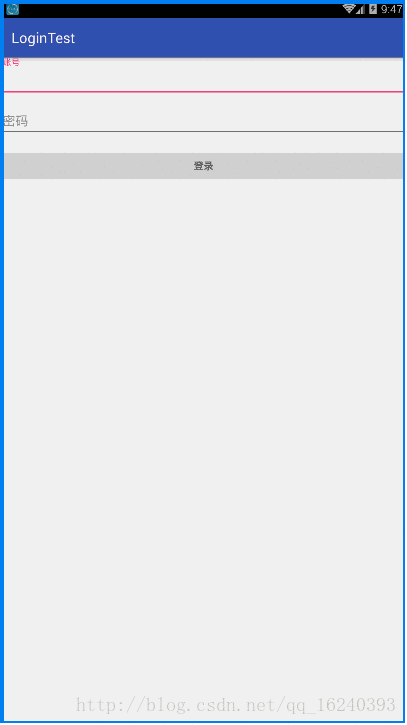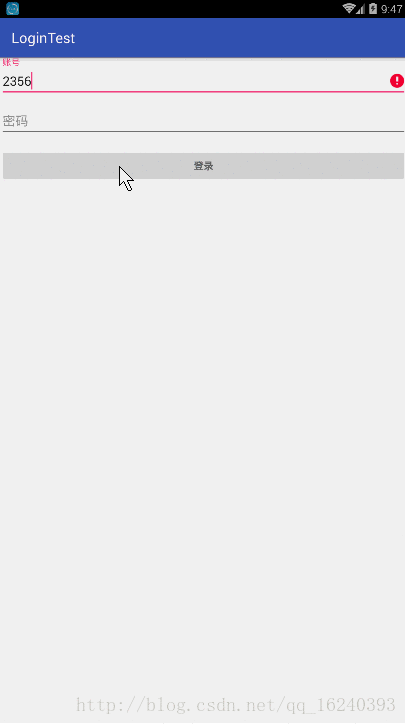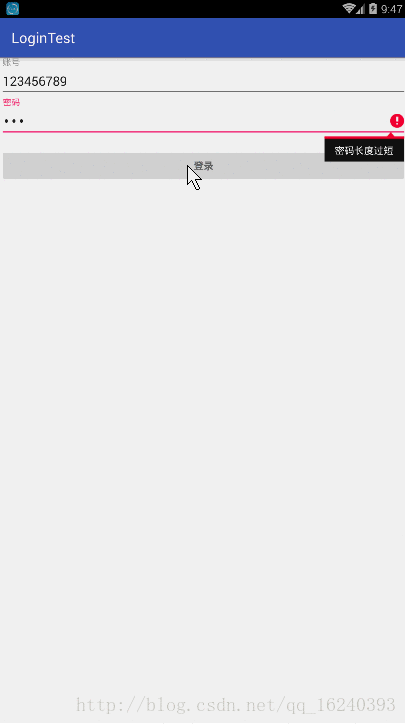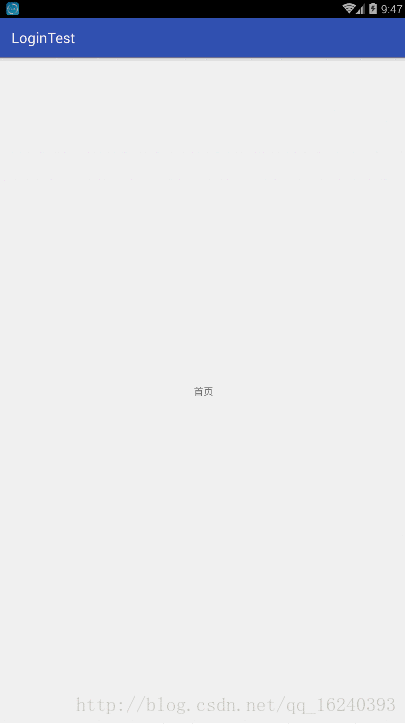
- android:onClick 无法成功映射到对应Activity问题的解决过程记录
陈金鑫
android
在学习android静态绑定按钮点击事件时出现报错:08-1300:30:32.510:E/AndroidRuntime(2039):java.lang.IllegalStateException:Couldnotexecutemethodoftheactivity08-1300:30:32.510:E/AndroidRuntime(2039): atandroid.view.View$1.o
- 最通用的跨平台引擎:ShiVa 3D引擎
pizi0475
图形图像其它文章图形引擎游戏引擎引擎跨平台脚本服务器sslsoap
ShiVa3D引擎是最通用的跨平台引擎,可以在Web浏览器运行并且也支持Windows,Mac,Linux,Wii,iPhone,iPad,Android,WebOS和AirplaySDK。该引擎支持SSL–securized插件扩展,很像PhysX引擎,FMOD声音库,ARToolkit和ScaleformHUD引擎。ClassicGeometry经典的图形处理支持多边形网,其中包括:-静态网格
- OpenCV开源机器视觉软件
视觉人机器视觉
杂说opencv开源人工智能
OpenCV(OpenSourceComputerVisionLibrary)是一个开源的计算机视觉和机器学习软件库,广泛应用于实时图像处理、视频分析、物体检测、人脸识别等领域。它由英特尔实验室于1999年发起,现已成为计算机视觉领域最流行的工具之一,支持多种编程语言(如C++、Python、Java)和操作系统(Windows、Linux、macOS、Android、iOS)。核心功能图像处理基
- android——Livedata、StateFlow、ShareFlow和Channel的介绍和使用
wy313622821
kotlin-javaandroid
目录一、LiveData介绍二、StateFlow介绍三、ShareFlow介绍四、Channel介绍小结一、LiveData介绍LiveData是一种在Android开发中用于观察数据变化的组件。它可以被观察者注册并在数据变化时通知观察者,从而实现数据的实时更新。LiveData具有生命周期感知能力,它会自动管理观察者的生命周期,确保观察者只会在活动状态下接收数据更新。示例代码classMyVi
- 技术教程 | 如何实现1v1音视频通话(含源码)
网易数智
WebRTC音视频ai人工智能实时音视频语音识别实时互动信息与通信
今天,给大家讲一下怎么实现1v1音视频通话,以下是教程内容:开发环境开发环境要求如下:环境要求说明JDK版本1.8.0及以上版本AndroidAPI版本API21、AndroidStudio5.0及以上版本CPU架构ARM64、ARMV7IDEAndroidStudio其他依赖Androidx,不支持support库。注意事项1对1娱乐社交场景方案的呼叫能力基于云信呼叫组件,技术原理一对一通话功能
- Android LiveData(一):介绍和简单使用
且听风吟9527
框架原理LiveData框架原理源码分析
传统的组件间的通信方式有Handler、BroadcastReceiver,Interface、EventBus等等方式实现,他们有自己适合的应用场景,也有各自的弊端。这里介绍新的组件通信同时LiveData,它是一个数据持有类,具有以下特点:数据可以被观察者订阅能够感知组件(Fragment、Activity、Service))的生命周期组件处于active状态时,会通知观察者有数据更新对于观察
- LiveData真的会被Flow替代吗?
Android-Developer
android
LiveData和Flow都是Android中用于响应式编程的工具,但它们有不同的使用场景和优缺点。先看一下LiveData和Flow的简单使用:LiveData是一种可观察的数据持有者,它可以感知生命周期并在数据发生变化时通知观察者。在Android中,LiveData通常用于将数据从ViewModel传递到UI层。以下是LiveData的使用步骤:1.创建LiveData对象可以通过继承Liv
