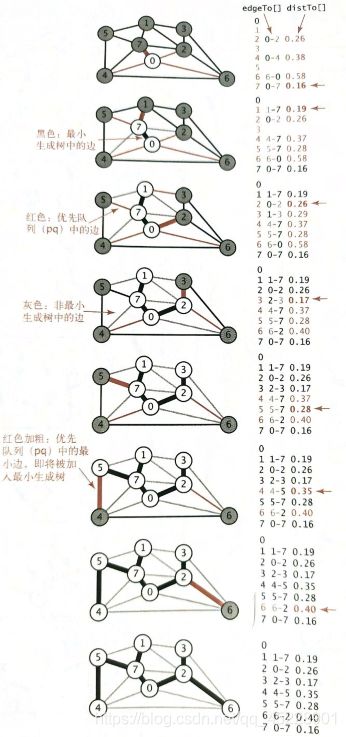
图2(最小生成树)
最小生成树
加权图是一种为每条边关联一个权值或是成本的图模型。
最小生成树。给定一幅加权无向图,找到它的一棵最小生成树。
定义。图的生成树是它的一棵含有其所有顶点无环连通子图。一幅加权图的最小生成树(MST) 是它的一棵权值(树中所有边的权值之和)最小的生成树。如图。

一些约定
- 只考虑连通图
- 边的权重不一定表示距离
- 边的权重可能是0或负数
- 边的权重各不相同
原理
树的两个重要性质:
- 用一条边连接树中任意个顶点都会产生一个新的环。
- 从树中删除一条边将会得到两棵独立的树。
切分定理。这条性质会把加权图中的所有顶点分为两个集合,检查横跨两个集合的所有边并识别哪条边应属于图的最小生成树。
定义。图的一种切分是将图的所有顶点分为两个非空,且不重叠的两个集合,横切边是一条连接属于两个不同集合的顶点的边。

命题(切分定理) 在一幅加权图中,給定任意的切分,它的横切边中的权重最小者必然属于图的最小生成树。
证明。 今e为权重最小的横切边,T为图的最小生成树。采用反证法:假设T不包含e。那么如果将e加入T,得到的图必然含有一条经过e的环,且这个环至少含有另一条横切边------设为f、f的权重必然大于e(因为e的权重是最小的且图中所有边的权重均不同)。那么删掉f而保留e就可以得到一棵权重更小的生成树。这和我们的假设T矛盾。
贪心算法
最小生成树的贪心算法:含有V个顶点的任意加权连通图,初始状态下所有边均为黑色,找到一种切分,它产生的横切边均不为黑色,将他权重最小的横切边标记为黑色。反复,知道标记了V-1条黑色的边为止。
加权无向图的数据类型
带权重的边的数据类型
package com.t_graphs;
/**
* 带权重的边的数据结构
* @author ming
* @create 2020-03-22 16:20
*/
public class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
private final int v; // 顶点
private final int w; // 另一个顶点
private final double weight; // 边的权重
/**
* 初始化顶点{@code v}和{@code w}之间的边定的{@code 权值}。
*/
public Edge(int v, int w, double weight) {
if (v < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex index must be a nonnegative integer");
if (w < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex index must be a nonnegative integer");
if (Double.isNaN(weight)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Weight is NaN");
this.v = v;
this.w = w;
this.weight = weight;
}
/**
* @return 这条边的权重
*/
public double weight() {
return weight;
}
/**
* @return 返回边的其中一个顶点
*/
public int either() {
return v;
}
/**
* 返回与给定顶点不同的这条边的端点。
* @return 这条边的另一个端点
*/
public int other(int vertex) {
if (vertex == v) return w;
else if (vertex == w) return v;
else throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal endpoint");
}
/**
* 按权重比较两条边。注意,{@code compareTo()}与{@code equals()}不一致,
* 它使用从{@code Object}继承的引用相等实现
*
* @return 一个负整数,零,或正整数取决于是否它的权值小于,等于,或大于参数边的权重
*
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge that) {
return Double.compare(this.weight, that.weight);
}
/**
* @return 这条边的字符串表示
*/
public String toString() {
return String.format("%d-%d %.5f", v, w, weight);
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Edge e = new Edge(12, 34, 5.67);
// System.out.println(e.either());
System.out.println(e);
}
}
加权无向图的数据类型
package com.t_graphs;
import com.lb_linkedlist.Bag;
import com.z_stack.Stack;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @author ming
* @create 2020-03-22 16:21
*/
public class EdgeWeightedGraph {
private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator");
private final int V; // 顶点总数
private int E; // 边的总数
private Bag<Edge>[] adj; //邻接表
/**
* 用{@code V}顶点和0条边初始化一个空的边加权图。
*/
public EdgeWeightedGraph(int V) {
if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices must be nonnegative");
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
adj = new Bag[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
adj[v] = new Bag<>();
}
}
/**
* 初始化一个带有{@code V}顶点和E边的随机加权图。
*/
