深入剖析Android音频之AudioPolicyService
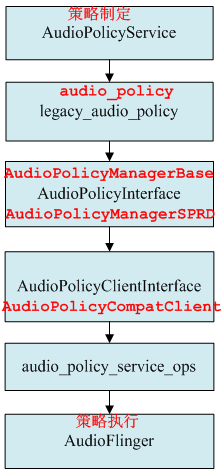
AudioPolicyService是策略的制定者,比如什么时候打开音频接口设备、某种Stream类型的音频对应什么设备等等。而AudioFlinger则是策略的执行者,例如具体如何与音频设备通信,如何维护现有系统中的音频设备,以及多个音频流的混音如何处理等等都得由它来完成。AudioPolicyService根据用户配置来指导AudioFlinger加载设备接口,起到路由功能。
![]()
AudioPolicyService启动过程
AudioPolicyService服务运行在mediaserver进程中,随着mediaserver进程启动而启动。
frameworks\av\media\mediaserver\ Main_mediaserver.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
sp proc(ProcessState::self());
sp sm = defaultServiceManager();
ALOGI("ServiceManager: %p", sm.get());
VolumeManager::instantiate(); // volumemanager have to be started before audioflinger
AudioFlinger::instantiate();
MediaPlayerService::instantiate();
CameraService::instantiate();
AudioPolicyService::instantiate();
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}
AudioPolicyService继承了模板类BinderService,该类用于注册native service。
frameworks\native\include\binder\ BinderService.h
template
class BinderService
{
public:
static status_t publish(bool allowIsolated = false) {
sp sm(defaultServiceManager());
return sm->addService(String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()), new SERVICE(), allowIsolated);
}
static void instantiate() { publish(); }
};
BinderService是一个模板类,该类的publish函数就是完成向ServiceManager注册服务。
static const char *getServiceName() { return "media.audio_policy"; }AudioPolicyService注册名为media.audio_policy的服务。
AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyService()
: BnAudioPolicyService() , mpAudioPolicyDev(NULL) , mpAudioPolicy(NULL)
{
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
const struct hw_module_t *module;
int forced_val;
int rc;
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
// start tone playback thread
mTonePlaybackThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmTone"), this);
// start audio commands thread
mAudioCommandThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmAudio"), this);
// start output activity command thread
mOutputCommandThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmOutput"), this);
/* instantiate the audio policy manager */
/* 加载audio_policy.default.so库得到audio_policy_module模块 */
rc = hw_get_module(AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module);
if (rc)
return;
/* 通过audio_policy_module模块打开audio_policy_device设备 */
rc = audio_policy_dev_open(module, &mpAudioPolicyDev);
ALOGE_IF(rc, "couldn't open audio policy device (%s)", strerror(-rc));
if (rc)
return;
//通过audio_policy_device设备创建audio_policy
rc = mpAudioPolicyDev->create_audio_policy(mpAudioPolicyDev, &aps_ops, this,
&mpAudioPolicy);
ALOGE_IF(rc, "couldn't create audio policy (%s)", strerror(-rc));
if (rc)
return;
rc = mpAudioPolicy->init_check(mpAudioPolicy);
ALOGE_IF(rc, "couldn't init_check the audio policy (%s)", strerror(-rc));
if (rc)
return;
/* SPRD: maybe set this property better, but here just change the default value @{ */
property_get("ro.camera.sound.forced", value, "1");
forced_val = strtol(value, NULL, 0);
ALOGV("setForceUse() !forced_val=%d ",!forced_val);
mpAudioPolicy->set_can_mute_enforced_audible(mpAudioPolicy, !forced_val);
ALOGI("Loaded audio policy from %s (%s)", module->name, module->id);
// 读取audio_effects.conf文件
if (access(AUDIO_EFFECT_VENDOR_CONFIG_FILE, R_OK) == 0) {
loadPreProcessorConfig(AUDIO_EFFECT_VENDOR_CONFIG_FILE);
} else if (access(AUDIO_EFFECT_DEFAULT_CONFIG_FILE, R_OK) == 0) {
loadPreProcessorConfig(AUDIO_EFFECT_DEFAULT_CONFIG_FILE);
}
}
- 创建AudioCommandThread (ApmTone、ApmAudio、ApmOutput)
- 加载legacy_ap_module
- 打开legacy_ap_device
- 创建legacy_audio_policy
- 读取audio_effects.conf
![]()
创建AudioCommandThread线程
在AudioPolicyService对象构造过程中,分别创建了ApmTone、ApmAudio、ApmOutput三个AudioCommandThread线程:
1、 ApmTone用于播放tone音;
2、 ApmAudio用于执行audio命令;
3、ApmOutput用于执行输出命令;
在第一次强引用AudioCommandThread线程对象时,AudioCommandThread的onFirstRef函数被回调,在此启动线程
void AudioPolicyService::AudioCommandThread::onFirstRef()
{
run(mName.string(), ANDROID_PRIORITY_AUDIO);
}
这里采用异步方式来执行audio command,当需要执行上表中的命令时,首先将命令投递到AudioCommandThread的mAudioCommands命令向量表中,然后通过mWaitWorkCV.signal()唤醒AudioCommandThread线程,被唤醒的AudioCommandThread线程执行完command后,又通过mWaitWorkCV.waitRelative(mLock, waitTime)睡眠等待命令到来。
加载audio_policy_module模块
audio_policy硬件抽象层动态库位于/system/lib/hw/目录下,命名为:audio_policy.$(TARGET_BOARD_PLATFORM).so。audiopolicy的硬件抽象层定义在hardware\libhardware_legacy\audio\audio_policy_hal.cpp中,AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID硬件抽象模块定义如下:
hardware\libhardware_legacy\audio\ audio_policy_hal.cpp【audio_policy.scx15.so】
struct legacy_ap_module HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
module: {
common: {
tag: HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
version_major: 1,
version_minor: 0,
id: AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
name: "LEGACY Audio Policy HAL",
author: "The Android Open Source Project",
methods: &legacy_ap_module_methods,
dso : NULL,
reserved : {0},
},
},
};
legacy_ap_module继承于audio_policy_module。
![]()
关于hw_get_module函数加载硬件抽象层模块的过程请参考Android硬件抽象Hardware库加载过程源码分析。
打开audio_policy_device设备
hardware\libhardware\include\hardware\ audio_policy.h
static inline int audio_policy_dev_open(const hw_module_t* module,
struct audio_policy_device** device)
