从零开始水安卓——安卓四大组件Content Provider
Content Provider
引言
之前已经介绍了安卓四大组件的三大——activity、service、broadcast receiver,而今天这篇文章,就是四大组件里最后一大了——Content Provider。之前介绍了安卓中几种持久化的方式,应用中的数据可以被“永久性”的存储下来,但是大多数情况下,这些数据只能被它的持有者所访问,其他应用程序无法访问和获取,那么有没有办法去实现跨应用的数据访问呢?显然是有的,而实现这一点的,正是今天要讲的Content Provider。
概述
- Content provider是一个进程使用另一个进程数据的标准接口。
- 它用来管理对结构化数据集进行的访问,对数据进行封装,并提供了用于定义数据安全的机制。
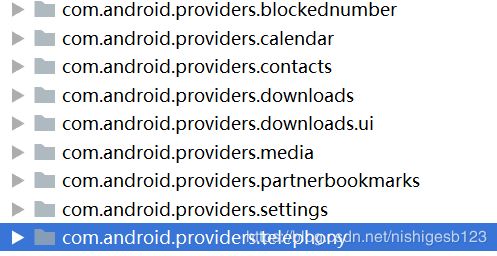
- Android系统本身也通过Content provider来管理数据,如音频,视频,图像,个人联系信息等。我们可以在android.provider包的参考文档中看到这些providers列表。在一定条件下,这些providers能够访问任何Android应用程序。
- providers最主要的目的是为了让其他应用程序使用provider的客户端对象访问provider。所以,providers和provider客户端共同提供了一个一致的标准数据接口用来处理进程间通信和安全的数据访问。
下面是API文档的描述:
内容提供程序管理一组共享的应用数据。您可以将数据存储在文件系统、SQLite 数据库、网络上或您的应用可以访问的任何其他永久性存储位置。 其他应用可以通过内容提供程序查询数据,甚至修改数据(如果内容提供程序允许)。 例如,Android 系统可提供管理用户联系人信息的内容提供程序。 因此,任何具有适当权限的应用都可以查询内容提供程序的某一部分,以读取和写入有关特定人员的信息。
内容提供程序也适用于读取和写入您的应用不共享的私有数据。 例如,记事本示例应用使用内容提供程序来保存笔记。
内容提供程序作为ContentProvider的子类实现,并且必须实现让其他应用能够执行事务的一组标准 API。
- 可以简单的理解,ContentProvider就是实现应用间数据共享的接口。
创建Content Provider
删除符合指定条件的记录
public int delete(Uri uri,String selection,String[] selectionArgs);插入一个新的记录
public Uri insert(Uri uri,ContentValues values);查询符合指定条件的记录
public Curcor query(Uri uri,String[] projection,String selection,String[] selectionArgs,String sortOrder);更新条例指定条件的记录
public int update(Uri uri,ContentValues values,String selection,String[] selectionArgs);创建数据存储后端
public boolean onCreate();//如数据库,文件,网络接口等,这里主要进行初始化工作基于给定URI
public String getType(Uri uri); //返回该URI表示的MIME类型在配置清单文件中声明
和四大组件其他组件类似,使用ContentProvider也需要在配置清单文件中进行声明,为了使别人可以通过配置清单提供的路径进行访问。
一般需要配置两个属性
- authorities(主机名/域名):对ContentProvider进行唯一标识,所以需要和类路径保持一致,虽然类名可能是大写,如?例中的HelloContentProvider,不过还是写成全部小写比较规范(大雾)
- name:实际上可以随便起,还是建议和ContentProvider类名保持一致
UriMatcher和ContentUris工具类
Uri匹配器(匹配Uri是否正确)
- 把我们需要匹配的Uri路径通过静态块代码添加到UriMatcher中
例如:
//静态块 添加Uri
static {
//路径是content://com.example.contentprovider.hellocontentprovider/person 则返回1
// (如果是查询,含义相当于查询person表)
uriMatcher.addURI(authority,"person",MULTIPLE_CODE);
//路径是content://com.example.contentprovider.hellocontentprovider/person/1 则返回2
// (如果是查询,含义相当于指定查询person表id为1)
//通配符 #匹配所有数字 *表示匹配所有字符串
uriMatcher.addURI(authority,"person/#",SINGLE_CODE);
}ContentUris有两个比较实用的方法:
- withAppendedid(uri, d)方法:用于为路径加上ID部分
- parselduri)方法:用于从路径中获取ID部分
例如:
@androidx.annotation.Nullable
@Override
public Uri insert(@androidx.annotation.NonNull Uri uri, @androidx.annotation.Nullable ContentValues values) {
//验证..