- Android开发实战班 - 应用架构 - LiveData/Flow 数据流
老码小张
Android开发实战班android架构
在MVVM架构中,数据流是连接ViewModel和View的重要桥梁,用于实现数据的观察和响应。Jetpack提供了两种主要的数据流机制:LiveData和Flow。本章节将深入讲解LiveData和Flow的概念、使用方法、区别以及在实际开发中的应用场景,帮助学员掌握数据流的应用。数据流概述数据流的作用:数据流用于在ViewModel和View之间传递数据,实现数据的观察和响应。数据流可以感知生
- DroidDissector本地部署
想做后端的小C
linux运维服务器
DroidDissector本地部署我启动的是MediumPhoneAPI30安卓虚拟机先决条件:把frida-server推送到虚拟机的/data/local/tmp/目录中cdH:\frida_serveradbpushH:\frida_server\frida-server-16.6.6-android-x86/data/local/tmp/
- 深入Android HandlerThread 使用及其源码完全解析
ThreadLocalForrest
androidjavaui
本篇我们将来给大家介绍HandlerThread这个类,以前我们在使用线程执行一个耗时任务时总会new一个Thread的线程去跑,当任务执行完后,线程就会自动被销毁掉,如果又由新的任务,我们又得新建线程.....我们假设这样的一个情景,我们通过listview去加载图文列表,当我们往下滑动时,这时需要不断去请求网络资源,也就是需要不断开线程去加载网络资源,如果每次都new一个Thread,这显然是
- Android GLSurfaceView 覆盖其它控件问题 (RK平台)
ansondroider
androidandroidGLSurfaceViewSurfaceViewOverlay
平台涉及主控:RK3566Android:11/13问题在使用GLSurfaceView播放视频的过程中,增加了一个播放控制面板,覆盖在视频上方.默认隐藏setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);点击屏幕再显示出来.然而,在RK3566上这个简单的功能却无法正常工作.通过缩小视频窗口可以看到,实际UI是已经展示,但是被GLSurfaceView覆盖了.在PixelAndroid1
- Android 调用系统服务接口获取屏幕投影(需要android.uid.system)
ansondroider
androidandroid投屏MediaProjection共享屏幕录屏
媒体投影借助Android5(API级别21)中引入的android.media.projectionAPI,您可以将设备屏幕中的内容截取为可播放、录制或投屏到其他设备(如电视)的媒体流。Android14(API级别34)引入了应用屏幕共享功能,让用户能够分享单个应用窗口(而非整个设备屏幕),无论窗口模式如何。应用屏幕共享功能会将状态栏、导航栏、通知和其他系统界面元素从共享显示屏中排除,即使应用
- Android渲染Latex公式的开源框架比较
sz_denny
开源
对比主流框架,介绍如下几款1、AndroidMath官网:GitHub-gregcockroft/AndroidMath:RenderbeautifulLaTeXMathEquationsinanAndroidView基于android原生view方式渲染优点:速度快,开源协议MITlicense缺点:不支持文字+公式混合渲染2、MathView官网:GitHub-jianzhongli/Math
- jlatexmath-android如何实现自定义渲染字符
sz_denny
android
使用jlatexmath-android的过程,如果出现个别字符渲染不了,会导致无法显示常用的做法是新增自定义字体+切换系统默认字体渲染,下面我们介绍第2种方法。修改流程:1、到jlatexmath-android的官网下载源码到本地,导入到IDE2、找到这个类JLatexMathDrawable3、在这个方法做替换操作publicBuilder(Stringlatex){//把latext里面不
- 【对比】远程桌面控制软件盘点(2025年)
