1. 首先简单的焦点控制在对应的布局控件里设置如下属性:
android:nextFocusUp="@id/下一个控件的id"
android:nextFocusDown=""
android:nextFocusLeft=""
android:nextFocusRight=""
分别对应该控件按下↑、↓、←、→键对应的下一个控件。
2.焦点控制逻辑:
翻看各大博客,对与AndroidTV焦点控制的理解都大同小异,接下来是我对与焦点控制的理解:
2.1Event事件机制:
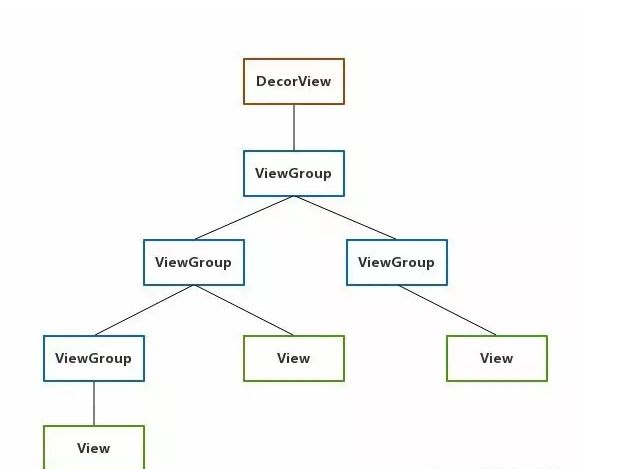
在哪些对象中进行的:
Activity -> Window -> ViewGroup -> View
包含拦截、分发、响应:
拦截发生在: onInterceptTouchEvent()方法中,当用户触发event事件后,由上层传入,当此方法返回true时,则被拦截不会继续往子view传递,由当前view的 onTouchEvent()来响该事件。
返回false时,不会被拦截,事件将继续传递 ,由子view调用当前view的 dispatchTouchEvent() 去分发, 最后由具体的控件去消费此事件。
分发:
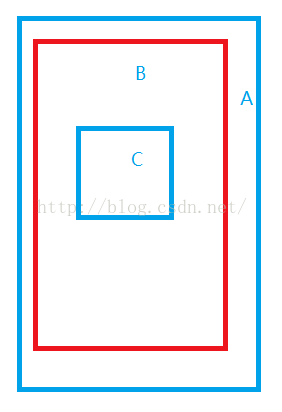
如图A:代表activity,B:代表ViewGroup(如:布局),C:代表View(如:button)
点击屏幕上的C时整个事件将会由A—B --C —B—A这样的顺序进行分发。
具体情况如下:
2.2按键事件:
KeyEvent:位于android.view下,KeyEvent主要有以下事件类型:
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_UP; 上
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN; 下
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT;左
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT;右
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER;确定键
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT; 右
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_XXX:数字键 (xx表示你按了数字几)
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK; 返回键
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_HOME;房子键
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_A: A-Z,26个字母
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_MENU菜单键。
首先看事件分发图:
如上图:
首先,KeyEvent会流转到ViewRootImpl中开始进行处理,具体方法是内部类ViewPostImeInputStage中的processKeyEvent。
代码如下:
private int processKeyEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
final KeyEvent event = (KeyEvent)q.mEvent;
...
// Deliver the key to the view hierarchy.
// 1. 先去执行mView的dispatchKeyEvent
if (mView.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
...
// Handle automatic focus changes.
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
int direction = 0;
...
if (direction != 0) {
View focused = mView.findFocus();
if (focused != null) {
// 2. 之后会通过focusSearch去找下一个焦点视图
View v = focused.focusSearch(direction);
if (v != null && v != focused) {
...
if (v.requestFocus(direction, mTempRect)) {
...
