Java反射和设计模式
本文是课上资料的总结非原创没有转载地址
目录
- Java反射
- 反射
- 为什么需要反射
- 类对象
- 反射相关的类
- 常见操作
- 获取类对象的方法(3种)
- 获取类中的构造方法
- 获取、调用类中的普通方法
- 获取、设置类中的属性
- 特例(带有数组参数的方法)
- 反射优点和缺点
- 使用反射模拟实际插件开发
- 内省
- 设计模式介绍
- 设计模式
- 单例设计模式
- 实现方式一:饿汉子(类加载时创建,天生线程安全)
- 实现方式二:懒汉子
- 实现方式三:静态内部类
- 简单工厂模式(不属于23种GOF设计模式之一)
- 案例
Java反射
反射
- 反射就是把Java类中的各种成分映射成一个个单独Java对象进行操作。
- 本质:就是类的解剖技术。
- 类中成分主要包括:成员变量,构造方法,包等。
为什么需要反射
- 需求:我公司定义了一组接口,然后第三方公司按照我公司的接口实现了一套功能,然后交给我们,但是我们公司的项目已经结束,如何实现动态加载第三方公司提供的功能?
- 插件开发(反射技术)
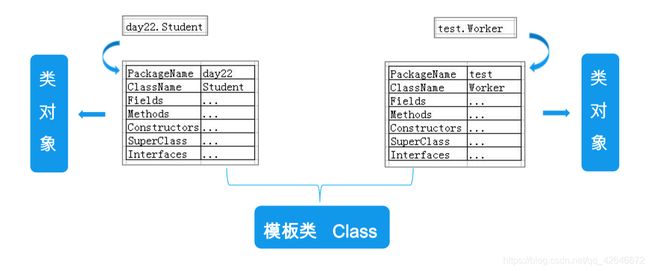
类对象
反射相关的类
- Class类——可获取类和类中的成员信息
- Filed类——可访问类的属性
- Method类——可调用类的方法
- Constructor类——可调用类的构造方法
常见操作
获取类对象的方法(3种)
- 通过类的对象的
getClass();方法,获取类对象
Student s = new Student();
Class<?> c = s.getClass();
- 通过“类名.class”获取类对象
Class<?> c = 类名.class;
- 通过静态方法获取类对象(推荐使用,不依靠类)
Class<?> c = Class.forName("包名.类名");
获取类中的构造方法
- 获取类中所有公开的构造方法
Constructor<?>[] constructors = c.getConstructors();
- 获取类中所有的构造方法(包括私有)
Constructor<?>[] constructors = c.getDeclaredConstructors();
- 获取无参的构造方法
Constructor<?> constructor = c.getConstructor();
// 使用获取的构造方法(返回值是Object)
Object s = constructor.newInstance();
- 获取带参的构造方法
Constructor<?> constructor = class1.getConstructor(int.class, String.class, int.class, String.class); //参数类型的类对象逗号分开
Object s = constructor.newInstance(110, "张三", 20, "北京"); // 有参构造
- 简单方法
Object s = c.newInstance();// 调用无参构造方法
- 获取私有的构造方法(破坏了封装性)
/*
直接使用是由构造方法,抛出IllegalAccessException非法访问异常
解决方法:使访问权限失效
*/
Constructor<?> constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class);
// 使访问权限失效
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object s = constructor.newInstance(112);
获取、调用类中的普通方法
- 获取类中所有公开的方法,包括继承的方法
Method[] methods = c.getMethods();
- 获取类中所有的方法,不包括继承的方法,包括私有的方法
Method[] methods = c.getDeclaredMethods();
- 获取指定方法名的方法
Method method_show = c.getMethod("show");
- 调用无参方法
method_show.invoke(s); // 等同于s.show();
- 调用带参方法
Method method_show1 = c.getMethod("show", String.class);
method_show1.invoke(s, "15458956245");
- 调用带返回值的
Method method_getName = c.getMethod("getName");
String name = (String) method_getName.invoke(s);
- 调用静态方法
Method method_print = c.getMethod("print");
method_print.invoke(null); // Student.print();
- 调用私有方法
Method method_show2 = c.getDeclaredMethod("show");
method_show2.setAccessible(true);
method_show2.invoke(s);
获取、设置类中的属性
- 获取类中所有私有属性(不包括继承)
Field[] fields = c.getDeclaredFields();
- 根据属性名获取属性(私有、并设置值)
Field stuNo = c.getDeclaredField("stuNo");
stuNo.setAccessible(true);
stuNo.set(s, 200); // 相当于zhangsan.stuNo = 200;
System.out.println(stuNo.get(s)); // zhangsan.stuNo;
特例(带有数组参数的方法)
- 错误格式
- 抛出异常IllegalArgumentException(无效的参数)
- 识别为可变参数
Method method_printNames = c.getMethod("printNames", String[].class);
method_printNames.invoke(s, new String[]{"张三", "李四"}); // s.printNames();
- 正确格式
- 强转为(Object)
Method method_printNames = c.getMethod("printNames", String[].class);
method_printNames.invoke(s, (Object) new String[]{"张三", "李四"}); // s.printNames();
反射优点和缺点
- 优点:
- 提高了Java程序的灵活性和扩展性,降低了耦合性,提高自适应能力
