转载自:
使用Guava retrying优雅的实现接口重调机制
Guava retrying:基于 guava 的重试组件
实际项目中,为了考虑网络抖动,加锁并发冲突等场景,我们经常需要对异常操作进行重试。优雅的重试 其实就是将业务处理逻辑和重试逻辑分离。
下面是原文地址:
API 接口调用异常和网络异常在我们日常开发中经常会遇到,这种情况下我们需要先重试几次才能将其标识为错误并在确认错误之后发送异常提醒。
Guava retrying 可以灵活的实现这一功能。Guava retrying在支持重试次数和重试频度控制基础上,能够兼容支持多个异常或者自定义实体对象的重试源定义,让重试功能有更多的灵活性。Guava retrying也是线程安全的,入口调用逻辑采用的是Java.util.concurrent.Callable的call方法。
使用Guava retrying很简单,我们只要做以下几步:
pom文件
2.0.0
com.github.rholder
guava-retrying
${guava-retry.version}
定义实现Callable接口的方法,以便Guava retrying能够调用
/**
* @desc 更新可代理报销人接口
* @author jianzhang11
* @date 2017/3/31 15:17
*/
private static Callable updateReimAgentsCall = new Callable() {
@Override
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
String url = ConfigureUtil.get(OaConstants.OA_REIM_AGENT);
String result = HttpMethod.post(url, new ArrayList());
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(result)){
throw new RemoteException("获取OA可报销代理人接口异常");
}
List oaReimAgents = JSON.parseArray(result, OAReimAgents.class);
if(CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(oaReimAgents)){
CacheUtil.put(Constants.REIM_AGENT_KEY,oaReimAgents);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}; 定义Retry对象并设置相关策略
Retryer retryer = RetryerBuilder
.newBuilder()
// 抛出runtime异常、checked异常时都会重试,但是抛出error不会重试。
.retryIfException()
// 自定义 指定返回值 也需要重试:返回false也需要重试
.retryIfResult(Predicates.equalTo(false))
// 重试时间间隔
.withWaitStrategy(WaitStrategies.fixedWait(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS))
// 尝试次数
.withStopStrategy(StopStrategies.stopAfterAttempt(3))
.build();
try {
retryer.call(updateReimAgentsCall);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
//e.printStackTrace();
} catch (RetryException e) {
logger.error("更新可代理报销人异常,需要发送提醒邮件");
} API说明
上面简单三步就能使用Guava retrying优雅的实现重调方法。接下来对其进行详细说明:
- RetryerBuilder是一个factory创建者,可以定制设置重试源且可以支持多个重试源,可以配置重试次数或重试超时时间,以及可以配置等待时间间隔,创建重试者Retryer实例。
- RetryerBuilder的重试源支持Exception异常对象和自定义对象,通过retryIfException 和 retryIfResult设置,同时支持多个且能互相兼容。
- retryIfException,抛出runtime异常、checked异常时都会重试,但是抛出error不会重试。
- retryIfRuntimeException只会在抛runtime异常的时候才重试,checked异常和error都不重试。
- retryIfExceptionOfType允许我们只在发生特定异常的时候才重试,比如 NullPointerException 和 IllegalStateException 都属于runtime异常,也包括自定义的error
如:
.retryIfExceptionOfType(Error.class)// 只在抛出error重试当然我们还可以在只有出现指定的异常的时候才重试,如:
.retryIfExceptionOfType(IllegalStateException.class)
.retryIfExceptionOfType(NullPointerException.class) 或者通过Predicate实现:
.retryIfException(Predicates.or(Predicates.instanceOf(NullPointerException.class),
Predicates.instanceOf(IllegalStateException.class))) retryIfResult可以指定你的Callable方法在返回值的时候进行重试,如:
// 返回false重试
.retryIfResult(Predicates.equalTo(false))
//以_error结尾才重试
.retryIfResult(Predicates.containsPattern("_error$")) - RetryListener:自定义重试监听器,可以用于异步记录错误日志,具体实例如下:
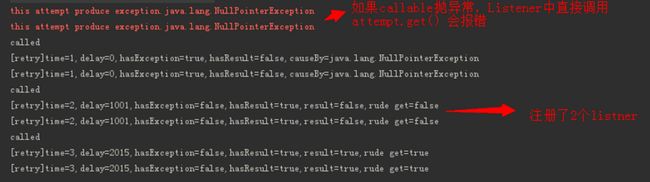
当发生重试之后,假如我们需要做一些额外的处理动作,比如发个告警邮件啥的,那么可以使用RetryListener。每次重试之后,guava-retrying会自动回调我们注册的监听。可以注册多个RetryListener,会按照注册顺序依次调用。
import com.github.rholder.retry.Attempt;
import com.github.rholder.retry.RetryListener;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class MyRetryListener implements RetryListener {
@Override
public void onRetry(Attempt attempt) {
// 第几次重试,(注意:第一次重试其实是第一次调用)
System.out.print("[retry]time=" + attempt.getAttemptNumber());
// 距离第一次重试的延迟
System.out.print(",delay=" + attempt.getDelaySinceFirstAttempt());
// 重试结果: 是异常终止, 还是正常返回
System.out.print(",hasException=" + attempt.hasException());
System.out.print(",hasResult=" + attempt.hasResult());
// 是什么原因导致异常
if (attempt.hasException()) {
System.out.print(",causeBy=" + attempt.getExceptionCause().toString());
} else {
// 正常返回时的结果
System.out.print(",result=" + attempt.getResult());
}
// bad practice: 增加了额外的异常处理代码
try {
Boolean result = attempt.get();
System.out.print(",rude get=" + result);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
System.err.println("this attempt produce exception." + e.getCause().toString());
}
System.out.println();
}
} 接下来在Retry对象中指定监听:
.withRetryListener(new MyRetryListener<>()) 效果如下:
- StopStrategy:停止重试策略,提供三种:
- StopAfterDelayStrategy 设定一个最长允许的执行时间;比如设定最长执行10s,无论任务执行次数,只要重试的时候超出了最长时间,则任务终止,并返回重试异常RetryException。
- NeverStopStrategy 不停止,用于需要一直轮训知道返回期望结果的情况。
- StopAfterAttemptStrategy 设定最大重试次数,如果超出最大重试次数则停止重试,并返回重试异常。
- WaitStrategy:等待时长策略(控制时间间隔),返回结果为下次执行时长:
- FixedWaitStrategy 固定等待时长策略。
- RandomWaitStrategy 随机等待时长策略(可以提供一个最小和最大时长,等待时长为其区间随机值)。
- IncrementingWaitStrategy 递增等待时长策略(提供一个初始值和步长,等待时间随重试次数增加而增加)。
- ExponentialWaitStrategy 指数等待时长策略。
- FibonacciWaitStrategy Fibonacci 等待时长策略。
- ExceptionWaitStrategy 异常时长等待策略。
- CompositeWaitStrategy 复合时长等待策略。