史上最强图解Treap总结, 不是浅谈!
大家都很强, 可与之共勉。
Treap = Tree + Heap.
树堆,在数据结构中也称Treap,是指有一个随机附加域满足堆的性质的二叉搜索树,其结构相当于以随机数据插入的二叉搜索树。其基本操作的期望时间复杂度为O(logn)。相对于其他的平衡二叉搜索树,Treap的特点是实现简单,且能基本实现随机平衡的结构。
Treap 维护堆的性质的方法只用到了左旋和右旋, 编程复杂度比Splay小一点, 并且在两者可完成的操作速度有明显优势
开始
每一个节点需要保存至少四个信息,当前节点的数值 ( val ), 优先级 ( key ), 左右儿子 ( ls, rs )。 除此之外, 可能还会保存以该节点为根的树的大小 ( siz ), 以及该节点相同的数个数 ( same )。
typedef class TreapNode {
public:
int val;
int siz, key, same;
TreapNode *ls, *rs;
inline TreapNode ( ) { }
inline TreapNode ( int val, TreapNode* & node ) : val ( val ), key ( rand ( ) ), siz ( 1 ), same ( 1 ) { ls = rs = node; }
inline void update ( ) {
siz = ls -> siz + rs -> siz + same;
}
} Node;当然, 博主是用的指针实现, 指针相比数组有更多的细节需要注意。 在BZOJ-3224中大概比RBT慢2ms。
关于随机函数
< cstdlib > 中的rand ( ) 速度比较慢, 而在数据结构中对于素的如果要求过高, 可以使用手写 rand ( )。
inline int rand ( ) {
static int seed = 233;
return seed = ( int ) seed * 482711LL % 2147483647;
}其中seed可以随便取一个非零的数。 具体原理是什么, 当然我也不会证明了。
首先是旋转操作
分为左旋和右旋, 我习惯用Zag, Zig来叫。
具体的代码如下
一定要记住的是当前节点的要旋转节点为null时, 不转。 否则root很有可能变成null, 将会影响一系列的操作。
inline void Zig ( Node* &nd ) {
tmp = nd -> ls;
if ( tmp == null ) return;
nd -> ls = tmp -> rs;
tmp -> rs = nd;
tmp -> siz = nd -> siz;
nd -> update ( );
nd = tmp;
}
inline void Zag ( Node* &nd ) {
tmp = nd -> rs;
if ( tmp == null ) return;
nd -> rs = tmp -> ls;
tmp -> ls = nd;
tmp -> siz = nd -> siz;
nd -> update ( );
nd = tmp;
}接下来是插入操作
插入的过程中, 一定要满足Treap的特点。
即左儿子的值比当前节点小, 右儿子的值比当前节点大。
与维护关于key值堆的性质
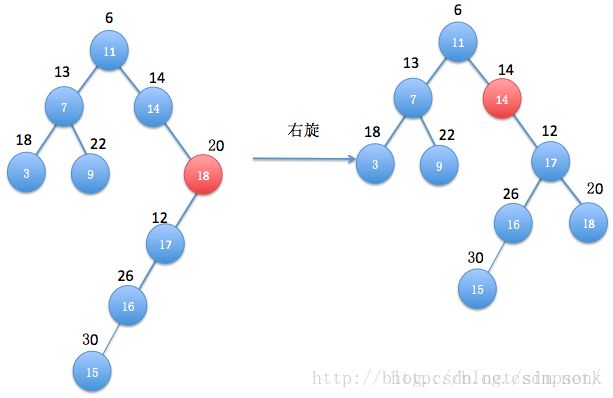
插入值为18,优先级为20的结点后,违反了最小堆的定义,因此要进行调整,把优先级小的往上提,也就是小的优先级插入的是右子树,那么需要进行一次左旋转( Zag ),这里进行一次旋转过后就OK了。
同样,这种情况左旋转,旋转后发现还是不满足最小堆的定义,并且小优先级的结点在左子树,所以还需要进行右旋转 ( Zig ),如下图所示:
右旋后,还是不满足性质, 还需要左旋 ( Zag ):
当然这是在递归调用之中实现的。
如果该节点为null, 就新开一个。 用构造函数会很方便。
如果遇到插入两个相同的值, 那么该节点的same直接+1就好。
完成每一个节点的插入, 都要update
这个update()操作的优秀之处就在于null空节点, 若使用NULL系统自带的空指针, 那么直接指向左右儿子就会指出去, 报错。。。
代码如下:
inline void Insert ( Node* &nd, int& val ) {
if ( nd == null ) {
nd = ++tail;
*nd = Node ( val, null );
return;
}
if ( nd -> val == val ) ++nd -> same;
else {
if ( val > nd -> val ) {
Insert ( nd -> rs, val );
if ( nd -> rs -> key < nd -> key )
Zag ( nd );
} else {
Insert ( nd -> ls, val );
if ( nd -> ls -> key < nd -> key )
Zig ( nd );
}
}
nd -> update ( );
}之后是删除操作
注意:
这是二叉树删除法
对比插入, 相对于删除要复杂一些, 可以直接看代码明白。
不要忘了update()!!!
inline void Delete ( Node* &nd, int x ) {
if ( nd == null ) return;
if ( nd -> val == x ) {
if ( nd -> same > 1 ) {
--nd -> same; nd -> update ( ); return;
}
if ( nd -> ls == null && nd -> rs == null ) { nd = null; return; }
else if ( nd -> ls == null && nd -> rs ) nd = nd -> rs;
else if ( nd -> ls && nd -> rs == null ) nd = nd -> ls;
if ( nd -> ls -> key < nd -> rs -> key ) { Zig ( nd ); Delete ( nd -> rs, x ); }
else { Zag ( nd ); Delete ( nd -> ls, x ); }
} else if ( x > nd -> val ) Delete ( nd -> rs, x );
else Delete ( nd -> ls, x );
nd -> update ( );
}
主要的就是这两个那么还有前驱,后驱,排名,第K大。
那么唯一注意的是前后驱在题目中的定义。
如BZOJ-1588
前后驱可以等于节点数值本身
那么就应该这么写
inline int query_pre ( Treap* &nd, int val ) {
if ( nd == null ) return 0xefefefef;
if ( val < nd -> val )
return query_pre ( nd -> ls, val );
return max ( nd -> val, query_pre ( nd -> rs, val ) );
}
inline int query_post ( Treap* &nd, int val ) {
if ( nd == null ) return 0x7fffffff;
if ( val > nd -> val )
return query_post ( nd -> rs, val );
return min ( nd -> val, query_post ( nd -> ls, val ) );
}如果是BZOJ-3224, 读错题了就Wa爽了。。。
inline void query_pre ( Node* &nd, int &ans, int val ) {
if ( nd == null ) return;
if ( val > nd -> val )
ans = nd -> val, query_pre ( nd -> rs, ans, val );
else query_pre ( nd -> ls, ans, val );
}
inline void query_post ( Node* &nd, int &ans, int val ) {
if ( nd == null ) return;
if ( val < nd -> val )
ans = nd -> val, query_post ( nd -> ls, ans, val );
else query_post ( nd -> rs, ans, val );
}当然根据定义也可以用kth 与 rank 两者一起求出前后驱。
具体代码及细节请读者自己推敲
给出完整版参考代码
注意的是 Init( ) 中的 null 维护的节点信息。
#include