Linux schedule 5、EAS(Energy-Aware Scheduling)
5、EAS(Energy-Aware Scheduling)
5.1、smp rebalance
通过搜索关键字“energy_aware()”,来查看EAS对smp负载均衡的影响。
可以看到EAS对负载均衡的策略是这样的:在overutilized的情况下,使用传统的smp/hmp负载均衡方法;在非overutilized的情况下,使用eas的均衡方法。
EAS的负载均衡和原有方法的区别有几部分:
- 1、在EAS使能且没有overutilized的情况下,hmp负载均衡不工作;
- 2、在EAS使能且没有overutilized的情况下,smp负载均衡不工作;
- 3、在EAS使能且没有overutilized的情况下,EAS的主要工作集中在进程唤醒/新建时选择运行cpu上select_task_rq_fair();
5.1.1、rebalance_domains()
- 1、在EAS使能且没有overutilized的情况下,hmp负载均衡不使能;
static void run_rebalance_domains(struct softirq_action *h)
{
struct rq *this_rq = this_rq();
enum cpu_idle_type idle = this_rq->idle_balance ?
CPU_IDLE : CPU_NOT_IDLE;
int this_cpu = smp_processor_id();
/* bypass load balance of HMP if EAS consideration */
if ((!energy_aware() && sched_feat(SCHED_HMP)) ||
(hybrid_support() && cpu_rq(this_cpu)->rd->overutilized))
hmp_force_up_migration(this_cpu);
/*
* If this cpu has a pending nohz_balance_kick, then do the
* balancing on behalf of the other idle cpus whose ticks are
* stopped. Do nohz_idle_balance *before* rebalance_domains to
* give the idle cpus a chance to load balance. Else we may
* load balance only within the local sched_domain hierarchy
* and abort nohz_idle_balance altogether if we pull some load.
*/
nohz_idle_balance(this_rq, idle);
rebalance_domains(this_rq, idle);
}- 2、在load_balance() -> find_busiest_group()中,如果在EAS使能且没有overutilized的情况下,不进行常规的smp负载均衡;
static struct sched_group *find_busiest_group(struct lb_env *env)
{
if (energy_aware() && !env->dst_rq->rd->overutilized && !same_clus)
goto out_balanced;
out_balanced:
env->imbalance = 0;
return NULL;
}
5.1.2、select_task_rq_fair()
参考4.1.2.3、select_task_rq_fair()这一节的详细描述。
5.2、cpufreq_sched/schedutil governor
sched governor比较传统interactive governor有以下优点:
- 1、负载变化的时间更快。interactive是20ms统计一次负载,而sched governor是在schedule_tick()中更新负载,tick的时间更短;
- 2、interactive的负载计算有问题:历史负载没有老化;历史频率除以现在频率不合理;
interactive governor的主要思想就是综合rt、cfs的负载,判断当前freq的capacity是否满足需求,是否需要调频。
5.2.1、rt request
针对CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_GOV_SCHED,rt有3条关键计算路径:
- 1、rt负载的(rq->rt_avg)的累加:scheduler_tick() -> task_tick_rt() -> update_curr_rt() -> sched_rt_avg_update()
rq->rt_avg = 累加时间分量 * 当前frq分量(最大1024)
static inline void sched_rt_avg_update(struct rq *rq, u64 rt_delta)
{
rq->rt_avg += rt_delta * arch_scale_freq_capacity(NULL, cpu_of(rq));
}- 2、rt负载的老化:scheduler_tick() -> __update_cpu_load() -> __update_cpu_load() -> sched_avg_update()
或者scheduler_tick() -> task_tick_rt() -> sched_rt_update_capacity_req() -> sched_avg_update()
rq->rt_avg的老化比较简单,每个period老化1/2。
void sched_avg_update(struct rq *rq)
{
/* (1) 默认老化周期为1s/2 = 500ms */
s64 period = sched_avg_period();
while ((s64)(rq_clock(rq) - rq->age_stamp) > period) {
/*
* Inline assembly required to prevent the compiler
* optimising this loop into a divmod call.
* See __iter_div_u64_rem() for another example of this.
