2019冬季PAT甲级 题解和反思
非科班跨考, 11月中旬把甲级题库155道粗略地刷完了一遍(在《算法笔记》的帮助下),然后从头开始二刷, 做了十几题以后觉得刷不完了, 加上其他考试的压力, 便搁置刷题计划, 考前一天将题库里面的关于图和树的题目的代码粗略地看了一遍,心想这次12月考试对明年的考研帮助也不大, 就当练手, 结果运气好, 全AC了。
这次的题目不难,会写Hello World, 离满分就不远了,如下:
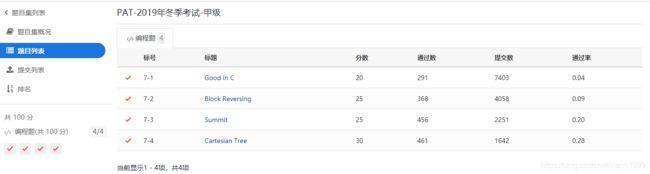
题目1:7-1 Good in C (20分)
When your interviewer asks you to write “Hello World” using C, can you do as the following figure shows?
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first part gives the 26 capital English letters A-Z, each in a 7×5 matrix of C’s and .'s. Then a sentence is given in a line, ended by a return. The sentence is formed by several words (no more than 10 continuous capital English letters each), and the words are separated by any characters other than capital English letters.
It is guaranteed that there is at least one word given.
Output Specification:
For each word, print the matrix form of each of its letters in a line, and the letters must be separated by exactly one column of space. There must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the word.
Between two adjacent words, there must be a single empty line to separate them. There must be no extra line at the beginning or the end of the output.
Sample Input:
..C..
.C.C.
C...C
CCCCC
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
.CCC.
C...C
C....
C....
C....
C...C
.CCC.
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
CCCCC
C....
C....
CCCC.
C....
C....
CCCCC
CCCCC
C....
C....
CCCC.
C....
C....
C....
CCCC.
C...C
C....
C.CCC
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCCC
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCCC
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
CCCCC
CCCCC
....C
....C
....C
....C
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C..C.
C.C..
CC...
C.C..
C..C.
C...C
C....
C....
C....
C....
C....
C....
CCCCC
C...C
C...C
CC.CC
C.C.C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
CC..C
C.C.C
C..CC
C...C
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.CCC.
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C....
C....
C....
.CCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C.C.C
C..CC
.CCC.
CCCC.
C...C
CCCC.
CC...
C.C..
C..C.
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C....
.CCC.
....C
C...C
.CCC.
CCCCC
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.C.C.
..C..
C...C
C...C
C...C
C.C.C
CC.CC
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.C.C.
..C..
.C.C.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.C.C.
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
CCCCC
....C
...C.
..C..
.C...
C....
CCCCC
HELLO~WORLD!
Sample Output:
C...C CCCCC C.... C.... .CCC.
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
CCCCC CCCC. C.... C.... C...C
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
C...C CCCCC CCCCC CCCCC .CCC.
C...C .CCC. CCCC. C.... CCCC.
C...C C...C C...C C.... C...C
C...C C...C CCCC. C.... C...C
C.C.C C...C CC... C.... C...C
CC.CC C...C C.C.. C.... C...C
C...C C...C C..C. C.... C...C
C...C .CCC. C...C CCCCC CCCC.
AC代码:
#include 坑点:
- 输入要用getline(cin, str), 不能用cin>>str,否则有三个测试点通过不了。
- 仔细考虑这个字符串: 231AFF 如果这个情况能通过, 那么基本问题不大了。如果是格式错误, 很有可能是这个字符串导致的。
反思:题写太少, 对字符串分隔的处理太原始, 对cctype头文件不熟悉, 考试不敢用, 多层循环中, 变得越频繁的量越要放到内层, 对多重循环很迟钝, 另外考试的时候遇到大数据, 最好直接将他复制到一个新建的cpp文件中, 专门用于测试, 和平时做题不同, 考试只能用ctrl+C和编辑粘贴来输入数据。
题目2: 7-2 Block Reversing (25分)
Given a singly linked list L. Let us consider every K nodes as a block (if there are less than K nodes at the end of the list, the rest of the nodes are still considered as a block). Your job is to reverse all the blocks in L. For example, given L as 1→2→3→4→5→6→7→8 and K as 3, your output must be 7→8→4→5→6→1→2→3.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains the address of the first node, a positive N (≤10^5)
which is the total number of nodes, and a positive K (≤N) which is the size of a block. The address of a node is a 5-digit nonnegative integer, and NULL is represented by −1.
Then N lines follow, each describes a node in the format:
Address Data Next
where Address is the position of the node, Data is an integer, and Next is the position of the next node.
Output Specification:
For each case, output the resulting ordered linked list. Each node occupies a line, and is printed in the same format as in the input.