public EdgeWeightedGraph(int V, int E) {
this(V);
if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
Random r = new Random();
int v = r.nextInt(V);
int w = r.nextInt(V);
double weight = Math.round(100 * r.nextInt()) / 100.0;
Edge e = new Edge(v, w, weight);
addEdge(e);
}
}
/**
* 从输入流初始化边缘加权图。格式为顶点数V,后面是边数E,后面是E对顶点和边权值,
* 每个条目之间用空格分隔。
*/
public EdgeWeightedGraph(In in) {
if (in == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null");
try {
V = in.readInt();
adj = (Bag<Edge>[]) new Bag[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
adj[v] = new Bag<Edge>();
}
int E = in.readInt();
if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int v = in.readInt();
int w = in.readInt();
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
double weight = in.readDouble();
Edge e = new Edge(v, w, weight);
addEdge(e);
}
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid input format in EdgeWeightedGraph constructor", e);
}
//
}
/**
* 初始化一个新的边加权图,它是{@code G}的深度副本。
*/
public EdgeWeightedGraph(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
this(G.V());
this.E = G.E();
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
// 反向操作,使邻接表与原始表的顺序相同
Stack<Edge> reverse = new Stack<>();
for (Edge e : G.adj[v]) {
reverse.push(e);
}
for (Edge e : reverse) {
adj[v].add(e);
}
}
}
/**
* @return 边权图中顶点的数目
*/
public int V() {
return V;
}
/**
* @return 这个边加权图的边数
*/
public int E() {
return E;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v) {
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
/**
* 将无向边{@code e}添加到此边加权图。
*/
public void addEdge(Edge e) {
// 获取边的2个顶点
int v = e.either();
int w = e.other(v);
// 判断顶点范围
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
// 将e边分别存入2个顶点的邻接表
adj[v].add(e);
adj[w].add(e);
E++;
}
/**
* @return 顶点{@code v}上的边,可迭代
*/
public Iterable<Edge> adj(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
/**
* @return 顶点度{@code v}
*/
public int degree(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();
}
/**
* @return 加权无向图中的所有边,所有边都是可迭代的
*/
public Iterable<Edge> edges() {
Bag<Edge> list = new Bag<>();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
int selfLoops = 0;
for (Edge e : adj(v)) { // 每一个点的邻接表迭代
if (e.other(v) > v) { // 边的一个顶点v,另一个顶点比v大
list.add(e);
}
}
}
return list;
}
/**
*
*/
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append(V + " " + E + NEWLINE);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
s.append(v + ": ");
for (Edge e : adj[v]) {
s.append(e + " ");
}
s.append(NEWLINE);
}
return s.toString();
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in);
System.out.println(G);
// EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(4,10);
//// System.out.println(G.toString());
// EdgeWeightedGraph G2 = new EdgeWeightedGraph(4);
// Edge e1 = new Edge(1, 2, 0.98);
// Edge e2 = new Edge(0, 2, 0.88);
// Edge e3 = new Edge(1, 3, 0.78);
// Edge e4 = new Edge(0, 3, 0.68);
// Edge e5 = new Edge(2, 3, 0.58);
// G2.addEdge(e1);
// G2.addEdge(e2);
// G2.addEdge(e3);
// G2.addEdge(e4);
// G2.addEdge(e5);