*/
asm("" : "+rm" (rq->age_stamp));
rq->age_stamp += period;
/* (2) 每个老化周期,负载老化为原来的1/2 */
rq->rt_avg /= 2;
rq->dl_avg /= 2;
}
}
|→
static inline u64 sched_avg_period(void)
{
/* (1.1) 老化周期 = sysctl_sched_time_avg/2 = 500ms */
return (u64)sysctl_sched_time_avg * NSEC_PER_MSEC / 2;
}- 3、rt request的更新:scheduler_tick() -> task_tick_rt() -> sched_rt_update_capacity_req() -> set_rt_cpu_capacity()
rt request的计算有点粗糙: request = rt_avg/(sched_avg_period() + delta),rt_avg中没有加上delta时间的负载。
static void sched_rt_update_capacity_req(struct rq *rq)
{
u64 total, used, age_stamp, avg;
s64 delta;
if (!sched_freq())
return;
/* (1) 最新的负载进行老化 */
sched_avg_update(rq);
/*
* Since we're reading these variables without serialization make sure
* we read them once before doing sanity checks on them.
*/
age_stamp = READ_ONCE(rq->age_stamp);
/* (2) avg=老化后的负载 */
avg = READ_ONCE(rq->rt_avg);
delta = rq_clock(rq) - age_stamp;
if (unlikely(delta < 0))
delta = 0;
/* (3) total时间=一个老化周期+上次老化剩余时间 */
total = sched_avg_period() + delta;
/* (4) avg/total=request,(最大频率=1024) */
used = div_u64(avg, total);
if (unlikely(used > SCHED_CAPACITY_SCALE))
used = SCHED_CAPACITY_SCALE;
/* (5) update request */
set_rt_cpu_capacity(rq->cpu, true, (unsigned long)(used), SCHE_ONESHOT);
}
|→
static inline void set_rt_cpu_capacity(int cpu, bool request,
unsigned long capacity,
int type)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_SCHED_ASSIST
if (true) {
#else
if (per_cpu(cpu_sched_capacity_reqs, cpu).rt != capacity) {
#endif
/* (5.1) 把RT负载更新到per_cpu(cpu_sched_capacity_reqs, cpu).rt */
per_cpu(cpu_sched_capacity_reqs, cpu).rt = capacity;
update_cpu_capacity_request(cpu, request, type);
}
}5.2.2、cfs request
同样,cfs也有3条关键计算路径:
- 1、cfs负载的(rq->rt_avg)的累加:scheduler_tick() -> task_tick_fair() -> entity_tick() -> update_load_avg()
- 2、cfs负载的老化:scheduler_tick() -> task_tick_fair() -> entity_tick() -> update_load_avg()
- 3、cfs request的更新:scheduler_tick() -> sched_freq_tick() -> set_cfs_cpu_capacity()
static void sched_freq_tick(int cpu)
{
struct sched_capacity_reqs *scr;
unsigned long capacity_orig, capacity_curr;
unsigned long capacity_req;
struct sched_domain *sd = rcu_dereference(per_cpu(sd_ea, cpu));
if (!sched_freq())
return;
capacity_orig = capacity_orig_of(cpu);
capacity_curr = capacity_curr_of(cpu);
/* (1) 如果当前频率已经是最高频率,直接返回
目前只支持频率从低往高调整?
*/
if (capacity_curr == capacity_orig)
return;
/*
* To make free room for a task that is building up its "real"
* utilization and to harm its performance the least, request
* a jump to bigger OPP as soon as the margin of free capacity is
* impacted (specified by capacity_margin).
*/
scr = &per_cpu(cpu_sched_capacity_reqs, cpu);
/* (2) 计算最新的(cfs capacity+ rt capacity) * (1126/1024)
放大一些,等于对capacity的需求request
ooooo这里的计算有问题:cpu_util(cpu)是带capacity分量的,而scr->rt是不带capacity分量的,不能直接相加?
*/
/* capacity_req which includes RT loading & capacity_margin */
capacity_req = sum_capacity_reqs(cpu_util(cpu), scr);
/* (3) 如果capacity request大于当前频率的capacity */
if (capacity_curr <= capacity_req) {
if (sd) {### 5.3.1、WALT的负载计算
const struct sched_group_energy *const sge = sd->groups->sge;
int nr_cap_states = sge->nr_cap_states;
int idx, tmp_idx;
int opp_jump_step;
for (idx = 0; idx < nr_cap_states; idx++) {
if (sge->cap_states[idx].cap > capacity_curr+1)
break;
}
/* (4) 尝试计算一个合理的频率等级来满足capacity request */
if (idx < nr_cap_states/3)
opp_jump_step = 2; /* far step */
else
opp_jump_step = 1; /* near step */
tmp_idx = idx + (opp_jump_step - 1);
idx = tmp_idx > (nr_cap_states - 1) ?