{
return module->methods->open(module, AUDIO_POLICY_INTERFACE,
(hw_device_t**)device);
}
通过legacy_ap_module模块的open方法来打开一个legacy_ap_device设备。
hardware\libhardware_legacy\audio\ audio_policy_hal.cpp
static int legacy_ap_dev_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
hw_device_t** device)
{
struct legacy_ap_device *dev;
if (strcmp(name, AUDIO_POLICY_INTERFACE) != 0)
return -EINVAL;
dev = (struct legacy_ap_device *)calloc(1, sizeof(*dev));
if (!dev)
return -ENOMEM;
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->device.common.version = 0;
dev->device.common.module = const_cast(module);
dev->device.common.close = legacy_ap_dev_close;
dev->device.create_audio_policy = create_legacy_ap;
dev->device.destroy_audio_policy = destroy_legacy_ap;
*device = &dev->device.common;
return 0;
}
打开得到一个legacy_ap_device设备,通过该抽象设备可以创建一个audio_policy对象。
![]()
创建audio_policy对象
在打开legacy_ap_device设备时,该设备的create_audio_policy成员初始化为create_legacy_ap函数指针,我们通过legacy_ap_device设备可以创建一个legacy_audio_policy对象。
rc = mpAudioPolicyDev->create_audio_policy(mpAudioPolicyDev, &aps_ops, this,
&mpAudioPolicy);
这里通过audio_policy_device设备创建audio策略对象
![]()
hardware\libhardware_legacy\audio\ audio_policy_hal.cpp
static int create_legacy_ap(const struct audio_policy_device *device,
struct audio_policy_service_ops *aps_ops,
void *service,
struct audio_policy **ap)
{
struct legacy_audio_policy *lap;
int ret;
if (!service || !aps_ops)
return -EINVAL;
lap = (struct legacy_audio_policy *)calloc(1, sizeof(*lap));
if (!lap)
return -ENOMEM;
lap->policy.set_device_connection_state = ap_set_device_connection_state;
…
lap->policy.dump = ap_dump;
lap->policy.is_offload_supported = ap_is_offload_supported;
lap->service = service;
lap->aps_ops = aps_ops;
lap->service_client = new AudioPolicyCompatClient(aps_ops, service);
if (!lap->service_client) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_new_compat_client;
}
lap->apm = createAudioPolicyManager(lap->service_client);
if (!lap->apm) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_create_apm;
}
*ap = &lap->policy;
return 0;
err_create_apm:
delete lap->service_client;
err_new_compat_client:
free(lap);
*ap = NULL;
return ret;
}
audio_policy实现在audio_policy_hal.cpp中,audio_policy_service_ops实现在AudioPolicyService.cpp中。create_audio_policy()函数就是创建并初始化一个legacy_audio_policy对象。
![]()
![]()
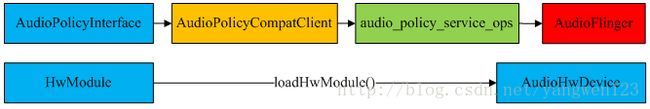
audio_policy与AudioPolicyService、AudioPolicyCompatClient之间的关系如下:
![]()
AudioPolicyClient创建
hardware\libhardware_legacy\audio\ AudioPolicyCompatClient.h
AudioPolicyCompatClient(struct audio_policy_service_ops *serviceOps,void *service) :
mServiceOps(serviceOps) , mService(service) {}
AudioPolicyCompatClient是对audio_policy_service_ops的封装类,对外提供audio_policy_service_ops数据结构中定义的接口。
AudioPolicyManager创建
extern "C" AudioPolicyInterface* createAudioPolicyManager(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface)
{
ALOGI("SPRD policy manager created.");
return new AudioPolicyManagerSPRD(clientInterface);
}
使用AudioPolicyClientInterface对象来构造AudioPolicyManagerSPRD对象,AudioPolicyManagerSPRD继承于AudioPolicyManagerBase,而AudioPolicyManagerBase又继承于AudioPolicyInterface。
![]()
hardware\libhardware_legacy\audio\ AudioPolicyManagerBase.cpp
AudioPolicyManagerBase::AudioPolicyManagerBase(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface)
:
#ifdef AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
Thread(false),
#endif //AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
//变量初始化
mPrimaryOutput((audio_io_handle_t)0),
mAvailableOutputDevices(AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE),
mPhoneState(AudioSystem::MODE_NORMAL),
mLimitRingtoneVolume(false), mLastVoiceVolume(-1.0f),
mTotalEffectsCpuLoad(0), mTotalEffectsMemory(0),
mA2dpSuspended(false), mHasA2dp(false), mHasUsb(false), mHasRemoteSubmix(false),
mSpeakerDrcEnabled(false), mFmOffGoing(false)
{
//引用AudioPolicyCompatClient对象,这样音频管理器AudioPolicyManager就可以使用audio_policy_service_ops中的接口
mpClientInterface = clientInterface;
for (int i = 0; i < AudioSystem::NUM_FORCE_USE; i++) {
mForceUse[i] = AudioSystem::FORCE_NONE;
}
mA2dpDeviceAddress = String8("");
mScoDeviceAddress = String8("");
mUsbCardAndDevice = String8("");
/**
* 优先加载/vendor/etc/audio_policy.conf配置文件,如果该配置文件不存在,则
* 加载/system/etc/audio_policy.conf配置文件,如果该文件还是不存在,则通过
* 函数defaultAudioPolicyConfig()来设置默认音频接口
*/
if (loadAudioPolicyConfig(AUDIO_POLICY_VENDOR_CONFIG_FILE) != NO_ERROR) {
if (loadAudioPolicyConfig(AUDIO_POLICY_CONFIG_FILE) != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGE("could not load audio policy configuration file, setting defaults");
defaultAudioPolicyConfig();
}
}
//设置各种音频流对应的音量调节点,must be done after reading the policy
initializeVolumeCurves();
// open all output streams needed to access attached devices
for (size_t i = 0; i < mHwModules.size(); i++) {
//通过名称打开对应的音频接口硬件抽象库
mHwModules[i]->mHandle = mpClientInterface->loadHwModule(mHwModules[i]->mName);
if (mHwModules[i]->mHandle == 0) {
ALOGW("could not open HW module %s", mHwModules[i]->mName);
continue;
}
// open all output streams needed to access attached devices
// except for direct output streams that are only opened when they are actually
// required by an app.
