PG虚拟文件描述符(VFD)机制——FD LRU池:postgresql-8.4.1/src/backend/storage/file/fd.c
- 引入虚拟文件描述符机制的痛点:单个进程可以轻易拥有超过系统限制的打开文件数
- 虚拟文件描述符机制的原理概述:VFD作为LRU池管理文件描述符,并根据需要打开和关闭实际需要的OS文件描述符。
FD LRU池的结构如下图所示:
代码解析
fd.c是PG后端代码中存储管理器中的一部分,此代码管理“虚拟”文件描述符(‘virtual’ file descriptors, VFD)的缓存。服务器出于各种原因打开许多文件描述符,包括基表(base tables),暂存文件(scratch files,例如,排序和哈希spool文件),以及对诸如system(3)之类的C库例程的随机调用;单个进程可以轻易拥有超过系统限制的打开文件数(open files)。 (在许多现代操作系统上,系统限制约为256,但在其他操作系统上,则可能低至32。) VFD作为LRU池进行管理,并根据需要打开和关闭实际需要的OS文件描述符。显然,如果使用这些接口,则所有后续操作也必须通过这些接口进行操作(文件类型不是真实的文件描述符,the File type is not a real file descriptor)。为了使该方案起作用,整个PG数据库服务器中的大多数(如果不是全部)例程都应使用这些接口,而不是自己调用C库例程(例如,open(2)和fopen(3))。否则,我们可能仍然会发现自己缺少真实的文件描述符。
注:该文件过去包含一堆东西来支持RAID级别0(jbod),1(双工 duplex)和5(异或奇偶校验 xor parity)。这些东西在本版本中全部删除了,因为调用它的并行查询处理代码全部删除了。如果您确实需要它,可以从原始POSTGRES源代码获取。
以下的头文件都在include文件夹中的相应文件中,而不是和源文件处于同一文件夹中。
#include "postgres.h"
#include "miscadmin.h"
#include "access/xact.h"
#include "catalog/pg_tablespace.h"
#include "storage/fd.h"
#include "storage/ipc.h"
#include "utils/guc.h"
文件描述符LRU池之外遗留的文件描述符相关
#define NUM_RESERVED_FDS 10
我们必须为system(),动态加载程序dynamic loader和其他尝试打开文件而不使用fd.c提供的函数保留一些文件描述符。 (虽然我们可以确定我们不会获得EMFILE,但由于任何其他进程消耗FD的缘故,我们无法保证不会获得ENFILE。因此,尝试不使用fd.c来打开文件是一个坏主意。 我们无法控制所有代码)因为这只是一个固定的设置,所以我们假设没有这样的代码可以使FD长期处于开放open状态。特别要注意的是,我们期望加载共享库不会导致打开文件数量的任何永久增加。 (截至2004年2月,对于大多数(如果不是全部)平台,这似乎都是正确的。)
#define FD_MINFREE 10 如果少于最小可用FD,阻塞
int max_files_per_process = 1000; 平台限制单个进程打开的文件数量
当许多进程执行相同的操作时,许多平台允许单个进程打开的文件数量超出其实际支持的数量。通过该GUC参数,DBA可以将max_safe_fds限制为小于postmaster的初始建议的工作范围。
文件描述符LRU池
文件描述符LRU池–> 最大fd数量
static int max_safe_fds = 32; /* default if not changed */
为VFD条目或AllocateFile / AllocateDir操作打开的文件描述符的最大数量。 它被初始化为一个保守值,并在引导程序bootstrap或独立后端standalone-backend情况下保持该值。 在正常的postmaster操作中,postmaster在初始化后期调用set_max_safe_fds()来更新该值,然后该值由派生子进程继承。注意:设置此变量时会考虑max_files_per_process的值,因此无需单独测试。
static int nfile = 0; 由VFD使用的文件描述符fd的数量
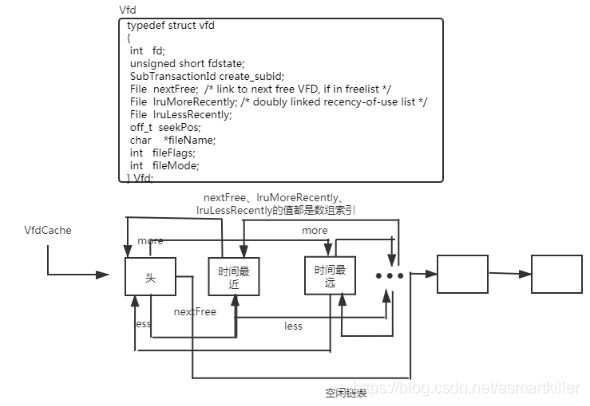
LRU池使用数组实现的,数组元素是vfd结构体虚拟文件描述符数组的指针和大小。 数组大小会根据需要增长。 “文件File”值是该数组的索引。请注意,VfdCache[0]不是可用的VFD,而只是列表头。
static Vfd *VfdCache;
static Size SizeVfdCache = 0;
typedef struct vfd
{
int fd; /* current FD, or VFD_CLOSED if none */
