面试中LeetCode常见算法整理——双指针
面试中LeetCode常见算法整理——双指针
1. 有序数组的Two Sum
167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted
class Solution {
public:
vector twoSum(vector& numbers, int target) {
int l = 0, r = numbers.size() - 1;
while (l < r)
{
if (numbers[l] + numbers[r] == target)
return { l + 1, r + 1 };
else if (numbers[l] + numbers[r] > target)
--r;
else
++l;
}
return vector();
}
}; 2. 两数平方和
633. Sum of Square Numbers
class Solution {
public:
bool judgeSquareSum(int c) {
if (c < 0)
return false;
int l = 0, r = sqrt(c);
while (l <= r)
{
int temp = c - l * l;
if (temp == r * r)
return true;
else if (temp > r*r)
++l;
else
--r;
}
return false;
}
};3. 反转字符串中的元音字符
345. Reverse Vowels of a String
class Solution {
public:
string reverseVowels(string s) {
int i = 0;
int j = s.size() - 1;
char temp;
while (i < j)
{
if (!isVowel(s[i]))
++i;
else if (!isVowel(s[j]))
--j;
else
swap(s[i++], s[j--]);
}
return s;
}
private:
inline bool isVowel(char c)
{
c = tolower(c);
if (c == 'a' || c == 'e' || c == 'i' || c == 'o' || c == 'u')
return true;
return false;
}
};4. 回文字符串
680. Valid Palindrome II
class Solution {
public:
bool validPalindrome(string s) {
int l = 0, r = s.length() - 1;
while (l < r)
{
if (s[l] != s[r])
return isPalindrome(s, l + 1, r) || isPalindrome(s, l, r - 1);
++l;
--r;
}
return true;
}
private:
//判断是否是回文字符串
bool isPalindrome(string s, int l, int r)
{
while (l < r)
{
if (s[l] != s[r])
return false;
++l;
--r;
}
return true;
}
};5. 归并两个有序数组
88. Merge Sorted Array
class Solution {
public:
void merge(vector& nums1, int m, vector& nums2, int n) {
int k = m + n - 1;
while (k >= 0)
{
if (n <= 0) //num2中无元素
nums1[k--] = nums1[--m];
else if(m <= 0) //nums1中无元素
nums1[k--] = nums2[--n];
else if(nums1[m - 1] >= nums2[n - 1])
nums1[k--] = nums1[--m];
else
nums1[k--] = nums2[--n];
}
}
}; 6. 判断链表是否存在环
141. Linked List Cycle
使用双指针,一个指针每次移动一个节点,一个指针每次移动两个节点,如果存在环,那么这两个指针一定会相遇。
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (!head || !head->next)
return false;
ListNode* pSlow = head;
ListNode* pFast = head->next;
while (pFast && pFast->next)
{
if (pSlow == pFast)
return true;
pSlow = pSlow->next;
pFast = pFast->next->next;
}
return false;
}
};统一写法
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (!head || !head->next)
return false;
ListNode* pSlow = head;
ListNode* pFast = head;
do
{
pSlow = pSlow->next;
pFast = pFast->next->next;
} while (pFast && pFast->next && pSlow != pFast);
if (pSlow == pFast)
return true;
return false;
}
};7. 链表中环的入口节点
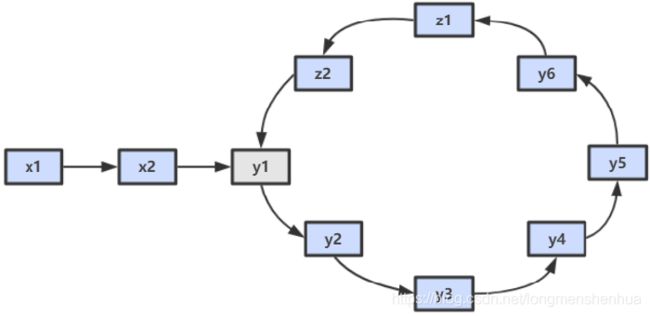
使用双指针,一个指针 fast 每次移动两个节点,一个指针 slow 每次移动一个节点。因为存在环,所以两个指针必定相遇在环中的某个节点上。假设相遇点在下图的 z1 位置,此时 fast 移动的节点数为 x+2y+z,slow 为 x+y,由于fast 速度比 slow 快一倍,因此 x+2y+z=2(x+y),得到 x=z。
在相遇点,slow 要到环的入口点还需要移动 z 个节点,如果让 fast 重新从头开始移动,并且速度变为每次移动一个节点,那么它到环入口点还需要移动 x 个节点。在上面已经推导出 x=z,因此 fast 和 slow 将在环入口点相遇。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead)
{
if (!pHead || !pHead->next)
return nullptr;
ListNode* pSlow = pHead;
ListNode* pFast = pHead;
//为保证到相遇节点时pFast走过的路径是pSlow的二倍,两者的起始位置要保持一致
//所以就采用了do-while循环结构
//判断链表是否有环也可以采用这种循环结构
//所以干脆统一用这种结构得了
do
{
pSlow = pSlow->next;
pFast = pFast->next->next;
} while (pFast && pFast->next && pFast != pSlow);
if (pSlow != pFast) //不存在环的情况
return nullptr;
pFast = pHead;
while (pFast != pSlow)
{
pFast = pFast->next;
pSlow = pSlow->next;
}
return pSlow;
}
};8. 最长子序列
524. Longest Word in Dictionary through Deleting
class Solution {
public:
string findLongestWord(string s, vector& d) {
string res = "";
for (auto str : d)
{
if (isValid(s, str))
{
if (str.length() > res.length())
res = str;
else if (str.length() == res.length() && str < res)
res = str;
}
}
return res;
}
private:
//s和t是否匹配
bool isValid(string s, string t)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while ( i< s.size() && j 9. 盛最多水的容器
11. Container With Most Water
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector& height) {
int res = INT_MIN;
int l = 0;
int r = height.size()-1;
while(l