String中空串与null的区别#抽取方法快捷键#字节数组转化成字符串#字符数组转化成字符串
String:
String也是个类,且重写了toString方法,返回是该对象本身
String s1="";
String s2=null;
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2); * null 和""的区别
* ""(空串)是一个String类的对象,可以调用String类中所有方法
* null是一个空值,不能调用任何方法,因为调用就会报空指针异常
//打印对象的引用如果是null就返回null
//如果不是null就返回对象的toString方法
抽取方法快捷键:alt+shift+m
String构造函数(字节数组转化成字符串)解码过程:
byte[] arr = {97,98,99};//默认字符集解码指定的 byte(字节) 数组
String s1 = new String(arr);//public String(byte[] bytes)解码,将计算机能看懂的(由0,1构成的字节)变成我们能看懂的字符串
System.out.println(s1);
byte[] arr2 = {97,98,99,100,101,102};
// public String(byte[] bytes,int index,int length)将byte数组解码,从index开始,解码length个
String s2 = new String(arr2, 2, 3);
System.out.println(s2);
*****************************
abc
cdechar[] arr = {'a','b','c'};
String s1 = new String(arr); //将字符数组转换为字符串
System.out.println(s1);
//String(char[] value, int offset, int count)将char数组转换为String字符串,从offset开始,转换count个
char[] arr2 = {'a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i'};
String s2 = new String(arr2, 3, 3);
System.out.println(s2);String s1 = "abc"; //String s1 = "abc"会进常量池,s1指向“abc”
String s2 = "abc"; //先看常量池是否有"abc"对象,如果没有创建,如果有直接s2指向“abc”
System.out.println(s1 == s2); //已有对象"abc"的地址值
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //s1和s2指向的是同一个对象
*************
true
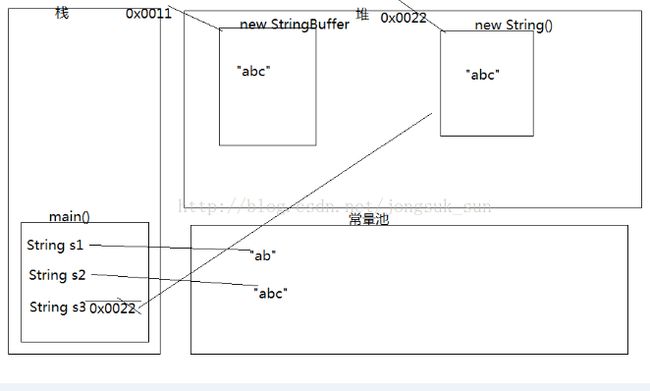
trueString s1 = new String("abc"); //这句话在内存中创建几个对象
//创建了两个对象,一个在常量池里,一个在堆里(是常量池的副本)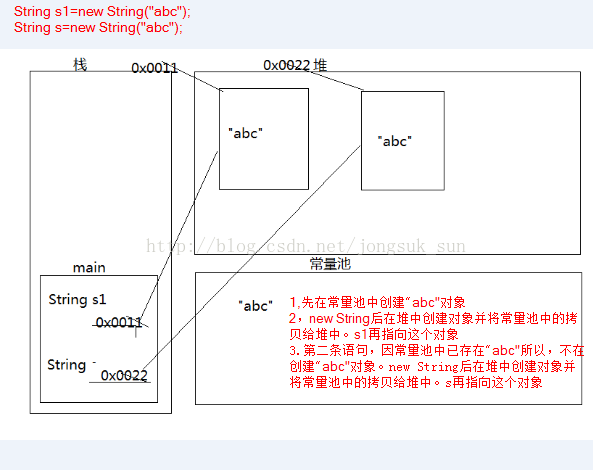
String s1 = "a" + "b" + "c"; //java有常量优化机制,在编译时已经是"abc"字符串了
String s2 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1 == s2); //s1,s2都记录的是常量池中"abc"的地址
*************************
true
trueString s1 = "ab"; //在常量池中创建"ab"
String s2 = "abc"; //在常量池中创建"abc"
String s3 = s1 + "c"; /*当字符串与对象用+连接的时候,底层会调用new StringBuffer在堆中生成一个对象,再调用
StringBuffer的append方法,对字符串进行添加。最后将StringBuffer对象转换为String对象并赋值给s3,s3记录的是堆内存对象的地址值*/
System.out.println(s2 == s3);
System.out.println(s3.equals(s2));
************************
false
true
String类中比较的方法
* boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同,区分大小写
* boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
* boolean contains(String str):判断大字符串中是否包含小字符串
* boolean startsWith(String str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串开头
* boolean endsWith(String str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串结尾
* boolean isEmpty():判断字符串是否为空。
String类的获取功能
* int length():获取字符串中字符的长度。(而非字节长度)
* char charAt(int index):获取指定索引位置的字符。(字符串类似于与数组,从0开始标号)
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "我是中国人";
System.out.println(s1.length()); //获取字符串中字符的个数
System.out.println(s2.length());
char c1 = s1.charAt(1); //通过索引获取字符
System.out.println(c1);
char c2 = s2.charAt(3);
System.out.println(c2);
for(int i = 0; i < s2.length(); i++) { //字符串的遍历方式
System.out.print(s2.charAt(i));
}
}
******************************
3
5
b
中
我是中国人* nt indexOf(int ch):返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
* int indexOf(String str):返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
String s1 = "abcdefc";
int index1 = s1.indexOf('c'); //返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
System.out.println(index1);
int index2 = s1.indexOf("ce"); //如果查找的字符串没有,返回-1
System.out.println(index2);
******************************
2
-1* int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex):返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。
* int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex):返回指定字符串在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。
String s1 = "abcabcitcast";
int index1 = s1.indexOf('c', 3);//返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。
System.out.println(index1);
int index2 = s1.indexOf("ca", 4);