(nr_cap_states - 1) : tmp_idx;
if (idx)
capacity_req = (sge->cap_states[idx].cap +
sge->cap_states[idx-1].cap)/2;
else
/* should not arrive here!*/
capacity_req = sge->cap_states[idx].cap + 2;
}
/* (5) 去掉request中的capacity分量,转化成scale_freq */
/* convert scale-invariant capacity */
capacity_req = capacity_req * SCHED_CAPACITY_SCALE / capacity_orig_of(cpu);
/* (6) update request,
ooooo这里有问题啊:capacity_req计算的时候是按照rt+cfs加起来计算的,怎么有把结果配置给了scr->cfs?
*/
/*
* If free room ~5% impact, jump to 1 more index hihger OPP.
* Whatever it should be better than capacity_max.
*/
set_cfs_cpu_capacity(cpu, true, capacity_req, SCHE_ONESHOT);
}
}
|→
static inline void set_cfs_cpu_capacity(int cpu, bool request,
unsigned long capacity, int type)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_SCHED_ASSIST
if (true) {
#else
if (per_cpu(cpu_sched_capacity_reqs, cpu).cfs != capacity) {
#endif
/* (6.1) 把RT负载更新到per_cpu(cpu_sched_capacity_reqs, cpu).cfs */
per_cpu(cpu_sched_capacity_reqs, cpu).cfs = capacity;
update_cpu_capacity_request(cpu, request, type);
}
}5.2.3、freq target
void update_cpu_capacity_request(int cpu, bool request, int type)
{
unsigned long new_capacity;
struct sched_capacity_reqs *scr;
/* The rq lock serializes access to the CPU's sched_capacity_reqs. */
lockdep_assert_held(&cpu_rq(cpu)->lock);
scr = &per_cpu(cpu_sched_capacity_reqs, cpu);
/* (1) 综合rt、cfs的request */
new_capacity = scr->cfs + scr->rt;
new_capacity = new_capacity * capacity_margin_dvfs
/ SCHED_CAPACITY_SCALE;
new_capacity += scr->dl;
#ifndef CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_SCHED_ASSIST
if (new_capacity == scr->total)
return;
#endif
scr->total = new_capacity;
if (request)
update_fdomain_capacity_request(cpu, type);
}
|→
static void update_fdomain_capacity_request(int cpu, int type)
{
unsigned int freq_new, cpu_tmp;
struct gov_data *gd;
unsigned long capacity = 0;
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_SCHED_ASSIST
int cid = arch_get_cluster_id(cpu);
struct cpumask cls_cpus;
#endif
struct cpufreq_policy *policy = NULL;
/*
* Avoid grabbing the policy if possible. A test is still
* required after locking the CPU's policy to avoid racing
* with the governor changing.
*/
if (!per_cpu(enabled, cpu))
return;
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_SCHED_ASSIST
gd = g_gd[cid];
/* bail early if we are throttled */
if (ktime_before(ktime_get(), gd->throttle))
goto out;
arch_get_cluster_cpus(&cls_cpus, cid);
/* find max capacity requested by cpus in this policy */
for_each_cpu(cpu_tmp, &cls_cpus) {
struct sched_capacity_reqs *scr;
if (!cpu_online(cpu_tmp))
continue;
scr = &per_cpu(cpu_sched_capacity_reqs, cpu_tmp);
capacity = max(capacity, scr->total);
}
freq_new = capacity * arch_scale_get_max_freq(cpu) >> SCHED_CAPACITY_SHIFT;
#else
if (likely(cpu_online(cpu)))
policy = cpufreq_cpu_get(cpu);
if (IS_ERR_OR_NULL(policy))
return;
if (policy->governor != &cpufreq_gov_sched ||
!policy->governor_data)
goto out;
gd = policy->governor_data;
/* bail early if we are throttled */
if (ktime_before(ktime_get(), gd->throttle))
goto out;
/* (1) 选择policy cpus中最大的capacity */
/* find max capacity requested by cpus in this policy */
for_each_cpu(cpu_tmp, policy->cpus) {
struct sched_capacity_reqs *scr;
scr = &per_cpu(cpu_sched_capacity_reqs, cpu_tmp);
capacity = max(capacity, scr->total);
}
/* (2) 把相对capacity转换成绝对freq */
/* Convert the new maximum capacity request into a cpu frequency */
freq_new = capacity * policy->max >> SCHED_CAPACITY_SHIFT;
if (freq_new == gd->requested_freq)
goto out;
#endif /* !CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_SCHED_ASSIST */
gd->requested_freq = freq_new;
gd->target_cpu = cpu;
/* (3) 使用irq_work或者直接配置的方式来配置新的频率
直接在schedule_tick()中配置频率的方式估计不会使用,因为这样会阻塞中断
*/
/*
* Throttling is not yet supported on platforms with fast cpufreq
* drivers.
