Webpack4学习笔记(三)——代码分割(多入口)
这是一个关于Webpack4的文章系列,其中包含以下文章:
- Webpack4学习笔记(一)——基本使用
- Webpack4学习笔记(二)——代码分割(单入口)
- Webpack4学习笔记(三)——代码分割(多入口)
- Webpack4学习笔记(四)——CSS处理
- Webpack4学习笔记(五)——分离production和development环境
- Webpack4学习笔记(六)——Webpack4+VueJS2项目搭建
本系列文章源代码:
git clone https://github.com/davenkin/webpack-learning.git
在上一篇中,我们讲到了单入口文件的代码分割配置,本文将对多入口的项目进行代码分割。
欢迎访问本文github源代码。
Webpack4默认配置
创建项目结构:
- 一共3个入口文件index1.html,index2.html和index3.html
- 每个入口文件对应一个js入口文件,分别为index1.js,index2.js和index3.js
- index1.js依赖于A-module,F-module,G-module,axios,lodash
- index2.js依赖于A-module,G-module,H-module,axios,jquery
- index3.js依赖于A-module,F-module,H-module,lodash,jquery
- index1.js异步依赖于B-module和C-module
- index2.js异步依赖于B-module和lodash
- index3.js异步依赖于C-module
- B-module和C-module同时依赖于D-module
- C-module依赖于E-module
配置多入口以及对应的HtmlWebpackPlugin如下:
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin;
function resolve(dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir)
}
module.exports = {
entry: {
'index1': './src/index1.js',
'index2': './src/index2.js',
'index3': './src/index3.js'
},
output: {
filename: '[name].[contenthash].js',
chunkFilename: '[name].[contenthash].js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'distribution')
},
//use inline-source-map for development:
devtool: 'inline-source-map',
//use source-map for production:
// devtool: 'source-map',
devServer: {
contentBase: './distribution'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
include: [resolve('src')],
exclude: [resolve('node_modules')]
}
]
},
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['distribution']),
new BundleAnalyzerPlugin({
openAnalyzer: false,
analyzerMode: 'static',
reportFilename: 'bundle-analyzer-report.html'
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index1.html',
filename: 'index1.html'
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index2.html',
filename: 'index2.html'
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index3.html',
filename: 'index3.html'
}),
new webpack.HashedModuleIdsPlugin()
]
}
;
此时运行cnpm run build,输出如下:
distribution/
├── async-b.3e6a567c8ad867591384.js
├── async-c.faa08dc1c722e8898326.js
├── bundle-analyzer-report.html
├── index1.c1bbbb105e63289639ac.js
├── index1.html
├── index2.08a076e70009b6c186ba.js
├── index2.html
├── index3.d500c907afa610e6d5f8.js
├── index3.html
└── vendors~async-lodash.d810246d214be5df29ec.js
回顾一下webpack的默认配置:
- 只对async的module进行分割处理
- 生成的分割文件要大于30k
- 对第三方库(node_modules目录下的库)进行处理
- 对引用大于等于2的module进行分割
可以看出,在默认情况下,webpack只对异步加载的库做了分割处理(生成了async-b.3e6a567c8ad867591384.js、async-c.faa08dc1c722e8898326.js和vendors~async-lodash.d810246d214be5df29ec.js),而其他所有的module都打包到了对应的index.*.js文件中。
改进默认配置
以上默认配置当然不是我们想要的,此时我们可以对配置稍作修改,即将默认的两个cacheGroup的chunks改为all,表示同时对静态加载(initial)和动态加载(async)起作用,以及设置生产的chunk不受最大文件大小限制。
...
optimization: {
runtimeChunk: {
"name": "manifest"
},
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'all',
minSize: 0
}
}
...
