Netty源码阅读之NioEventLoop简析
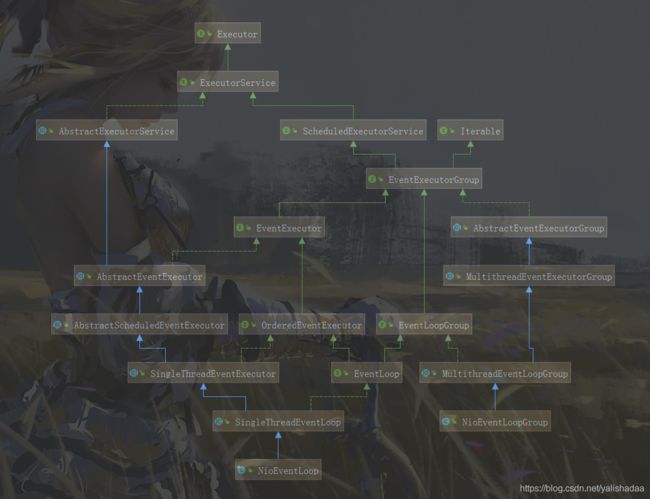
在Netty中NioEventLoop以及NioEventLoopGroup是很重要的两个类,而NioEventLoopGroup主要是对NioEventLoop进行管理;首先来看一下这两个类的关系图(错综复杂):
图 1
1. NioEventLoopGroup初始化流程
通过分析NioEventLoopGroup的构造方法的调用栈我们能够看到在io.netty.channel.MultithreadEventLoopGroup的构造方法中进行了创建:
当未指定具体的线程数目的时候,Netty会提出一个默认的线程数:DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);
}而该数值在同一类下的静态代码块中进行了设置:
static {
DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt(
"io.netty.eventLoopThreads", Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2));
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads: {}", DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS);
}
}显而易见,默认的线程数量为2*cpu数目。
继续深入,打开io.netty.util.concurrent.MultithreadEventExecutorGroup这个类,查看其构造方法:
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor,
EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) {
if (nThreads <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));
}
if (executor == null) {
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());//创建线程执行器
}
//构造NioEventLoop的过程
children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception type
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {
if (!success) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
children[j].shutdownGracefully();
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
EventExecutor e = children[j];
try {
while (!e.isTerminated()) {
e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {
// Let the caller handle the interruption.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);//生成线程选择器
final FutureListener通过上面的代码流程可知,首先是创建线程执行器,
线程执行器中传入一个默认的线程工厂:newDefaultThreadFactory,在线程工厂中进行nio线程的创建并进行线程的命名:
public static String toPoolName(Class poolType) {
if (poolType == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("poolType");
}
String poolName = StringUtil.simpleClassName(poolType);
switch (poolName.length()) {
case 0:
return "unknown";
case 1:
return poolName.toLowerCase(Locale.US);
default:
if (Character.isUpperCase(poolName.charAt(0)) && Character.isLowerCase(poolName.charAt(1))) {
return Character.toLowerCase(poolName.charAt(0)) + poolName.substring(1);
} else {
return poolName;
}
}
}线程名称类似于:nioEventLoop-x-x这种形式;同时,将根据线程数目创建一个同等容量的EventExecutor数组,数组中通过newChild()方法塞入一个EventExecutor对象,当然这只是一个抽象方法,具体的实现根据不同的类来决定,若在这个过程中有一个线程发生了异常,则会从当前的这个线程开始,将前面从第一个线程开始,关闭对应的线程执行器;之后再初始化线程选择器工厂,并通过轮询算法来处理本次的所有EventLoop事件,加入线程工厂的时候,采用了策略模式,会有一个2次幂的判断,如果上述的数组长度为2的幂次方,那么选用PowerOfTowEventExecutorChooser(executors)
,否则将选用GenericEventExecutorChooser(executors)
public EventExecutorChooser newChooser(EventExecutor[] executors) {
if (isPowerOfTwo(executors.length)) {
return new PowerOfTowEventExecutorChooser(executors);
} else {
return new GenericEventExecutorChooser(executors);
}
}而这两种方式主要在遍历数组的时候存在区别,当为2的次幂的时候,采用如下方式进行遍历:
public EventExecutor next() {
return executors[idx.getAndIncrement() & executors.length - 1];
}反之则采用如下的方式进行数组的遍历:
public EventExecutor next() {
return executors[Math.abs(idx.getAndIncrement() % executors.length)];
}由上面的分析,我们可以得出Netty中的EventLoop处理关系图:
图 2
2. NioEventLoop启动逻辑
启动的入口为:io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#doBind0()方法:
private static void doBind0(
final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel,
final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// This method is invoked before channelRegistered() is triggered. Give user handlers a chance to set up
// the pipeline in its channelRegistered() implementation.
