ERROR 1327 (42000): Undeclared variable:
select into from 和 insert into select都是用来复制表的
两者的主要区别为:
1)select into from 要求目标表不存在,因为在插入时会自动创建。
2) insert into select from 要求目标表存在
一、INSERT INTO SELECT语句
1、语句形式为:
Insert into Table2(field1,field2,...) select value1,value2,... from Table1
2、注意地方:
(1)要求目标表Table2必须存在,并且字段field,field2...也必须存在
(2)注意Table2的主键约束,如果Table2有主键而且不为空,则 field1, field2...中必须包括主键
(3)注意语法,不要加values,和插入一条数据的sql混了,不要写成:
Insert into Table2(field1,field2,...) values (select value1,value2,... from Table1)
(4)由于目标表Table2已经存在,所以我们除了插入源表Table1的字段外,还可以插入常量。
二、SELECT INTO FROM语句
语句形式为:
SELECT vale1, value2 into Table2 from Table1
要求目标表Table2不存在,因为在插入时会自动创建表Table2,并将Table1中指定字段数据复制到Table2中 。
总结复制表的基本语句(从旧表复制到新表):
1、create table newTable as select * from oldTabel; 既复制表结构,也复制表内容;
2、create table newTable as select * from oldTable where 1=2; 只复制表结构,不复制表内容;
3、insert into newTable select * form oldTable; 不复制表结构,只复制表内容
或者 select value1,value2 into newTable form oldTable;
ERROR 1327 (42000): Undeclared variable:
select into from 提示 Undeclared variable.....错误的解决办法 && select into from 和 insert into select 的用法和区别
然而今天在使用 SELECT INTO FROM 备份mysql数据表的时候,运行相关 sql 语句的时候却一直返回 [Err] 1327 - Undeclared variable: ...... 这种错误,实在不解,经过查询相关资料才知道,原来 mysql 数据库是不支持 SELECT INTO FROM 这种语句的,但是经过研究是可以通过另外一种变通的方法解决这个问题的,下面就来说说解决这个错误!
mysql> select user,host into user2 from user;
ERROR 1327 (42000): Undeclared variable: user2解决方法是:
create table user2 (select * from user);这种方法会将old_table中所有的内容都拷贝过来,用这种方法需要注意,new_table中没有了old_table中的primary key,Extra,auto_increment等属性,需要自己手动加,具体参看后面的修改表即字段属性.
mysql> create table user2 (select * from user);
Query OK, 6 rows affected (0.18 sec)
Records: 6 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0mysql> create table user01 (select user,password,host from user);
Query OK, 6 rows affected (0.20 sec)
Records: 6 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from user01;
+------+----------+-----------+
| user | password | host |
+------+----------+-----------+
| root | | localhost |
| root | | lmr |
| root | | 127.0.0.1 |
| root | | ::1 |
| | | localhost |
| | | lmr |
+------+----------+-----------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> desc user01;
+----------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| user | char(16) | NO | | | |
| password | char(41) | NO | | | |
| host | char(60) | NO | | | |
+----------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)注意: SELECT INTO 复制表或表结构的时候,只是得到了一个“外壳”,就像克隆人一样,只是得到了一个躯体,个人的意识、回忆都不会克隆的。像原表的主键、外键、约束、触发 器、索引都不会被复制过来CREATE TABLE 表名 AS SELECT 语句
1.新表不存在
create table new_table select * from old_talbe;
这种方法会将old_table中所有的内容都拷贝过来,用这种方法需要注意,new_table中没有了old_table中的primary key,Extra,auto_increment等属性,需要自己手动加,具体参看后面的修改表即字段属性.
只复制表结构到新表
# 第一种方法,和上面类似,只是数据记录为空,即给一个false条件
create table new_table select * from old_table where 1=2;
# 第二种方法
create table new_table like old_table;
2.新表存在
复制旧表数据到新表(假设两个表结构一样)
insert into new_table select * from old_table;
复制旧表数据到新表(假设两个表结构不一样)
insert into new_table(field1,field2,.....) select field1,field2,field3 from old_table;
复制全部数据
select * into new_table from old_table;
只复制表结构到新表
select * into new_talble from old_table where 1=2;
create table a like b;
create table c_relation as select c.memberId,m.merchantId,memb.phone from c_merchant as m inner join c_customer c on c.userId=m.userId inner join c_member memb on memb.id=c.memberId where memb.status=10;
由上面的使用 CREATE TABLE 表名 AS SELECT 语句可以看出:
1:只会复制表数据和表结构,不会有任何约束。
2:当 where 条件不成立时,只复制表结构,没有任务数据
EG:
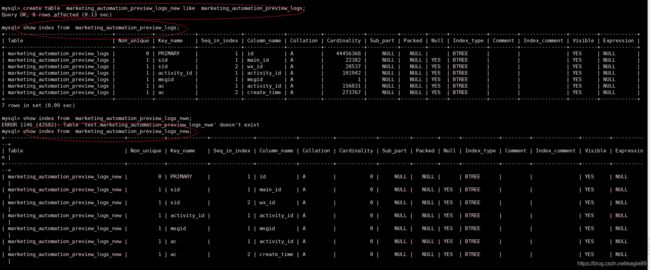
mysql> create table marketing_automation_preview_logs_new like marketing_automation_preview_logs;
mysql> show index from marketing_automation_preview_logs;
mysql> show index from marketing_automation_preview_logs_new;
mysql> insert into marketing_automation_preview_logs_new (select * from marketing_automation_preview_logs where act_time> '1588521600');
mysql> select count(*) from marketing_automation_preview_logs_new;
mysql> select count(*) from marketing_automation_preview_logs where act_time> '1588521600';
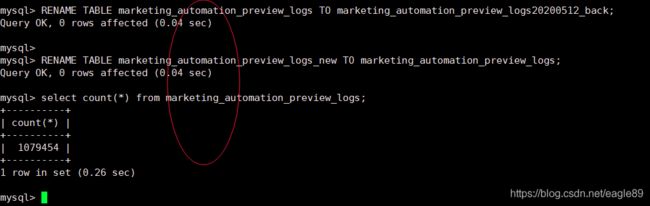
mysql> RENAME TABLE marketing_automation_preview_logs TO marketing_automation_preview_logs20200512_back;
mysql> RENAME TABLE marketing_automation_preview_logs_new TO marketing_automation_preview_logs;
mysql> select count(*) from marketing_automation_preview_logs;
总结:
create table marketing_automation_preview_logs_new like marketing_automation_preview_logs;
insert into marketing_automation_preview_logs_new (select * from marketing_automation_preview_logs where act_time> '1588521600');
RENAME TABLE marketing_automation_preview_logs TO marketing_automation_preview_logs20200512_back;
RENAME TABLE marketing_automation_preview_logs_new TO marketing_automation_preview_logs;
show index from marketing_automation_preview_logs;
select count(*) from marketing_automation_preview_logs;
mysql8 参考手册--SELECT ... INTO语句
SELECT ... INTO形式SELECT 使查询结果存储在变量或将其写入文件:
SELECT ... INTO var_list 选择列值并将其存储到变量中。
SELECT ... INTO OUTFILE将选定的行写入文件。可以指定列和行终止符以生成特定的输出格式。
SELECT ... INTO DUMPFILE 将单行写入文件而没有任何格式。
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/select-into.html