Sample Input:
00100 8 3
71120 7 88666
00000 4 99999
00100 1 12309
68237 6 71120
33218 3 00000
99999 5 68237
88666 8 -1
12309 2 33218
Sample Output:
71120 7 88666
88666 8 00000
00000 4 99999
99999 5 68237
68237 6 00100
00100 1 12309
12309 2 33218
33218 3 -1
AC代码:
#include 反思:链表题往sort上面靠拢, 肯定有解决方法, 而且几乎是模板。这题和PAT B1025几乎一摸一样,暑假的时候做过一些乙级题目, 这道题的前后几道题都做了, 恰巧没做这道, 好在这题不算难。 另外, 如果不用sort的话, 我可能会用vector, 但是考试的时候头脑是紧张的, 很可能会出错。还是按照模板来, 稳妥一点。
题目3:7-3 Summit (25分)
A summit (峰会) is a meeting of heads of state or government. Arranging the rest areas for the summit is not a simple job. The ideal arrangement of one area is to invite those heads so that everyone is a direct friend of everyone.
Now given a set of tentative arrangements, your job is to tell the organizers whether or not each area is all set.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives two positive integers N (≤ 200), the number of heads in the summit, and M, the number of friendship relations. Then M lines follow, each gives a pair of indices of the heads who are friends to each other. The heads are indexed from 1 to N.
Then there is another positive integer K (≤ 100), and K lines of tentative arrangement of rest areas follow, each first gives a positive number L (≤ N), then followed by a sequence of L distinct indices of the heads. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each of the K areas, print in a line your advice in the following format:
if in this area everyone is a direct friend of everyone, and no friend is missing (that is, no one else is a direct friend of everyone in this area), print Area X is OK…
if in this area everyone is a direct friend of everyone, yet there are some other heads who may also be invited without breaking the ideal arrangement, print Area X may invite more people, such as H. where H is the smallest index of the head who may be invited.
if in this area the arrangement is not an ideal one, then print Area X needs help. so the host can provide some special service to help the heads get to know each other.
Here X is the index of an area, starting from 1 to K.
Sample Input:
8 10
5 6
7 8
6 4
3 6
4 5
2 3
8 2
2 7
5 3
3 4
6
4 5 4 3 6
3 2 8 7
2 2 3
1 1
2 4 6
3 3 2 1
Sample Output:
Area 1 is OK.
Area 2 is OK.
Area 3 is OK.
Area 4 is OK.
Area 5 may invite more people, such as 3.
Area 6 needs help.
AC代码:
#include 反思:这是一种很著名的数据结构,但是我现在一时想不起来了hhhh, 这道题之前做过, 我记得第一次做的时候没用多长时间, 但是这次做反而由于考试太紧张, 在一些细节上(把索引当作节点了)出毛病, 最后用printf()一个一个查, 才发现自己大脑当时已经很糊涂了, 由于这题数据量很小, 而且为了追求速度, 代码有点放荡不羁, 想到哪写哪, 考试的时候这样做挺好的, 平时还是要多讲究细节。
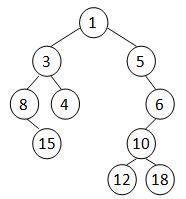
题目4:7-4 Cartesian Tree (30分)
A Cartesian tree is a binary tree constructed from a sequence of distinct numbers. The tree is heap-ordered, and an inorder traversal returns the original sequence. For example, given the sequence { 8, 15, 3, 4, 1, 5, 12, 10, 18, 6 }, the min-heap Cartesian tree is shown by the figure.
Your job is to output the level-order traversal sequence of the min-heap Cartesian tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts from giving a positive integer N (≤30), and then N distinct numbers in the next line, separated by a space. All the numbers are in the range of int.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the min-heap Cartesian tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.
Sample Input:
10
8 15 3 4 1 5 12 10 18 6
Sample Output:
1 3 5 8 4 6 15 10 12 18
AC代码:
#include 反思: 遇到这种很短的树题目, 我是很窃喜的, 因为我觉得这种题的解法往往是比较巧妙或者有套路的,重点在于找规律, 这道题的规律我在读题的时候就发现了, 知道要怎么建树, 但是脑袋运转不过来, 不知道怎么用程序递归实现,主要是因为几个套路之间互相干扰, 不晓得用哪个合适, 在回想了几个套路(前中后序互推, 排序二叉树的insert), 认为这道题和前中后序互推最相近, 按照套路写就完事了。 结果程序一运行就崩溃,调试过程中加几个printf()查看变量,调试得还比较顺利。
整体反思:
- 这次的策略比较正确, 没有在一道题上面死磕, 第一题题目没看懂, 更别说思路了, 直接看后面题是比较好的策略,再回来看时思路会清楚很多。
- 和平时做题不同, 考试的时候要ctrl+c之后编辑粘贴才行, 平时也要习惯用这种方法。
- 考试的时候应该提前在纸上写上本题可能的坑点(%05d, getline(), -0之类的), 调试的时候会节省时间。
- 调试的时候直接用printf()反而更省时间, 如果开启调试模式的话, 搞不好DEVC++直接崩溃了(涉及到容器的时候)。
- 二三四题大概每个都用了30分钟左右, 一半时间在做第一题, 才勉强做出来。越来越感觉PAT考的是思维的缜密度, 在细节上拉开差据。
- 由于习惯了晴神的编程风格, 很多时候看不懂或者抵触看其他人的代码,让人错过了很多优秀巧妙的思路, 柳神的代码虽然简洁, 但有种刻意为之的感觉, 个人智商一般的, 还是规规矩矩按套路写比较好, 规范变量命名, 考试的时候很紧张, 很难有什么创新思路(也可能是因为我第一次考,不熟悉)。