// System.out.println(G2.toString());
for (Edge edges : G2.edges()) {
System.out.println(edges.toString());
}
}
}
Prim算法
第一种计算最小生成树的方法叫做Prim算法,它的每一步都会为一棵生长中的树添加一条边。开始这棵树只有一个顶点,然后会向它添加V-1条边,每次总是将下一条连接树中的顶点与不在树中的顶点且权重最小的边(黑色表示)加入树中(即由树中的顶点所定义的切分中的一条横切边),如图4.3.9所示。
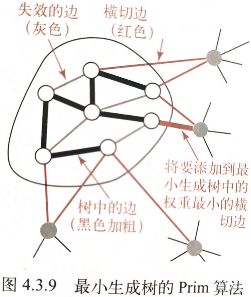
维护横切边的集合
- 向树中加入一条边,也要加入一个顶点。要维护包含所有横切边的集合(使用一条队列MinPQ< Edge >根据权重比较所有边),就要将加入的这个顶点与其他顶点连接的不在树中的边加入队列。
- 新加入树中的顶点与其他已经在树中的顶点的所有边都失效(灰色)。Prim的即时实现会将这样边从优先队列中删除,而延时实现会将这些边先留在队列中,等到要删除再去检查有效性。
Prim算法的延时实现
package com.t_graphs.MST;
import com.dl_queue.Queue;
/**
* Prim 最小生成树的延时实现
*
* @author ming
* @create 2020-03-23 10:04
*/
public class LazyPrimMST {
// private static final double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12;
private double weight; // MST总权重
private Queue<Edge> mst; // MST的边
private boolean[] marked; // MST的顶点
private MinPQ<Edge> pq; // 横切边(包括失效边)
/**
* 计算一个边加权图的最小生成树(森林)。
*/
public LazyPrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
mst = new Queue<>();
pq = new MinPQ<>();
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) // 遍历所有顶点
if (!marked[v]) prim(G, v); // 得到最小生成树(森林)
}
// 运行Prim算法
private void prim(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int s) {
scan(G, s);
while (!pq.isEmpty()) { // pq中为空
Edge e = pq.delMin(); // pq上权重最小的边
int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v); // 两个端点
// assert marked[v] || marked[w];
if (marked[v] && marked[w]) continue; // 跳过失效的边
mst.enqueue(e); // 将边e添加到MST
weight += e.weight();
if (!marked[v]) scan(G, v); // 将v或w添加到树中
if (!marked[w]) scan(G, w);
}
}
// 标记顶点v并将所有连接 v 与 未被标记的顶点 的边加入到pq
private void scan(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v) {
// assert !marked[v];
marked[v] = true;
for (Edge e : G.adj(v))
if (!marked[e.other(v)]) pq.insert(e);
}
/**
* @return 最小生成树(或森林)中的边为边的迭代
*/
public Iterable<Edge> edges() {
return mst;
}
/**
* @return 最小生成树(或森林)中边权值的和
*/
public double weight() {
return weight;
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
MinPQ优先队列
package com.t_graphs.MST;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* 优先队列
* @author ming
* @create 2020-03-23 10:05
*/
public class MinPQ<Key> implements Iterable<Key> {
private Key[] pq; // 将数据存储在索引1到n处
private int n; // 优先队列中的数据个数
private Comparator<Key> comparator; // 比较器
/**
* 使用给定的初始容量初始化空优先队列。
*/
public MinPQ(int initCapacity) {
pq = (Key[]) new Object[initCapacity + 1];
n = 0;
}
/**
* 初始化空优先队列。
*/
public MinPQ() {
this(1);
}
/**
* 用给定的初始容量初始化空优先队列,
* 使用给定的比较器。
*/
public MinPQ(int initCapacity, Comparator<Key> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
pq = (Key[]) new Object[initCapacity + 1];
n = 0;
}
/**
* @return 如果此优先队列为空,则返回true。
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return n == 0;
}
/**
* @return 此优先级队列上的键数
*/
public int size() {
return n;
}
/**
* @return 此优先队列上的最小键
*/
public Key min() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow");
return pq[1];
}
// 帮助函数使堆数组的大小加倍
private void resize(int capacity) {
// assert capacity > n;