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
//匹配码返回1,成功
case MULTIPLE_CODE:
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
long id = db.insert(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,null,values);
//ContentUris可以把id添加到uri后面
uri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(uri,id);
db.close();
break;
}
return uri;
}访问Content Provider
当外部应用需要对Content Provider中的数据进行添加、删除、修改和查询等操作时,可以使用Content Resolver类来完成。
获取ContentResolver对象
使用Activity提供的getContentResolver()方法
ContentResolver cr = getContentResolver();与ContentProvider类似,Content Resolver类提供的方法也不外乎数据德增删查改。
添加数据
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values)
//该方法用于往ContentProvider添加数据删除数据
public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs)
//该方法用于从ContentProvider删除数据修改数据
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection,String[] selectionArgs)
//该方法用于更新ContentProvider中的数据查询数据
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection,String[ selectionArgs, String sortOrder)
//该方法用于从ContentProvider中获取数据
测试源码
MainActivity
package com.example.contentprovider;
import android.content.ContentResolver;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
public void add(View view){
System.out.println("执行了添加操作");
ContentResolver cr = this.getContentResolver();
//解析uri,content表示访问一个ContentProvider,后面跟的内容和配置清单里的authorities一致,下同
Uri uri=Uri.parse("content://com.example.contentprovider.hellocontentprovider/person");
ContentValues values =new ContentValues();
values.put(PersonMetadata.Person.NAME,"测试1");
values.put(PersonMetadata.Person.AGE,1);
//调用ContentProvider的添加方法,需要uri和values,下面的几个方法也类似
cr.insert(uri,values);
System.out.println("添加操作结束");
}
public void delete(View view){
System.out.println("执行了删除操作");
ContentResolver cr =this.getContentResolver();
//删除第一条记录
Uri uri=Uri.parse("content://com.example.contentprovider.hellocontentprovider/person/1");
cr.delete(uri,null,null);
System.out.println("删除操作结束");
}
public void update(View view){
System.out.println("执行了更新操作");
ContentResolver cr =this.getContentResolver();
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://com.example.contentprovider.hellocontentprovider/person/1");
ContentValues values=new ContentValues();
values.put(PersonMetadata.Person.NAME,"第一条记录被修改了");
values.put(PersonMetadata.Person.AGE,"2");
cr.update(uri,values,null,null);
System.out.println("更新操作结束");
}
public void query(View view){
System.out.println("执行了查询操作");
ContentResolver cr = this.getContentResolver();
Uri uri=Uri.parse("content://com.example.contentprovider.hellocontentprovider/person");
Cursor c = cr.query(uri,null,null,null,null);
while (c.moveToNext()){
System.out.println(c.getInt(c.getColumnIndexOrThrow(PersonMetadata.Person._ID)));
System.out.println(c.getString(c.getColumnIndexOrThrow(PersonMetadata.Person.NAME)));
System.out.println(c.getInt(c.getColumnIndexOrThrow(PersonMetadata.Person.AGE)));
}
c.close();
System.out.println("查询操作结束");
}
}
activity_main.xml
HelloContentProvider.java
package com.example.contentprovider;
import android.content.ContentProvider;
import android.content.ContentUris;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.UriMatcher;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.net.Uri;
public class HelloContentProvider extends ContentProvider {
private DatabaseAdapter.DatabaseHelper dbHelper;
//创建一个Uri的匹配器
private static UriMatcher uriMatcher=new UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH);
//authorities比较长,所以定义成常量
private static final String authority = "com.example.contentprovider.hellocontentprovider";
private static final int SINGLE_CODE = 2;//返回单个记录的匹配码
private static final int MULTIPLE_CODE = 1;//返回多个记录的匹配码
//定义两种不同的类型
private static final String SINGLE_TYPE ="vnd.android.cursor.item/person";