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
// Give the focused view a last chance to handle the dpad key.
if (mView.dispatchUnhandledMove(focused, direction)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
} else {
// find the best view to give focus to in this non-touch-mode with no-focus
// 3. 如果当前本来就没有焦点视图,也会通过focusSearch找一个视图
View v = focusSearch(null, direction);
if (v != null && v.requestFocus(direction)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
}
}
return FORWARD;
}
看上面的代码可以了解:
先执行mView的dispatchKeyEvent()方法,再通过focusSearch()去找下一个焦点视图,如果当前没由焦点视图也会执行focusSearch()找一个视图。
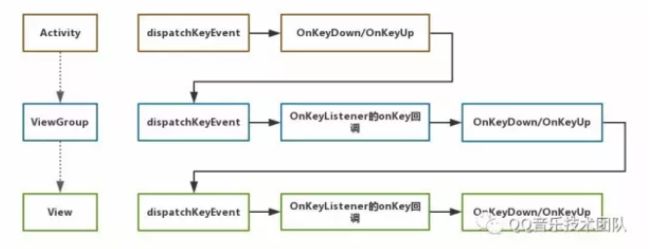
2.2.1 dispatchKeyEvent()执行流程
DecorView →Activity→ViewGroup→view。
DecorView 的 dispatchKeyEvent ():
public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) { ... ... if (!mWindow.isDestroyed()) { // Activity实现了Window.Callback接口,具体可以参考 Activity.java 源码. final Window.Callback cb = mWindow.getCallback(); // mFeatureId < 0,表示为 application 的 DecorView. // cb.dispatchKeyEven 调用的是 Activity 的 dispatchKeyEven. final boolean handled = cb != null && mFeatureId < 0 ? cb.dispatchKeyEvent(event) : super.dispatchKeyEvent(event); // 是否消耗掉事件. if (handled) { return true; } } return isDown ? mWindow.onKeyDown(mFeatureId, event.getKeyCode(), event) : mWindow.onKeyUp(mFeatureId, event.getKeyCode(), event); }
这里将会调用Activty的dispatchKeyEvent();
Activity 的 dispatchKeyEvent ():
// 补充知识点: // 这就是为何在 Activity 直接 return true,事件被消耗,就不执行焦点搜索等等操作了. // 所以这里也是可以做 焦点控制的,最好是在 event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN 进行. // 因为android 的 ViewRootlmpl 的 processKeyEvent 焦点搜索与请求的地方 进行了判断 // if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) { ... ... Window win = getWindow(); // 调用 PhoneWindow 的 superDispatchKeyEvent // 里面又调用 mDecor.superDispatchKeyEvent(event) // mDecor 为 DecorView. if (win.superDispatchKeyEvent(event)) { return true; } View decor = mDecor; if (decor == null) decor = win.getDecorView(); // onKeyDown,onKeyUp,onKeyLongPress 等等回调的处理. // 只有 onKeyDown return true 可以进行焦点控制, // 因为android 的 ViewRootlmpl 的 processKeyEvent 焦点搜索与请求的地方 进行了判断 // if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) return event.dispatch(this, decor != null ? decor.getKeyDispatcherState() : null, this); }
ViewGroup的dispatchKeyEvent():
@Override public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) { ... if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_FOCUSED | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) == (PFLAG_FOCUSED | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) { // 1.1 以View的身份处理KeyEvent if (super.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) { return true; } } else if (mFocused != null && (mFocused.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS) == PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS) { // 1.2 以ViewGroup的身份把KeyEvent交给mFocused处理 if (mFocused.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) { return true; } } ... return false; }
通过flag的判断,有两个处理路径,也可以看到在处理keyEvent时,ViewGroup扮演两个角色:
View的角色,也就是此时keyEvent需要在自己与其他View之间流转。:调用自身的dispathKeyEvent()。
ViewGroup的角色,此时keyEvent需要在自己的子View之间流转 。:调用当前焦点子View的dispatchKeyEvent()。
再来看看view的dispatchKeyEvent():
