FutureTask源码解读
FutureTask一般和Executor、Thread一起使用,本章节就FutureTask类进行解读。
一、相关依赖
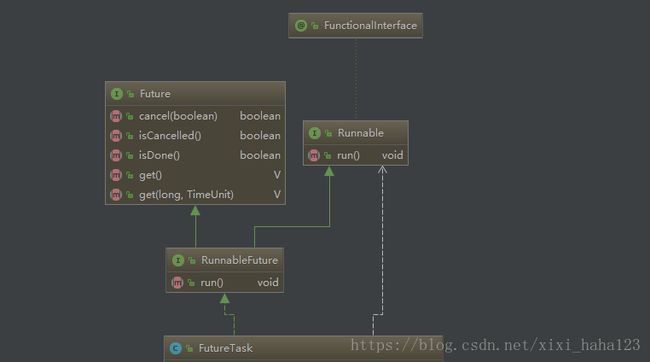
从图中可以得到FutureTask与接口RunnableFuture、Future、Runnable有关。
Future接口: 异步结果计算时使用
- cancel(boolean):取消task的执行,如果task已完成、已被取消、或者由于某些原因取消不了,则返回false。
- isCancelled():判断task是否在正常完成前取消掉了。
- isDone():判断task是否完成了。
- get():等待task完成,并获取执行结果。可能会抛出异常。
- get(long,TimeUnit):在指定的时间内等待task完成,并获取执行结果。可能抛出异常(含TimeoutException)
RunnableFuture接口:简单理解为Future+Runnable
二、FutureTask介绍
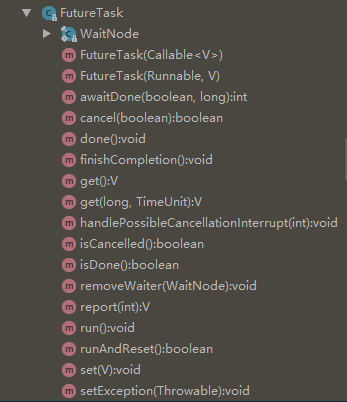
讲解上述方法前,先了解一下task中状态的变更流程。
/*
* 可能的状态变更:
* NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMAL
* NEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL
* NEW -> CANCELLED
* NEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED
*/
private volatile int state;
private static final int NEW = 0; //新建的
private static final int COMPLETING = 1; //完成的中间状态
private static final int NORMAL = 2; //已正常完成
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; //异常终止
private static final int CANCELLED = 4; //已取消
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; //中断时的中间状态
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; //已中断FutureTask构造函数:
//直接通过callable的形式
public FutureTask(Callable callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW; // 刚创建的状态为new
}
//通过runnable的形式,如果执行成功,则返回指定的result。result可以为null
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW; // 刚创建的状态为new
} Q:为什么带runnable的构造函数还能指定result?
A:因为Runnable.run()无返回值,而Callable.call()是有返回值。
//Executors中的部分方法
public static Callable callable(Runnable task, T result) {
if (task == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new RunnableAdapter(task, result);
}
static final class RunnableAdapter<T> implements Callable<T> {
final Runnable task;
final T result;
RunnableAdapter(Runnable task, T result) {
this.task = task;
this.result = result;
}
public T call() {
task.run();
return result; //直接将传入的result值返回
}
} 讲解FutureTask.run()方法前,先来继续了解下FutureTask剩余的几个成员变量
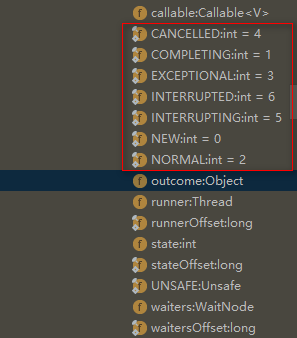
callable:底层调用,调用完后,会被赋值为null
outcome:用于存储返回结果,可以是正常执行结果,也可以是异常信息
UNSAFE:可直接操作内存的类。详情百度
runner:最后执行callable的线程
runnerOffset:UNSAFE使用的,runner成员变量在FutureTask类中的偏移量
state:就是当前task的状态,含NEW、COMPLETING等
stateOffset:UNSAFE使用的,state成员变量在FutureTask类中的偏移量
waiters:等待的线程
waitersOffset:UNSAFE使用的,waiters成员变量在FutureTask类中的偏移量
FutureTask.run()
public void run() {
//如果状态不是new,则说明该task已经执行过了(state>0),就不需要再次执行了
//如果状态为new,则尝试把当前线程赋值过去,如果赋值失败,只能返回
if (state != NEW || !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();//调用callable.call(),执行task
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex); //抛出异常则设置异常
}
if (ran)
set(result); //正常完成则设置对应的完成结果
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING) //任务处于中断中的状态,则进行中断操作
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
protected void setException(Throwable t) {//异常设置
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) { //将状态位设置成中间状态COMPLETING
outcome = t; //设置输出的为异常信息
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL); //将状态更为最终状态EXCEPTIONAL
finishCompletion();
}
}
protected void set(V v) {//正常返回值设置
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {//将状态位设置成中间状态COMPLETING
outcome = v;//设置输出为正常返回结果
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // 将状态更为最终状态NORMAL
finishCompletion();
}
}
//由中间状态到最终状态变更时,都需进行的操作
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) { //尝试将waiters全部置为null
for (;;) {//将waiters下对应的链式thread挨个唤醒
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);//唤醒操作,LockSupport.park()阻塞
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // 减少内存占用
}
protected void done() { } //子类可重写该方法,实现回调
/**
* 确保cancel(true)产生的中断发生在run或runAndReset方法过程中。
*/
private void handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(int s) {
// It is possible for our interrupter to stall before getting a
// chance to interrupt us. Let's spin-wait patiently.
