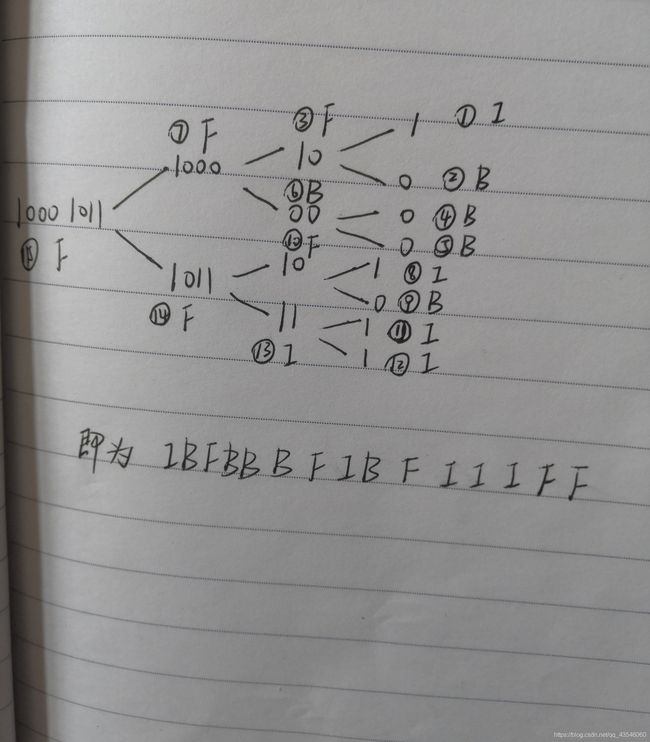
acm——加工并储存的数据结构
Fence Repair
#include二叉树:
例题一:
洛谷oj——求先序遍历
思路:选择后序遍历中的最后一个字符,从前往后去搜索中序遍历
最后递归实现遍历左右子树
#include例题二:
洛谷oj——新二叉树
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/johnwayne0317/article/details/86763052
#include#include