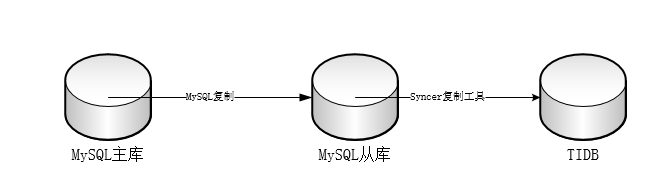
因生产环境mysql中有较多复杂sql且运行效率低,因此采用tidb作为生产环境的从库进行部分慢sql及报表的读写分离。其中MySQL至TIDB采用Syncer工具同步。
关于TIDB的安装及Syncer可参照官网指引进行,搭建的主从复制架构如下:
因该方式中TiDB的数据是通过Syncer同步的,且TIDB无show slave status命令查看复制情况,故自己开发脚本对MySQL至TIDB的复制延迟进行监控,并且将结果进行图形化展示以便于直观分析,而且此方法也可以监控MySQL主从延迟,类似于percona toolkit的pt-heartbeat 。
一、 准备工作
1. 监控所需工具
监控:Python 2.7及以上,安装pymysql(或MySQLdb),其中linux升级python及pip安装可参考之前的博文
Python升级:https://www.cnblogs.com/gjc592/p/9223005.html
pip安装: https://www.cnblogs.com/gjc592/p/9272209.html
图形化展示:Python plotly、matplotlib或pandas包
2. 监控延迟思路
1)创建监控数据库(monitor)及相关表(monitor_time,monitor_result)
2)每隔固定时间(看监控精确度,如0.5s)将当期时间或时间戳的结果更新到mysql的监控表中
3)对比mysql与tidb对应的监控库(monitor库)中的monitor_time表的时间差,并将结果记录在monitor_result里
3. 可视化展示结果
用Python 的plotly、matplotlib或pandas等展示监控结果
二、延时监控实施步骤
1. 创建数据库及相关表,并将其加入Syncer同步中
-- 创建监控数据库monitor; CREATE DATABASE `monitor`; USE `monitor`; -- 创建监控时间表monitor_time; CREATE TABLE `monitor_time` ( `t` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- 初始化数据,因后面监控程序定时更新该条记录 insert into monitor_time select 1; -- 创建监控结果表monitor_result; CREATE TABLE `monitor_result` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `t` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '延迟时间', `add_time` timestamp NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '监控记录生成时间', `t_mysql` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'mysql主从延迟时长', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
2. 创建监控账号并授权
单独创建一个用于监控该延迟的账号,并添加相应的权限。
CREATE USER monitor@'192.168.3.42' IDENTIFIED BY 'monitor'; GRANT SELECT ,INSERT ,UPDATE ON monitor.* TO monitor@'192.168.3.42';
3. 监控脚本
每隔0.5s更新一次monitor_time 表,自定义时间(如例子中10s)获取一次监控结果,并将记录写入数据库中
import os,time import pymysql while True: t = time.time() t1= int(round(t * 1000)) conn = pymysql.connect(host='*.*.*.*',port=3306,user='monitor',passwd='monitor') cur = conn.cursor() sql_update = "update monitor.monitor_time set t="+str(t1) cur.execute(sql_update) conn.commit() conn.close() time.sleep(0.5)
import os,time import pymysql while True: conn_sor = pymysql.connect(host='*.*.*.*',port=3306,user='monitor',passwd='monitor') cur_sor = conn_sor.cursor() conn_138 = pymysql.connect(host='*.*.*.*',port=3306,user='monitor',passwd='monitor') cur_138 = conn_138.cursor() conn_des = pymysql.connect(host='*.*.*.*',port=4000,user='monitor',passwd='monitor') cur_des = conn_des.cursor() sql_get_time = "select t from monitor.monitor_time " cur_sor.execute(sql_get_time) v_src_tuple=cur_sor.fetchone() t_sor=v_src_tuple[0] cur_des.execute(sql_get_time) v_des_tuple=cur_des.fetchone() t_des=v_des_tuple[0] cur_138.execute(sql_get_time) v_138_tuple=cur_138.fetchone() t_138=v_138_tuple[0] t1 = t_sor/1000 - t_des/1000 t2 = t_sor/1000 - t_138/1000 sql_insert = "insert into monitor.monitor_result(t,t_mysql) select "+str(t1)+","+str(t2) cur_sor.execute(sql_insert) conn_sor.commit() conn_sor.close() conn_des.close() time.sleep(10)
将2个脚本放在监控服务器上运行
python monitor_tidb.py &
python get_tidb_delay.py &
三 可视化展示
以下是其中一种实现方式,其他如折线图方式可执行修改
# __author__ : 'GJC' # __created__ : '2018/9/17' # coding=utf-8 import pymysql import plotly.plotly from plotly.graph_objs import * import plotly.graph_objs as abc import matplotlib.pyplot as plt host = "*.*.*.*" user = "monitor" passwd = "monitor" db = "monitor" port = 3306 charset = "utf8" conn = pymysql.connect( host=host, port=port, user=user, passwd=passwd, db=db, charset=charset, ) cur = conn.cursor() re = cur.execute("SELECT add_time,t,t_mysql FROM monitor.monitor_result_t ") dfs = cur.fetchall() listx = [] listy = [] listy2 = [] for row in dfs: listx.append(row[0]) listy.append(row[1]) listy2.append(row[2]) cur.close() conn.commit() conn.close() length = listy.__len__() data_1 = abc.Scatter( x=listx, y=listy, name='syncer_delay_time_tidb', mode='markers', marker=dict( size=10, color="rgba(255,47,167,.9)", line=dict( width=2, color='rgb(2,2,2)' ) ) ) data_2 = abc.Scatter( x=listx, y=listy2, name='syncer_delay_time_mysql', mode='markers', marker=dict( size=10, color="rgba(255,47,167,.9)", line=dict( width=2, color='rgb(3,3,3)' ) ) ) data1 = Data([data_1]) plotly.offline.plot(data1) data2 = Data([data_2]) plotly.offline.plot(data2)
部分时间段效果如下:
耿小厨已开通个人微信公众号,想进一步沟通或想了解其他文章的同学可以关注我
![]()