- 允许程序创建和控制任何类的对象,无需提前硬编码目标类
- 缺点:
- 性能问题
- 代码维护问题
使用反射模拟实际插件开发
- 定义一个接口CarService接口
/**
* 汽车接口
*/
public interface CarService {
// 行驶
void run();
// 转向
void turn(String direction);
}
- 创建两个类实现CarService
- Build Project项目(快捷键Ctrl+F9)
- 找到根目录–>out–>下实现类的“.class”拷贝出来
注意:此位置记住,后续还需把文件拷贝回来,拷贝出去是防止后续步骤误删此处文件
- 根目录下创建CarClass.txt文件,并写入两个类的
全类名(快捷键:选中文件Ctrl+Alt+Shift+C)
注意:一行一个
- 删除实现类的“.java”文件
- 把“.class”文件拷贝回原位置
- 创建测试类Demo
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
try{
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("CarClass.txt"));
String data = null;
while ((data = br.readLine()) != null) {
Class<?> myClass = Class.forName(data);
if (myClass != null) {
Object car = myClass.newInstance();
if (car instanceof CarService) {
CarService carService = (CarService) car;
carService.run();
carService.turn("西");
}
}
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("加载失败:" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
br.close();
}
}
}
内省
- 内省:采用反射机制实现对属性操作的一种机制
- PropertyDescriptor 属性描述符,代表一个属性
- BeanInfo 实体类信息,包含类的信息
- Introspector 工具类
- 实体类
- 测试类
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.使用反射创建一个Car对象
Class<?> class1 = Class.forName("night.Car");
Object mycar = class1.newInstance();
System.out.println(mycar.toString());
// 2.使用反射给属性赋值,不能使用字段
// 基础方法
/*Field field = class1.getDeclaredField("brand");
Method setBrand = class1.getMethod("setBrand", field.getType());*/
// 3.使用内省属性赋值(已知属性名)
PropertyDescriptor pd1 = new PropertyDescriptor("brand", class1);
Method setBrand = pd1.getWriteMethod();
setBrand.invoke(mycar, "宝马");
PropertyDescriptor pd2 = new PropertyDescriptor("color", class1);
Method setColor = pd2.getWriteMethod();
setColor.invoke(mycar, "红色");
PropertyDescriptor pd3 = new PropertyDescriptor("price", class1);
Method setPrice = pd3.getWriteMethod();
setPrice.invoke(mycar, 100000);
System.out.println(mycar.toString());
// 4.使用BeanInfo获取类的信息
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(class1);
PropertyDescriptor[] pds = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDescriptor pd : pds) {
System.out.println(pd.getName() + " : " + pd.getPropertyType());
}
}
}
设计模式介绍
- 什么是设计模式
- 一套被反复使用、多数人知晓的、经过分类编目的、代码设计经验的总结。
- 简单理解:特定问题的固定解决方法。(意思:套路)
- 好处:使用设计模式是为了可重用代码、让代码更容易被人理解、保证代码可靠性、重用性。
设计模式
- 在Gof的《设计模式》书中描述了23种设计模式,可分为三大类:
- 创建型模式,共五种:工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、单例模式、建造者模式、原型模式。
- 结构型模式,共七种:适配器模式、装饰者模式、代理模式、外观模式、桥接模式、组合模式、享元模式。
- 行为型模式,共十一种:策略模式、模板方法模式、观察者模式、迭代子模式、责任链模式、命令模式、备忘录模式、状态模式、访问者模式、中介者模式、解释器模式。
单例设计模式
- 单例(Singleton):只允许创建一个该类的对象。
- 实现单例三个步骤
- 是优化构造方法
- 在类内部创建一个对象
- 在类中添加一个公开的方法,返回单例对象
- 实现单例三个步骤
实现方式一:饿汉子(类加载时创建,天生线程安全)
- 基础形式
/**
* 使用饿汉子实现单例
* 特点:
* (1)类一加载就实例化,没有线程安全问题
* (2)生命周期长
*/
public class SingleTon {
// 1.私有化构造方法
private SingleTon() {
}
// 2.在内部创建这个对象
private static final SingleTon INSTANCE = new SingleTon();
// 3.公开的方法,返回这个对象
public static SingleTon getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
}
注意:可以被反射破解
