stm32 Fatfs 读写SD卡
读写SD是嵌入式系统中一个比较基础的功能,在很多应用中都可以用得上SD卡。折腾了几天,总算移植成功了 最新版Fatfs(Fatfs R0.09) ,成功读写SD卡下文件。
FatFs ( http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html)是一个通用的文件系统模块,用于在小型嵌入式系统中实现FAT文件系统。 FatFs 的编写遵循ANSI C,因此不依赖于硬件平台。它可以嵌入到便宜的微控制器中,如 8051, PIC, AVR, SH, Z80, H8, ARM 等等,不需要做任何修改。
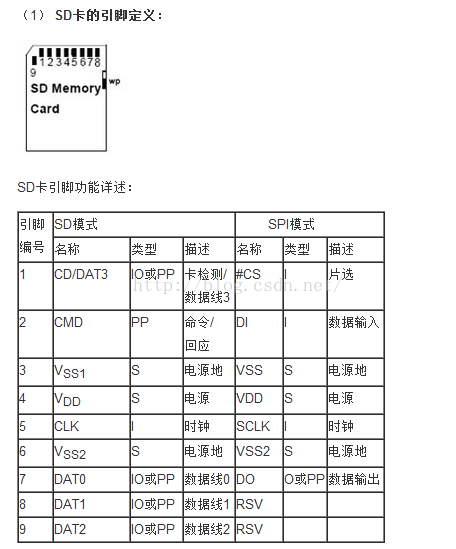
1. SD卡/TF卡 硬件接口
SD卡有两种操作接口,SDIO和SPI。 使用SDIO口的速度比较快,SPI的速度比较慢 。
SD卡引脚描述如下: SD卡SPI接法如下:
我使用的是正点原子的开发板,所以采用的是SPI接口的模式。
TF卡SDIO 模式和SPI模式 引脚定义:
可以发现Micro SD卡只有8个引脚是因为比SD卡少了一个Vss。使用TF转SD的卡套套在Micro SD卡上,这样一来大小就和SD卡一样大,这时候卡套上的9个引脚就和SD卡一样了,你可以完全当做SD卡来操作。
2. SD卡底层驱动
SD卡的操作比较复杂,需要多看看一些文档 。 这里附上SD底层驱动代码,代码说明详见注释
Sd卡SPi操作底层代码 : sdcard.c sdcard.h
3. Fatfs 移植
FatFs 软件包中相关文件:
ffconf.h FatFs 模块配置文件
ff.h FatFs 和应用模块公用的包含文件
ff.c FatFs 模块
diskio.h FatFs and disk I/O 模块公用的包含文件
integer.h 数据类型定义
option 可选的外部功能
diskio.c FatFs 与disk I/O 模块接口层文件(不属于 FatFs 需要由用户提供)
FatFs 配置,文件系统的配置项都在 ffconf.h 文件之中:
(1) _FS_TINY :这个选项在R0.07 版本之中开始出现,在之前的版本都是以独立的文件出现,现在通过一个宏来修改使用起来更方便;
(2) _FS_MINIMIZE、_FS_READONLY、_USE_STRFUNC、_USE_MKFS、_USE_FORWARD 这些宏是用来对文件系统进行裁剪
(3) _CODE_PAGE :本选项用于设置语言码的类型
(4) _USE_LFN :取值为0~3,主要用于长文件名的支持及缓冲区的动态分配:
0:不支持长文件名;
1:支持长文件名存储的静态分配,一般是存储在BSS 段;
2:支持长文件名存储的动态分配,存储在栈上;
3:支持长文件名存储的动态分配,存储在堆上。
(5) _MAX_LFN :可存储长文件的最大长度,其值一般为(12~255),但是缓冲区一般占(_MAX_LFN + 1) * 2 bytes;
(6) _LFN_UNICODE :为1 时才支持unicode 码;
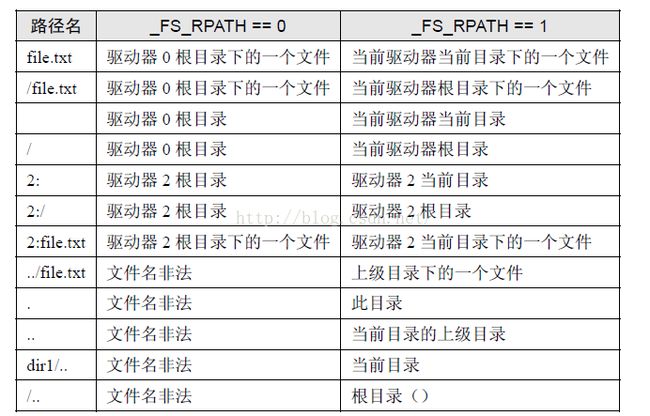
(7) _FS_RPATH :R0.08a 版本改动配置项,取值范围0~2:
0:去除相对路径支持和函数;
1:开启相对路径并且开启f_chdrive()和f_chdir()两个函数;
2:在1 的基础上添加f_getcwd()函数。
(8) _VOLUMES :支持的逻辑设备数目;
(9) _MAX_SS :扇区缓冲的最大值,其值一般为512;
(10) _MULTI_PARTITION:定义为1 时,支持磁盘多个分区;
(11) _USE_ERASE :R0.08a 新加入的配置项,设置为1 时,支持扇区擦除;
(12) _WORD_ACCESS :如果定义为1,则可以使用word 访问;
(13) _FS_REENTRANT :定义为1 时,文件系统支持重入,但是需要加上跟操作系统信号量相关的几个函数,函数在syscall.c 文件中;
(14) _FS_SHARE :文件支持的共享数目。
Fatfs 开源文件系统 从R0.07e 之后 版本开始就不再提供底层接口文件 diskio.c 模板,这里附上根据
以上SD卡底层驱动对应的 diskio.c 源码:
#include "common.h"
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Inidialize a Drive */
DSTATUS disk_initialize (
BYTE drv /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
)
{
u8 state;
if(drv)
{
return STA_NOINIT; //仅支持磁盘0的操作
}
state = SD_Init();
if(state == STA_NODISK)
{
return STA_NODISK;
}
else if(state != 0)
{
return STA_NOINIT; //其他错误:初始化失败
}
else
{
return 0; //初始化成功
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Return Disk Status */
DSTATUS disk_status (
BYTE drv /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
)
{
if(drv)
{
return STA_NOINIT; //仅支持磁盘0操作
}
//检查SD卡是否插入
if(!SD_DET())
{
return STA_NODISK;
}
return 0;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Read Sector(s) */
DRESULT disk_read (
