setContentView() 究竟都做了什么?
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/crazy1235/article/details/51471280
这个函数是在常见不过的了!
setContentView(R.layout.activity_test_view);但是调用了这个函数设置Activity布局的时候,android系统究竟做了什么操作呢?
往下看!
setContentView()
我们新建项目模式都是使用的 Theme.AppCompat 主题,Activity都是继承于 AppCompatActivity 的!
OK,下面来一步步跟踪源码!
在AppCompatActivity中:
@Override
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getDelegate().setContentView(layoutResID);
}调用的是 getDelegate() 中对应的 setContentView() 函数。
@NonNull
public AppCompatDelegate getDelegate() {
if (mDelegate == null) {
mDelegate = AppCompatDelegate.create(this, this);
}
return mDelegate;
}AppCompatDelegate 及其子类
AppCompatDelegate 是 AppCompat代理类!
调用AppCompatDelegate中的静态方法create() :
public static AppCompatDelegate create(Activity activity, AppCompatCallback callback) {
return create(activity, activity.getWindow(), callback);
}接着又调用了另外一个重载的静态函数!
private static AppCompatDelegate create(Context context, Window window,
AppCompatCallback callback) {
final int sdk = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
if (BuildCompat.isAtLeastN()) {
return new AppCompatDelegateImplN(context, window, callback);
} else if (sdk >= 23) {
return new AppCompatDelegateImplV23(context, window, callback);
} else if (sdk >= 14) {
return new AppCompatDelegateImplV14(context, window, callback);
} else if (sdk >= 11) {
return new AppCompatDelegateImplV11(context, window, callback);
} else {
return new AppCompatDelegateImplV9(context, window, callback);
}
}在这个函数里根据系统版本来创建不同的代理实现类!
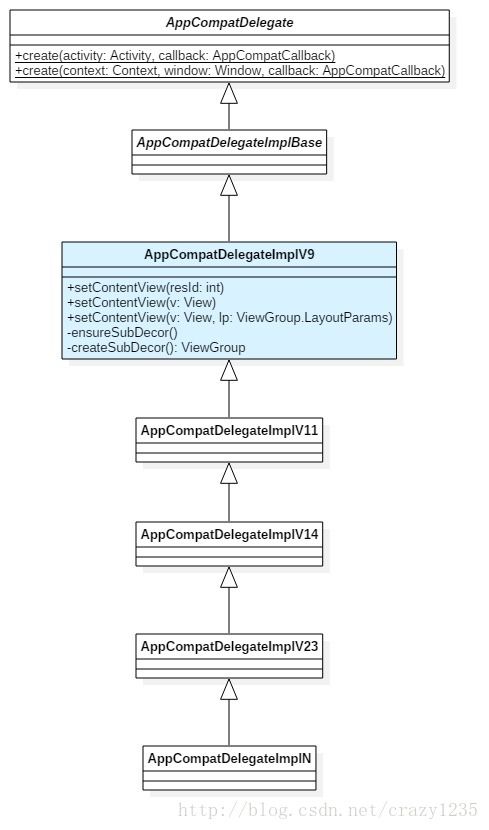
通过查看这几个类的源码可以发现它们之间的继承关系如下图:
可以看出,setContentView() 方法实现是在 AppCompatDelegateImplV9 这个类中!
@Override
public void setContentView(View v) {
ensureSubDecor(); //
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup) mSubDecor.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
contentParent.removeAllViews();
contentParent.addView(v);
mOriginalWindowCallback.onContentChanged();
}
@Override
public void setContentView(int resId) {
ensureSubDecor(); //
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup) mSubDecor.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
contentParent.removeAllViews();
LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(resId, contentParent);
mOriginalWindowCallback.onContentChanged();
}
@Override
public void setContentView(View v, ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp) {
ensureSubDecor(); //
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup) mSubDecor.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
contentParent.removeAllViews();
contentParent.addView(v, lp);
mOriginalWindowCallback.onContentChanged();
}我们平时在Activity中主要用到的就是 public void setContentView(int resId) 这个函数!就那这个来说!
ensureSubDecor()
三个重载函数内部都是首先调用了 ensureSubDecor() 这个函数!
private void ensureSubDecor() {
if (!mSubDecorInstalled) {
mSubDecor = createSubDecor(); // !!!
