使用Matplotlib绘制3D动画
"""
============
3D animation
============
A simple example of an animated plot... In 3D!
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d as p3
import matplotlib.animation as animation
def Gen_RandLine(length, dims=2):
"""
Create a line using a random walk algorithm
length is the number of points for the line.
dims is the number of dimensions the line has.
"""
lineData = np.empty((dims, length))
lineData[:, 0] = np.random.rand(dims) # 初始化起点
for index in range(1, length):
# scaling the random numbers by 0.1 so
# movement is small compared to position.
# subtraction by 0.5 is to change the range to [-0.5, 0.5]
# to allow a line to move backwards.
step = ((np.random.rand(dims) - 0.5) * 0.1) # 步长
# 下一步的位置
lineData[:, index] = lineData[:, index - 1] + step
return lineData # 返回一个shape为(3,25)的数组,3维坐标25帧
def update_lines(num, dataLines, lines):
for line, data in zip(lines, dataLines):
# NOTE: there is no .set_data() for 3 dim data...
line.set_data(data[0:2, :num])
line.set_3d_properties(data[2, :num])
return lines
# Attaching 3D axis to the figure
fig = plt.figure()
ax = p3.Axes3D(fig)
# Fifty lines of random 3-D lines (长为50的数组,每个元素为shape为3,25的ndarray,最后实际效果就是50条路径)
data = [Gen_RandLine(25, 3) for index in range(50)]
# Creating fifty line objects.
# NOTE: Can't pass empty arrays into 3d version of plot()
lines = [ax.plot(dat[0, 0:1], dat[1, 0:1], dat[2, 0:1])[0] for dat in data] # 每条路径的起始点
# Setting the axes properties
ax.set_xlim3d([0.0, 1.0])
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylim3d([0.0, 1.0])
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlim3d([0.0, 1.0])
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
ax.set_title('3D Test')
# Creating the Animation object
line_ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, update_lines, 25, fargs=(data, lines),
interval=50, blit=False)
plt.show()
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
#初始化图例
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
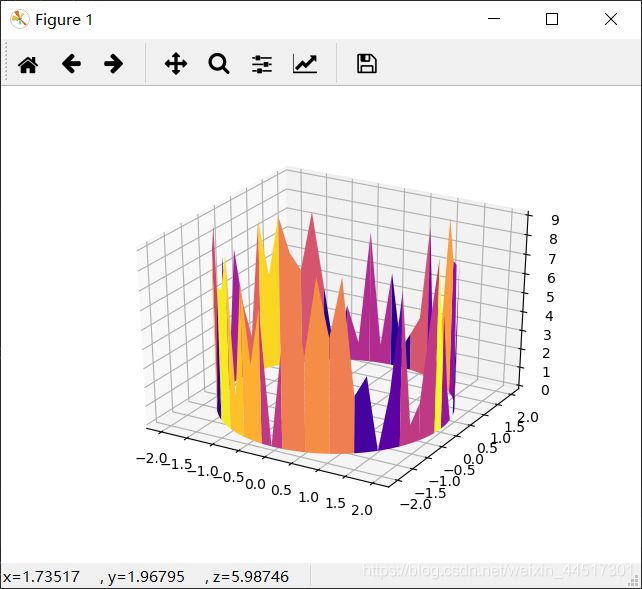
#设置X,Y的取值
r = [2,2]
p = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 64)
R, P = np.meshgrid(r, p)
X, Y = R * np.cos(P), R * np.sin(P)
r1=[1,0]
#设置Z的范围
ax.set_zlim(0, 10)
try:
while True:
#清除原有图像
plt.cla()
p1 = np.random.randint(10, size=64)
R1, P1 = np.meshgrid(r1, p1)
#设置Z值
Z = R1*P1
#画3D图
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=plt.cm.plasma)
#通过暂停和清除来不断更新图像,形成动图
plt.pause(0.5)
except:
pass
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import numpy as np
plt.style.use('dark_background')
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(xlim=(-50, 50), ylim=(-50, 50))
line, = ax.plot([], [], lw=2)
# initialization function
def init():
# creating an empty plot/frame
line.set_data([], [])
return line,
# lists to store x and y axis points
xdata, ydata = [], []
# simulate ghost effect of oscilloscope
def ghostImage(x, y):
xdata.append(x)
ydata.append(y)
if len(xdata) > 60:
del xdata[0]
del ydata[0]
return xdata, ydata
# animation function
def animate(i):
# t is a parameter
t = i / 100.0
# x, y values to be plotted
x = 40 * np.sin(2 * 2 * np.pi * (t + 0.3))
y = 40 * np.cos(3 * 2 * np.pi * t)
# appending new points to x, y axes points list
line.set_data(ghostImage(x, y))
return line,
# setting a title for the plot
plt.title('Creating a Lissajous figure with matplotlib')
# hiding the axis details
plt.axis('off')
# call the animator
anim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init,
frames=400, interval=20, blit=True)
# save the animation as gif file
anim.save('figure.gif', writer='imagemagick')

然后使用ImageMagick的convert命令,将多幅静态帧转换成gif,使用以下命令:
convert -delay 10 *.png gif.gif