BYTE drv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */
DWORD sector, /* Sector address (LBA) */
BYTE count /* Number of sectors to read (1..255) */
)
{
u8 res=0;
if (drv || !count)
{
return RES_PARERR; //仅支持单磁盘操作,count不能等于0,否则返回参数错误
}
if(!SD_DET())
{
return RES_NOTRDY; //没有检测到SD卡,报NOT READY错误
}
if(count==1) //1个sector的读操作
{
res = SD_ReadSingleBlock(sector, buff);
}
else //多个sector的读操作
{
res = SD_ReadMultiBlock(sector, buff, count);
}
/*
do
{
if(SD_ReadSingleBlock(sector, buff)!=0)
{
res = 1;
break;
}
buff+=512;
}while(--count);
*/
//处理返回值,将SPI_SD_driver.c的返回值转成ff.c的返回值
if(res == 0x00)
{
return RES_OK;
}
else
{
return RES_ERROR;
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Write Sector(s) */
#if _READONLY == 0
DRESULT disk_write (
BYTE drv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */
DWORD sector, /* Sector address (LBA) */
BYTE count /* Number of sectors to write (1..255) */
)
{
u8 res;
if (drv || !count)
{
return RES_PARERR; //仅支持单磁盘操作,count不能等于0,否则返回参数错误
}
if(!SD_DET())
{
return RES_NOTRDY; //没有检测到SD卡,报NOT READY错误
}
// 读写操作
if(count == 1)
{
res = SD_WriteSingleBlock(sector, buff);
}
else
{
res = SD_WriteMultiBlock(sector, buff, count);
}
// 返回值转换
if(res == 0)
{
return RES_OK;
}
else
{
return RES_ERROR;
}
}
#endif /* _READONLY */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Miscellaneous Functions */
DRESULT disk_ioctl (
BYTE drv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE ctrl, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
DRESULT res;
if (drv)
{
return RES_PARERR; //仅支持单磁盘操作,否则返回参数错误
}
//FATFS目前版本仅需处理CTRL_SYNC,GET_SECTOR_COUNT,GET_BLOCK_SIZ三个命令
switch(ctrl)
{
case CTRL_SYNC:
SD_CS_ENABLE();
if(SD_WaitReady()==0)
{
res = RES_OK;
}
else
{
res = RES_ERROR;
}
SD_CS_DISABLE();
break;
case GET_BLOCK_SIZE:
*(WORD*)buff = 512;
res = RES_OK;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_COUNT:
*(DWORD*)buff = SD_GetCapacity();
res = RES_OK;
break;
default:
res = RES_PARERR;
break;
}
return res;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* User defined function to give a current time to fatfs module */
/* 31-25: Year(0-127 org.1980), 24-21: Month(1-12), 20-16: Day(1-31) */
/* 15-11: Hour(0-23), 10-5: Minute(0-59), 4-0: Second(0-29 *2) */
DWORD get_fattime (void)
{
return 0;
}
这里的结构函数为Fatfs提供和SD卡的通信接口。 在 最新版本的Fatfs中还加入了对中文文件名的支持,需要修改 ffconf.h
#define _CODE_PAGE 936 //- Simplified Chinese GBK (DBCS, OEM, Windows)
同时应该添加 option/cc936.c文件。但是这个文件有700多K占相当大的ROM, 像stm32F103RBT6这种小FLASH的MCU根本不行 ,加入当前工程文件中代码将增加160KB 左右。
配置好Stm32的串口和SPI等IO口设置后,就可以使用Fatfs做一些文件操作了。
4. Fatfs 文件操作
文件分配表FAT(File AllocationTable)用来记录文件所在位置的表格.它对于硬盘的使用是非常重要的,假若丢失文件分配表,那么硬盘上的数据就会因无法定位而不能使用了。