// If a title was set before we installed the decor, propagate it now
CharSequence title = getTitle();
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(title)) {
onTitleChanged(title);
}
applyFixedSizeWindow();
onSubDecorInstalled(mSubDecor);
mSubDecorInstalled = true;
PanelFeatureState st = getPanelState(FEATURE_OPTIONS_PANEL, false);
if (!isDestroyed() && (st == null || st.menu == null)) {
invalidatePanelMenu(FEATURE_SUPPORT_ACTION_BAR);
}
}
}mSubDecorInstalled 默认是false,所以初次会调用 createSubDecor() 来创建 mSubDecor,实际上它就是一个ViewGroup!
private ViewGroup createSubDecor() {
// [1]. 主题验证!
TypedArray a = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme);
if (!a.hasValue(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme_windowActionBar)) {
a.recycle();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"You need to use a Theme.AppCompat theme (or descendant) with this activity.");
}
// [2]. 初始化相关特征标志!
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme_windowNoTitle, false)) {
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
} else if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme_windowActionBar, false)) {
requestWindowFeature(FEATURE_SUPPORT_ACTION_BAR);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme_windowActionBarOverlay, false)) {
requestWindowFeature(FEATURE_SUPPORT_ACTION_BAR_OVERLAY);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme_windowActionModeOverlay, false)) {
requestWindowFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_MODE_OVERLAY);
}
mIsFloating = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme_android_windowIsFloating, false);
a.recycle();
// [3]. window对象创建decor view
mWindow.getDecorView();
final LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(mContext);
ViewGroup subDecor = null; // subDecor是一个ViewGroup
// [4]. 判断是否有title
if (!mWindowNoTitle) {
if (mIsFloating) {
// (1)如果是浮动窗口形式 -- abc_dialog_title_material.xml
subDecor = (ViewGroup) inflater.inflate(
R.layout.abc_dialog_title_material, null);
// Floating windows 不允许有actionbar
mHasActionBar = mOverlayActionBar = false;
} else if (mHasActionBar) {
TypedValue outValue = new TypedValue();
mContext.getTheme().resolveAttribute(R.attr.actionBarTheme, outValue, true);
Context themedContext;
if (outValue.resourceId != 0) {
themedContext = new ContextThemeWrapper(mContext, outValue.resourceId);
} else {
themedContext = mContext;
}
// (2) 费浮动窗口形式 -- abc_screen_toolbar.xml
subDecor = (ViewGroup) LayoutInflater.from(themedContext)
.inflate(R.layout.abc_screen_toolbar, null);
mDecorContentParent = (DecorContentParent) subDecor
.findViewById(R.id.decor_content_parent);
mDecorContentParent.setWindowCallback(getWindowCallback());
// ... 省略代码
}
}
} else {
// (3) abc_screen_simple_overlay_action_mode.xml
if (mOverlayActionMode) {
subDecor = (ViewGroup) inflater.inflate(
R.layout.abc_screen_simple_overlay_action_mode, null);
} else {
// (4) abc_screen_simple.xml
subDecor = (ViewGroup) inflater.inflate(R.layout.abc_screen_simple, null);
}
// ... 省略代码
// [5]. 如果此时subDecor为空,则抛异常~
if (subDecor == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"AppCompat does not support the current theme features: { "
+ "windowActionBar: " + mHasActionBar
+ ", windowActionBarOverlay: "+ mOverlayActionBar
+ ", android:windowIsFloating: " + mIsFloating
+ ", windowActionModeOverlay: " + mOverlayActionMode
+ ", windowNoTitle: " + mWindowNoTitle
+ " }");
}
if (mDecorContentParent == null) {
mTitleView = (TextView) subDecor.findViewById(R.id.title);
}
// Make the decor optionally fit system windows, like the window's decor
ViewUtils.makeOptionalFitsSystemWindows(subDecor);
// [6]. 获取ContentFrameLayout
final ContentFrameLayout contentView = (ContentFrameLayout) subDecor.findViewById(
R.id.action_bar_activity_content);
// [7]. 获取PhoneWindow中的content布局对象
final ViewGroup windowContentView = (ViewGroup) mWindow.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
if (windowContentView != null) {
// There might be Views already added to the Window's content view so we need to
// migrate them to our content view
while (windowContentView.getChildCount() > 0) {
final View child = windowContentView.getChildAt(0);
windowContentView.removeViewAt(0);
contentView.addView(child);
}
// [8]. 将contentView的id更改为android.R.id.content
windowContentView.setId(View.NO_ID);
contentView.setId(android.R.id.content);
// The decorContent may have a foreground drawable set (windowContentOverlay).