此时输出:
distribution/
├── async-b.fea9cc8ccb4c8c61f9c6.js
├── async-b~async-c.3290278114f34ed3a1cd.js
├── async-c.dab143479fff8a09776f.js
├── bundle-analyzer-report.html
├── index1.ebb1247940df7f5b54b7.js
├── index1.html
├── index2.d75b21ef39cced9d7c7a.js
├── index2.html
├── index3.823261ed02e3ede4c764.js
├── index3.html
├── manifest.0c4e4338d067666d041d.js
├── vendors~async-lodash~index1~index3.8cf11deabd773d32d46c.js
├── vendors~index1~index2.3bcd0a827baa477b6164.js
└── vendors~index2~index3.3c1c550be5409b787677.js
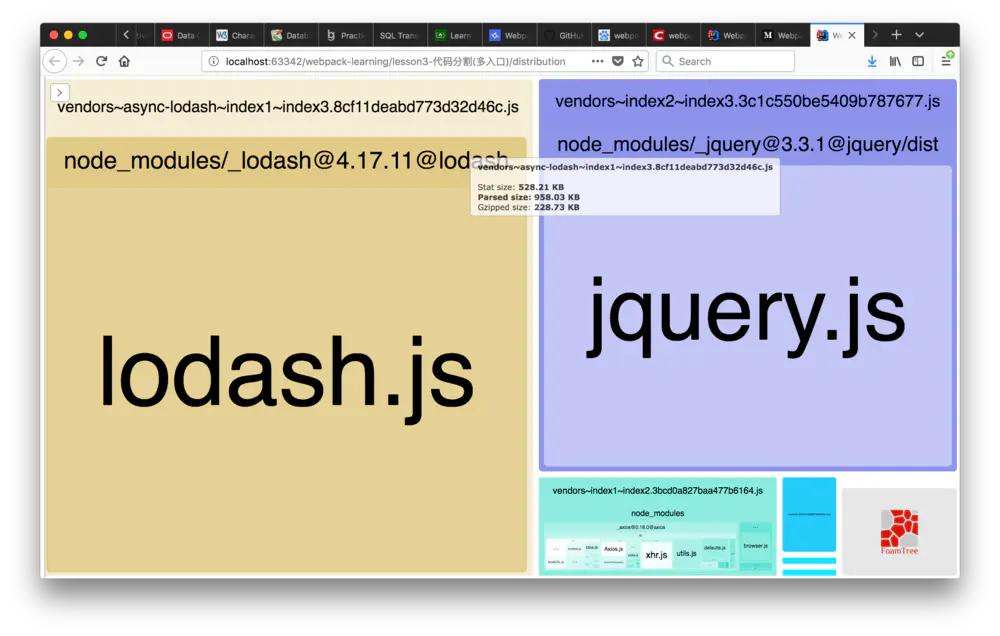
生成的bundle报告如下:
默认配置bundle报告
此时的解释如下:
async-b~async-c.3290278114f34ed3a1cd.js文件是新生产的,是由于B-module和C-module同时依赖于D-module产生的;vendors~async-lodash~index1~index3.8cf11deabd773d32d46c.js包含了lodash库,是由于index1.js、index3.js静态依赖了lodash,同时index2.js中对lodash有异步依赖;vendors~index1~index2.3bcd0a827baa477b6164.js包含了axios库,是由于index1和index2同时引用了axios;vendors~index2~index3.3c1c550be5409b787677.js包含了jquery库,是由于index2和index3同时引用了jquery。
此时有以下问题:
- 通过HtmlWebpackPlugin生成的三个index.html文件引用了所有的静态依赖,即index1引用了index2和index3的依赖,反之亦然,这当然没有达到分离页面的目的;
- 三个index.js文件共享或者部分共享了A-module、F-module、G-module和H-module,但是共享模块还是重复出现在了生成的index.js文件中。
总结起来,我们希望:
- 提取webpack的runtime代码到单独的文件
- 所有静态依赖第三方库被分割到同一个文件中
- 所有动态依赖的第三方库分别分割到单独的文件,这样才能享受异步加载的好处,即只加载所需要的
- 所有动态依赖的自研发模块分别分割到单独的文件
- 被多次引用的自研发模块统一放到一个文件中,便于多个入口共享
- 配置缓存
定制化配置
为了全新配置webpack,我们先去除掉默认的2个cacheGroup:
...
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
default: false,
vendors: false
}
}
}
...
此时输出:
distribution/
├── async-b.307ba84dd97982af85a7.js
├── async-c.772e9f7104fef1be4aa1.js
├── async-lodash.2a8965ea7a405e680873.js
├── bundle-analyzer-report.html
├── index1.293bba8e0b6d369ab674.js
├── index1.html
├── index2.3b788dea9a926b1f8c76.js
├── index2.html
├── index3.182fc2fbba6ad900fe00.js
├── index3.html
└── manifest.a4f48ab9287b147792e1.js
可以自行分析以上输出结果的原因。
对于第1点,webpack自带支持:
...
optimization: {
runtimeChunk: {
"name": "manifest"
},
...