for (size_t j = 0; j < mHwModules[i]->mOutputProfiles.size(); j++)
{
const IOProfile *outProfile = mHwModules[i]->mOutputProfiles[j];
//打开mAttachedOutputDevices对应的输出
if ((outProfile->mSupportedDevices & mAttachedOutputDevices) &&
((outProfile->mFlags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT) == 0)) {
//将输出IOProfile封装为AudioOutputDescriptor对象
AudioOutputDescriptor *outputDesc = new AudioOutputDescriptor(outProfile);
//设置当前音频接口的默认输出设备
outputDesc->mDevice = (audio_devices_t)(mDefaultOutputDevice & outProfile->mSupportedDevices);
//打开输出,在AudioFlinger中创建PlaybackThread线程,并返回该线程的id
audio_io_handle_t output = mpClientInterface->openOutput(
outProfile->mModule->mHandle,
&outputDesc->mDevice,
&outputDesc->mSamplingRate,
&outputDesc->mFormat,
&outputDesc->mChannelMask,
&outputDesc->mLatency,
outputDesc->mFlags);
if (output == 0) {
delete outputDesc;
} else {
//设置可以使用的输出设备为mAttachedOutputDevices
mAvailableOutputDevices =(audio_devices_t)(mAvailableOutputDevices | (outProfile->mSupportedDevices & mAttachedOutputDevices));
if (mPrimaryOutput == 0 && outProfile->mFlags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY) {
mPrimaryOutput = output;
}
//将输出描述符对象AudioOutputDescriptor及创建的PlaybackThread线程id以键值对形式保存
addOutput(output, outputDesc);
//设置默认输出设备
setOutputDevice(output,(audio_devices_t)(mDefaultOutputDevice & outProfile->mSupportedDevices),true);
}
}
}
}
ALOGE_IF((mAttachedOutputDevices & ~mAvailableOutputDevices),
"Not output found for attached devices %08x",
(mAttachedOutputDevices & ~mAvailableOutputDevices));
ALOGE_IF((mPrimaryOutput == 0), "Failed to open primary output");
updateDevicesAndOutputs();
// add for bug158794 start
char bootvalue[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
// prop sys.boot_completed will set 1 when system ready (ActivityManagerService.java)...
property_get("sys.boot_completed", bootvalue, "");
if (strncmp("1", bootvalue, 1) != 0) {
startReadingThread();
}
// add for bug158794 end
#ifdef AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
...
#endif //AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
}
AudioPolicyManagerBase对象构造过程中主要完成以下几个步骤:
1、 loadAudioPolicyConfig(AUDIO_POLICY_CONFIG_FILE)加载audio_policy.conf配置文件;
2、 initializeVolumeCurves()初始化各种音频流对应的音量调节点;
3、 加载audio policy硬件抽象库:mpClientInterface->loadHwModule(mHwModules[i]->mName)
4、 打开attached_output_devices输出:
mpClientInterface->openOutput();
5、 保存输出设备描述符对象:addOutput(output, outputDesc);
![]()
读取audio_policy.conf文件
Android为每种音频接口定义了对应的硬件抽象层,且编译为单独的so库。
![]()
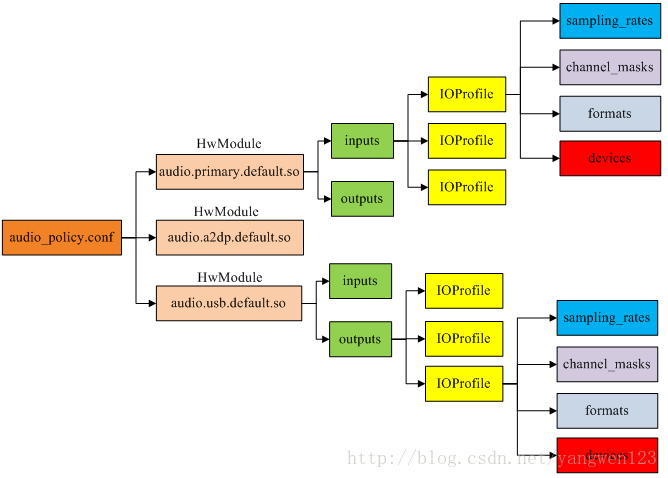
每种音频接口定义了不同的输入输出,一个接口可以具有多个输入或者输出,每个输入输出有可以支持不同的音频设备。通过读取audio_policy.conf文件可以获取系统支持的音频接口参数。
audio_policy.conf文件定义了两种音频配置信息:
1、 当前系统支持的音频输入输出设备及默认输入输出设备;
![]()
这些信息时通过global_configuration配置项来设置,在global_configuration中定义了三种音频设备信息:
attached_output_devices:已连接的输出设备;
default_output_device:默认输出设备;
attached_input_devices:已连接的输入设备;
1、 系统支持的音频接口信息;
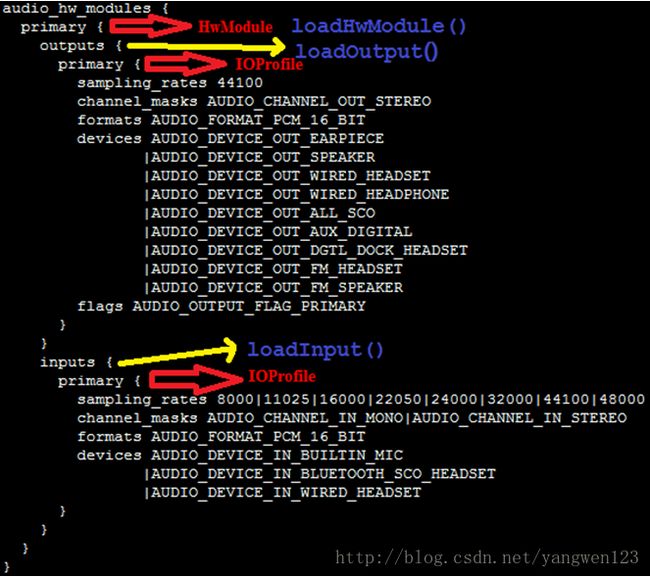
audio_policy.conf定义了系统支持的所有音频接口参数信息,比如primary、a2dp、usb等,对于primary定义如下:
![]()
a2dp定义:
![]()
usb定义:
![]()
每种音频接口包含输入输出,每种输入输出又包含多种输入输出配置,每种输入输出配置又支持多种音频设备。AudioPolicyManagerBase首先加载/vendor/etc/audio_policy.conf,如果该文件不存在,则加/system/etc/audio_policy.conf。
status_t AudioPolicyManagerBase::loadAudioPolicyConfig(const char *path)
{
cnode *root;
char *data;
data = (char *)load_file(path, NULL);
if (data == NULL) {
return -ENODEV;
}
root = config_node("", "");
//读取配置文件
config_load(root, data);
//解析global_configuration
loadGlobalConfig(root);
//解析audio_hw_modules
loadHwModules(root);
config_free(root);
free(root);
free(data);
ALOGI("loadAudioPolicyConfig() loaded %s\n", path);
return NO_ERROR;
}
通过loadGlobalConfig(root)函数来读取这些全局配置信息。
void AudioPolicyManagerBase::loadGlobalConfig(cnode *root)
{
cnode *node = config_find(root, GLOBAL_CONFIG_TAG);
if (node == NULL) {
return;
}
node = node->first_child;
while (node) {
//attached_output_devices AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_EARPIECE
if (strcmp(ATTACHED_OUTPUT_DEVICES_TAG, node->name) == 0) {
mAttachedOutputDevices = parseDeviceNames((char *)node->value);
ALOGW_IF(mAttachedOutputDevices == AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE,
"loadGlobalConfig() no attached output devices");
ALOGV("loadGlobalConfig()mAttachedOutputDevices%04x", mAttachedOutputDevices);
//default_output_device AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
} else if (strcmp(DEFAULT_OUTPUT_DEVICE_TAG, node->name) == 0) {
mDefaultOutputDevice= (audio_devices_t)stringToEnum(sDeviceNameToEnumTable,ARRAY_SIZE(sDeviceNameToEnumTable),(char *)node->value);
ALOGW_IF(mDefaultOutputDevice == AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE,
