Mybatis源码分析(03)-配置文件解析-mappers标签四种配置方式的处理
文章目录
- mappers标签四种配置方式
- 源码分析
mappers标签四种配置方式
上一篇中提到XMLConfigBuilder.mapperElement()方法,该方法用于对核心配置文件中
源码分析
回到mapperElement()方法,可以看出对映射文件不同引入方式的解析
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
//使用包名引入
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
//使用类路径引入
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
//使用本地文件路径引入
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
//使用接口类引入
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
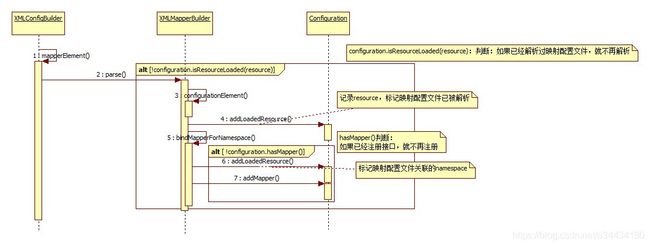
如果使用类路径或本地文件路径引入,mybatis会先注册接口,然后并且解析xml,扫描接口中的注解,时序图如下:
使用类路径或本地文件路径引入,会先调用XMLMapperBuilder.parse()方法:
public void parse() {
//判断是否已经加载过该映射配置文件
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
//从根节点开始解析
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
//将映射配置文件添加到loadedResources集合中,该集合记录了已经加载的映射配置文件
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
//注册Mapper接口
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
// 处理configurationElement()方法中解析失败的节点
parsePendingResultMaps();
// 处理configurationElement()方法中解析失败的节点
parsePendingCacheRefs();
// 处理configurationElement()方法中解析失败的SQL语句节点
parsePendingStatements();
}
而在bindMapperForNamespace()会调用configuration.addMapper(),完成mapper接口的注册,以及接口中注解的解析:
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
//获取映射配置文件的命名空间
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
//通过反射得到namespace对应的Class对象
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) { //是否已经注册boundType接口
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace); //记录namespace
configuration.addMapper(boundType); //调用MapperRegistry.addMapper()方法,注册boundType接口
}
}
}
}
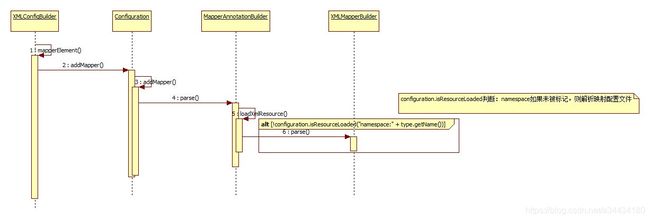
如果使用包名或接口类引入,mybatis会先解析xml,然后再去注册接口,扫描接口中的注解,时序图如下:
先调用configuration.addMapper()方法
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) { //已经注册,抛出异常
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type)); //完成注册
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse(); //解析接口文件中的注解,以及对应的映射配置文件
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
然后,会调用MapperAnnotationBuilder.parse()方法,该方法内部会进行映射配置文件的解析,以及注解的解析:
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
//加载与这个接口相关联的xml文件
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) {
parseStatement(method); //解析注解形式的statement
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
在loadXmlResource()方法中,又会调用XMLMapperBuilder.parse()方法进行映射配置文件的解析
从这个方法可以看出,映射配置文件是通过 type.getName(),也就是接口的全类名找到的,这也就是为什么使用包名或接口类引入mapper接口,要求映射配置文件必须与接口同包同名了
private void loadXmlResource() {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we check a flag
// to prevent loading again a resource twice
// this flag is set at XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace
//XMLMapperBuilder.bindMapperForNamespace()方法中的
// 使用configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace)标记namespace之后
//就不会再进行xml解析了
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded("namespace:" + type.getName())) {
String xmlResource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".xml";
// #1347
InputStream inputStream = type.getResourceAsStream("/" + xmlResource);
if (inputStream == null) {
// Search XML mapper that is not in the module but in the classpath.
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(type.getClassLoader(), xmlResource);
} catch (IOException e2) {
// ignore, resource is not required
}
}
if (inputStream != null) {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(), xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName());
xmlParser.parse();
}
}
}
总结:在使用mappers标签,用包名和接口类引入mapper接口时,调用的顺序是configuration.addMapper()->XMLMapperBuilder.parse(),而使用本地文件路径和类路径引入映射配置文件时,调用的顺序是XMLMapperBuilder.parse()->configuration.addMapper(),当然为了避免不断地循环调用下去,会利用configuration.addLoadedResource()和configuration.isResourceLoaded()去设置和判断flag。