Key[] temp = (Key[]) new Object[capacity];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
temp[i] = pq[i];
}
pq = temp;
}
/**
* 向此优先级队列添加key。
*/
public void insert(Key x) {
// 如果需要,将数组的大小加倍
if (n == pq.length - 1) resize(2 * pq.length);
// 添加x,并对其进行过滤以保持堆不变
pq[++n] = x;
swim(n); // 上浮操作
// assert isMinHeap();
}
/**
* @return 删除优先队列上的最小键,并将最小键的值返回
*/
public Key delMin() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow");
Key min = pq[1]; // 临时变量保存最小键
exch(1, n--); // 将最小键与最后键互换,n--可以看作删除最小键
sink(1); // 下沉
pq[n + 1] = null; // 避免浪费,帮助垃圾回收
if ((n > 0) && (n == (pq.length - 1) / 4)) resize(pq.length / 2);
// assert isMinHeap();
return min;
}
private void swim(int k) {
while (k > 1 && greater(k / 2, k)) {
exch(k, k / 2);
k = k / 2;
}
}
private void sink(int k) {
while (2 * k <= n) {
int j = 2 * k;
if (j < n && greater(j, j + 1)) j++;
if (!greater(k, j)) break;
exch(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
/**
* @param i 父结点
* @param j 子节点
* @return true 父结点 > 子节点
*/
private boolean greater(int i, int j) {
if (comparator == null) { // 默认比较器
return ((Comparable<Key>) pq[i]).compareTo(pq[j]) > 0;
} else { // 自定义比较器
return comparator.compare(pq[i], pq[j]) > 0;
}
}
private void exch(int i, int j) {
Key swap = pq[i];
pq[i] = pq[j];
pq[j] = swap;
}
/**
* @return 按升序遍历键的迭代器
*/
public Iterator<Key> iterator() {
return new HeapIterator();
}
private class HeapIterator implements Iterator<Key> {
// 创建一个新的pq
private MinPQ<Key> copy;
// add all items to copy of heap
// takes linear time since already in heap order so no keys move
public HeapIterator() {
if (comparator == null) copy = new MinPQ<Key>(size());
else copy = new MinPQ<Key>(size(), comparator);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
copy.insert(pq[i]);
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return !copy.isEmpty();
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public Key next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return copy.delMin();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
Prim算法的即时实现
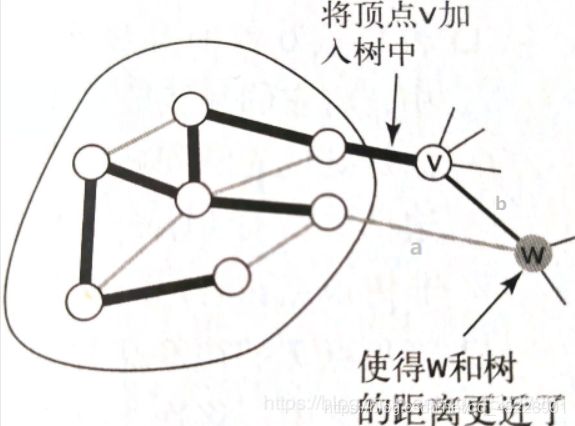
当将顶点v添加到树中时,对于每个非树顶点w产生的变化只可能使得w到最小生成树的距离最近。换言之,不需要在优先队列中保存所有从w到树顶点的边,而只需要保存其中权重最小的那一条,在将v添加到树中后检查是否需要更新这条权重最小的边(因为v-w的权重可能更小),如图添加v之前a边为w到树中顶点权重最小的边,添加v之后b变成了w到树中顶点权重最小的边。
故只会在优先队列中保存每个非树顶点w的一条边:将它与树中的顶点连接起来的权重最小的那条边。
package com.t_graphs.MST;
import com.dl_queue.Queue;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
/**
* Prim算法即时实现
*
* @author ming
* @create 2020-03-24 16:06
*/
public class PrimMST {
// private static final double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12;
private Edge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] 点v不在树,edgeTo[v]是将v和树连接的最短边
private double[] distTo; // distTo[v]为边edgeTo[v]的权重
private boolean[] marked; // 如果v在树上,marked[v] = true
private IndexMinPQ<Double> pq; // 有效的横切边
/**
* 计算一个边加权图的最小生成树(或森林)。
*/
public PrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
edgeTo = new Edge[G.V()];
distTo = new double[G.V()];