// Remove this as we handle it ourselves
if (windowContentView instanceof FrameLayout) {
((FrameLayout) windowContentView).setForeground(null);
}
}
// [9]. 对PhoneWindow设置ContentView
mWindow.setContentView(subDecor);
// [10]. 设置attach监听
contentView.setAttachListener(new ContentFrameLayout.OnAttachListener() {
@Override
public void onAttachedFromWindow() {}
@Override
public void onDetachedFromWindow() {
dismissPopups();
}
});
return subDecor;
}方法体里面步骤标注的比较详细了。
下面针对关键的几步详细说一下!
requestWindowFeature
@Override
public boolean requestWindowFeature(int featureId) {
featureId = sanitizeWindowFeatureId(featureId);
if (mWindowNoTitle && featureId == FEATURE_SUPPORT_ACTION_BAR) {
return false; // Ignore. No title dominates.
}
if (mHasActionBar && featureId == Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE) {
// Remove the action bar feature if we have no title. No title dominates.
mHasActionBar = false;
}
switch (featureId) {
case FEATURE_SUPPORT_ACTION_BAR:
throwFeatureRequestIfSubDecorInstalled();
mHasActionBar = true;
return true;
case FEATURE_SUPPORT_ACTION_BAR_OVERLAY:
throwFeatureRequestIfSubDecorInstalled();
mOverlayActionBar = true;
return true;
case FEATURE_ACTION_MODE_OVERLAY:
throwFeatureRequestIfSubDecorInstalled();
mOverlayActionMode = true;
return true;
case Window.FEATURE_PROGRESS:
throwFeatureRequestIfSubDecorInstalled();
mFeatureProgress = true;
return true;
case Window.FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS:
throwFeatureRequestIfSubDecorInstalled();
mFeatureIndeterminateProgress = true;
return true;
case Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE:
throwFeatureRequestIfSubDecorInstalled();
mWindowNoTitle = true;
return true;
}
return mWindow.requestFeature(featureId);
}从这个方法可以看出,我们在Activity里面调用requestWindowFeature(xxx),实际上就是设定了先关参数的状态(布尔值)!
但是每个case语句首先都调用了 throwFeatureRequestIfSubDecorInstalled() ;
private void throwFeatureRequestIfSubDecorInstalled() {
if (mSubDecorInstalled) {
throw new AndroidRuntimeException(
"Window feature must be requested before adding content");
}
}上面提到 mSubDecorInstalled 这个标志初始为false,在我们调用setContentView()的函数内部 变成了true。
所以当在 setContentView() 方法后面再次调用 requestWindowFeature(xxx) 时,就会抛出运行时异常!
所以说在Activity中onCreate() 函数中,requestWindowFeature() 要写在setContentView() 的前面!
mWindow.getDecorView()
mWindow是一个Window对象,Window是一个抽象类,实现子类是 PhoneWindow 。
该mWindow对象是从activity中获得的!
public static AppCompatDelegate create(Activity activity, AppCompatCallback callback) {
return create(activity, activity.getWindow(), callback);
}那么具体PhoneWindow的创建这里先不谈!
直接看PhoneWindow中的先关函数:
@Override
public final View getDecorView() {
if (mDecor == null || mForceDecorInstall) {
installDecor();
}
return mDecor;
}mDecor 是一个 DecorView 对象。
private void installDecor() {
mForceDecorInstall = false;
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor(-1); // [1]. 创建decorView对象
// ... 省略代码
} else {
mDecor.setWindow(this);
}
if (mContentParent == null) {
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor); // [2].
// ... 省略代码
}
}installDecor() 方法体内部主要的函数是上面标注出来的那两行!
protected DecorView generateDecor(int featureId) {
// ...省略
return new DecorView(context, featureId, this, getAttributes());
}generateDecor() 方法体很简单,直接创建了一个DecorView对象返回!
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
// Apply data from current theme.
