String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder
1、创建String的两种方法
(1)直接赋值 String str="字符串";
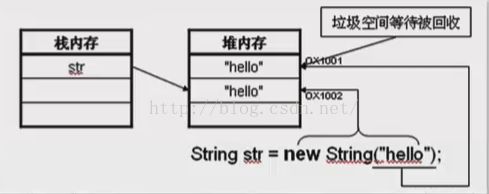
(2)使用new关键字(在内存中开辟了两个空间来存放字符串) String str=new String("字符串");
2、字符换的比较
“==”比较的是地址,而equals()比较的是内容
String str="Hello";
String str1=new String("Hello");
System.out.println(str==str1);//false
System.out.println(str.equals(str1));//true
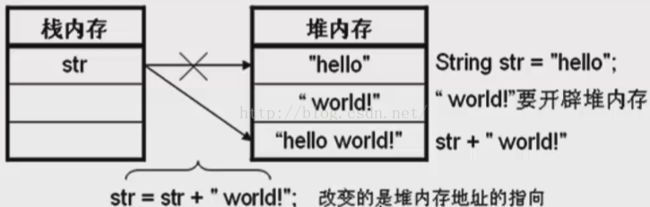
3、String字符串内容不能更改
String str="hello";
String str1=str+"World";
System.out.println(str.equals(str1);
4、String字符串的常用方法
(1)字符串长度:length()方法
(2)字符串转换为数组:toCharArray()
(3)从字符串中取出指定位置的字符:charAt() (从0开始计算)
(4)字符串与byte数组的转换:getBytes()
示例:
public class String1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String str="abcdefg";
byte bytes[]=str.getBytes();
for(int i=0;i(6)去掉字符串前后的空格:trim()
(7)从字符串中取出子字符串:subString()
str=str.substring(int beginIndex);截取掉str从首字母起长度为beginIndex的字符串,将剩余字符串赋值给str;
str=str.substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex);截取str中从beginIndex开始至endIndex结束时的字符串,并将其赋值给str;(包含beginIndex,不包含endIndex)
public class String1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String str="[email protected]";
System.out.println(str.substring(1));//输出:[email protected]
System.out.println(str.substring(2,6));//输出:0901
}
}
(8)大小写转换:toLowerCase() toUpperCase()
(9)判断字符串的开头结尾字符:endsWith() startWith()
public class String1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String str="[email protected]";
System.out.println(str.startsWith("1"));//true
System.out.println(str.endsWith("m"));//true
}
}(10)替换String字符串中一个字符:replace()
String str="[email protected]";
// replace all '0' characters with 'b' characters.
String replacestr=str.replace('0', 'b');
System.out.println(replacestr);//[email protected]
5、StringBuffer(操作类,可更改字符串)
public class String1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
StringBuffer str=new StringBuffer();
str.append("jikexueyuan");
System.out.println(str.toString());//jikexueyuan
tell(str);
System.out.println(str.toString());//jikexueyuani love jikexueyuan
}
public static void tell(StringBuffer s){
s.append("i love jikexueyuan");
}
}public class String1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="hello";
System.out.println(str.toString());//hello
tell(str);
System.out.println(str.toString());//hello
}
public static void tell(String s){
s="i love jikexueyuan";
}
}6、StringBuffer常用方法
append、insert、replace、indexof(用法和String类似)
public class String1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sbf=new StringBuffer();
sbf.append("hello");
sbf.insert(0,"i love");
System.out.println(sbf.toString());//i lovehello
sbf.replace(1, 3, "AAA");
System.out.println(sbf.toString());//iAAAovehello
}
}7、StringBuffer类的应用
因为String加等相关操作都会在内存中创建一个新的对象,耗内存,所以引入StringBuffer类来操作字符串。
8、StringBuilder类
(1)与StringBuffer类似。一个可变的字符序列,该类被设计作用StringBuffer的一个简易替换,用在字符串缓冲区被单个线程使用的时候。建议优先考虑该类,速度比StringBuffer要快。
(2)但是如果涉及到线程安全问题,建议使用StringBuffer
(3)常用方法:append()、insert()
(4)与StringBuffer比较:StringBuffer是线程安全的,StringBuilder是线程不安全的