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
pq = new IndexMinPQ<>(G.V());
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // 正无穷大常数,每条边的权重可能为“+”“-”“0”
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) // 从每个顶点开始查找
if (!marked[v]) prim(G, v); // 最小生成森林
// check optimality conditions
// assert check(G);
}
// 在图G中运行Prim算法,从顶点s开始
private void prim(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int s) {
distTo[s] = 0.0;
pq.insert(s, distTo[s]);
while (!pq.isEmpty()) { // 优先队列空
int v = pq.delMin(); // 得到优先队列中最小键
scan(G, v);
}
}
// 扫描顶点v
private void scan(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v) {
marked[v] = true; // 代表v此时加入到树中
for (Edge e : G.adj(v)) { // v的邻接边e
int w = e.other(v); // v的邻接点w
if (marked[w]) continue; // w已在树中,v-w是过时的边
if (e.weight() < distTo[w]) { // 点v加入树中,导致点w到树中权重最小的边发生改变。(见上图中的边a,b)
distTo[w] = e.weight(); // 用w到树中权重更小的边代替
edgeTo[w] = e; // 将边e表示为w到树中的权重最小的边
if (pq.contains(w)) pq.decreaseKey(w, distTo[w]); // 如果点w在优先队列中,将边e的权重更新
else pq.insert(w, distTo[w]); // 点w不在优先队列中,将w和dist[w]加入优先队列
}
}
}
/**
* @return 最小生成树(或森林)中的边为边的迭代
*/
public Iterable<Edge> edges() {
Queue<Edge> mst = new Queue<>();
for (int v = 0; v < edgeTo.length; v++) {
Edge e = edgeTo[v];
if (e != null) {
mst.enqueue(e);
}
}
return mst;
}
/**
* @return 最小生成树(或森林)中边权值的和
*/
public double weight() {
double weight = 0.0;
for (Edge e : edges())
weight += e.weight();
return weight;
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in);
PrimMST mst = new PrimMST(G);
for (Edge e : mst.edges()) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.printf("%.5f\n", mst.weight());
}
}
优先队列IndexMinPQ
package com.t_graphs.MST;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* 优先队列
*
* @author ming
* @create 2020-03-24 16:09
*/
public class IndexMinPQ<Key extends Comparable<Key>> implements Iterable<Integer> {
private int maxN; // PQ上元素的最大数目
private int n; // PQ上的元素数
private int[] pq; // 从索引为1的位置开始存元素
private int[] qp; // 元素i在堆中的位置
private Key[] keys; // keys[i] = 优先级
/**
* 初始容量初始化空优先队列。
*/
public IndexMinPQ(int maxN) {
if (maxN < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.maxN = maxN;
n = 0;
keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[maxN + 1];
pq = new int[maxN + 1];
qp = new int[maxN + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= maxN; i++)
qp[i] = -1;
}
/**
* @return @code true}如果这个优先队列是空的;
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return n == 0;
}
/**
* @return {@code true}如果{@code i}是这个优先队列的索引;
*/
public boolean contains(int i) {
validateIndex(i);
return qp[i] != -1;
}
/**
* @return 此优先级队列上的键数
*/
public int size() {
return n;
}
/**
* 将键与索引{@code i}关联。
*/
public void insert(int i, Key key) {
validateIndex(i);
if (contains(i)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is already in the priority queue");
n++;
qp[i] = n; // 元素i在对中的位置为n(从1开始)
/*
相比于一般的优先队列,通过直接比较元素i的大小,来排序(上浮或下沉)。
此优先队列每个元素i都有一个优先级keys[i],
需要通过比较每个元素的优先级keys[i]来排序(上浮或下沉)。
*/
pq[n] = i; // 存入元素
keys[i] = key; // 元素i的优先级
swim(n); // 上浮操作
}
/**