T-I-M
零散笔记远程控制桌面控制
远程手机连接电脑的软件可以帮助用户实现远程控制、文件传输、屏幕共享等功能。这些软件通常适用于技术支持、远程办公、设备管理等场景。以下是一些好用且常用的远程连接工具:1.向日葵(Sunlogin)特点:国内知名远程控制软件,支持跨平台操作(Windows、Mac、Linux、Android、iOS)。提供免费版和付费版,功能强大且易于使用。支持远程桌面、文件传输、远程开机(需硬件支持)等功能。内网穿
- Android 包体积优化
鹭岛猥琐男
Android包体积优化优化
目前公司的智能家居项目是一个2017年开始的产品,属于祖传项目。去年又经历了一次AndroidX的升级,以及一次小范围的UI样式改版。因为是智能家居相关项目,涉及到的设备比较多,随着设备接入越来越多,且产品和UI对于不同设备之间的相关提示图片等做不到通用,导致图片资源也越来越多。以及一些冗余代码等也没有及时的优化等,导致包体积越来越大,对包体积的优化就越来越重要了。记录下包体积优化前的安装包大小:
- android中的CheckBox改变背景图片显示大小
辄也
android
在androidStudio的xml文件设置布局时,对于checkBox选中后,展示大小不同的背景图片1.首先需要一个选择器存放背景图片,设置选中和未选中状态2.在布局文件中设置对应的checkBox,如果对应选中的图片大小不一样的时候,使用一下布局方式可以展示出对应的大小;主要实现时布局中的android:background="@null"android:button="@drawable/s
- android 系统状态栏高度,关于Android状态栏高度为0仍显示的问题
weixin_40005330
android系统状态栏高度
前言这里有一个比较坑的事,系统将状态栏的高度已经设置为0,然后界面上确实已经看不到时间,WiFi等图标,也无法通过下拉,显示通知栏。但在某些应用的activity上,还是会出现activity的状态栏,这个一开始还以为是activity的标题栏,但到了后面,发现这是状态栏。应用层更改Activity的窗口风格而这里的状态栏可以在activity的onCreate方法中通过如下方法隐藏掉:prote
- Qt for Android下QMessageBox背景黑色、文字点击闪烁
子建莫敌
Qtqtandroidc++QMessageBox文字闪烁背景黑色
最近在基于Qt开发安卓应用的时候,在红米平板上默认QMessageBox出现之后,背景黑色,并且点击提示文字会出现闪烁,影响用户体验。问题分析1、设置QMessageBox样式,设置背景色、文字颜色,如下所示:QMessageBox{background:white;color:white;}尝试之后,问题仍存在2、继承QMessageBox,自定义MessageboxMessagebox:pub
- react-native入门之核心组件与原生组件
crayon-shin-chan
surprise#react-nativereactnativereact
文档:核心组件与原生组件·ReactNative中文网1.简介ReactNative是一个使用React和应用平台的原生功能来构建Android和iOS应用的开源框架。可以使用JavaScript来访问移动平台的API,使用React组件来描述UI的外观和行为2.视图在Android和iOS开发中,一个视图是UI的基本组成部分屏幕上的一个小矩形元素、可用于显示文本、图像或响应用户输入。甚至应用程序
- PyTorch模型安卓部署流程(NCNN)全流程实战(2)代码详细解析
咕咕学不会咋办
pytorchandroidpython
代码来源PyTorch模型安卓部署流程(NCNN)全流程实战(1)至于为什么要备注,因为我基础不好,就得一点一点来适合和我一样的慢羊羊学习项目整体结构1.布局文件不解析了比较简单最简单的线性布局main.xml2.资源文件string.xmlsqueezencnn在Android开发中,资源文件(通常以.xml结尾)用于定义静态内容,如字符串、颜色、尺寸等。res/values/strings.x
- 为什么选择Linux而放弃windows,比较Windows和Mac它出色的优势在哪儿?
MAX在码字
程序人生程序员LinuxWindowsMac