public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) { ... ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo; // 1.3 如果设置了mOnKeyListener,则优先走onKey方法 if (li != null && li.mOnKeyListener != null && (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED && li.mOnKeyListener.onKey(this, event.getKeyCode(), event)) { return true; } // 1.4 把View自己当作参数传入,调用KeyEvent的dispatch方法 if (event.dispatch(this, mAttachInfo != null ? mAttachInfo.mKeyDispatchState : null, this)) { return true; } ... return false; }
View这里,会优先处理OnKeyListener的onKey回调。然后才可能会走KeyEvent的dispatch,最终走到View的OnKeyDown或者OnKeyUp。
大体的流转顺序总结如下图:
其中任何一步都可以通过return true的方式来消费掉这个KeyEvent,结束这个分发过程。
按键事件分发结束,接下来让我们看看如和查找焦点。
3.焦点查找方法。
如果dispatchKeyEvent没有消耗掉KeyEvent,会由系统来处理焦点移动。
通过view的focusSearch方法找到下一个获取焦点的View,然后调用requestFocus设置焦点。
3.1:focusSearch()
// View.java public View focusSearch(@FocusRealDirection int direction) { if (mParent != null) { return mParent.focusSearch(this, direction); } else { return null; } }
由上面的代码可以看出,View不会直接去查找,而是会交给其parent的focusSearch方法去查找,也就是ViewGroup的focusSearch()方法去查找。
ViewGroup的focusSearch()方法:
// ViewGroup.java public View focusSearch(View focused, int direction) { if (isRootNamespace()) { // root namespace means we should consider ourselves the top of the // tree for focus searching; otherwise we could be focus searching // into other tabs. see LocalActivityManager and TabHost for more info return FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(this, focused, direction); } else if (mParent != null) { return mParent.focusSearch(focused, direction); } return null; }
这里会判断是否为根布局,也就是顶层布局,如果是则最后交给FocusFinder去查找。
如果不是则会接调用上层parent的focusSearch()。
isRootNamespace的()
/** * {@hide} * * @param isRoot true if the view belongs to the root namespace, false * otherwise */ public void setIsRootNamespace(boolean isRoot) { if (isRoot) { mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_IS_ROOT_NAMESPACE; } else { mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_IS_ROOT_NAMESPACE; } }
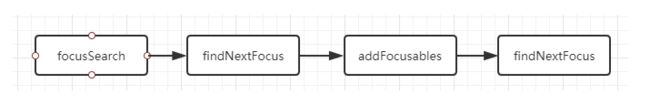
3.2:findNextFocus():
位于顶层的ViewGroup把自己和当前焦点(View)以及方向传入。
findNextFocus()代码:
// FocusFinder.java public final View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, int direction) { return findNextFocus(root, focused, null, direction); } private View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, Rect focusedRect, int direction) { View next = null; if (focused != null) { // 2.1 优先从xml或者代码中指定focusid的View中找 next = findNextUserSpecifiedFocus(root, focused, direction); } if (next != null) { return next; } ArrayListfocusables = mTempList; try { focusables.clear(); root.addFocusables(focusables, direction); if (!focusables.isEmpty()) { // 2.2 其次,根据算法去找,原理就是找在方向上最近的View next = findNextFocus(root, focused, focusedRect, direction, focusables); } } finally { focusables.clear(); } return next; }
这里root是上面isRootNamespace()为true的ViewGroup,focused是当前焦点视图
优先找开发者指定的下一个focus的视图 ,就是在xml或者代码中指定NextFocusDirection Id的视图。
其次,根据算法去找,原理就是找在方向上最近的视图。
4.按键焦点查找流程
4.1界面第一次进入的时候,是如何获取到焦点的
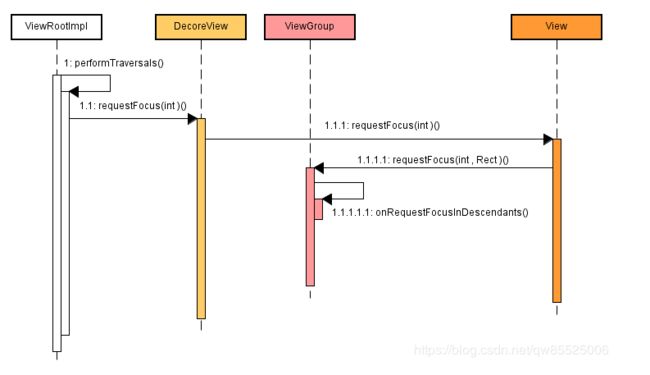
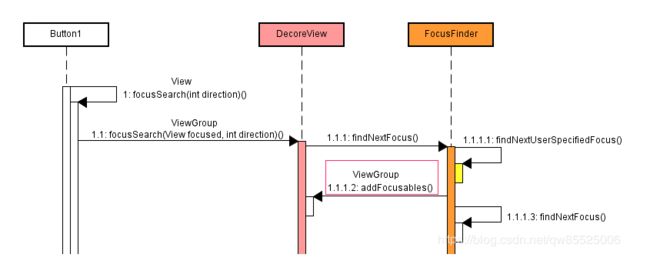
先看下DecoreView的流程图:
上图ViewRootImpl类中 performTraversals方法:
.. ... if (mFirst) { if (mView != null) { if (!mView.hasFocus()) { // 调用 View 的 requestFocus(int direction) mView.requestFocus(View.FOCUS_FORWARD); } ... ... } ... ...