* @return 与一个最小键(权重最小的横切边的权重)相关联的索引
*/
public int delMin() {
if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow");
int min = pq[1];
exch(1, n--); // 最小元素与末尾元素互换并n--
sink(1); // 将换来的元素下沉
// assert min == pq[n + 1];
qp[min] = -1; // 删除
keys[min] = null; // 来帮助收集垃圾
pq[n + 1] = -1; // 不必要的
return min;
}
/**
* 将与索引{@code i}关联的优先级减小到指定优先级。
*/
public void decreaseKey(int i, Key key) {
validateIndex(i);
// i不在优先队列中
if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue");
// i的优先级等于要更改的优先级
if (keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling decreaseKey() with a key equal to the key in the priority queue");
// i的优先级大于要更改的优先级
if (keys[i].compareTo(key) < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling decreaseKey() with a key strictly greater than the key in the priority queue");
keys[i] = key; // 更改优先级
swim(qp[i]); // i的优先级减小会上浮
}
/**
* Remove the key associated with index {@code i}.
*
* @param i the index of the key to remove
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN}
* @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i}
*/
public void delete(int i) {
validateIndex(i);
if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue");
int index = qp[i];
exch(index, n--);
swim(index);
sink(index);
keys[i] = null;
qp[i] = -1;
}
// 如果i是无效索引,则抛出IllegalArgumentException
private void validateIndex(int i) {
if (i < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is negative: " + i);
if (i >= maxN) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index >= capacity: " + i);
}
private boolean greater(int i, int j) {
return keys[pq[i]].compareTo(keys[pq[j]]) > 0; // 比较优先级
}
private void exch(int i, int j) {
int swap = pq[i];
pq[i] = pq[j];
pq[j] = swap;
qp[pq[i]] = i;
qp[pq[j]] = j;
}
private void swim(int k) {
while (k > 1 && greater(k / 2, k)) {
exch(k, k / 2);
k = k / 2;
}
}
private void sink(int k) {
while (2 * k <= n) {
int j = 2 * k;
if (j < n && greater(j, j + 1)) j++;
if (!greater(k, j)) break;
exch(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
/**
* @return 按升序遍历键的迭代器
*/
@Override
public Iterator<Integer> iterator() {
return new HeapIterator();
}
private class HeapIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {
// 创建一个新的pq
private IndexMinPQ<Key> copy;
// 将所有元素添加到堆的副本中
// 需要线性时间,因为已经在堆顺序,所以没有键移动
public HeapIterator() {
copy = new IndexMinPQ<>(pq.length - 1); // pq[0]并没有使用,故元素个数为pq.length - 1
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
copy.insert(pq[i], keys[pq[i]]);
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return !copy.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public Integer next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return copy.delMin();
}
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
Kurskal算法
第二种算法是主要思想按照边的权重排序处理,它们将加入最小生成树中,加入的边不会与已加入的边构成环直到树中含有v-1条边为止。
Kurskal一般还是比Prim慢。

补充:union-find算法

设计数据结构保存程序已知的所有整数对的足够多的信息。并判断一对新对象是否相连。-----动态连通性问题。

以触点作为索引的对应的parent[]元素都是同一个分量另一个触点的名称(也可能是自己),再有这个触点链接到第三个触点。最终会到达一个根触点。当两触点能到达同一个根触点时它们存在同一个连通分量中。
代码实现