unsigned short fdstate; /* bitflags for VFD's state */
SubTransactionId create_subid; /* for TEMPORARY fds, creating subxact */
File nextFree; /* link to next free VFD, if in freelist */
File lruMoreRecently; /* doubly linked recency-of-use list */
File lruLessRecently;
off_t seekPos; /* current logical file position */
char *fileName; /* name of file, or NULL for unused VFD */
/* NB: fileName is malloc'd, and must be free'd when closing the VFD */
int fileFlags; /* open(2) flags for (re)opening the file */
int fileMode; /* mode to pass to open(2) */
} Vfd;
LRU池的底层虽然是数组,但是通过lruMoreRecently和lruLessRecently成员变量定位下一个vfd元素,也就是就是环形队列。( typedef int File )这里的File被定义为Int类型,也就是数组索引。
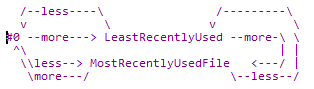
VfdCache[0]可以看成最近最少使用和最近最多使用集于一身,当使用lruMoreRecently成员进行寻址时,它就是最近最少使用,可以通过它找到真正的最近最少使用的vfd。同样可以通过lruLessRecently成员进行寻址,找到真正最近最多使用的vfd。VfdCache[0]的fd成员永远为VFD_CLOSED(#define VFD_CLOSED (-1) 当该VFD结构体无效时,fd值会被设置为-1)。除了VfdCache[0],只有真正打开的vfd(赋值了真正的文件描述符FD)才能放入环形队列。
- 打开的vfd的fd成员赋值了真正的文件描述符FD
- 虚打开(“virtually” open)的vfd的fileName成员为非空
相关操作函数
- Delete - delete a file from the Lru ring
- LruDelete - remove a file from the Lru ring and close its FD
- Insert - put a file at the front of the Lru ring
- LruInsert - put a file at the front of the Lru ring and open it
- ReleaseLruFile - Release an fd by closing the last entry in the Lru ring
- AllocateVfd - grab a free (or new) file record (from VfdArray)
- FreeVfd - free a file record
Insert:将索引file的Vfd结构体插入环形队列的front。该Vfd是lru中MostRecently(最近使用)的。主要重点在将新Vfd插入环形队列的front位置时,更新VfdCache[0]、新Vfd、旧VfdCache[front]的lruMoreRecently成员和lruLessRecently成员的关系。

LruInsert:将索引file的Vfd结构体插入环形队列,成功返回0,重新打开失败返回-1,并设置errno。
static int
LruInsert(File file)
{
Vfd *vfdP;
Assert(file != 0);
DO_DB(elog(LOG, "LruInsert %d (%s)",
file, VfdCache[file].fileName));
vfdP = &VfdCache[file];
if (FileIsNotOpen(file))
{
while (nfile + numAllocatedDescs >= max_safe_fds)
{
if (!ReleaseLruFile())
break;
}
/*
* The open could still fail for lack of file descriptors, eg due to
* overall system file table being full. So, be prepared to release
* another FD if necessary...