private static final String MULTIPLE_TYPE ="vnd.android.cursor.dir/person";
//静态块 添加Uri
static {
//路径是content://com.example.contentprovider.hellocontentprovider/person 则返回1
// (如果是查询,含义相当于查询person表)
uriMatcher.addURI(authority,"person",MULTIPLE_CODE);
//路径是content://com.example.contentprovider.hellocontentprovider/person/1 则返回2
// (如果是查询,含义相当于指定查询person表id为1)
//通配符 #匹配所有数字 *表示匹配所有字符串
uriMatcher.addURI(authority,"person/#",SINGLE_CODE);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
//注意是getContext来获取上下文
dbHelper = new DatabaseAdapter.DatabaseHelper(getContext());
return true;
}
@androidx.annotation.Nullable
@Override
public Cursor query(@androidx.annotation.NonNull Uri uri, @androidx.annotation.Nullable String[] projection, @androidx.annotation.Nullable String selection, @androidx.annotation.Nullable String[] selectionArgs, @androidx.annotation.Nullable String sortOrder) {
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case SINGLE_CODE:
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
long id=ContentUris.parseId(uri);
selection = PersonMetadata.Person._ID+"=?";
selectionArgs = new String[]{String.valueOf(id)};
return db.query(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,projection,selection,selectionArgs,null,null,sortOrder);
case MULTIPLE_CODE:
db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
return db.query(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,projection,selection,selectionArgs,null,null,sortOrder);
}
return null;
}
//
@androidx.annotation.Nullable
@Override
public String getType(@androidx.annotation.NonNull Uri uri) {
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
case SINGLE_CODE:
return SINGLE_TYPE;
case MULTIPLE_CODE:
return MULTIPLE_TYPE;
}
return null;
}
@androidx.annotation.Nullable
@Override
public Uri insert(@androidx.annotation.NonNull Uri uri, @androidx.annotation.Nullable ContentValues values) {
//验证..
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
//匹配码返回1,成功
case MULTIPLE_CODE:
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
long id = db.insert(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,null,values);
//ContentUris可以把id添加到uri后面
uri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(uri,id);
db.close();
break;
}
return uri;
}
@Override
public int delete(@androidx.annotation.NonNull Uri uri, @androidx.annotation.Nullable String selection, @androidx.annotation.Nullable String[] selectionArgs) {
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
//带id
case SINGLE_CODE:
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
long id = ContentUris.parseId(uri);
selection= PersonMetadata.Person._ID+"=?";
selectionArgs= new String[]{String.valueOf(id)};
int row = db.delete(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,selection,selectionArgs);
db.close();
return row;
//不带id,因为delete提供一个selection参数,所以不带id也是允许的
case MULTIPLE_CODE:
db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
row = db.delete(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,selection,selectionArgs);
db.close();
return row;
}
return 0;
}
@Override
public int update(@androidx.annotation.NonNull Uri uri, @androidx.annotation.Nullable ContentValues values, @androidx.annotation.Nullable String selection, @androidx.annotation.Nullable String[] selectionArgs) {
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){
//带id
case SINGLE_CODE:
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
long id = ContentUris.parseId(uri);
selection= PersonMetadata.Person._ID+"=?";
selectionArgs= new String[]{String.valueOf(id)};
int row = db.update(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,values,selection,selectionArgs);
db.close();
return row;
//不带id,因为delete提供一个selection参数,所以不带id也是允许的
case MULTIPLE_CODE:
db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