System.out.println(index2);
****************************
5
8* lastIndexOf
String s1 = "abcitcastabc";
int index1 = s1.lastIndexOf('a');//从后向前找,将字符对应的索引返回
System.out.println(index1);
int index2 = s1.lastIndexOf("ab");
System.out.println(index2);
int index3 = s1.lastIndexOf('a', 8); //从指定的位置向前找,第一次字符出现的索引
System.out.println(index3);
******************************
9
9
6* String substring(int start):从指定位置开始截取字符串,默认到末尾。
* String substring(int start,int end):从指定位置开始到指定位置结束截取字符串。
String s1 = "abcitcastabc";
//String s2 = s1.substring(3); //从指定位置开始截取字符串,默认到末尾。产生新的字符串
//System.out.println(s2);
String s3 = s1.substring(3, s1.length());//包含头,不包含尾(左闭右开)
System.out.println(s3);
******************************
itcastabc* byte[] getBytes():把字符串转换为字节数组。
String s1 = "abc";
byte[] arr = s1.getBytes();//编码,将我们看的懂的,变成计算机看的懂的
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
String s2 = "你好你好";
byte[] arr2 = s2.getBytes("uTf-8");//可以指定编码方式(但要注意抛出异常),默认为Unicode(一个中文占2字节)
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr2[i] + " ");
}
//-60 -29 -70 -61 -60 -29 -70 -61 通过String的构造函数解码
//-28 -67 -96 -27 -91 -67 -28 -67 -96 -27 -91 -67 utf-8编码(一个中文占3个字节)
byte[] arr3 = {-28,-67,-96,-27,-91,-67,-28,-67,-96,-27,-91,-67};
String s3 = new String(arr3,"uTf-8");//解码过程,将机器码转化成我们能看懂的,也可指定解码方式new String(需解码的字节数组,"编码表")
System.out.println(s3);//注意:用什么码表编就用什么码表解
******************************
97 98 99
-28 -67 -96 -27 -91 -67 -28 -67 -96 -27 -91 -67 你好你好* char[] toCharArray():把字符串转换为字符数组。
String s = "itcast传智播客";
char[] arr = s.toCharArray(); //将字符串转换为字符数组,一个中文对应一个字符
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
*****************************
i t c a s t 传 智 播 客 * static String valueOf(char[] chs):把字符数组转成字符串。
* static String valueOf(int i):把int类型的数据转成字符串。
* 注意:String类的valueOf方法可以把任意类型的数据转成字符串。 valueOf方法是静态方法可以直接:String.valueOf()调用。
char[] arr = {'1','2','3'};
String s1 = String.valueOf(arr); //将字符数组转换成对应的字符串
System.out.println(s1);
String s2 = String.valueOf(10);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(10 + "");//任何数与字符串""用加号连接产生新的字符串。也可以将10转换成对应的字符串
********************************
123
10
10* String toUpperCase():把字符串转成大写。
* String concat(String str):把字符串拼接。
String s1 = "abcDEFgh";
System.out.println(s1.toLowerCase());//将所有的字符转换成小写
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());//将所有的字符转换成大写
System.out.println(s1);
String s2 = "abc";
String s3 = "def";
String s4 = s2.concat(s3);//将两个字符串连接
System.out.println(s4);
**********************************
abcdefgh
ABCDEFGH
abcDEFgh
abcdef* 举例:
* int[] arr = {1,2,3};
* 输出结果:
* "[1, 2, 3]"
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
String temp = "[";//字符串与数组中每个字符相连
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { //遍历数组,获取每一个元素
//temp = temp + arr[i] + ", "; //[1, 2, 3]
/*if(i == arr.length -1) {
temp = temp + arr[i] + "]"; //[1, 2, 3]
}else {
temp = temp + arr[i] + ", "; //[1, 2,
}*/
temp = temp + ((i == arr.length -1) ? arr[i] + "]" : arr[i] + ", ");
//(判断条件)?语句一:语句二
}
System.out.println(temp);
}
*************************
[1,2,3]* String replace(char old,char new)
* String replace(String old,String new)
String s = "itcast";
String s2 = s.replace('s', 'o');//替换,将已有字符替换,如果没有被替换的字符,打印原字符串
System.out.println(s2);
String s3 = s.replace("cas", "ooo");
System.out.println(s3);
*****************************
itcost
itoootString的去除字符串两空格及案例演示
* String trim()
String s = " itcast ";
String s2 = s.trim(); //去除前后空格
System.out.println(s2);
************************
itcast String的按字典顺序比较两个字符串及案例演示
* int compareTo(String str)
String s1 = "a";
String s2 = "aaaa"; //如果两个字符串中的字符一样,个数不一样比较长度。
int x = s1.compareTo(s2);//按照码表值比较两个字符串的大小,返回值:正数,0,负数
System.out.println(x);
****************************
-3