IO流整理及案例(文件复制),NIO的概念
目录
1.IO流
1)数据传输类型分类
2)数据流向分类
3)按功能作用分类
2.文件复制案例(IO流与NIO管道)
1)IO流复制
2)NIO通道复制
3.NIO
1)NIO的核心
1) NIO示例
流是对数据传输的抽象,特性是进行数据的传输.
按照流向可以分为输入流和输出流.
按数据的处理类型可以分为字节流和字符流.
1.IO流
1)数据传输类型分类
字节流:传输的单位是字节,用于处理所有数据类型,字节流的操作不会经过缓冲区(内存)而是直接操作文本本身
字符流:传输的单位是字符,用于处理文本类型,字符流的操作会先经过缓冲区(内存)然后通过缓冲区再操作文件
2)数据流向分类
输入流:InputStream,FileInputStream,DataInputStream,Reader,FileReader...
输出流:OutputStream,FileOutputStream,DataOutputStream,Writer,FileWriter...
3)按功能作用分类
节点流:直接与数据相连,进行数据的读写;
->常用的是InputStream,FileInputStream,OutputStream,FileOutputStream
处理流:是指在节点流上套接了一层;
->BufferedInputStrean,BufferedOutputStream,BufferedReader,BufferedWriter
转换流:将字节流转换为字符流;
->InputStreamReader,OutputStreamReader
2.文件复制案例(IO流与NIO管道)
1)IO流复制
package com.glperry.demo.io;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 用于IO流的分析总结
* 从IO流的体系来说,分为字节流和字符流
* ->字节流:以字节为单位,处理所有类型的数据 byte. 最小
* ->字符流:以字符为单位,只能处理字符型数据
* ->使用总结:只要是纯文本,优先字符流,其他的都要使用字节流
* 字节流->字符流 转换可通过InputStreamReader/OutPutStreamWriter
* 字符流->字节流 无法转换
* @Date: 2019-08-28
*/
public class IOAnalysis {
/**
* 字节流写入文本/InputStream/OutputStream
*/
@Test
public void streamCopy() throws IOException {
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1.txt");
//输入 iDoLoveJava
os.write("iDoLoveJava".getBytes());
os.flush();
os.close();
}
/**
* 字节流复制文本/InputStream/OutputStream
*/
@Test
public void streamCopyII() throws IOException {
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1_bak.txt");
File file = new File("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1.txt");
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(bytes))>0){
os.write(bytes,0,len);
}
os.flush();
os.close();
}
/**
* 字节流复制图片/InputStream/OutputStream
*/
@Test
public void streamCopyIII() throws IOException {
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1_bak.jpg");
File file = new File("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1.jpg");
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(bytes))>0){
os.write(bytes,0,len);
}
os.flush();
os.close();
}
/**
* 字符流复制文本/InputStream/OutputStream
*/
@Test
public void readerCopy() throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1_bakII.txt");
File file = new File("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len = fr.read(chs);
while (len!=-1){
fw.write(chs,0,len);
fw.flush();
len = fr.read(chs);
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
/**
* 字符流复制图片/Reader/Writer,字符流传输图片出现图片错误!!!
*/
@Test
public void readerCopyII() throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1_bakII.jpg");
File file = new File("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1.jpg");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len = fr.read(chs);
while (len!=-1){
fw.write(chs,0,len);
fw.flush();
len = fr.read(chs);
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
}
2)NIO通道复制
/**
* NIO(Java1.4后New IO,第二种IO)方式复制文件,循环读取方式
*/
@Test
public void nioCopy() throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//定义输入输出路径
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\14MB.jpg");
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1_nio2.jpg");
//操作文件不通过流而是通过管道
FileChannel iChannel = is.getChannel();
FileChannel oChannel = os.getChannel();
//定义缓冲区Buffer分配缓存空间
ByteBuffer buff = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
long end = 0;
//循环读取写出数据
while(iChannel.read(buff)!=-1){
iChannel.read(buff);
//读写文件时修改缓冲区的读写模式
buff.flip();
oChannel.write(buff);
//刷新缓冲区
buff.clear();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
System.out.println(end-start);
}
/**
* NIO(Java1.4后New IO,第二种IO)方式复制文件,自带方法
*/
@Test
public void nioCopyII() throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//定义输入输出路径
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\14MB.jpg");
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E:\\PerryWorkspace\\demo\\src\\main\\resources\\io\\1_nio2.jpg");
//操作文件不通过流而是通过管道
FileChannel iChannel = is.getChannel();
FileChannel oChannel = os.getChannel();
oChannel.transferFrom(iChannel,0,iChannel.size());
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
}总结:通过复制文件NIO与IO对比,可以得出NIO自带方法平均执行时间最短,只有IO流的一半. 文件复制应该选用NIO自带方法.
