector& outs, float confThreshold, float nmsThreshold)
{
vector classIds;
vector confidences;
vector boxes;
for (size_t i = 0; i < outs.size(); ++i)
{
// Scan through all the bounding boxes output from the network and keep only the
// ones with high confidence scores. Assign the box's class label as the class
// with the highest score for the box.
float* data = (float*)outs[i].data;
for (int j = 0; j < outs[i].rows; ++j, data += outs[i].cols)
{
Mat scores = outs[i].row(j).colRange(5, outs[i].cols);
Point classIdPoint;
double confidence;
// Get the value and location of the maximum score
minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &confidence, 0, &classIdPoint);
if (confidence > confThreshold)
{
int centerX = (int)(data[0] * frame.cols);
int centerY = (int)(data[1] * frame.rows);
int width = (int)(data[2] * frame.cols);
int height = (int)(data[3] * frame.rows);
int left = centerX - width / 2;
int top = centerY - height / 2;
classIds.push_back(classIdPoint.x);
confidences.push_back((float)confidence);
boxes.push_back(Rect(left, top, width, height));
}
}
}
// Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with
// lower confidences
vector indices;
NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold, indices);
size_t i;
for (i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = indices[i];
Rect box = boxes[idx];
drawPred(classIds[idx], confidences[idx], box.x, box.y,box.x + box.width, box.y + box.height, frame);
}
cout << "目标数量数量:" << i << endl;
}
最终测试,1500张图片,漏识别零件1个,没有误识别,就是没有零件的地方和不同型号的零件一定不会被识别出来。这样就达到了检测目的。