前言:MacOS全封闭,只支持自家硬件,设计风格和使用体验比较独特;Windows半封闭,虽然源码不开放,但适配市面上几乎所有的x86机器,Windows和各家硬件厂商总体是合作共建生态圈,从市场份额看,Windows是个人电脑桌面操作系统的霸主;Linux内核开放、开源,可以基于Linux内核开发一系列各种各样的操作系统(其中最著名的是Android系统),支持x86、ARM等各种硬件,是目前嵌
- android studio调用python_Android-Python混合开发 1 (java和python互相调用)
weixin_39630095
androidstudio调用python
众所周知,python的语法简洁,并且拥有丰富强大的开源库,如果能把python移植到Android系统,能够用Android和python混合开发一款app,那就太酷了。要想移植python,得需要下载源码并且交叉编译才行。这个过程太复杂。在这里,介绍一款第三方,复杂的过程交给它处理,我们只需要处理逻辑相关的python代码即可。Chaquopy0x01集成1)打开项目根目录下的build.gr
- [Android] 在AndroidStudio中使用Python
Microsoda
androidpython开发语言
这篇文章不包含Python的安装教程,请确保你已经安装好Python解释器。安装Chaquopy在/build.gradle中添加如下语句:plugins{id'com.chaquo.python'version'14.0.2'applyfalse}在/app/src/build.gradle中添加如下语句:plugins{id'com.android.application'id'com.cha
- 基于微信小程序的毕业设计——花店管理系统(附源码+论文)
picking_bananas
微信小程序课程设计小程序毕业设计
关键词:微信小程序;花店管理;花室管理;毕业;我们专注于软件开发工程领域,熟练掌握多种开发技术,包括基于SpringBoot、Vue.js、SSM框架的应用开发,以及针对AndroidAPP和微信小程序的开发。(具体流程参见文章最后段落)一、引言随着移动互联网的普及和微信小程序的崛起,越来越多的传统行业开始利用小程序进行数字化转型。花店作为一个具有浪漫和文化意义的行业,通过微信小程序可以更好地满足
- 基于微信小程序的设计—挂号管理系统设计(附论文+源码)
picking_bananas
微信小程序小程序毕业设计课程设计
关键词:微信小程序;挂号管理;名医推荐;毕业;论文;我们专注于软件开发工程领域,熟练掌握多种开发技术,包括基于SpringBoot、Vue.js、SSM框架的应用开发,以及针对AndroidAPP和微信小程序的开发。(具体流程参见文章最后段落)一、引言随着移动设备的普及和微信小程序技术的发展,医疗服务的移动化已成为趋势。挂号是医疗服务中一个关键环节,对于患者来说,方便、快捷的挂号方式是他们所期待的
- 基于微信小程序的毕业设计——社区宠物管理系统(附源码+论文)
picking_bananas
微信小程序课程设计宠物小程序
关键词:SpringBoot;宠物管理;宠物医院;宠物店管理;毕业;我们专注于软件开发工程领域,熟练掌握多种开发技术,包括基于SpringBoot、Vue.js、SSM框架的应用开发,以及针对AndroidAPP和微信小程序的开发。(具体流程参见文章最后段落)摘要随着移动互联网的普及,微信小程序因其便捷性受到了广大用户的青睐。本文旨在探讨如何利用微信小程序设计一个社区宠物管理系统,以提升社区居民对
- 使用Android Studio编写Python代码
海上的风浪
androidstudiopythonandroidAndroid
使用AndroidStudio编写Python代码随着移动应用的快速发展,AndroidStudio成为了开发者们首选的集成开发环境。虽然AndroidStudio主要用于开发Android应用程序,但是我们也可以在其中编写和运行Python代码。在本文中,我将详细介绍如何在AndroidStudio中编写Python代码,并附上相应的源代码。首先,确保你已经安装了AndroidStudio并且环
- 23设计模式详解「全23种」
小北编程
Java精选设计模式
✍️作者简介:小北编程(专注于HarmonyOS、Android、Java、Web、TCP/IP等技术方向)博客主页:开源中国、稀土掘金、51cto博客、博客园、知乎、简书、慕课网、CSDN如果文章对您有一定的帮助请关注✨、点赞、收藏、评论。如需转载请参考【转载须知】文章目录设计模式介绍一、什么是设计模式二、设计模式表述三、设计模式分类1.创建型模式(CreationalPatterns):2.结