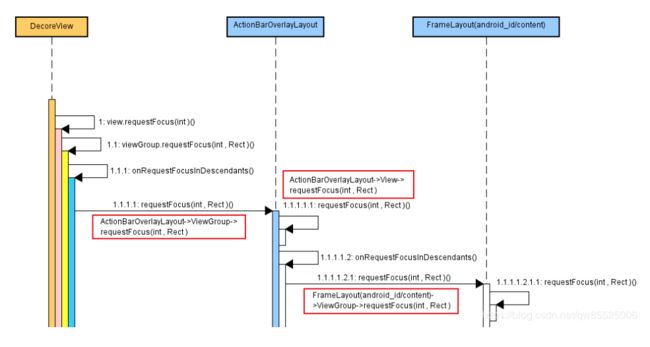
整体的过程:
ViewRootlmpl.performTraversals→DecoreView.requestFocus→ActionBarOverlayLayout.requestFocus→FrameLayout(android:id/content).requestFocus→FrameLayout(activity_test.xml).requestFocus→Button1(activity_test.xml).requestFocus
代码步骤:
View.java public final boolean requestFocus(int direction) { // 因为 DecoreView 继承 ViewGroup // ViewGroup 重写了此函数, // 会调用 ViewGroup 的 requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) return requestFocus(direction, null); } ViewGroup.java public boolean requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) { // 关注内容: // 处理 DescendantFocusabilit // 1)FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS 先分发给Child View进行处理,如果所有的Child View都没有处理,则自己再处理 // 2)FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS ViewGroup先对焦点进行处理,如果没有处理则分发给child View进行处理 // 3)FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS ViewGroup本身进行处理,不管是否处理成功,都不会分发给ChildView进行处理 // setDescendantFocusability 可以设置. int descendantFocusability = getDescendantFocusability(); switch (descendantFocusability) { case FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS: return super.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect); case FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS: { // 其它的 ActionBarOverlayLayout,Content等继承ViewGroup // 默认进入 FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS,因为 ViewGroup 初始化的时候设置了 // setDescendantFocusability(FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS); // mViewFlags 判断 FOCUSABLE_MASK,FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE. // Button 以上的父布局,不满足以上条件判断,全部都是 直接 return false. final boolean took = super.requestFocus( direction, previouslyFocusedRect); // took=false, 调用 onRequestFocusInDescendants 遍历子控件进行请求 return took ? took : onRequestFocusInDescendants(direction, previouslyFocusedRect); } case FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS: { // DecoreView 进入这里,因为 PhoneWindow 给 DecoreView 初始化 设置 // setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS); // setIsRootNamespace(true); // 像 RecyclerView, Leanback 也会进入这里. // 遍历子控件进行请求 final boolean took = onRequestFocusInDescendants( direction, previouslyFocusedRect); // took=true,子控件有焦点,不调用 super.request...,反之. return took ? took : super.requestFocus( direction, previouslyFocusedRect); } ... ... } } View.java public boolean requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) { return requestFocusNoSearch(direction, previouslyFocusedRect); } ViewGroup.java // 补充知识点: onRequestFocusInDescendants 是可以做焦点记忆控制的. protected boolean onRequestFocusInDescendants(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) { .. ... for (int i = index; i != end; i += increment) { View child = children[i]; if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) { // if (child.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect)) { return true; } } } return false; }
Button1获取焦点:
关键代码是 View.java 的函数 handleFocusGainInternal : mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FOCUSED 和 mParent.requestChildFocus(this, this)