对于2点——将所有静态的第三方依赖放到同一个文件中,加入新的cacheGroup:
...
vendor: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
chunks: 'initial',
enforce: true,
priority: 10,
name:'vendor'
},
...
此时输出结果为:
distribution/
├── async-b.746904f01aa1ee1a3ebf.js
├── async-c.ae11130d2a156dd0cd38.js
├── async-lodash.94774aad37c3e3b3ffd5.js
├── bundle-analyzer-report.html
├── index1.1a681451c20c863521af.js
├── index1.html
├── index2.75fd2ae406bc3e9c80e8.js
├── index2.html
├── index3.2346ee3070558cfd4514.js
├── index3.html
├── manifest.01548d0ad9752b82550b.js
└── vendor.1cebf8197aed820a040a.js
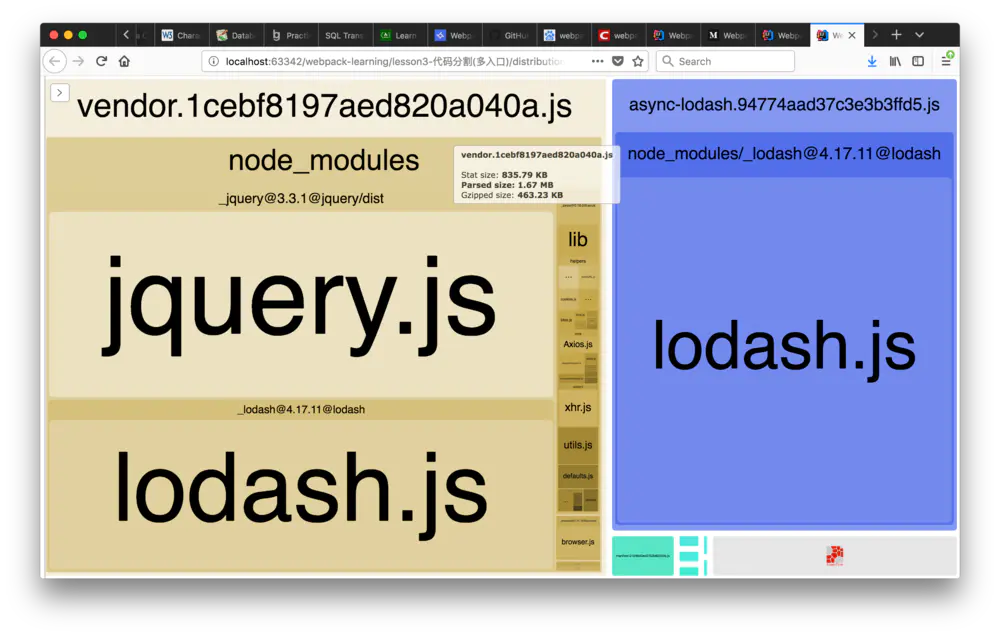
可以看到多处了一个vendor.1cebf8197aed820a040a.js,其中包含了所有共享的第三方依赖(包含jqueyr,lodash和axios):
自定义vendor时生成的bundle文件
这里需要注意的是,如果我们将name:'vendor'注释掉,得到输出为:
distribution/
├── async-b.e5df1370e07de32529d8.js
├── async-c.f895770163eede087e4b.js
├── async-lodash.bd05aecc5150c500c4ca.js
├── bundle-analyzer-report.html
├── index1.c414820b7d2a7e2c7ee1.js
├── index1.html
├── index2.6df28b7e4f8781eb350e.js
├── index2.html
├── index3.b9c0043a4618a996a90d.js
├── index3.html
├── manifest.8afba4dce338a6b3895e.js
├── vendor~index1~index2.3bcd0a827baa477b6164.js
├── vendor~index1~index3.46207ef9f2a7f266d467.js
└── vendor~index2~index3.7f319d43972c29e2233f.js
此时webpack会根据实际模块的共享关系,分开生成精确的chunk文件,比如如果A和B同时依赖于C,那么webpack会专门为A和B生成对应的chunk文件。
相比之下,当配置了name:'vendor'时,所有的依赖都在一个池子里,好处是指定了名字在稍后配置HtmlWebpackPlugin时好操作一下,缺点是如果一个chunk只依赖于池子中的某一小部分,那么也需要引用整个池子。webpack官网推荐不要配置name:'vendor',但是在多页面的场景下,笔者发现配置了name:'vendor'会更方便一下,下文在配置HtmlWebpackPlugin会讲到。
对于第3点——将所有动态依赖的第三方库放到各自单独的文件中,这一点是webpack的默认行为,因此我们不用做什么操作。
对于第4点——所有动态依赖的自研发模块分别分割到单独的文件,情况跟第3点一样,不用做操作。
对于第5点——将所有依赖的自研发模块放到同一个文件中,这里我们配置只有被依赖2次或者以上的模块才被放到common中,并且优先级低于vendor,配置如下:
...