"loadGlobalConfig() default device not specified");
ALOGV("loadGlobalConfig() mDefaultOutputDevice %04x", mDefaultOutputDevice);
//attached_input_devices AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC
} else if (strcmp(ATTACHED_INPUT_DEVICES_TAG, node->name) == 0) {
mAvailableInputDevices = parseDeviceNames((char *)node->value) & ~AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN;
ALOGV("loadGlobalConfig() mAvailableInputDevices %04x", mAvailableInputDevices);
//speaker_drc_enabled
} else if (strcmp(SPEAKER_DRC_ENABLED_TAG, node->name) == 0) {
mSpeakerDrcEnabled = stringToBool((char *)node->value);
ALOGV("loadGlobalConfig() mSpeakerDrcEnabled = %d", mSpeakerDrcEnabled);
}
node = node->next;
}
}
audio_policy.conf同时定义了多个audio 接口,每一个audio 接口包含若干output和input,而每个output和input又同时支持多种输入输出模式,每种输入输出模式又支持若干种设备。
通过loadHwModules ()函数来加载系统配置的所有audio 接口:
void AudioPolicyManagerBase::loadHwModules(cnode *root)
{
//audio_hw_modules
cnode *node = config_find(root, AUDIO_HW_MODULE_TAG);
if (node == NULL) {
return;
}
node = node->first_child;
while (node) {
ALOGV("loadHwModules() loading module %s", node->name);
//加载音频接口
loadHwModule(node);
node = node->next;
}
}
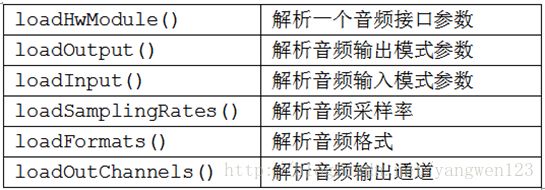
由于audio_policy.conf可以定义多个音频接口,因此该函数循环调用loadHwModule()来解析每个音频接口参数信息。Android定义HwModule类来描述每一个audio 接口参数,定义IOProfile类来描述输入输出模式配置。
到此就将audio_policy.conf文件中音频接口配置信息解析到了AudioPolicyManagerBase的成员变量mHwModules、mAttachedOutputDevices、mDefaultOutputDevice、mAvailableInputDevices中。
初始化音量调节点
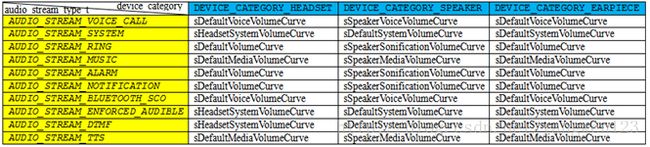
音量调节点设置在Android4.1与Android4.4中的实现完全不同,在Android4.1中是通过VolumeManager服务来管理,通过devicevolume.xml文件来配置,但Android4.4取消了VolumeManager服务,将音量控制放到AudioPolicyManagerBase中。在AudioPolicyManagerBase中定义了音量调节对应的音频流描述符数组:
StreamDescriptor mStreams[AudioSystem::NUM_STREAM_TYPES];initializeVolumeCurves()函数就是初始化该数组元素:
void AudioPolicyManagerBase::initializeVolumeCurves()
{
for (int i = 0; i < AUDIO_STREAM_CNT; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < DEVICE_CATEGORY_CNT; j++) {
mStreams[i].mVolumeCurve[j] =
sVolumeProfiles[i][j];
}
}
// Check availability of DRC on speaker path: if available, override some of the speaker curves
if (mSpeakerDrcEnabled) {
mStreams[AUDIO_STREAM_SYSTEM].mVolumeCurve[DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER] =
sDefaultSystemVolumeCurveDrc;
mStreams[AUDIO_STREAM_RING].mVolumeCurve[DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER] =
sSpeakerSonificationVolumeCurveDrc;
mStreams[AUDIO_STREAM_ALARM].mVolumeCurve[DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER] =
sSpeakerSonificationVolumeCurveDrc;
mStreams[AUDIO_STREAM_NOTIFICATION].mVolumeCurve[DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER] =sSpeakerSonificationVolumeCurveDrc;
}
}
sVolumeProfiles数组定义了不同音频设备下不同音频流对应的音量调节档位,定义如下:
数组元素为音量调节档位,每种模式下的音量调节都包含4个档位,定义如下:
加载audio_module模块
AudioPolicyManager通过读取audio_policy.conf配置文件,可以知道系统当前支持那些音频接口以及attached的输入输出设备、默认输出设备。接下来就需要加载这些音频接口的硬件抽象库。
这三中音频接口硬件抽象定义如下:
/vendor/sprd/open-source/libs/audio/audio_hw.c 【audio.primary.scx15.so】
struct audio_module HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.module_api_version = AUDIO_MODULE_API_VERSION_0_1,
.hal_api_version = HARDWARE_HAL_API_VERSION,
.id = AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "Spreadtrum Audio HW HAL",
.author = "The Android Open Source Project",
.methods = &hal_module_methods,
},
};
external/bluetooth/bluedroid/audio_a2dp_hw/audio_a2dp_hw.c【audio.a2dp.default.so】
struct audio_module HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = 1,
.version_minor = 0,
.id = AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "A2DP Audio HW HAL",
.author = "The Android Open Source Project",
.methods = &hal_module_methods,
},
};
hardware/libhardware/modules/usbaudio/audio_hw.c【audio. usb.default.so】
struct audio_module HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.module_api_version = AUDIO_MODULE_API_VERSION_0_1,
.hal_api_version = HARDWARE_HAL_API_VERSION,
.id = AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "USB audio HW HAL",
.author = "The Android Open Source Project",
.methods = &hal_module_methods,
},
};
AudioPolicyClientInterface提供了加载音频接口硬件抽象库的接口函数,通过前面的介绍,我们知道,AudioPolicyCompatClient通过代理audio_policy_service_ops实现AudioPolicyClientInterface接口。
hardware\libhardware_legacy\audio\ AudioPolicyCompatClient.cpp
audio_module_handle_t AudioPolicyCompatClient::loadHwModule(const char *moduleName)
{
return mServiceOps->load_hw_module(mService, moduleName);
}
AudioPolicyCompatClient将音频模块加载工作交给audio_policy_service_ops
frameworks\av\services\audioflinger\ AudioPolicyService.cpp