- flutter_boost接入及分析
Huang兄
Flutterandroidandroiddartflutterfluterboost
2019-09-12文章目录集成过程添加依赖在flutter_nodule侧在原生Android侧尝试flutter_boost流程在flutter中打开flutter或者原生在flutter中关闭页面flutter_boost地址:https://github.com/alibaba/flutter_boost集成之后的项目地址:https://github.com/huangyuanlove/
- java线程的无限循环和退出
3213213333332132
java
最近想写一个游戏,然后碰到有关线程的问题,网上查了好多资料都没满足。
突然想起了前段时间看的有关线程的视频,于是信手拈来写了一个线程的代码片段。
希望帮助刚学java线程的童鞋
package thread;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date
- tomcat 容器
BlueSkator
tomcatWebservlet
Tomcat的组成部分 1、server
A Server element represents the entire Catalina servlet container. (Singleton) 2、service
service包括多个connector以及一个engine,其职责为处理由connector获得的客户请求。
3、connector
一个connector
- php递归,静态变量,匿名函数使用
dcj3sjt126com
PHP递归函数匿名函数静态变量引用传参
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Current To-Do List</title>
</head>
<body>
- 属性颜色字体变化
周华华
JavaScript
function changSize(className){
var diva=byId("fot")
diva.className=className;
}
</script>
<style type="text/css">
.max{
background: #900;
color:#039;
- 将properties内容放置到map中
g21121
properties
代码比较简单:
private static Map<Object, Object> map;
private static Properties p;
static {
//读取properties文件
InputStream is = XXX.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("xxx.properti
- [简单]拼接字符串
53873039oycg
字符串
工作中遇到需要从Map里面取值拼接字符串的情况,自己写了个,不是很好,欢迎提出更优雅的写法,代码如下:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.uti
- Struts2学习
云端月影
最近开始关注struts2的新特性,从这个版本开始,Struts开始使用convention-plugin代替codebehind-plugin来实现struts的零配置。
配置文件精简了,的确是简便了开发过程,但是,我们熟悉的配置突然disappear了,真是一下很不适应。跟着潮流走吧,看看该怎样来搞定convention-plugin。
使用Convention插件,你需要将其JAR文件放
- Java新手入门的30个基本概念二
aijuans
java新手java 入门
基本概念: 1.OOP中唯一关系的是对象的接口是什么,就像计算机的销售商她不管电源内部结构是怎样的,他只关系能否给你提供电就行了,也就是只要知道can or not而不是how and why.所有的程序是由一定的属性和行为对象组成的,不同的对象的访问通过函数调用来完成,对象间所有的交流都是通过方法调用,通过对封装对象数据,很大限度上提高复用率。 2.OOP中最重要的思想是类,类是模板是蓝图,