View.java private boolean requestFocusNoSearch(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) { // need to be focusable // Button 默认 android:focusable="true" // button1 以上的父布局都没有设置此类属性,进入这里,直接就 return false. if ((mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE_MASK) != FOCUSABLE || (mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != VISIBLE) { return false; } // need to be focusable in touch mode if in touch mode // 当 button1 没有设置 android:focusableInTouchMode="true" 的时候, // 直接 return false,那么界面上是没有任何控件获取到焦点的. // 鼠标|触摸支持的属性. if (isInTouchMode() && (FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE != (mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE))) { return false; } // need to not have any parents blocking us if (hasAncestorThatBlocksDescendantFocus()) { return false; } // 关键函数 handleFocusGainInternal(direction, previouslyFocusedRect); return true; } void handleFocusGainInternal(@FocusRealDirection int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) { if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) == 0) { // 关键代码,设置 有焦点的标志位. // 这个时候 button1 已经标志上焦点 mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FOCUSED; // 获取父布局的老焦点. View oldFocus = (mAttachInfo != null) ? getRootView().findFocus() : null; // 调用此函数,告诉上一层父布局,让它做一些事情. if (mParent != null) { mParent.requestChildFocus(this, this); } // 此函数是全局焦点监听的回调. // 调用方式: View.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalFocusChangeListener if (mAttachInfo != null) { mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnGlobalFocusChange(oldFocus, this); } // 回调处理. onFocusChanged(true, direction, previouslyFocusedRect); // 刷新按键的 selector drawable state状态 refreshDrawableState(); } } ViewGroup.java public void requestChildFocus(View child, View focused) { if (getDescendantFocusability() == FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS) { return; } // Unfocus us, if necessary super.unFocus(focused); // We had a previous notion of who had focus. Clear it. if (mFocused != child) { if (mFocused != null) { mFocused.unFocus(focused); } // 保存上一级的焦点view. mFocused = child; } // 一层层调用回去父布局,相当于 // FrameLayout(activity_test.xml) 的 mFocused 是 Button1. // FrameLayout(android:id/content) 的 mFocused 是 FrameLayout(activity_test.xml) // ActionBarOverlayLayout 的 mFocused 是 FrameLayout(android:id/content) // 最后 DecoreView 的 mFocused 是 ActionBarOverlayLayout // 在最后的后面,ViewRootImpl 会调用 // requestChildFocus,又会再次调用 // performTraversals刷新界面.(再执行 layout, draw) // 形成了一个关联, dispatchKeyEvent 的 mFocused 也在使用. if (mParent != null) { mParent.requestChildFocus(this, focused); } } // ViewRootImpl.java @Override public void requestChildFocus(View child, View focused) { checkThread(); scheduleTraversals(); }
初步获取焦点已经了解,接下来看看焦点是如何从 view2 →view2的。
4.2按键焦点的搜索过程
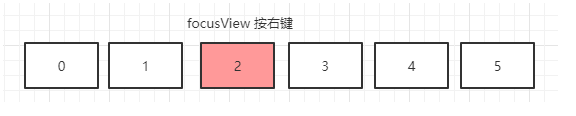
focusView(2) 按下右键后:由上面的3.焦点查找方法可以得出下图:
在没有消耗 dispatchKeyEvent的情况下:
FocusSearch 一层层上去,调用 FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus… … 后,在 …addFocusables 下,将所有带焦点属性的 view 全部加到数组里面去,然后通用方向,位置等查找相近的view. 最后找到的是 focusView(3).
