Java8 forEach 使用
1. forEach and Map
普通方式遍历 Map
Map items = new HashMap<>();
items.put("A", 10);
items.put("B", 20);
items.put("C", 30);
items.put("D", 40);
items.put("E", 50);
items.put("F", 60);
for (Map.Entry entry : items.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Item : " + entry.getKey() + " Count : " + entry.getValue());
} 在 java8 中,可以使用 forEach + lambda 表达式循环 Map。
Map items = new HashMap<>();
items.put("A", 10);
items.put("B", 20);
items.put("C", 30);
items.put("D", 40);
items.put("E", 50);
items.put("F", 60);
items.forEach((k,v)->System.out.println("Item : " + k + " Count : " + v));
items.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println("Item : " + k + " Count : " + v);
if("E".equals(k)){
System.out.println("Hello E");
}
}); 2. forEach and List
普通方式遍历 List
List items = new ArrayList<>();
items.add("A");
items.add("B");
items.add("C");
items.add("D");
items.add("E");
for(String item : items){
System.out.println(item);
} 在 java8 中,可以使用 forEach + lambda 表达式或方法引用循环 List。
List items = new ArrayList<>();
items.add("A");
items.add("B");
items.add("C");
items.add("D");
items.add("E");
//lambda
//Output : A,B,C,D,E
items.forEach(item->System.out.println(item));
//Output : C
items.forEach(item->{
if("C".equals(item)){
System.out.println(item);
}
});
//method reference
//Output : A,B,C,D,E
items.forEach(System.out::println);
//Stream and filter
//Output : B
items.stream()
.filter(s->s.contains("B"))
.forEach(System.out::println); foreach语句是java5的新特征之一,在遍历数组、集合方面,foreach为开发人员提供了极大的方便。
foreach语句是for语句的特殊简化版本,但是foreach语句并不能完全取代for语句,然而,任何的foreach语句都可以改写为for语句版本。
foreach并不是一个关键字,习惯上将这种特殊的for语句格式称之为“foreach”语句。从英文字面意思理解foreach也就是“for 每一个”的意思。实际上也就是这个意思。
foreach的语句格式:
for(元素类型t 元素变量x : 遍历对象obj){
引用了x的java语句;
}
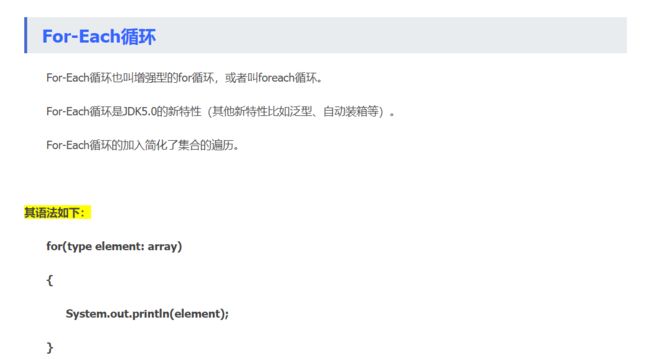
foreach比for的好处和弊端
好处:相对于for来说方便了对容器的遍历
弊端:没有索引,不能操作元素中的元素
For-Each循环的缺点:丢掉了索引信息。
当遍历集合或数组时,如果需要访问集合或数组的下标,那么最好使用旧式的方式来实现循环或遍历,而不要使用增强的for循环,因为它丢失了下标信息。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class ForeachTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.out.println("----------旧方式遍历------------");
//旧式方式
for(int i=0; i list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
System.out.println("----------方式1-----------");
//第一种方式,普通for循环
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
{
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
System.out.println("----------方式2-----------");
//第二种方式,使用迭代器
for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext();)
{
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
System.out.println("----------方式3-----------");
//第三种方式,使用增强型的for循环
for(String str: list)
{
System.out.println(str);
}
}
} public class ForEachDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
funciton_2();
// testHashSet();
}
public static void funciton_2() {
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList();
arr.add(new Person("a", 18));
arr.add(new Person("b", 18));
for (Person p : arr) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
public static void testHashSet() {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("abc1");
coll.add("add2");
coll.add("add3");
coll.add("add4");
coll.add("add5");
coll.add("add6");
for (String s : coll) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
public static void function_1() {
String[] str = { "abc", "a2bb", "a2aa" };
for (String s : str) {
System.out.println(s.length());
System.out.println(s);
}
}
public static void function() {
int[] arr = { 2121, 5454, 545, 4, 54 };
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}