第三方库shiro-redis所引起的内存泄露问题分析
现象
线上某系统运行不到一周,响应速度变慢,并且多次重启,排查时发现CPU占用到100%,但这段时间系统并发量并未改变,数据库、缓存等也没发现异常。
排查过程
1、top指令查看哪个进程占用CPU高
发现确实是该系统的java进程。
2、使用 top -Hp 进程id 看哪个线程,然后利用jstack命令查看对应线程一直在干什么
很经典的排查线上CPU 100%问题的操作步骤,注意要转十六进制 .
最终发现是GC操作占用CPU。
3、此处怀疑是某处有内存泄露,使用jmap -histo:live 进程id | head -20 查看占用内存最多的对象有哪些
此处注意: ‘jmap’ 命令导出堆转储文件时(‘jmap -dump:live,format=b,file=文件名称 进程id’) 时,会触发Full GC!!!触发Full GC可能导致线上服务不可用。因此要慎重使用,比如如果是多实例部署的话,先隔离一个实例,避免对线上产生影响。‘jmap -histo:live’ 这条命令则没那么恐怖的后果。
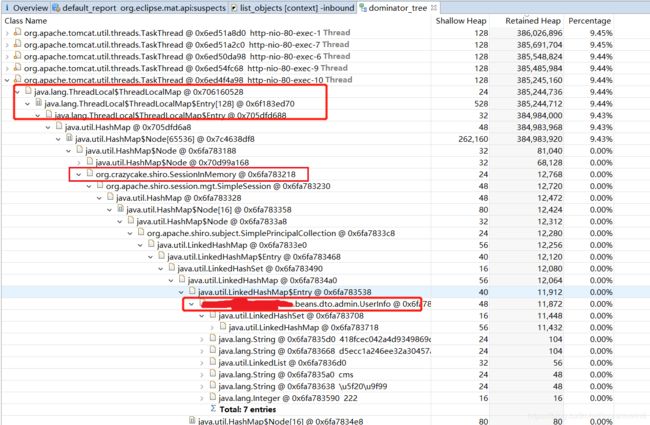
由于打印出的结果主要是对象签名,不太容易看,于是最终还是导出了一份堆转储文件,用MAT分析,下面是截图
参见标红的位置,首先可以看到是某处ThreadLocalMap一直有堆积、没有被释放。
然后进一步往下追,可以看到出问题的地方是org.crazycake.shiro.SessionInMemory,对应的业务对象是UserInfo这个自定义类的对象。
源码分析
org.crazycake.shiro.SessionInMemory 这个类来自于shiro-redis包,用于在shiro中使用redis缓存session。出问题的代码,是shiro-redis 3.2.0版本中的RedisSessionDAO 读取session的代码,如下:
@Override
protected Session doReadSession(Serializable sessionId) {
if (sessionId == null) {
logger.warn("session id is null");
return null;
}
Session s = getSessionFromThreadLocal(sessionId);
if (s != null) {
return s;
}
logger.debug("read session from redis");
try {
s = (Session) valueSerializer.deserialize(redisManager.get(keySerializer.serialize(getRedisSessionKey(sessionId))));
setSessionToThreadLocal(sessionId, s);
} catch (SerializationException e) {
logger.error("read session error. settionId=" + sessionId);
}
return s;
}
private Session getSessionFromThreadLocal(Serializable sessionId) {
Session s = null;
if (sessionsInThread.get() == null) {
return null;
}
Map<Serializable, SessionInMemory> sessionMap = (Map<Serializable, SessionInMemory>) sessionsInThread.get();
SessionInMemory sessionInMemory = sessionMap.get(sessionId);
if (sessionInMemory == null) {
return null;
}
Date now = new Date();
/*
此处有问题:仅判断了当前传入的sessionId对应的session是否过期,若过期则删除。那么,其他session呢?一直还在sessionMap中、没有被移除!
*/
long duration = now.getTime() - sessionInMemory.getCreateTime().getTime();
if (duration < sessionInMemoryTimeout) {
s = sessionInMemory.getSession();
logger.debug("read session from memory");
} else {
sessionMap.remove(sessionId);
}
return s;
}
有问题的地方在getSessionFromThreadLocal中,仅判断了当前传入的sessionId对应的session是否过期,若过期则删除;其他session一直没有做任何操作,显然,这将导致其他session一直还存在于sessionMap中、不会被释放,进而导致OOM。
shiro-redis的作者显然也意识到了这个问题,在shiro-redis 3.2.3时,此处代码修改如下:
@Override
protected Session doReadSession(Serializable sessionId) {
if (sessionId == null) {
logger.warn("session id is null");
return null;
}
//此处添加了标志位判断,用户可以关闭ThreadLocal缓存
if (this.sessionInMemoryEnabled) {
Session session = getSessionFromThreadLocal(sessionId);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
}
Session session = null;
logger.debug("read session from redis");
try {
session = (Session) valueSerializer.deserialize(redisManager.get(keySerializer.serialize(getRedisSessionKey(sessionId))));
if (this.sessionInMemoryEnabled) {
setSessionToThreadLocal(sessionId, session);
}
} catch (SerializationException e) {
logger.error("read session error. settionId=" + sessionId);
}
return session;
}
private Session getSessionFromThreadLocal(Serializable sessionId) {
if (sessionsInThread.get() == null) {
return null;
}
Map<Serializable, SessionInMemory> sessionMap = (Map<Serializable, SessionInMemory>) sessionsInThread.get();
SessionInMemory sessionInMemory = sessionMap.get(sessionId);
if (sessionInMemory == null) {
return null;
}
long liveTime = getSessionInMemoryLiveTime(sessionInMemory);
if (liveTime > sessionInMemoryTimeout) {
sessionMap.remove(sessionId);
return null;
}
logger.debug("read session from memory");
return sessionInMemory.getSession();
}
解决
有两种解决方案:
- 1)不要使用ThreadLocal缓存session,直接从redis中获取。该方式会一定程度上降低性能,需要频繁访问redis。
- 2)getSessionFromThreadLocal()方法获取session的时候,顺便检查其他session是否超时,如果超时则移除掉,避免session的不断累积。
本人倾向于第1种,升级shiro-redis包到3.2.3,并且在创建RedisSessionDAO时,关闭ThreadLocal缓存功能。
如下面代码:
@Bean(name = "redisSessionDAO")
public RedisSessionDAO getSessionDAO() {
RedisSessionDAO redisSessionDAO = new RedisSessionDAO();
...
//禁用通过ThreadLocal来存储当前session信息
redisSessionDAO.setSessionInMemoryEnabled(false);
return redisSessionDAO;
}
第2种方案,需要修改shiro-redis源码,有需要的童鞋可以动手实现一下,但注意session很多时,采用检查、删除的方式可能也会有一定性能损耗,需要实际压测权衡一下哪种方案更好。
参考资料
- shiro-redis引起的内存泄漏问题分析
- (一次java 内存泄漏问题的解决过程)[https://blog.csdn.net/u012954380/article/details/103007726/]