static audio_module_handle_t aps_load_hw_module(void *service,const char *name)
{
sp af = AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger();
if (af == 0) {
ALOGW("%s: could not get AudioFlinger", __func__);
return 0;
}
return af->loadHwModule(name);
}
AudioPolicyService又将其转交给AudioFlinger
frameworks\av\services\audioflinger\ AudioFlinger.cpp
audio_module_handle_t AudioFlinger::loadHwModule(const char *name)
{
if (!settingsAllowed()) {
return 0;
}
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
return loadHwModule_l(name);
}
audio_module_handle_t AudioFlinger::loadHwModule_l(const char *name)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAudioHwDevs.size(); i++) {
if (strncmp(mAudioHwDevs.valueAt(i)->moduleName(), name, strlen(name)) == 0) {
ALOGW("loadHwModule() module %s already loaded", name);
return mAudioHwDevs.keyAt(i);
}
}
audio_hw_device_t *dev;
//加载音频接口对应的so库,得到对应的音频接口设备audio_hw_device_t
int rc = load_audio_interface(name, &dev);
if (rc) {
ALOGI("loadHwModule() error %d loading module %s ", rc, name);
return 0;
}
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_INIT;
rc = dev->init_check(dev);
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_IDLE;
if (rc) {
ALOGI("loadHwModule() init check error %d for module %s ", rc, name);
return 0;
}
if ((mMasterVolumeSupportLvl != MVS_NONE) &&
(NULL != dev->set_master_volume)) {
AutoMutex lock(mHardwareLock);
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_SET_MASTER_VOLUME;
dev->set_master_volume(dev, mMasterVolume);
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_IDLE;
}
audio_module_handle_t handle = nextUniqueId();
mAudioHwDevs.add(handle, new AudioHwDevice(name, dev));
ALOGI("loadHwModule() Loaded %s audio interface from %s (%s) handle %d",
name, dev->common.module->name, dev->common.module->id, handle);
return handle;
}
函数首先加载系统定义的音频接口对应的so库,并打开该音频接口的抽象硬件设备audio_hw_device_t,为每个音频接口设备生成独一无二的ID号,同时将打开的音频接口设备封装为AudioHwDevice对象,将系统中所有的音频接口设备保存到AudioFlinger的成员变量mAudioHwDevs中。
函数load_audio_interface根据音频接口名称来打开抽象的音频接口设备audio_hw_device_t。
static int load_audio_interface(const char *if_name, audio_hw_device_t **dev)
{
const hw_module_t *mod;
int rc;
//根据名字加载audio_module模块
rc = hw_get_module_by_class(AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, if_name, &mod);
ALOGE_IF(rc, "%s couldn't load audio hw module %s.%s (%s)", __func__,
AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, if_name, strerror(-rc));
if (rc) {
goto out;
}
//打开audio_device设备
rc = audio_hw_device_open(mod, dev);
ALOGE_IF(rc, "%s couldn't open audio hw device in %s.%s (%s)", __func__,
AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, if_name, strerror(-rc));
if (rc) {
goto out;
}
if ((*dev)->common.version != AUDIO_DEVICE_API_VERSION_CURRENT) {
ALOGE("%s wrong audio hw device version %04x", __func__, (*dev)->common.version);
rc = BAD_VALUE;
goto out;
}
return 0;
out:
*dev = NULL;
return rc;
}
hardware\libhardware\include\hardware\ Audio.h
static inline int audio_hw_device_open(const struct hw_module_t* module,
struct audio_hw_device** device)
{
return module->methods->open(module, AUDIO_HARDWARE_INTERFACE,
(struct hw_device_t**)device);
}
hardware\libhardware_legacy\audio\ audio_hw_hal.cpp
static int legacy_adev_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
hw_device_t** device)
{
struct legacy_audio_device *ladev;
int ret;
if (strcmp(name, AUDIO_HARDWARE_INTERFACE) != 0)
return -EINVAL;
ladev = (struct legacy_audio_device *)calloc(1, sizeof(*ladev));
if (!ladev)
return -ENOMEM;
ladev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
ladev->device.common.version = AUDIO_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0;
ladev->device.common.module = const_cast(module);
ladev->device.common.close = legacy_adev_close;
ladev->device.get_supported_devices = adev_get_supported_devices;
…
ladev->device.dump = adev_dump;
ladev->hwif = createAudioHardware();
if (!ladev->hwif) {
ret = -EIO;
goto err_create_audio_hw;
}
*device = &ladev->device.common;
return 0;
err_create_audio_hw:
free(ladev);
return ret;
}
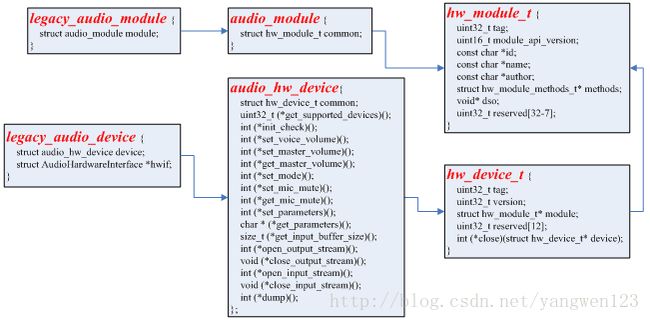
打开音频接口设备过程其实就是构造并初始化legacy_audio_device对象过程,legacy_audio_device数据结构关系如下:
legacy_adev_open函数就是创建并初始化一个legacy_audio_device对象:
到此就加载完系统定义的所有音频接口,并生成相应的数据对象,如下图所示:
打开音频输出
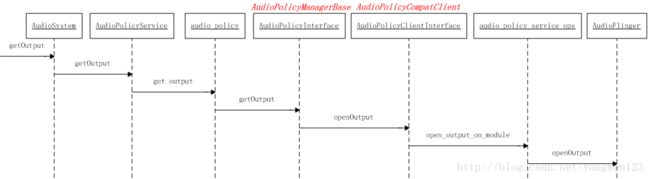
AudioPolicyService加载完所有音频接口后,就知道了系统支持的所有音频接口参数,可以为音频输出提供决策。
为了能正常播放音频数据,需要创建抽象的音频输出接口对象,打开音频输出过程如下:
audio_io_handle_t AudioPolicyCompatClient::openOutput(audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_devices_t *pDevices,
uint32_t *pSamplingRate,
audio_format_t *pFormat,
audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask,