package com.t_graphs.MST;
/**
* union-find算法
* 改进
* union-union算法
*
* @author ming
* @create 2020-03-28 18:29
*/
public class UF {
private int[] parent; // 分量标识符
private byte[] rank; //
private int count; // 分量数量
/**
* 使用{@code n}个元素{@code 0}通过{@code n-1}初始化一个空的union-find数据结构。
* 最初,每个元素都在自己的分量中。
*/
public UF(int n) {
if (n < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
count = n;
parent = new int[n];
rank = new byte[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i; // 初始情况每个触点都在自己得分量中
rank[i] = 0;
}
}
/**
* @return {@code p}(0-N-1)所在分量的标识符
*/
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
while (p != parent[p]) {
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]; // 直接找触点p的父结点的父结点
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
/**
* Returns the number of sets.
* 返回集合的数目。
*
* @return 集合的数量(在 { @ code 1 } 和 { @ code n } 之间)
*/
public int count() {
return count;
}
/**
* @return 如果{@code p}和{@code q}在同一集合中,则{@code true};
* {@code false} otherwise
* @deprecated Replace with two calls to {@link #find(int)}.
*/
@Deprecated
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
/**
* 将p与q之间添加一条连接。
*/
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return; // p、q位于同一分量中
// p、q不在同一分量中
if (rank[rootP] < rank[rootQ]) parent[rootP] = rootQ; //
else if (rank[rootP] > rank[rootQ]) parent[rootQ] = rootP;
else {
parent[rootQ] = rootP; //
rank[rootP]++;
}
count--;
}
// 验证p是一个有效的索引
private void validate(int p) {
int n = parent.length;
if (p < 0 || p >= n) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n - 1));
}
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
UF uf = new UF(10);
uf.union(4, 3);
uf.union(3, 8);
uf.union(6, 5);
uf.union(8, 9);
uf.union(1, 2);
uf.union(5, 0);
uf.union(1, 7);
uf.union(0, 2);
System.out.println(uf.count());
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("i"+i +":" + uf.find(i));
}
for (byte b : uf.rank) {
System.out.println(b);
}
}
}
Kruskal算法实现
package com.t_graphs.MST;
import com.dl_queue.Queue;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
/**
* @author ming
* @create 2020-03-28 18:26
*/
public class KruskalMST {
private double weight; // MST的总权重
private Queue<Edge> mst = new Queue<>(); // MST边
/**
* 计算一个边加权图的最小生成树(或森林)。
* */
public KruskalMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
// 通过传递边数组来更有效地构建堆
MinPQ<Edge> pq = new MinPQ<>();
for (Edge e : G.edges()) {
pq.insert(e);
}
// 运行贪婪算法
UF uf = new UF(G.V()); // 判断无效边。。
while (!pq.isEmpty() && mst.size() < G.V() - 1) { // 优先队列不为空,最小生成数未找齐
Edge e = pq.delMin(); // 队列中最短的边
int v = e.either();
int w = e.other(v); // 最短边的两个顶点w、v
if (uf.find(v) != uf.find(w)) { // 触点v与w不在同一分量
uf.union(v, w); // 合并v和w分量
mst.enqueue(e); // 添加边缘e到mst
weight += e.weight();
}
}
// check optimality conditions
// assert check(G);
}
/**
* @return 最小生成树(或林)中的边为边的迭代
*/
public Iterable<Edge> edges() {
return mst;
}
/**
* @return 最小生成树(或森林)中边权值的和
*/
public double weight() {
return weight;
}
/**
* Unit
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}