- 改进(抛出异常)
/**
* 使用饿汉子实现单例
* 特点:
* (1)类一加载就实例化,没有线程安全问题
* (2)生命周期长
*/
public class SingleTon {
private static boolean flag = true;
// 1.私有化构造方法
public SingleTon() {
if (flag) {
flag = false;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("禁止反射破解");
}
}
// 2.在内部创建这个对象
private static final SingleTon INSTANCE = new SingleTon();
// 3.公开的方法,返回这个对象
public static SingleTon getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
}
注意:无法完全解决反射破解问题
实现方式二:懒汉子
- 基础形式
/**
* 懒汉子写法:
* 特点:
* (1)不使用,不会实例化
* (2)有线程安全问题,生命周期短
*/
public class SingleTon2 {
// 1.私有化构造方法
private SingleTon2() {
}
// 2.在内部创建对象
private static SingleTon2 instance;
// 3.创建一个方法返回这个对象
public static SingleTon2 getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SingleTon2();
}
return instance;
}
}
注意:
多线程时可能出现同时在if里睡眠,导致多个线程同时new SingleTon2();
- 改进一(加锁)
/**
* 懒汉子写法:
* 特点:
* (1)不使用,不会实例化
* (2)有线程安全问题,生命周期短
*/
public class SingleTon2 {
// 1.私有化构造方法
private SingleTon2() {
}
// 2.在内部创建对象
private static SingleTon2 instance;
// 3.创建一个方法返回这个对象
public static SingleTon2 getInstance() {
synchronized (SingleTon2.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SingleTon2();
}
}
return instance;
}
}
注意:
改进一,容易使多个线程同时进入锁(判断锁)导致形成重量级锁,影响程序执行效率
- 改进二(嵌套外层if)
- 实例化对象的过程有三个步骤
- 在堆里开辟空间,属性赋值为默认值
- 初始化属性,并调用构造方法(这一条也可分为两步)
- 把地址赋值给变量
注意:实例化对象时,正常执行步骤1–>2–>3,但JVM可能会优化成1–>3–>2
/**
* 懒汉子写法:
* 特点:
* (1)不使用,不会实例化
* (2)有线程安全问题,生命周期短
*/
public class SingleTon2 {
// 1.私有化构造方法
private SingleTon2() {
}
// 2.在内部创建对象
private static SingleTon2 instance;
// 3.创建一个方法返回这个对象
public static SingleTon2 getInstance() {
if (instance == null) { // 目的:提高执行效率
synchronized (SingleTon2.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SingleTon2(); // [^1]
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
注意:
外层if只是提高效率
[^1]: 如果此处实例化对象的步骤为1–>3–>2多线程有可能报空指针异常
- 改进三(volatile关键字)
- volatile:
- 保证线程可见性
- 禁止指令重排序
- 在创建对象是加入关键字volatile防止指令重排序
- 并设置反射解决方式
/**
* 懒汉子写法:
* 特点:
* (1)不使用,不会实例化
* (2)有线程安全问题,生命周期短
*/
public class SingleTon2 {
private static boolean flag = true;
// 1.私有化构造方法
public SingleTon2() {
if (flag) {
flag = false;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("禁止反射破解");
}
}
// 2.在内部创建对象
private volatile static SingleTon2 instance;
// 3.创建一个方法返回这个对象
public static SingleTon2 getInstance() {
if (instance == null) { // 目的:提高执行效率
synchronized (SingleTon2.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SingleTon2();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
实现方式三:静态内部类
- 特点:
- 生命周期解决了
- 线程安全也没有
/**
* 静态内部类写法
* 特点:
* (1)生命周期解决了
* (2)线程安全也没有
*/
public class SingleTon3 {
private static boolean flag = true;
private SingleTon3() {
if (flag) {
flag = false;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("禁止反射破解");
}
}
// 静态内部类(不使用不执行,调用静态内部类才执行)
private static class Holder {
private static final SingleTon3 INSTANCE = new SingleTon3();
}
public static SingleTon3 getInstance() {
return Holder.INSTANCE;
}
}
简单工厂模式(不属于23种GOF设计模式之一)