*/
if (cpufreq_driver_slow)
irq_work_queue_on(&gd->irq_work, cpu);
else
cpufreq_sched_try_driver_target(cpu, policy, freq_new, type);
out:
if (policy)
cpufreq_cpu_put(policy);
}
5.3、WALT(Windows Assisted Load Tracking)
在qualcomm 8898中,使用了WALT作为负载计算方法,也使用了自己的负载均衡算法来使用WALT负载。代码中使用CONFIG_SCHED_HMP来标示qualcomm自己负载均衡方法。
5.3.1、WALT的负载计算
Walt的本质也是时间窗分量,结合freq分量、capacity分量等一起表达的一个负载相对值。我们首先来看看几个分量的计算方法。
- 1、cluster->efficiency计算:从dts中读取,我们可以看到,四个小核的efficiency是1024,四个大核的efficiency是1638;
static struct sched_cluster *alloc_new_cluster(const struct cpumask *cpus)
{
cluster->efficiency = arch_get_cpu_efficiency(cpumask_first(cpus));
if (cluster->efficiency > max_possible_efficiency)
max_possible_efficiency = cluster->efficiency;
if (cluster->efficiency < min_possible_efficiency)
min_possible_efficiency = cluster->efficiency;
}
unsigned long arch_get_cpu_efficiency(int cpu)
{
return per_cpu(cpu_efficiency, cpu);
}
static void __init parse_dt_cpu_power(void)
{
/*
* The CPU efficiency value passed from the device tree
* overrides the value defined in the table_efficiency[]
*/
if (of_property_read_u32(cn, "efficiency", &efficiency) < 0) {
}
per_cpu(cpu_efficiency, cpu) = efficiency;
}
从 arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/sdm660.dtsi读到"efficiency"配置:
cpus {
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <0>;
CPU0: cpu@0 {
efficiency = <1024>;
};
CPU1: cpu@1 {
efficiency = <1024>;
};
CPU2: cpu@2 {
efficiency = <1024>;
};
CPU3: cpu@3 {
efficiency = <1024>;
};
CPU4: cpu@100 {
efficiency = <1638>;
};
CPU5: cpu@101 {
efficiency = <1638>;
};
CPU6: cpu@102 {
efficiency = <1638>;
};
CPU7: cpu@103 {
efficiency = <1638>;
};
cpu-map {
cluster0 {
core0 {
cpu = <&CPU0>;
};
core1 {
cpu = <&CPU1>;
};
core2 {
cpu = <&CPU2>;
};
core3 {
cpu = <&CPU3>;
};
};
cluster1 {
core0 {
cpu = <&CPU4>;
};
core1 {
cpu = <&CPU5>;
};
core2 {
cpu = <&CPU6>;
};
core3 {
cpu = <&CPU7>;
};
};
};
}
- 2、cluster->capacity:计算和最小值的正比:capacity = 1024 * (cluster->efficiency*cluster_max_freq(cluster)) / (min_possible_efficiency*min_max_freq)
- 3、cluster->max_possible_capacity:计算和最小值的正比:capacity = 1024 * (cluster->efficiency*cluster->max_possible_freq) / (min_possible_efficiency*min_max_freq)
- 4、cluster->load_scale_factor:计算和最大值的反比:lsf = 1024 * (max_possible_efficiency*max_possible_freq) / (cluster->efficiency*cluster_max_freq(cluster))
- 5、cluster->exec_scale_factor:计算和最大值的正比:exec_scale_factor = 1024 * cluster->efficiency / max_possible_efficiency
static void update_all_clusters_stats(void)
{
struct sched_cluster *cluster;
u64 highest_mpc = 0, lowest_mpc = U64_MAX;
pre_big_task_count_change(cpu_possible_mask);
for_each_sched_cluster(cluster) {
u64 mpc;
/* (1) 计算cluster->capacity:capacity = efficiency * cluster_max_freq
最小值:min_possible_efficiency*min_max_freq = 1024,
计算和最小值的正比:capacity = 1024 * (cluster->efficiency*cluster_max_freq(cluster)) / (min_possible_efficiency*min_max_freq)
*/
cluster->capacity = compute_capacity(cluster);
/* (2) 计算cluster->max_possible_capacity:capacity = efficiency * cluster_max_freq