- jedis 简单使用
antlove
javarediscachecommandjedis
jedis.RedisOperationCollection.java
package jedis;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
pub
- PL/SQL的函数和包体的基础
百合不是茶
PL/SQL编程函数包体显示包的具体数据包
由于明天举要上课,所以刚刚将代码敲了一遍PL/SQL的函数和包体的实现(单例模式过几天好好的总结下再发出来);以便明天能更好的学习PL/SQL的循环,今天太累了,所以早点睡觉,明天继续PL/SQL总有一天我会将你永远的记载在心里,,,
函数;
函数:PL/SQL中的函数相当于java中的方法;函数有返回值
定义函数的
--输入姓名找到该姓名的年薪
create or re
- Mockito(二)--实例篇
bijian1013
持续集成mockito单元测试
学习了基本知识后,就可以实战了,Mockito的实际使用还是比较麻烦的。因为在实际使用中,最常遇到的就是需要模拟第三方类库的行为。
比如现在有一个类FTPFileTransfer,实现了向FTP传输文件的功能。这个类中使用了a
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(7)编写控制结构
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
*编写控制结构
*/
--条件分支语句
--简单条件判断
DECLARE
v_sal NUMBER(6,2);
BEGIN
select sal into v_sal from emp
where lower(ename)=lower('&name');
if v_sal<2000 then
update emp set
- 【Log4j二】Log4j属性文件配置详解
bit1129
log4j
如下是一个log4j.properties的配置
log4j.rootCategory=INFO, stdout , R
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appe
- java集合排序笔记
白糖_
java
public class CollectionDemo implements Serializable,Comparable<CollectionDemo>{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2958090810811192128L;
private int id;
private String nam
- java导致linux负载过高的定位方法
ronin47
定位java进程ID
可以使用top或ps -ef |grep java
![图片描述][1]
根据进程ID找到最消耗资源的java pid
比如第一步找到的进程ID为5431
执行
top -p 5431 -H
![图片描述][2]
打印java栈信息
$ jstack -l 5431 > 5431.log
在栈信息中定位具体问题
将消耗资源的Java PID转
- 给定能随机生成整数1到5的函数,写出能随机生成整数1到7的函数
bylijinnan
函数
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
public class RandNFromRand5 {
/**
题目:给定能随机生成整数1到5的函数,写出能随机生成整数1到7的函数。
解法1:
f(k) = (x0-1)*5^0+(x1-
- PL/SQL Developer保存布局
Kai_Ge
近日由于项目需要,数据库从DB2迁移到ORCAL,因此数据库连接客户端选择了PL/SQL Developer。由于软件运用不熟悉,造成了很多麻烦,最主要的就是进入后,左边列表有很多选项,自己删除了一些选项卡,布局很满意了,下次进入后又恢复了以前的布局,很是苦恼。在众多PL/SQL Developer使用技巧中找到如下这段:
&n
- [未来战士计划]超能查派[剧透,慎入]
comsci
计划
非常好看,超能查派,这部电影......为我们这些热爱人工智能的工程技术人员提供一些参考意见和思想........
虽然电影里面的人物形象不是非常的可爱....但是非常的贴近现实生活....