3.NIO
标准的IO面向数据流,基于字节流和字符流进行操作的;
而NIO是面向缓冲区,数据从Channel读取到Buffer缓冲区,随后在Buffer中处理数据。基于通道(Channel)和缓冲区(Buffer)进行操作,数据总是从通道读取到缓冲区中,或者从缓冲区写入到通道中。
对于NIO是非阻塞,主要体现在SocketChannel上,channel设置为非阻塞,channel的accept/读写方法是非阻塞的,且Selector使得单线程可以注册多个channel,监听多个通道的事件,采用轮询的方式监听selector上是否有需要处理的事件,如果有,则进行处理.
而 FileChannel用于文件传输复制,进行读写的时候是阻塞的,也未提供设置是否阻塞的方法.
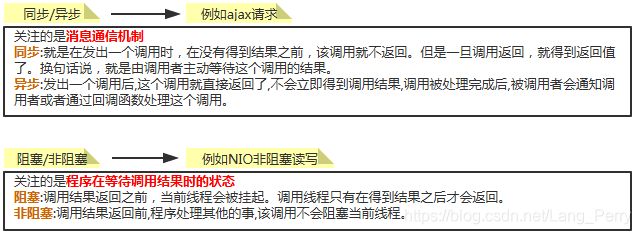
补充下同步异步/阻塞非阻塞知识:
1)NIO的核心
#核心元素
Buffer:一块缓存区,包含元素position,limit,capacity,mark
常用的Buffer类:ByteBuffer,CharBuffer,DoubleBuffer,FloatBuffer,IntBuffer,LongBuffer,ShortBuffer,MappedByteBuffer
Channel:通道,类似于IO中的流(Stream),双向异步的
常用的Channel类:FileChannel,DatagramChannel,SocketChannel,ServerSocketChannel
Selector:选择处理器,通过注册到Channel中,Selector用于单个线程注册多个Channel,监听多个通道的事件.
selectionKey是Channel在Selector中注册的句柄/指针/标记.
1) NIO示例
上面有NIO使用Channel和Buffer的文件复制案例,下面将给出Channel,Buffer,Selector请求处理案例(客户端发送数据,服务端获取)
#服务端
package com.glperry.demo.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.SocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* 服务端,接收数据
* @Date: 2019-08-29
*/
public class NioServer{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//打开一个服务连接通道
ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//创建服务连接地址
InetSocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(8888);
//通道绑定服务地址
channel.bind(socketAddress);
//设置服务端通道非阻塞
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//打开选择处理器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//模拟多个用户,使用selector选择器进行响应
//首先第一步进来的所有连接都是为了接入
channel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//selector 处理接入
while (selector.select()>0){
//可能客户到请求一次进来多个,进行判断
Iterator iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
//获取其中的每个请求
SelectionKey next = iterator.next();
//判断请求是属于 连接过的还是未连接过的
if(next.isAcceptable()){ //没连接过,直接跟踪,设置为读取状态
SocketChannel accept = channel.accept();//通道允许接入请求
accept.configureBlocking(false);//设置非阻塞
accept.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ); //设置为读取数据
}
if(next.isReadable()){ //连接过,直接读取
SelectableChannel channel2 = next.channel();
channel2.configureBlocking(false);
//读取通道信息
readMsg(channel2);
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
private static void readMsg(SelectableChannel channel2) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) channel2;
SocketAddress localAddress = channel.getLocalAddress();
//设置缓存区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//读取数据
int len;
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while ((len = channel.read(buffer))>0){
buffer.flip();//刷新缓存区
buffer.get(b, 0, len);
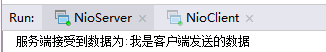
System.out.println("服务端接受到数据为:"+new String(b,0,len));
}
}
}
#客户端
package com.glperry.demo.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 客户端 发送数据
* @Date: 2019-08-29
*/
public class NioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//声明连接地址对象 nio框架使用tcp协议绑定ip和端口
InetSocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888);
//打开一个和服务端连接的通道
SocketChannel channel = SocketChannel.open();
channel.connect(socketAddress);
//设置通道为非阻塞
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//设置缓存区大小
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//控制台的输入数据输出
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNext()){
//清除缓存区的数据
buffer.clear();
//获取控制台的数据
String data = scanner.nextLine();
buffer.put(data.getBytes());
//刷新 缓存区的数据,与IO流的flush类似
buffer.flip();
channel.write(buffer);
}
}
}
#控制台输出的结果