Android Input输入系统之二:KeyEvent注入事件及事件分发流程
相关参考:
《Android按键Input KeyEvent》
《Android Input输入系统之一:KeyEvent事件监听》
《Android Input输入系统之二:KeyEvent注入事件及事件分发流程》
《Android Input输入系统之三:KeyEvent事件分发和上层应用层对事件的接收》
《Android Input输入系统之四:KeyEvent事件中的InputChannel通信》
《Android Input输入系统之五:按键调节音量加减》
在上一篇文章中,《Android Input输入系统之一:KeyEvent事件监听及事件分发流程》,讲解的是读取设备节点/dev/input/event0,并且将事件上应用层分发的流程。
这篇文章讲解的是,模拟按键消息,通过注入事件的方式响应按键消息,并且向上应用层分发的流程。
注意的是,两者向app层分发按键消息的流程是一样的。
//adb命令
adb shell input keyevent 24
注入按键消息
import android.hardware.input.InputManager;
KeyEvent key = KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_DOWN;
InputManager.getInstance().injectInputEvent(key, 0);
framework/base/core/java/android/hardware/input/InputManager.java
framework/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
framework/base/core/java/android/hardware/input/IInputManager.aidl
InputManager中的injectInputEvent()调用,通过IInputManager.aidl
调用到InputManagerService中的injectInputEvent()
framework/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
@Override // Binder call
public boolean injectInputEvent(InputEvent event, int mode) {
return injectInputEventInternal(event, Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY, mode);
}
private boolean injectInputEventInternal(InputEvent event, int displayId, int mode) {
if (event == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("event must not be null");
}
if (mode != InputManager.INJECT_INPUT_EVENT_MODE_ASYNC
&& mode != InputManager.INJECT_INPUT_EVENT_MODE_WAIT_FOR_FINISH
&& mode != InputManager.INJECT_INPUT_EVENT_MODE_WAIT_FOR_RESULT) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("mode is invalid");
}
final int pid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int uid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final int result;
try {
result = nativeInjectInputEvent(mPtr, event, displayId, pid, uid, mode,
INJECTION_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, WindowManagerPolicy.FLAG_DISABLE_KEY_REPEAT);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
switch (result) {
case INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PERMISSION_DENIED:
Slog.w(TAG, "Input event injection from pid " + pid + " permission denied.");
throw new SecurityException(
"Injecting to another application requires INJECT_EVENTS permission");
case INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_SUCCEEDED:
return true;
case INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_TIMED_OUT:
Slog.w(TAG, "Input event injection from pid " + pid + " timed out.");
return false;
case INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_FAILED:
default:
Slog.w(TAG, "Input event injection from pid " + pid + " failed.");
return false;
}
}
关注:nativeInjectInputEvent()
nativeInjectInputEvent()是一个native层Jni接口,实现在com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp中。
base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
nativeInjectInputEvent(){
//省略一部分代码
//...
return (jint) im->getInputManager()->getDispatcher()->injectInputEvent(
& keyEvent, displayId, injectorPid, injectorUid, syncMode, timeoutMillis,
uint32_t(policyFlags));
//省略一部分代码
//...
}
调用的是InputDispatcher::injectInputEvent()
native/services/inputflinger/InputDispatcher.cpp,依旧还是native层。
InputDispatcher.cpp的injectInputEvent()中会去判断key类型。这个函数是比较重要的函数,最终的按键消息就是在这里发向应用层的。
//1.调用了PhoneWindowManager中的interceptKeyBeforeQueueing,
// 代码路径:frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\policy\PhoneWindowManager.java
mPolicy->interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(keyEvent, /*byref*/ policyFlags);
//2.根据Event类型,创建EventEntry
firstInjectedEntry = new KeyEntry(keyEvent->getEventTime(),
keyEvent->getDeviceId(), keyEvent->getSource(),
policyFlags, action, flags,
keyEvent->getKeyCode(), keyEvent->getScanCode(), keyEvent->getMetaState(),
keyEvent->getRepeatCount(), keyEvent->getDownTime());
lastInjectedEntry = firstInjectedEntry;
//3.调用enqueueInboundEventLocked,并判断是否唤醒InputDispatcherThread线程
bool needWake = false;
for (EventEntry* entry = firstInjectedEntry; entry != NULL; ) {
EventEntry* nextEntry = entry->next;
needWake |= enqueueInboundEventLocked(entry);
entry = nextEntry;
}
//4.调用mLooper->wake(),唤醒InputDispatcherThread线程
if (needWake) {
mLooper->wake();
}
//5.InputDispatcherThread线程中执行了dispatchOnce(),将事件分发出去
bool InputDispatcherThread::threadLoop() {
mDispatcher->dispatchOnce();
return true;
}
//6.dispatchOnce()调用了dispatchOnceInnerLocked,最终将事件分发给应用层
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
// Run a dispatch loop if there are no pending commands.