row = db.update(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,values,selection,selectionArgs);
db.close();
return row;
}
return 0;
}
}
DatabaseAdapter.java
package com.example.contentprovider;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
public class DatabaseAdapter {
private DatabaseHelper dbHelper;
//适配器构造方法
public DatabaseAdapter(Context context){
dbHelper = new DatabaseHelper(context);
}
//提供相应添加数据库方法
public void save(Person person){
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(PersonMetadata.Person.NAME,person.getName());
values.put(PersonMetadata.Person.AGE,person.getAge());
db.insert(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,null,values);
db.close();
}
public void delete(int id){
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
db.delete(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,PersonMetadata.Person._ID+"=?",new String[]{String.valueOf(id)});
db.close();
}
public void update(Person person){
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(PersonMetadata.Person.NAME,person.getName());
values.put(PersonMetadata.Person.AGE,person.getAge());
String where = PersonMetadata.Person._ID+"=?";
String[] args = {String.valueOf(person.getId())};
db.update(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,values,where,args);
db.close();
}
public ArrayList findAll(){
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
Cursor c = db.query(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,null,null,null,null,null,null);
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
Person person = null;
while (c.moveToNext()){
person = new Person();
person.setId(c.getInt(c.getColumnIndex(PersonMetadata.Person._ID)));
person.setName(c.getString(c.getColumnIndex(PersonMetadata.Person.NAME)));
person.setAge(c.getInt(c.getColumnIndex(PersonMetadata.Person.AGE)));
list.add(person);
}
c.close();
db.close();
return list;
}
public Person findById(int id){
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
Cursor c = db.query(PersonMetadata.Person.TABLE_NAME,null, PersonMetadata.Person._ID+"=?",new String[]{String.valueOf(id)},null,null,null);
Person person = null;
while (c.moveToNext()){
person = new Person();
person.setId(c.getInt(c.getColumnIndex(PersonMetadata.Person._ID)));
person.setName(c.getString(c.getColumnIndex(PersonMetadata.Person.NAME)));
person.setAge(c.getInt(c.getColumnIndex(PersonMetadata.Person.AGE)));
}
c.close();
db.close();
return person;
}
public static class DatabaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static final String CREATE_TABLE = "CREATE TABLE person(_id INTEGER PRIMARY " +
"KEY AUTOINCREMENT,name TEXT,age INT)";
private static final String DROP_TABEL ="DROP TABLE IF EXISTS person";
private static final String DB_NAME ="cp.db";
private static final int VERSION = 1;
public DatabaseHelper(@Nullable Context context) {
super(context, DB_NAME, null, VERSION);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
db.execSQL(CREATE_TABLE);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
db.execSQL(DROP_TABEL);
db.execSQL(CREATE_TABLE);
}
}
}
Person.java
package com.example.contentprovider;
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
PersonMetadata.java
package com.example.contentprovider;
import android.provider.BaseColumns;
public final class PersonMetadata {
public static abstract class Person implements BaseColumns{
public static final String TABLE_NAME ="person";
public static final String NAME ="name";
public static final String AGE = "age";
}
}
测试效果
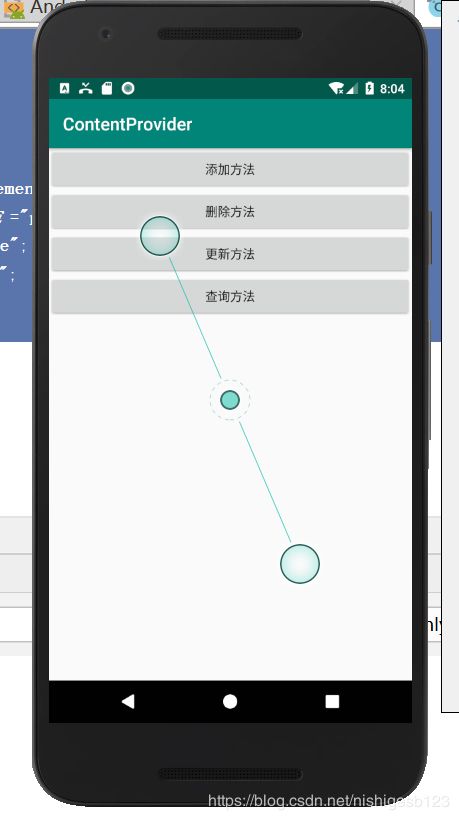
整体界面
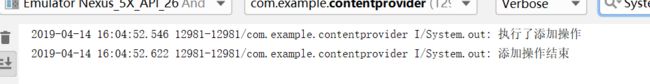
先点击添加
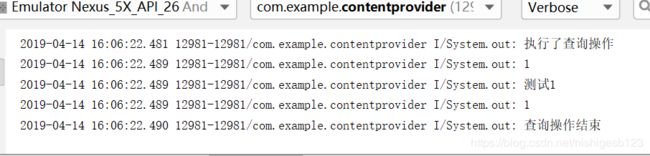
再点击查询(三条语句先后为——序号——姓名——年龄)
再点击更新
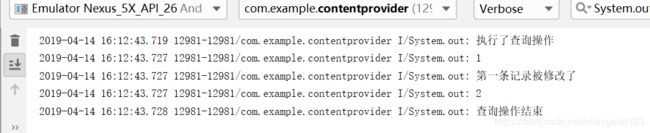
再进行一次查询,可以看到记录已经被修改
点击删除
再点击查询,将只有查询操作的提示文本,而没有查询结果的内容显示,说明已经进行了删除