uint32_t *pLatencyMs,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo)
{
return mServiceOps->open_output_on_module(mService,module, pDevices, pSamplingRate,
pFormat, pChannelMask, pLatencyMs,
flags, offloadInfo);
}
static audio_io_handle_t aps_open_output_on_module(void *service,
audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_devices_t *pDevices,
uint32_t *pSamplingRate,
audio_format_t *pFormat,
audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask,
uint32_t *pLatencyMs,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo)
{
sp af = AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger();
if (af == 0) {
ALOGW("%s: could not get AudioFlinger", __func__);
return 0;
}
return af->openOutput(module, pDevices, pSamplingRate, pFormat, pChannelMask,
pLatencyMs, flags, offloadInfo);
}
audio_io_handle_t AudioFlinger::openOutput(audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_devices_t *pDevices,
uint32_t *pSamplingRate,
audio_format_t *pFormat,
audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask,
uint32_t *pLatencyMs,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo)
{
PlaybackThread *thread = NULL;
struct audio_config config;
config.sample_rate = (pSamplingRate != NULL) ? *pSamplingRate : 0;
config.channel_mask = (pChannelMask != NULL) ? *pChannelMask : 0;
config.format = (pFormat != NULL) ? *pFormat : AUDIO_FORMAT_DEFAULT;
if (offloadInfo) {
config.offload_info = *offloadInfo;
}
//创建一个音频输出流对象audio_stream_out_t
audio_stream_out_t *outStream = NULL;
AudioHwDevice *outHwDev;
ALOGV("openOutput(), module %d Device %x, SamplingRate %d, Format %#08x, Channels %x, flags %x",
module,
(pDevices != NULL) ? *pDevices : 0,
config.sample_rate,
config.format,
config.channel_mask,
flags);
ALOGV("openOutput(), offloadInfo %p version 0x%04x",
offloadInfo, offloadInfo == NULL ? -1 : offloadInfo->version );
if (pDevices == NULL || *pDevices == 0) {
return 0;
}
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
//从音频接口列表mAudioHwDevs中查找出对应的音频接口,如果找不到,则重新加载音频接口动态库
outHwDev = findSuitableHwDev_l(module, *pDevices);
if (outHwDev == NULL)
return 0;
//取出module对应的audio_hw_device_t设备
audio_hw_device_t *hwDevHal = outHwDev->hwDevice();
//为音频输出流生成一个独一无二的id号
audio_io_handle_t id = nextUniqueId();
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_OUTPUT_OPEN;
//打开音频输出流
status_t status = hwDevHal->open_output_stream(hwDevHal,
id,
*pDevices,
(audio_output_flags_t)flags,
&config,
&outStream);
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_IDLE;
ALOGV("openOutput() openOutputStream returned output %p, SamplingRate %d, Format %#08x, "
"Channels %x, status %d",
outStream,
config.sample_rate,
config.format,
config.channel_mask,
status);
if (status == NO_ERROR && outStream != NULL) {
//使用AudioStreamOut来封装音频输出流audio_stream_out_t
AudioStreamOut *output = new AudioStreamOut(outHwDev, outStream, flags);
//根据flag标志位,创建不同类型的线程
if (flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD) {
thread = new OffloadThread(this, output, id, *pDevices);
ALOGV("openOutput() created offload output: ID %d thread %p", id, thread);
} else if ((flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT) ||
(config.format != AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT) ||
(config.channel_mask != AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO)) {
thread = new DirectOutputThread(this, output, id, *pDevices);
ALOGV("openOutput() created direct output: ID %d thread %p", id, thread);
} else {
thread = new MixerThread(this, output, id, *pDevices);
ALOGV("openOutput() created mixer output: ID %d thread %p", id, thread);
}
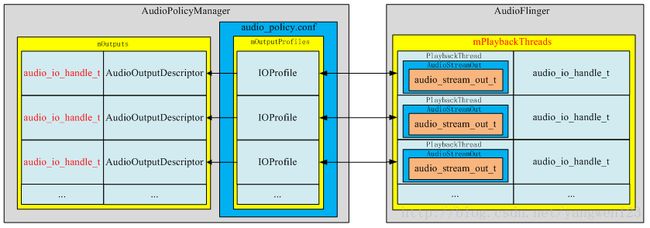
//将创建的线程及id以键值对的形式保存在mPlaybackThreads中
mPlaybackThreads.add(id, thread);
if (pSamplingRate != NULL) {
*pSamplingRate = config.sample_rate;
}
if (pFormat != NULL) {
*pFormat = config.format;
}
if (pChannelMask != NULL) {
*pChannelMask = config.channel_mask;
}
if (pLatencyMs != NULL) {
*pLatencyMs = thread->latency();
}
// notify client processes of the new output creation
thread->audioConfigChanged_l(AudioSystem::OUTPUT_OPENED);
// the first primary output opened designates the primary hw device
if ((mPrimaryHardwareDev == NULL) && (flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY)) {
ALOGI("Using module %d has the primary audio interface", module);
mPrimaryHardwareDev = outHwDev;
AutoMutex lock(mHardwareLock);
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_SET_MODE;
hwDevHal->set_mode(hwDevHal, mMode);
mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_IDLE;
}
return id;
}
return 0;
}
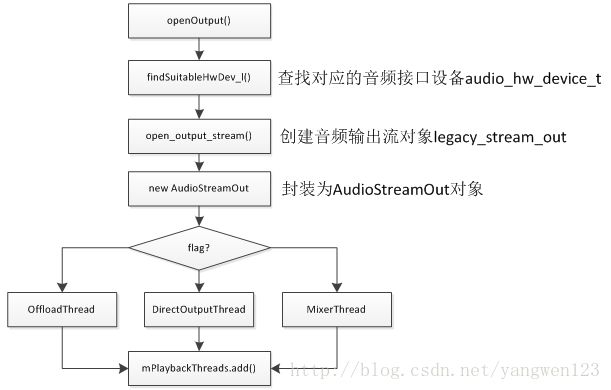
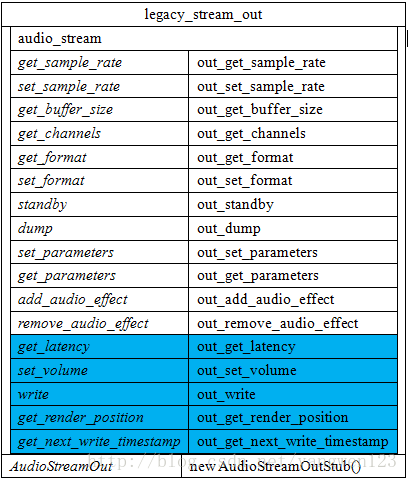