*/
vfdP->fd = BasicOpenFile(vfdP->fileName, vfdP->fileFlags,
vfdP->fileMode);
if (vfdP->fd < 0)
{
DO_DB(elog(LOG, "RE_OPEN FAILED: %d", errno));
return vfdP->fd;
}
else
{
DO_DB(elog(LOG, "RE_OPEN SUCCESS"));
++nfile;
}
/* seek to the right position */
if (vfdP->seekPos != (off_t) 0)
{
off_t returnValue;
returnValue = lseek(vfdP->fd, vfdP->seekPos, SEEK_SET);
Assert(returnValue != (off_t) -1);
}
}
/*
* put it at the head of the Lru ring
*/
Insert(file);
return 0;
}
![]()
需要提前处理的逻辑是检查file中fd是否有效,即不为-1。如果无效,尝试通过C函数库open API获取有效的fd(BasicOpenFile)。如果目前占用的fd数量(有效的vfd占用的fd、AllocateFile占用的和AllocateDir占用的)大于最多能打开的fd,需要释放lru池中的fd。根据vfd的seekPos来更新打开的fd的指针位置。最后将file插入环形队列的front。
Delete:将索引file的Vfd结构体从环形队列中删除。
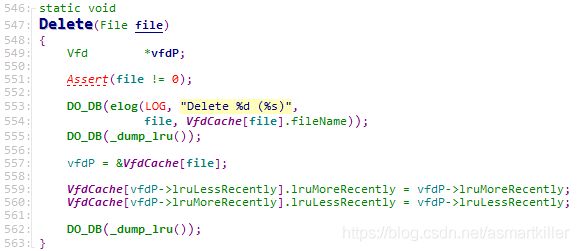
LruDelete:将索引file的Vfd结构体从环形队列中删除。和Delete相比,该函数将打开文件的当前指针位置保存到vfd,并且关闭文件,设置vfd的状态为无效。
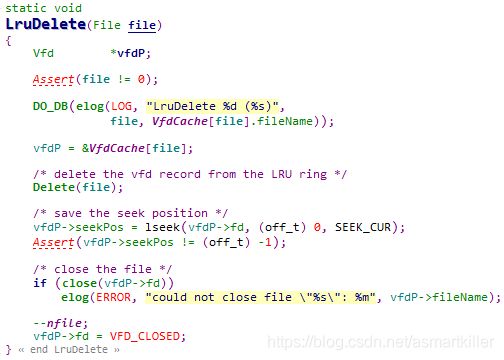
ReleaseLruFile:删除lru池中最近最少使用的vfd,使用LruDelete函数处理,不仅从Lru中剔除还将打开文件的当前指针位置保存到vfd,并且关闭文件,设置vfd的状态为无效。

如果vfd中的fileName不为NULL,需要free。将fdstate设置为0x0,将该vfd节点插入空闲vfd链表头部

AllocateVfd函数从空闲vfd链表中分配vfd节点,并将节点索引返回(失败返回0)。如果空闲vfd链表中没有空闲节点,增加数组的大小(原大小的两倍,但不超过32),使用realloc进行空间申请,清空新申请的空间,并加新节点添加到空闲vfd链表中。
static File
AllocateVfd(void)
{
Index i;
File file;
DO_DB(elog(LOG, "AllocateVfd. Size %lu", SizeVfdCache));
Assert(SizeVfdCache > 0); /* InitFileAccess not called? */
if (VfdCache[0].nextFree == 0)
{
/*
* The free list is empty so it is time to increase the size of the
* array. We choose to double it each time this happens. However,
* there's not much point in starting *real* small.
*/
Size newCacheSize = SizeVfdCache * 2;
Vfd *newVfdCache;
if (newCacheSize < 32)
newCacheSize = 32;
/*
* Be careful not to clobber VfdCache ptr if realloc fails.
*/
newVfdCache = (Vfd *) realloc(VfdCache, sizeof(Vfd) * newCacheSize);
if (newVfdCache == NULL)
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_OUT_OF_MEMORY),
errmsg("out of memory")));
VfdCache = newVfdCache;
/*
* Initialize the new entries and link them into the free list.
*/
for (i = SizeVfdCache; i < newCacheSize; i++)
{
MemSet((char *) &(VfdCache[i]), 0, sizeof(Vfd));
VfdCache[i].nextFree = i + 1;
VfdCache[i].fd = VFD_CLOSED;
}
VfdCache[newCacheSize - 1].nextFree = 0;
VfdCache[0].nextFree = SizeVfdCache;
/*
* Record the new size
*/
SizeVfdCache = newCacheSize;
}
file = VfdCache[0].nextFree;
VfdCache[0].nextFree = VfdCache[file].nextFree;
return file;
}
打印lru中的以最近使用遍历的vfd的顺序

可配置关键点:单个进程打开的文件数量(max_files_per_process)
源自肥叔菌的cnblogs精华博客系列:https://www.cnblogs.com/feishujun/p/PostgreSQLSourceAnalysis_vfd01.html