&nbs
- Google Map API V2
dai_lm
google map
以后如果要开发包含google map的程序就更麻烦咯
http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2013/01/01/2841390.html
找到篇不错的文章,大家可以参考一下
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_c2839d410101jahv.html
1. 创建Android工程
由于v2的key需要G
- java数据计算层的几种解决方法2
datamachine
javasql集算器
2、SQL
SQL/SP/JDBC在这里属于一类,这是老牌的数据计算层,性能和灵活性是它的优势。但随着新情况的不断出现,单纯用SQL已经难以满足需求,比如: JAVA开发规模的扩大,数据量的剧增,复杂计算问题的涌现。虽然SQL得高分的指标不多,但都是权重最高的。
成熟度:5星。最成熟的。
- Linux下Telnet的安装与运行
dcj3sjt126com
linuxtelnet
Linux下Telnet的安装与运行 linux默认是使用SSH服务的 而不安装telnet服务 如果要使用telnet 就必须先安装相应的软件包 即使安装了软件包 默认的设置telnet 服务也是不运行的 需要手工进行设置 如果是redhat9,则在第三张光盘中找到 telnet-server-0.17-25.i386.rpm
- PHP中钩子函数的实现与认识
dcj3sjt126com
PHP
假如有这么一段程序:
function fun(){
fun1();
fun2();
}
首先程序执行完fun1()之后执行fun2()然后fun()结束。
但是,假如我们想对函数做一些变化。比如说,fun是一个解析函数,我们希望后期可以提供丰富的解析函数,而究竟用哪个函数解析,我们希望在配置文件中配置。这个时候就可以发挥钩子的力量了。
我们可以在fu
- EOS中的WorkSpace密码修改
蕃薯耀
修改WorkSpace密码
EOS中BPS的WorkSpace密码修改
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
蕃薯耀 201
- SpringMVC4零配置--SpringSecurity相关配置【SpringSecurityConfig】
hanqunfeng
SpringSecurity
SpringSecurity的配置相对来说有些复杂,如果是完整的bean配置,则需要配置大量的bean,所以xml配置时使用了命名空间来简化配置,同样,spring为我们提供了一个抽象类WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter和一个注解@EnableWebMvcSecurity,达到同样减少bean配置的目的,如下:
applicationContex
- ie 9 kendo ui中ajax跨域的问题
jackyrong
AJAX跨域
这两天遇到个问题,kendo ui的datagrid,根据json去读取数据,然后前端通过kendo ui的datagrid去渲染,但很奇怪的是,在ie 10,ie 11,chrome,firefox等浏览器中,同样的程序,
浏览起来是没问题的,但把应用放到公网上的一台服务器,
却发现如下情况:
1) ie 9下,不能出现任何数据,但用IE 9浏览器浏览本机的应用,却没任何问题
- 不要让别人笑你不能成为程序员
lampcy
编程程序员
在经历六个月的编程集训之后,我刚刚完成了我的第一次一对一的编码评估。但是事情并没有如我所想的那般顺利。
说实话,我感觉我的脑细胞像被轰炸过一样。
手慢慢地离开键盘,心里很压抑。不禁默默祈祷:一切都会进展顺利的,对吧?至少有些地方我的回答应该是没有遗漏的,是不是?
难道我选择编程真的是一个巨大的错误吗——我真的永远也成不了程序员吗?
我需要一点点安慰。在自我怀疑,不安全感和脆弱等等像龙卷风一
- 马皇后的贤德
nannan408
马皇后不怕朱元璋的坏脾气,并敢理直气壮地吹耳边风。众所周知,朱元璋不喜欢女人干政,他认为“后妃虽母仪天下,然不可使干政事”,因为“宠之太过,则骄恣犯分,上下失序”,因此还特地命人纂述《女诫》,以示警诫。但马皇后是个例外。
有一次,马皇后问朱元璋道:“如今天下老百姓安居乐业了吗?”朱元璋不高兴地回答:“这不是你应该问的。”马皇后振振有词地回敬道:“陛下是天下之父,
- 选择某个属性值最大的那条记录(不仅仅包含指定属性,而是想要什么属性都可以)
Rainbow702
sqlgroup by最大值max最大的那条记录
好久好久不写SQL了,技能退化严重啊!!!
直入主题:
比如我有一张表,file_info,
它有两个属性(但实际不只,我这里只是作说明用):
file_code, file_version
同一个code可能对应多个version
现在,我想针对每一个code,取得它相关的记录中,version 值 最大的那条记录,
SQL如下:
select
*
- VBScript脚本语言
tntxia
VBScript
VBScript 是基于VB的脚本语言。主要用于Asp和Excel的编程。
VB家族语言简介
Visual Basic 6.0
源于BASIC语言。
由微软公司开发的包含协助开发环境的事
- java中枚举类型的使用
xiao1zhao2
javaenum枚举1.5新特性
枚举类型是j2se在1.5引入的新的类型,通过关键字enum来定义,常用来存储一些常量.
1.定义一个简单的枚举类型
public enum Sex {
MAN,
WOMAN
}
枚举类型本质是类,编译此段代码会生成.class文件.通过Sex.MAN来访问Sex中的成员,其返回值是Sex类型.
2.常用方法
静态的values()方