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {
channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}主要是进行端口的绑定。
接着往下查看execute()方法:
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
if (inEventLoop) {
addTask(task);
} else {
startThread();
addTask(task);
if (isShutdown() && removeTask(task)) {
reject();
}
}
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}在execute()方法中,首先通过inEventLoop()方法判断当前的线程是否是在eventLoop中,值得注意的是,每一个NioEventLoop都维护着一个taskQueue,读写任务都将被丢进这个队列中进行维护:
@Override
protected Queue newTaskQueue(int maxPendingTasks) {
// This event loop never calls takeTask()
return PlatformDependent.newMpscQueue(maxPendingTasks);
} 这是Netty实现异步串行无锁化的关键;回归正题,如果已经在evetLoop中了,那么直接将当前的任务添加到任务队列中,否则将执行doStartThread()方法:
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (interrupted) {
thread.interrupt();
}
boolean success = false;
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception from an event executor: ", t);
} finally {
for (;;) {
int oldState = STATE_UPDATER.get(SingleThreadEventExecutor.this);
if (oldState >= ST_SHUTTING_DOWN || STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, oldState, ST_SHUTTING_DOWN)) {
break;
}
}
// Check if confirmShutdown() was called at the end of the loop.
if (success && gracefulShutdownStartTime == 0) {
logger.error("Buggy " + EventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + " implementation; " +
SingleThreadEventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + ".confirmShutdown() must be called " +
"before run() implementation terminates.");
}
try {
// Run all remaining tasks and shutdown hooks.
for (;;) {
if (confirmShutdown()) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
try {
cleanup();
} finally {
STATE_UPDATER.set(SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, ST_TERMINATED);
threadLock.release();
if (!taskQueue.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn(
"An event executor terminated with " +
"non-empty task queue (" + taskQueue.size() + ')');
}
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
}
}
});
}通过SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run()方法,Netty中的channel将不断轮询处理channel事件:
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
default:
// fallthrough
}
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}在事件循环中不仅需要处理IO事件也需要处理非IO事件,IO事件处理通过processSelectedKeys方法来进行,而非IO事件通过runAllTasks()方法进行处理,IO事件以及非IO事件的默认占比各为50%,值得注意的是:SelectStrategy.SELECT这种情况:
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp) throws IOException {
Selector selector = this.selector;
try {
int selectCnt = 0;
long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
for (;;) {
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
if (selectCnt == 0) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
}
break;
}
// If a task was submitted when wakenUp value was true, the task didn't get a chance to call
// Selector#wakeup. So we need to check task queue again before executing select operation.
// If we don't, the task might be pended until select operation was timed out.
// It might be pended until idle timeout if IdleStateHandler existed in pipeline.
if (hasTasks() && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
selectCnt ++;
if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get() || hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks()) {
// - Selected something,
// - waken up by user, or
// - the task queue has a pending task.
// - a scheduled task is ready for processing
break;
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
// Thread was interrupted so reset selected keys and break so we not run into a busy loop.
// As this is most likely a bug in the handler of the user or it's client library we will
// also log it.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2426
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely because " +
"Thread.currentThread().interrupt() was called. Use " +
"NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully() to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");
}
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
long time = System.nanoTime();
if (time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos) {
// timeoutMillis elapsed without anything selected.
selectCnt = 1;
} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 &&
selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {
// The selector returned prematurely many times in a row.
// Rebuild the selector to work around the problem.
logger.warn(
"Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row; rebuilding Selector {}.",
selectCnt, selector);
rebuildSelector();
selector = this.selector;
// Select again to populate selectedKeys.
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
currentTimeNanos = time;
}
if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",
selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",
selector, e);
}
// Harmless exception - log anyway
}
}在这种情况下,每次对selectCnt这个标志位进行自增的操作,后续通过计算:
time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos若满足,则seletCnt重新置为1,最后若一旦超过SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD(512),那么需要重建selector,Netty正是通过这种方式规避了空轮询的bug。