使用 Matlab+OpenCV 进行摄像头标定
推荐一下个人博客
使用 Matlab+OpenCV 进行摄像头标定
OpenCV配置
配置可见OpenCV
张正友方法简介
张正友标定法是指张正友教授1998年提出的单平面棋盘格的摄像机标定方法。文中提出的方法介于传统标定法和自标定法之间,但克服了传统标定法需要的高精度标定物的缺点,而仅需使用一个打印出来的棋盘格就可以。同时也相对于自标定而言,提高了精度,便于操作。因此张氏标定法被广泛应用于计算机视觉方面。
张正友方法实际是求解三维世界坐标系中的坐标 [X,Y,Z,1]T 到二维像素平面 [u,v,1]T 的单应关系。
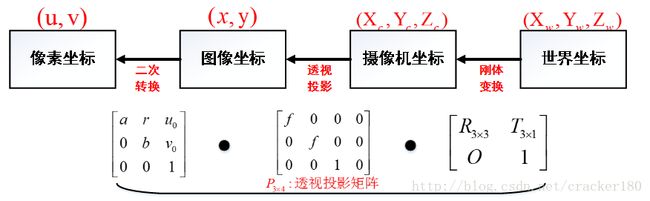
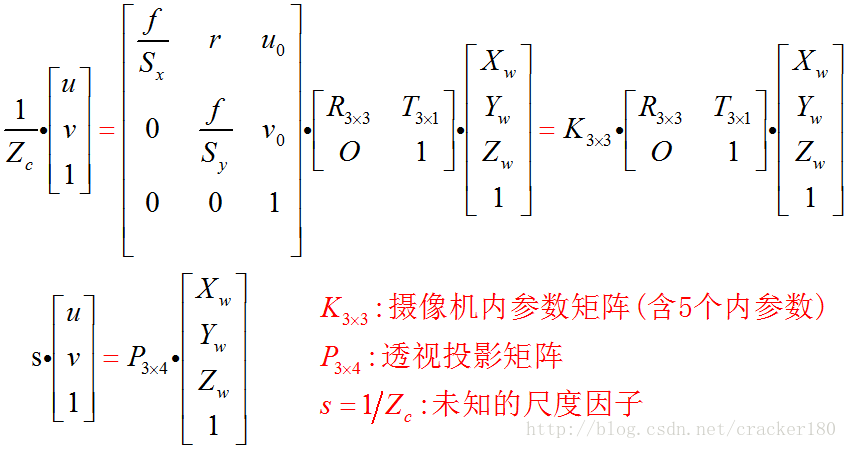
具体推导可参考张正友方法推导详情
具体代码实现
- 使用OpenCV打开摄像头拍摄照片
int TakePhoto(char *path, int choice)
{
char keyCode;
VideoCapture capture(choice);//打开制定摄像头
int count = 1;
if (!capture.isOpened())
return -1;
Mat frame;
while (keyCode = cvWaitKey(30))
{
if (keyCode == 27)
{
break;
}//如果按esc键退出拍摄
capture >> frame;
imshow("读取视频", frame);
if (keyCode == 13)
{//按enter拍摄图片
std::string name = std::string(path) + "chess" + std::to_string(count) + ".jpg";
imwrite(name, frame);//将图片保存为jpg文件
++count;
}
}
return 1;
}
- 使用 Matlab/OpenCV 获取图片中的棋盘格点
- Matlab
for i = 1:5
imageFileName = sprintf('image%d.tif', i);
imageFileNames{i} = fullfile(matlabroot, 'toolbox', 'vision',...
'visiondata','calibration','webcam',imageFileName);
end
% 读取图片
[imagePoints, boardSize, imagesUsed] = detectCheckerboardPoints(imageFileNames);
% 获取棋盘格点坐标
imageFileNames = imageFileNames(imagesUsed);
for i = 1:numel(imageFileNames)
I = imread(imageFileNames{i});
subplot(2, 2, i);
imshow(I); hold on; plot(imagePoints(:,1,i), imagePoints(:,2,i), 'ro');
end
% 显示棋盘格点- OpenCV + C++
for (int i = 0; i < FILES_NUMBER; ++i) {
std::string file_name = FILE_PATH + FILE_NAME + std::to_string(i + 1) + FILE_TYPE;
Mat image = imread(file_name);
//按顺序读取图片
std::vector- 使用OpenCV计算变换矩阵
std::vector<std::vector- 从像素坐标计算世界坐标
CvMat *rotation = cvCreateMat(3, 3, CV_64FC1), tmp = rotation_matrix;
cvRodrigues2(&tmp, rotation);//将旋转向量转换为旋转矩阵
cv::Mat H(cvarrToMat(rotation));
cv::Mat translation_ve;//平移向量
translate_matrix.copyTo(translation_ve);
H.at<double>(0, 2) = translation_ve.at<double>(0, 0);
H.at<double>(1, 2) = translation_ve.at<double>(1, 0);
H.at<double>(2, 2) = translation_ve.at<double>(2, 0);
cv::Mat hu;
hu = camera_matrix * H;
cv::Mat hu2 = hu.inv();
double a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9;
a1 = hu2.at<double>(0, 0);
a2 = hu2.at<double>(0, 1);
a3 = hu2.at<double>(0, 2);
a4 = hu2.at<double>(1, 0);
a5 = hu2.at<double>(1, 1);
a6 = hu2.at<double>(1, 2);
a7 = hu2.at<double>(2, 0);
a8 = hu2.at<double>(2, 1);
a9 = hu2.at<double>(2, 2);
Point2f tmp_point;
double xe = point.x;//图像中点坐标x
double ye = point.y;//图像中点坐标y
tmp_point.x = (a1*xe + a2*ye + a3) / (a7*xe + a8*ye + a9);//世界坐标中x值
tmp_point.y = (a4*xe + a5*ye + a6) / (a7*xe + a8*ye + a9);//世界坐标中Y值具体代码可见Github
如果有用希望给个star