Fatfs 文件系统减轻了操作SD卡的工作量,调用其提供的函数就可以方便的操作文件,读写删改等。
这里提供一个main.c 示例:
#include "common.h"
#include
FRESULT scan_files (char* path);
#define F_PUTS 1 //测试向文件写入字符串
#define F_READ 1 //测试从文件中读出数据
#define F_UNLINK 0 //测试删除文件
#define SCAN_FILES 1 //测试目录扫描
FATFS fs;
FRESULT res;
FIL file;
UINT br;
BYTE buffer[4096]; //以上变量作为全局变量 可以避免一些Bug
int main(void)
{
u16 i,n;
//stm32 初始化
RCC_Configuration();
NVIC_Configuration();
USART_Configuration();
SPI_Configuration();
GPIO_Configuration();
//fatfs 操作
f_mount(0, &fs);
//如果data.txt存在,则打开;否则,创建一个新文件
res = f_open(&file, "0:/data.txt",FA_OPEN_ALWAYS|FA_READ|FA_WRITE );
if(res!=FR_OK)
{
printf("\r\n f_open() fail .. \r\n");
}else{
printf("\r\n f_open() success .. \r\n");
}
#if F_READ
while(1){ //使用f_read读文件
res = f_read(&file, buffer, 1, &br); //一次读一个字节知道读完全部文件信息
if (res == FR_OK )
{
printf("%s",buffer);
}else{
printf("\r\n f_read() fail .. \r\n");
}
if(f_eof(&file)) {break;}
}
/*if( f_gets(buffer,sizeof(buffer),&file) != NULL) //使用f_gets读文件 ,存在 Bugs 待调试
{
printf("%s",buffer);
}else{
printf("\r\n f_gets() fail .. \r\n");
} */
#endif
#if F_PUTS
//将指针指向文件末
//res = f_lseek(&file,(&file)->fsize);
res = f_lseek(&file,file.fsize);
n = f_puts("\r\n hello dog ..\r\n", &file) ; //向文件末写入字符串
if(n<1) //判断写是否成功
{
printf("\r\n f_puts() fail .. \r\n");
}else{
printf("\r\n f_puts() success .. \r\n");
}
#endif
#if F_UNLINK
res = f_unlink("test.jpg"); //前提SD下存在一个test.jpg
if(res!=FR_OK)
{
printf("\r\n f_unlink() fail .. \r\n");
}else{
printf("\r\n f_unlink() success .. \r\n");
}
#endif
#if SCAN_FILES
printf("\r\n the directory files : \r\n");
scan_files("/"); //扫描根目录
#endif
f_close(&file);
f_mount(0, NULL);
while(1);
}
FRESULT scan_files (
char* path /* Start node to be scanned (also used as work area) */
)
{
FRESULT res;
FILINFO fno;
DIR dir;
int i;
char *fn; /* This function is assuming non-Unicode cfg. */
#if _USE_LFN
static char lfn[_MAX_LFN + 1];
fno.lfname = lfn;
fno.lfsize = sizeof lfn;
#endif
res = f_opendir(&dir, path); /* Open the directory */
if (res == FR_OK) {
i = strlen(path);
for (;;) {
res = f_readdir(&dir, &fno); /* Read a directory item */
if (res != FR_OK || fno.fname[0] == 0) break; /* Break on error or end of dir */
if (fno.fname[0] == '.') continue; /* Ignore dot entry */
#if _USE_LFN
fn = *fno.lfname ? fno.lfname : fno.fname;
#else
fn = fno.fname;
#endif
if (fno.fattrib & AM_DIR) { /* It is a directory */
sprintf(&path[i], "/%s", fn);
res = scan_files(path);
if (res != FR_OK) break;
path[i] = 0;
} else { /* It is a file. */
printf("\r\n %s/%s \r\n", path, fn);
}
}
}
return res;
}
其中 目录扫描函数 scan_files( char * path) 参数格式如下:
这里使用到了f_puts()函数,所以必须在ffconf.h 中修改 #define _USE_STRFUNC 1