TypedArray a = getWindowStyle();
// [1]. 读取属性设置标志和状态
mIsFloating = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowIsFloating, false);
int flagsToUpdate = (FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN|FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR)
& (~getForcedWindowFlags());
if (mIsFloating) {
setLayout(WRAP_CONTENT, WRAP_CONTENT);
setFlags(0, flagsToUpdate);
} else {
setFlags(FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN|FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR, flagsToUpdate);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowNoTitle, false)) {
requestFeature(FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
} else if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowActionBar, false)) {
// Don't allow an action bar if there is no title.
requestFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
}
// ... 省略代码
// [2]. 映射decor布局
int layoutResource;
int features = getLocalFeatures();
if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_SWIPE_TO_DISMISS)) != 0) {
// (1)screen_swipe_dismiss.xml
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_swipe_dismiss;
} else if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_LEFT_ICON) | (1 << FEATURE_RIGHT_ICON))) != 0) {
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogTitleIconsDecorLayout, res, true);
// (2) dialog_title_icons.xml
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
// (3) screen_title_icons.xml
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title_icons;
}
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
} else if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_PROGRESS) | (1 << FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS))) != 0
&& (features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) == 0) {
// (4) screen_progress.xml
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_progress;
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_CUSTOM_TITLE)) != 0) {
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogCustomTitleDecorLayout, res, true);
// (5). dialog_custom_title.xml
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
// (6). screen_custom_title.xml
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_custom_title;
}
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_NO_TITLE)) == 0) {
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogTitleDecorLayout, res, true);
// (7). dialog_title.xml
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) != 0) {
// (8). screen_action_bar.xml
layoutResource = a.getResourceId(
R.styleable.Window_windowActionBarFullscreenDecorLayout,
R.layout.screen_action_bar);
} else {
// (9). screen_title.xml
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title;
}
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_MODE_OVERLAY)) != 0) {
// (10). screen_simple_overlay_action_mode.xml
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple_overlay_action_mode;
} else {
// (11). screen_simple.xml
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple;
}
// [3]. 开始更新decor -- mChanging = true;
mDecor.startChanging();
// [4]. 加载 layoutResourc 放到 decor 中
mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource);
// [5]. 找到 【com.android.internal.R.id.content】 对应的View
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
if (contentParent == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Window couldn't find content container view");
}
// ...
// 设置背景,title,titleColor等属性
// [6]. 结束更新decor -- mChanging = false;
mDecor.finishChanging();
return contentParent;
}在 generateLayout() 函数内部,根据features 等一些列参数判断,一共有11种布局!
screen_swipe_dismiss.xml
dialog_title_icons.xml
screen_title_icons.xml
screen_progress.xml
dialog_custom_title.xml
screen_custom_title.xml
dialog_title.xml
screen_action_bar.xml
screen_title.xml
screen_simple_overlay_action_mode.xml
screen_simple.xml
但是不管是哪个布局,里面都有一个id是 @android:id/content 的控件!
DecorView.onResourcesLoaded()
mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource);将上一步得到的布局映射出来添加到mDecor 这个ViewGroup 中!
void onResourcesLoaded(LayoutInflater inflater, int layoutResource) {
mStackId = getStackId();
// ... 省略代码
mDecorCaptionView = createDecorCaptionView(inflater);
final View root = inflater.inflate(layoutResource, null);
if (mDecorCaptionView != null) {
if (mDecorCaptionView.getParent() == null) {
addView(mDecorCaptionView,
new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
mDecorCaptionView.addView(root,
new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
} else {
// Put it below the color views.
addView(root, 0, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
mContentRoot = (ViewGroup) root;
initializeElevation();
}从上面代码块看出,addView() 函数将layoutResource映射出来的布局添加到DecorView中!并且宽高参数都是 MATCH_PARENT !
OK,再接着上面的createSubDecor() 往下分析。
// [3]. window对象创建decor view
mWindow.getDecorView();
final LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(mContext);
ViewGroup subDecor = null; // subDecor是一个ViewGroup
此时window的decor view创建完毕!
接下来映射 subDecor 布局根据不同情况也对应了下面4种布局:
abc_dialog_title_material.xml
abc_screen_toolbar.xml
abc_screen_simple_overlay_action_mode.xml
abc_screen_simple
但是无论哪种布局,里面都 include 一个 abc_screen_content_include.xml 布局
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
.support.v7.widget.ContentFrameLayout
android:id="@id/action_bar_activity_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top"
android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" />
final ContentFrameLayout contentView = (ContentFrameLayout) subDecor.findViewById(
R.id.action_bar_activity_content);
final ViewGroup windowContentView = (ViewGroup) mWindow.findViewById(android.R.id.content);所以contentView 就是这个ContentFrameLayout布局!
windowContentView 是 我们上面提到的android.R.id.content对应的布局!