打开音频输出流过程其实就是创建AudioStreamOut对象及PlaybackThread线程过程。首先通过抽象的音频接口设备audio_hw_device_t来创建输出流对象legacy_stream_out。
static int adev_open_output_stream(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
audio_io_handle_t handle,
audio_devices_t devices,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
struct audio_config *config,
struct audio_stream_out **stream_out)
{
struct legacy_audio_device *ladev = to_ladev(dev);
status_t status;
struct legacy_stream_out *out;
int ret;
//分配一个legacy_stream_out对象
out = (struct legacy_stream_out *)calloc(1, sizeof(*out));
if (!out)
return -ENOMEM;
devices = convert_audio_device(devices, HAL_API_REV_2_0, HAL_API_REV_1_0);
//创建AudioStreamOut对象
out->legacy_out = ladev->hwif->openOutputStream(devices, (int *) &config->format,
&config->channel_mask,
&config->sample_rate, &status);
if (!out->legacy_out) {
ret = status;
goto err_open;
}
//初始化成员变量audio_stream
out->stream.common.get_sample_rate = out_get_sample_rate;
…
*stream_out = &out->stream;
return 0;
err_open:
free(out);
*stream_out = NULL;
return ret;
}
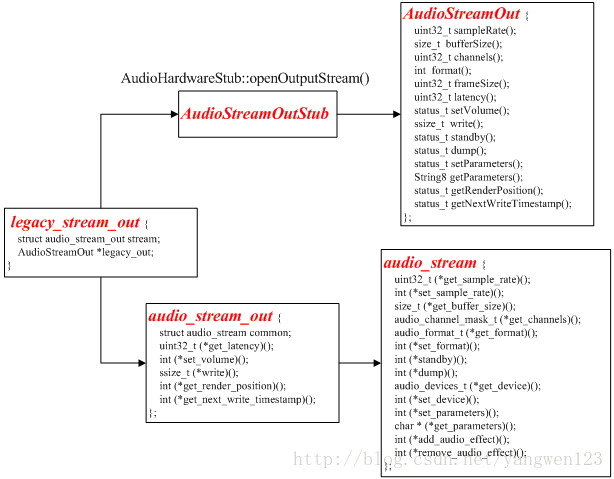
由于legacy_audio_device的成员变量hwif的类型为AudioHardwareInterface,因此通过调用AudioHardwareInterface的接口openOutputStream()来创建AudioStreamOut对象。
AudioStreamOut* AudioHardwareStub::openOutputStream(
uint32_t devices, int *format, uint32_t *channels, uint32_t *sampleRate, status_t *status)
{
AudioStreamOutStub* out = new AudioStreamOutStub();
status_t lStatus = out->set(format, channels, sampleRate);
if (status) {
*status = lStatus;
}
if (lStatus == NO_ERROR)
return out;
delete out;
return 0;
}
打开音频输出后,在AudioFlinger与AudioPolicyService中的表现形式如下:
打开音频输入
audio_io_handle_t AudioPolicyCompatClient::openInput(audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_devices_t *pDevices,
uint32_t *pSamplingRate,
audio_format_t *pFormat,
audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask)
{
return mServiceOps->open_input_on_module(mService, module, pDevices,pSamplingRate, pFormat, pChannelMask);
}
static audio_io_handle_t aps_open_input_on_module(void *service,
audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_devices_t *pDevices,
uint32_t *pSamplingRate,
audio_format_t *pFormat,
audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask)
{
sp af = AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger();
if (af == 0) {
ALOGW("%s: could not get AudioFlinger", __func__);
return 0;
}
return af->openInput(module, pDevices, pSamplingRate, pFormat, pChannelMask);
}
audio_io_handle_t AudioFlinger::openInput(audio_module_handle_t module,
audio_devices_t *pDevices,
uint32_t *pSamplingRate,
audio_format_t *pFormat,
audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask)
{
status_t status;
RecordThread *thread = NULL;
struct audio_config config;
config.sample_rate = (pSamplingRate != NULL) ? *pSamplingRate : 0;
config.channel_mask = (pChannelMask != NULL) ? *pChannelMask : 0;
config.format = (pFormat != NULL) ? *pFormat : AUDIO_FORMAT_DEFAULT;
uint32_t reqSamplingRate = config.sample_rate;
audio_format_t reqFormat = config.format;
audio_channel_mask_t reqChannels = config.channel_mask;
audio_stream_in_t *inStream = NULL;
AudioHwDevice *inHwDev;
if (pDevices == NULL || *pDevices == 0) {
return 0;
}
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
inHwDev = findSuitableHwDev_l(module, *pDevices);
if (inHwDev == NULL)
return 0;
audio_hw_device_t *inHwHal = inHwDev->hwDevice();
audio_io_handle_t id = nextUniqueId();
status = inHwHal->open_input_stream(inHwHal, id, *pDevices, &config,&inStream);
ALOGV("openInput() openInputStream returned input %p, SamplingRate %d, Format %d, Channels %x, "
"status %d",
inStream,
config.sample_rate,
config.format,
config.channel_mask,
status);
// If the input could not be opened with the requested parameters and we can handle the
// conversion internally, try to open again with the proposed parameters. The AudioFlinger can
// resample the input and do mono to stereo or stereo to mono conversions on 16 bit PCM inputs.
if (status == BAD_VALUE &&reqFormat == config.format && config.format == AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT && (config.sample_rate <= 2 * reqSamplingRate) &&
(popcount(config.channel_mask) <= FCC_2) && (popcount(reqChannels) <= FCC_2)) {
ALOGV("openInput() reopening with proposed sampling rate and channel mask");
inStream = NULL;
status = inHwHal->open_input_stream(inHwHal, id, *pDevices, &config, &inStream);
}
if (status == NO_ERROR && inStream != NULL) {
#ifdef TEE_SINK
// Try to re-use most recently used Pipe to archive a copy of input for dumpsys,
// or (re-)create if current Pipe is idle and does not match the new format
...