if (s == INTERRUPTING)
while (state == INTERRUPTING)
Thread.yield(); // 让出cpu时间片,等待cancel(true)执行完成,此时INTERRUPTING必然能更成INTERRUPTED
// assert state == INTERRUPTED;
// We want to clear any interrupt we may have received from
// cancel(true). However, it is permissible to use interrupts
// as an independent mechanism for a task to communicate with
// its caller, and there is no way to clear only the
// cancellation interrupt.
//
// Thread.interrupted();
} FutureTask.runAndReset():周期性执行,每次正常执行完后状态依然是New
protected boolean runAndReset() {
if (state != NEW || !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, null, Thread.currentThread()))
return false;
boolean ran = false;
int s = state;
try {
Callable c = callable;
if (c != null && s == NEW) {
try {
c.call(); // 与run()相比,少了设置返回结果,以及状态变更
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
setException(ex); //设置异常
}
}
} finally {
runner = null;
s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
return ran && s == NEW; //判断执行完后是否重置成功
} FutureTask.get():获取task的执行结果
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING) //如果是中间状态,则等待task完成
s = awaitDone(false, 0L); //等待过程
return report(s); //返回最后的值
}
//含超时时间的取值过程
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
//如果是中间状态,就等待task完成,如果超过了指定时间,task仍未完成,则抛出超时异常
if (s <= COMPLETING && (s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s); //返回对应的结果
}
//返回的可以是异常,或是正常结果
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {
Object x = outcome;
if (s == NORMAL)
return (V)x;
if (s >= CANCELLED)
throw new CancellationException();
throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);
}
//等待完成,可能是是中断、异常、正常完成,timed:true,考虑等待时长,false:不考虑等待时长
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos) throws InterruptedException {
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L; //如果设置了超时时间
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;) {
/**
* 有优先级顺序
* 1、如果线程已中断,则直接将当前节点q从waiters中移出
* 2、如果state已经是最终状态了,则直接返回state
* 3、如果state是中间状态(COMPLETING),意味很快将变更过成最终状态,让出cpu时间片即可
* 4、如果发现尚未有节点,则创建节点
* 5、如果当前节点尚未入队,则将当前节点放到waiters中的首节点,并替换旧的waiters
* 6、线程被阻塞指定时间后再唤醒
* 7、线程一直被阻塞直到被其他线程唤醒
*
*/
if (Thread.interrupted()) {// 1
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) {// 2
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING) // 3
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null) // 4
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued) // 5
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {// 6
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L) {
removeWaiter(q); //从waiters中移出节点q
return state;
}
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
}
else // 7
LockSupport.park(this);
}
}
static final class WaitNode {
volatile Thread thread;
volatile WaitNode next;
WaitNode() { thread = Thread.currentThread(); } //链式的Thread
}
private void removeWaiter(WaitNode node) {
if (node != null) {
node.thread = null; //将需要去除的节点,thread赋值为null
retry:
for (;;) {
for (WaitNode pred = null, q = waiters, s; q != null; q = s) {
s = q.next;
if (q.thread != null)
pred = q;
else if (pred != null) { //q.thread==null,表示该节点是需要在队列中去除的节点,故直接将pred.next=s,重组队列
pred.next = s;
if (pred.thread == null) //如果这个pred节点恰好是需要去除的节点,则进行循环,重组队列
continue retry;
}
else if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, s))
continue retry;
}
break;
}
}
}FutureTask.cancel(boolean):取消task,根据boolean值来决定是否可进行中断操作
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
//如果状态不为NEW,且无法将状态更新为INTERRUPTING或CANCELLED,则直接返回取消失败
if (!(state == NEW && UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED)))
return false;
try {
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {//允许运行中进行中断操作
try {
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt(); //并不是实时取消!
} finally {
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED); //中断成功,则置为最终状态
}
}
} finally {
finishCompletion(); //同前面讲解
}
return true;
}FutureTask.isCancelled():判断取消是否成功
public boolean isCancelled() { //如果state为以下取值:CANCELLED、INTERRUPTING、INTERRUPTED 均表示取消成功。
return state >= CANCELLED;
}FutureTask.isDone():判断task是否已经执行了
public boolean isDone() {//只要状态>NEW 就满足
return state != NEW;
}