common: {
chunks: "all",
minChunks: 2,
name:'common',
enforce: true,
priority: 5
},
...
此时的输出中会多一个common.d5aa5a7133b80ff5743b.js文件,其中包含了A-module,F-module,G-moduel,H-module和D-module;而对于E-module,由于只被C-module依赖了一次,因此直接消化在了C-module对应的输出文件中。
请注意,这里的chunks的值应该设置成all,是因为B-module和C-module是动态加载的,而他们虽然静态引用了D-module,但是要使D-module出现在common中,只能设置chunks为all。
对于第6点,配置HashedModuleIdsPlugin:
...
const webpack = require('webpack');
...
new webpack.HashedModuleIdsPlugin()
...
此时,输出的3个index.html文件为:
index1.html:
Webpack4代码分隔(多入口)-index1
index2.html:
Webpack4代码分隔(多入口)-index2
index3.html:
Webpack4代码分隔(多入口)-index3
可以看到(正如前文所说),所有index.html文件中都包含了所有的依赖文件,这当然不是我们想要的,因此修改HtmlWebpackPlugin插件:
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index1.html',
filename: 'index1.html',
chunks:['index1','manifest','vendor','common']
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index2.html',
filename: 'index2.html',
chunks:['index2','manifest','vendor','common']
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index3.html',
filename: 'index3.html',
chunks:['index3','manifest','vendor','common']
}),
可以看到,HtmlWebpackPlugin依赖于chunk的名字,这也是为什么前文提到需要为cacheGroup设置name字段的原因,不然webpack会自动为我们生成很多动态的名字,这样无法配置HtmlWebpackPlugin。
最后,总结一下,对于多入口的项目来说,配置如下:
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin;
function resolve(dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir)
}
module.exports = {
entry: {
'index1': './src/index1.js',
'index2': './src/index2.js',
'index3': './src/index3.js'
},
output: {
filename: '[name].[contenthash].js',
chunkFilename: '[name].[contenthash].js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'distribution')
},
//use inline-source-map for development:
devtool: 'inline-source-map',
//use source-map for production:
// devtool: 'source-map',
devServer: {
contentBase: './distribution'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
include: [resolve('src')],
exclude: [resolve('node_modules')]
}
]
},
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['distribution']),
new BundleAnalyzerPlugin({
openAnalyzer: false,
analyzerMode: 'static',
reportFilename: 'bundle-analyzer-report.html'
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index1.html',
filename: 'index1.html',
chunks: ['index1', 'manifest', 'vendor', 'common']
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index2.html',
filename: 'index2.html',
chunks: ['index2', 'manifest', 'vendor', 'common']
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index3.html',
filename: 'index3.html',
chunks: ['index3', 'manifest', 'vendor', 'common']
}),
new webpack.HashedModuleIdsPlugin()
],
optimization: {
runtimeChunk: {
"name": "manifest"
},
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
default: false,
vendors: false,
vendor: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
chunks: 'initial',
enforce: true,
priority: 10,
name: 'vendor'
},
common: {
chunks: "all",
minChunks: 2,
name: 'common',
enforce: true,
priority: 5
}
}
}
}
}
;
在下一篇文章中,我们将讲到CSS的处理。
作者:无知者云
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/741d9c98c395
来源:简书
简书著作权归作者所有,任何形式的转载都请联系作者获得授权并注明出处。