#endif
AudioStreamIn *input = new AudioStreamIn(inHwDev, inStream);
// Start record thread
// RecordThread requires both input and output device indication to forward to audio
// pre processing modules
thread = new RecordThread(this,
input,
reqSamplingRate,
reqChannels,
id,
primaryOutputDevice_l(),
*pDevices
#ifdef TEE_SINK
, teeSink
#endif
);
mRecordThreads.add(id, thread);
ALOGV("openInput() created record thread: ID %d thread %p", id, thread);
if (pSamplingRate != NULL) {
*pSamplingRate = reqSamplingRate;
}
if (pFormat != NULL) {
*pFormat = config.format;
}
if (pChannelMask != NULL) {
*pChannelMask = reqChannels;
}
// notify client processes of the new input creation
thread->audioConfigChanged_l(AudioSystem::INPUT_OPENED);
return id;
}
return 0;
}
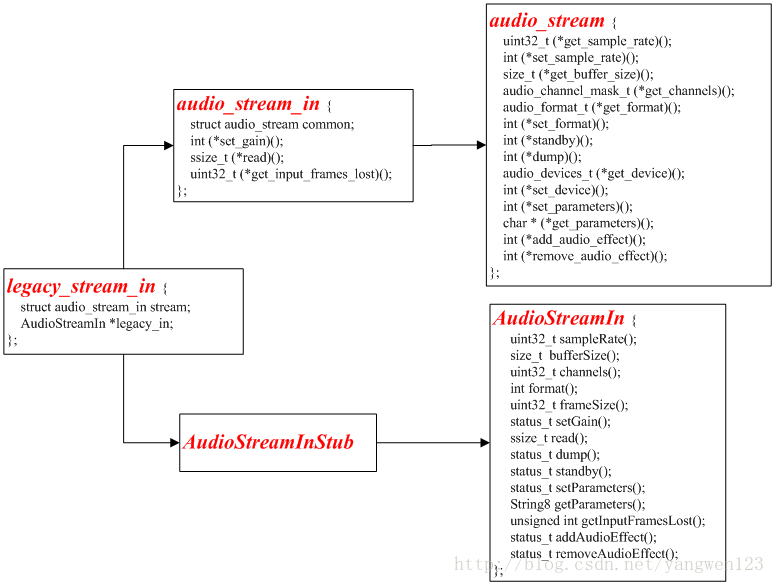
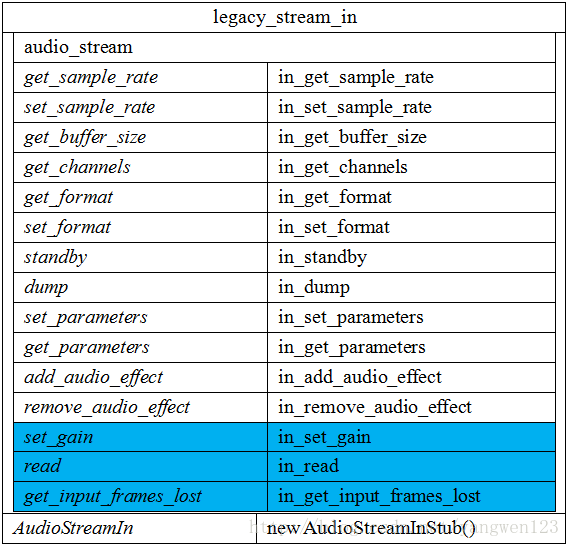
打开音频输入流过程其实就是创建AudioStreamIn对象及RecordThread线程过程。首先通过抽象的音频接口设备audio_hw_device_t来创建输出流对象legacy_stream_in。
static int adev_open_input_stream(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
audio_io_handle_t handle,
audio_devices_t devices,
struct audio_config *config,
struct audio_stream_in **stream_in)
{
struct legacy_audio_device *ladev = to_ladev(dev);
status_t status;
struct legacy_stream_in *in;
int ret;
in = (struct legacy_stream_in *)calloc(1, sizeof(*in));
if (!in)
return -ENOMEM;
devices = convert_audio_device(devices, HAL_API_REV_2_0, HAL_API_REV_1_0);
in->legacy_in = ladev->hwif->openInputStream(devices, (int *) &config->format,
&config->channel_mask,
&config->sample_rate,
&status, (AudioSystem::audio_in_acoustics)0);
if (!in->legacy_in) {
ret = status;
goto err_open;
}
in->stream.common.get_sample_rate = in_get_sample_rate;
…
*stream_in = &in->stream;
return 0;
err_open:
free(in);
*stream_in = NULL;
return ret;
}
AudioStreamIn* AudioHardwareStub::openInputStream(
uint32_t devices, int *format, uint32_t *channels, uint32_t *sampleRate,
status_t *status, AudioSystem::audio_in_acoustics acoustics)
{
// check for valid input source
if (!AudioSystem::isInputDevice((AudioSystem::audio_devices)devices)) {
return 0;
}
AudioStreamInStub* in = new AudioStreamInStub();
status_t lStatus = in->set(format, channels, sampleRate, acoustics);
if (status) {
*status = lStatus;
}
if (lStatus == NO_ERROR)
return in;
delete in;
return 0;
}
打开音频输入创建了以下legacy_stream_in对象:
打开音频输入后,在AudioFlinger与AudioPolicyService中的表现形式如下:
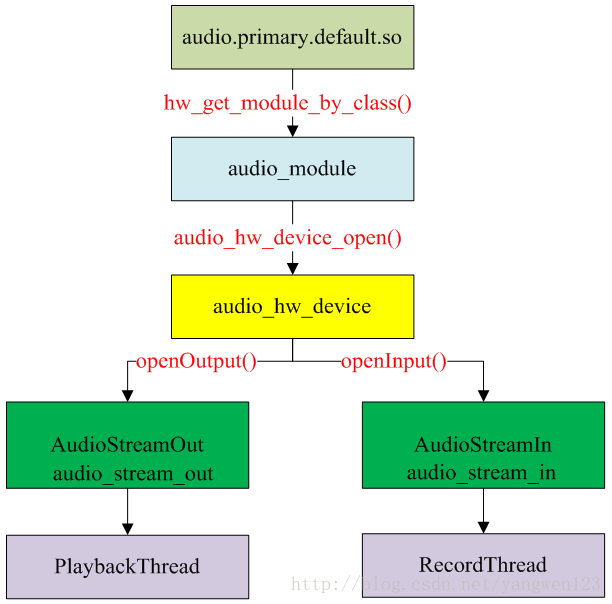
当AudioPolicyManagerBase构造时,它会根据用户提供的audio_policy.conf来分析系统中有哪些audio接口(primary,a2dp以及usb),然后通过AudioFlinger::loadHwModule加载各audio接口对应的库文件,并依次打开其中的output(openOutput)和input(openInput):
->打开音频输出时创建一个audio_stream_out通道,并创建AudioStreamOut对象以及新建PlaybackThread播放线程。
-> 打开音频输入时创建一个audio_stream_in通道,并创建AudioStreamIn对象以及创建RecordThread录音线程。