由于那11中布局中android.R.id.content对应的布局不同,所以这里使用 ViewGroup 进行转化!
windowContentView.setId(View.NO_ID);
contentView.setId(android.R.id.content);接着讲decorView中的 android.R.id.content 对应的控件id 设置为 View.NO_ID
将 subDecor 中 R.id.action_bar_activity_content 对应的布局 ID 设置为 android.R.id.content
PhoneWindow.setContentView()
最后是 mWindow.setContentView(subDecor);
在PhoneWindow中有三个setContentView() 重载函数!
@Override
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
// ...
}
@Override
public void setContentView(View view) {
setContentView(view, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
@Override
public void setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
// ...
}我们只来关注第三个。
@Override
public void setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
// mContentParent !!! 注意这个变量
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
// 是否需要transition动画
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
view.setLayoutParams(params);
final Scene newScene = new Scene(mContentParent, view);
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mContentParent.addView(view, params);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
mContentParentExplicitlySet = true;
}当有过度场景动画时,view的添加实在Scene进入的时候!
Scene.java
public void enter() {
// Apply layout change, if any
if (mLayoutId > 0 || mLayout != null) {
// empty out parent container before adding to it
getSceneRoot().removeAllViews();
if (mLayoutId > 0) {
LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(mLayoutId, mSceneRoot);
} else {
mSceneRoot.addView(mLayout);
}
}
// ...
}mSceneRoot 就是上面构造Scene传入的 mContentParent , mLayout 是构造Scene传入的view, 也就是 AppCompatDelegateImplV9 里面的 subDecor
当没有过度动画,直接将subDecor添加到mContentParent 中!
而 mContentParent 是谁呢???
它就是PhonWindow 类中 installDecor() 函数中,通过 generateLayout(mDecor) 生成的ViewGroup!
在 generateLayout() 函数体内:
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);public static final int ID_ANDROID_CONTENT = com.android.internal.R.id.content;OK。这个conetentParent就是 R.id.content对应的布局!
也就是说 mContentParent 就是 R.id.content对应的布局!
所以,mWindow.setContentView(subDecor); 就是把subDecor添加到了R.id.content 的布局中了!
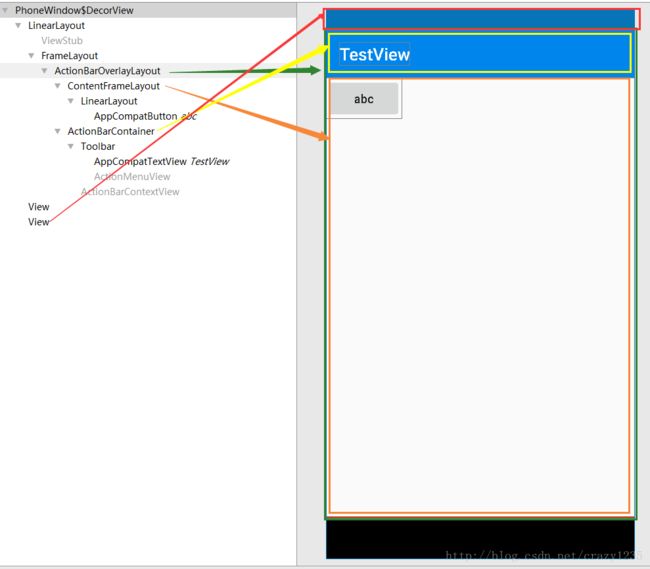
而此时添加完毕之后,R.id.content对应的布局就变成了 subDecor里面的 原 R.id.action_bar_activity_content 对应的 ContentFrameLayout 布局!
至此, ensureSubDecor() 的过程分析完毕!
在回过头看AppCompatDelegateImplV9.java 中的 setContentView() 函数!
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup) mSubDecor.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
contentParent.removeAllViews();
contentParent.addView(v, lp);此时就可看出,我们在Activity中调用setContentView(xxx),就是把布局添加到了android.R.id.content对应的布局中。
ContentFrameLayout就是ID被更改为android.R.id.content的布局!也是我们在activity中设置布局的父布局!