// The dispatch loop might enqueue commands to run afterwards.
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);
}
// Run all pending commands if there are any.
// If any commands were run then force the next poll to wake up immediately.
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {
nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;
}
} // release lock
// Wait for callback or timeout or wake. (make sure we round up, not down)
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}
具体dispatchOnceInnerLocked中是怎么将事件分开给应用层的呢?
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(){
//TYPE_KEY类型
done = dispatchKeyLocked(currentTime, typedEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
}
dispatchKeyLocked(){
//省略一部分代码
//...
// Dispatch the key.
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);
return true;
}
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets){
//省略一部分代码
//...
prepareDispatchCycleLocked();
}
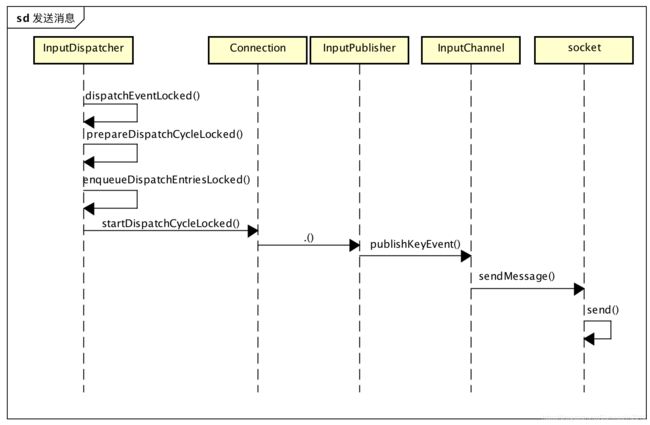
调用了prepareDispatchCycleLocked,其中又调用了enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked,最后调用了startDispatchCycleLocked()。
startDispatchCycleLocked()中,EventEntry::TYPE_KEY类型的事件执行的是:
// Publish the key event.
status = connection->inputPublisher.publishKeyEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
keyEntry->deviceId, keyEntry->source,
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags,
keyEntry->keyCode, keyEntry->scanCode,
keyEntry->metaState, keyEntry->repeatCount, keyEntry->downTime,
keyEntry->eventTime);
即framework/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp中,
status_t InputPublisher::publishKeyEvent(uint32_t seq,
int32_t deviceId,
int32_t source,
int32_t action,
int32_t flags,
int32_t keyCode,
int32_t scanCode,
int32_t metaState,
int32_t repeatCount,
nsecs_t downTime,
nsecs_t eventTime){
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::TYPE_KEY;
msg.body.key.seq = seq;
msg.body.key.deviceId = deviceId;
msg.body.key.source = source;
msg.body.key.action = action;
msg.body.key.flags = flags;
msg.body.key.keyCode = keyCode;
msg.body.key.scanCode = scanCode;
msg.body.key.metaState = metaState;
msg.body.key.repeatCount = repeatCount;
msg.body.key.downTime = downTime;
msg.body.key.eventTime = eventTime;
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}
调用了InputChannel的sendMessage()方法。InputChannel定义在InputTransport的内部。
status_t InputChannel::sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg) {
size_t msgLength = msg->size();
ssize_t nWrite;
do {
nWrite = ::send(mFd, msg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);
} while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
//省略一部分代码
//...
}
关注代码:nWrite = ::send(mFd, msg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);
InputChannel的本质是linux本地套接字,linux本地套接字可以用于进程间通信,InputChannel的openInputChannelPair方法中使用了socketpair函数创建了Linux本地套接字,socketpair会返回两个文件描述符,持有这两个文件描述符的进程就可以进行进程间的通信。
所以这里的InputChannel的sendMessage(),本质上是一个socket通信。
参考资料:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/f05d6b05ba17