private int processKeyEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) { ... ... // 以上代码不消耗事件. // 判断 action 为 ACTION_DOWN 才处理焦点搜索以及请求. if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) { // 根据按键判断,设置 direction 属性. if (direction != 0) { // 一层层查找(根据mFocused),最后获取到 button1. View focused = mView.findFocus(); if (focused != null) { // button1_view 调用 focusSearch(), 右键,direction=66 View v = focused.focusSearch(direction); // 最终返回 v = button2 if (v != null && v != focused) { // do the math the get the interesting rect // of previous focused into the coord system of // newly focused view focused.getFocusedRect(mTempRect); if (mView instanceof ViewGroup) { ((ViewGroup) mView).offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords( focused, mTempRect); ((ViewGroup) mView).offsetRectIntoDescendantCoords( v, mTempRect); } // button2 View 调用 requestFocus // 这里的过程 和 第一次获取焦点button1请求是一样的. if (v.requestFocus(direction, mTempRect)) { // 播放音效 playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants .getContantForFocusDirection(direction)); return FINISH_HANDLED; } } // 进行最后的垂死挣扎, // 这里其实可以处理一些焦点问题或者滚动翻页问题. // 滚动翻页的demo可以参考 原生 Launcher 的 Workspace.java // Give the focused view a last chance to handle the dpad key. if (mView.dispatchUnhandledMove(focused, direction)) { return FINISH_HANDLED; } } else { // 这里处理第一次无焦点 view 的情况. // 基本上和有焦点view 的情况差不多. View v = focusSearch(null, direction); if (v != null && v.requestFocus(direction)) { return FINISH_HANDLED; } } } } ... ... }
button1下一个焦点搜索流程图:
View v = focused.focusSearch(direction); # focused=>button1 direction=>66
Button1_View→focusSearch(int direction)→FrameLayout(activity_test.xml)_ViewGroup→focusSearch(View focused, int direction)→。。。→FrameLayout(activity_test.xml)_ViewGroup→
focusSearch(View focused, int direction)→DecoreView_ViewGroup→FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(this, focused, direction)→FocusFinder.findNextFocus()→ViewGroup.addFocusables()->。。。
代码流程:
View.java public View focusSearch(@FocusRealDirection int direction) { if (mParent != null) { // button1 的父布局ViewGroup调用 focusSearch return mParent.focusSearch(this, direction); } else { return null; } } ViewGroup.java // 像 RecyclerView 会重写 focusSearch 进行焦点搜索. // 也是调用的 FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus // leanback 的 GridLayoutmanger 也重写了 onAddFocusables. public View focusSearch(View focused, int direction) { // 只有 DecoreView 设置了 setIsRootNamespace // 最终由 DecoreView 进入这里. if (isRootNamespace()) { // 传入参数(this: DecoreView focused: button1 direction: 66) return FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(this, focused, direction); } else if (mParent != null) { return mParent.focusSearch(focused, direction); } return null; } FocusFinder.java findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, int direction)->findNextFocus(root, focused, null, direction)-> private View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, Rect focusedRect, int direction) { View next = null; if (focused != null) { // 关于XML布局中的 android:nextFocusRight 等等的查找. next = findNextUserSpecifiedFocus(root, focused, direction); } if (next != null) { return next; } ArrayListfocusables = mTempList; try { focusables.clear(); // 要进行 findNextFocus,关键在于 addFocusables,一层层调用下去. // DecorView_View.addFocusables // DecorView_ViewGroup.addFocusables // ActionBarOverlayLayout_ViewGroup.addFocusables // FrameLayout(android:id/content)_ViewGroup.addFocusables // FrameLayout(activity_test.xml)_ViewGroup.addFocusables // 到最后 button1, button2 添加到 views 数组中,也就是 focusables . root.addFocusables(focusables, direction); if (!focusables.isEmpty()) { // 关键函数 findNextFocus,想深入了解是如何查找到下一个焦点的, // 可以去看看源码,这里不进行过多篇幅的讲解. // focusables 数组有 button1, button2 // 内部调用 findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection,这里进行了一些判断,查找某个方向比较近的view. next = findNextFocus(root, focused, focusedRect, direction, focusables); } } finally { focusables.clear(); } return next; } ViewGroup.java public void addFocusables(ArrayList views, int direction, int focusableMode) { final int focusableCount = views.size(); final int descendantFocusability = getDescendantFocusability(); ... ... for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View child = children[i]; // 循环 child view 调用 addFocusables,一层层调用下去,将满足条件的添加进 views 数组. if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) { child.addFocusables(views, direction, focusableMode); } } } if ... ... // 调用 view 的 addFocusables,父布局是不满足条件的,直接返回了. super.addFocusables(views, direction, focusableMode); } } View.java public void addFocusables(ArrayList views, int direction, int focusableMode) { if (views == null) { return; } if (!isFocusable()) { return; } if ((focusableMode & FOCUSABLES_TOUCH_MODE) == FOCUSABLES_TOUCH_MODE && isInTouchMode() && !isFocusableInTouchMode()) { return; } // button1 以上条件满足,加入views数组. // button2 以上条件也满足,加入views数组. // 同理,焦点记忆的原理就很简单了,后续会讲解. views.add(this); }