- 简单工厂模式是属于传火箭型模式,又叫做静态工厂方法(Static Factory Method)模式,但不属于23种GOF设计模式之一。简单工厂模式是由一一个工厂对象决定创建哪一种产品类的实例。
- (可能因为太过简单)
- 简单工厂四个角色:
- 工厂角色:负责创建具体的产品
- 父类产品:作为所有产品的父类,使用抽象类表示
- 子类产品:具体的产品
- 客户程序:使用工厂和产品的程序
案例
- 服装厂:生产服装
- 分析:
- 需要一个服装工厂类:工厂,类中具有生产服装的功能(创建服装对象)ClothesFactory
- 服装类(父类产品):抽象类表示,Clothes
- 服装子类(具体产品):普通类表示,裤子(Trousers)、T恤(TShirt)、夹克(Jacket)
- 客户程序:使用工厂的程序。
- 服装类(父类产品):抽象类表示,Clothes
public abstract class Clothes {
// 准备布料
public abstract void prepare();
// 制作
public abstract void make();
// 打包
public abstract void box();
}
- 服装子类(具体产品):普通类表示,裤子(Trousers)、T恤(TShirt)、夹克(Jacket)
裤子(Trousers)
public class Trousers extends Clothes {
@Override
public void prepare() {
System.out.println("开始准备裤子布料");
}
@Override
public void make() {
System.out.println("开始制作裤子。。。");
System.out.println("。。。。。。");
System.out.println("裤子制作完毕");
}
@Override
public void box() {
System.out.println("开始打包裤子。。。");
}
}
T恤(TShirt)
public class TShirt extends Clothes {
@Override
public void prepare() {
System.out.println("开始准备T恤布料");
}
@Override
public void make() {
System.out.println("开始制作T恤。。。");
System.out.println("。。。。。。");
System.out.println("T恤制作完毕");
}
@Override
public void box() {
System.out.println("开始打包T恤。。。");
}
}
夹克(Jacket)
public class Jacket extends Clothes {
@Override
public void prepare() {
System.out.println("开始准备夹克布料");
}
@Override
public void make() {
System.out.println("开始制作夹克。。。");
System.out.println("。。。。。。");
System.out.println("夹克制作完毕");
}
@Override
public void box() {
System.out.println("开始打包夹克。。。");
}
}
- 配置文件(映射具体产品类的序号)
- 此文件在项目根目录下,文件名为clothes.properties
1=night.demo.Trousers
2=night.demo.TShirt
3=night.demo.Jacket
- 服装工厂类:工厂,类中具有生产服装的功能(创建服装对象)ClothesFactory
/**
* (1)开闭原则:对于扩展时开放的,对于修改时关闭的。
*/
public class ClothesFactory {
private static Properties prop = new Properties();
static {
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("clothes.properties");
prop.load(fr);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("初始化衣服失败!");
} finally {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 静态方法
public static Clothes creatClothes(int type) { // type=1——T恤 2——裤子 3——夹克
Clothes clothes = null;
/*if (type==1) {
clothes = new TShirt();
} else if (type == 2) {
clothes = new Trousers();
} else if (type == 3) {
clothes = new Jacket();
}*/
if (prop.containsKey(type)) {
String className = prop.getProperty(type + "");
try {
Class<?> class1 = Class.forName(className);
clothes = (Clothes) class1.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (clothes != null) {
clothes.prepare();
clothes.make();
clothes.box();
}
return clothes;
}
}
- 客户程序:使用工厂的程序。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("------------欢迎来到服装厂-----------");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("-----------1-裤子 2-T恤 3-夹克 0-退出----------------");
int choice = sc.nextInt();
if (choice == 0) {
break;
}
Clothes clothes = ClothesFactory.creatClothes(choice);
if (clothes != null) {
System.out.println("购买成功;");
} else {
System.out.println("购买失败,请重新输入");
}
}
System.out.println("欢迎下次光临!");
}
}