最小值:min_possible_efficiency*min_max_freq = 1024,
计算和最小值的正比:capacity = 1024 * (cluster->efficiency*cluster->max_possible_freq) / (min_possible_efficiency*min_max_freq)
*/
mpc = cluster->max_possible_capacity =
compute_max_possible_capacity(cluster);
/* (3) 计算cluster->load_scale_factor: lsf = efficiency * cluster_max_freq
最大值:max_possible_efficiency*max_possible_freq = 1024
计算和最大值的反比:lsf = 1024 * (max_possible_efficiency*max_possible_freq) / (cluster->efficiency*cluster_max_freq(cluster))
*/
cluster->load_scale_factor = compute_load_scale_factor(cluster);
/* (4) 计算cluster->exec_scale_factor:
最大值:max_possible_efficiency = 1024
计算和最大值的正比:exec_scale_factor = 1024 * cluster->efficiency / max_possible_efficiency
*/
cluster->exec_scale_factor =
DIV_ROUND_UP(cluster->efficiency * 1024,
max_possible_efficiency);
if (mpc > highest_mpc)
highest_mpc = mpc;
if (mpc < lowest_mpc)
lowest_mpc = mpc;
}
max_possible_capacity = highest_mpc;
min_max_possible_capacity = lowest_mpc;
__update_min_max_capacity();
sched_update_freq_max_load(cpu_possible_mask);
post_big_task_count_change(cpu_possible_mask);
}
|→
static int compute_capacity(struct sched_cluster *cluster)
{
int capacity = 1024;
capacity *= capacity_scale_cpu_efficiency(cluster);
capacity >>= 10;
capacity *= capacity_scale_cpu_freq(cluster);
capacity >>= 10;
return capacity;
}
||→
/*
* Return 'capacity' of a cpu in reference to "least" efficient cpu, such that
* least efficient cpu gets capacity of 1024
*/
static unsigned long
capacity_scale_cpu_efficiency(struct sched_cluster *cluster)
{
return (1024 * cluster->efficiency) / min_possible_efficiency;
}
||→
/*
* Return 'capacity' of a cpu in reference to cpu with lowest max_freq
* (min_max_freq), such that one with lowest max_freq gets capacity of 1024.
*/
static unsigned long capacity_scale_cpu_freq(struct sched_cluster *cluster)
{
return (1024 * cluster_max_freq(cluster)) / min_max_freq;
}
|→
static int compute_load_scale_factor(struct sched_cluster *cluster)
{
int load_scale = 1024;
/*
* load_scale_factor accounts for the fact that task load
* is in reference to "best" performing cpu. Task's load will need to be
* scaled (up) by a factor to determine suitability to be placed on a
* (little) cpu.
*/
load_scale *= load_scale_cpu_efficiency(cluster);
load_scale >>= 10;
load_scale *= load_scale_cpu_freq(cluster);
load_scale >>= 10;
return load_scale;
}
||→
/*
* Return load_scale_factor of a cpu in reference to "most" efficient cpu, so
* that "most" efficient cpu gets a load_scale_factor of 1
*/
static inline unsigned long
load_scale_cpu_efficiency(struct sched_cluster *cluster)
{
return DIV_ROUND_UP(1024 * max_possible_efficiency,
cluster->efficiency);
}
||→
/*
* Return load_scale_factor of a cpu in reference to cpu with best max_freq
* (max_possible_freq), so that one with best max_freq gets a load_scale_factor
* of 1.
*/
static inline unsigned long load_scale_cpu_freq(struct sched_cluster *cluster)
{
return DIV_ROUND_UP(1024 * max_possible_freq,
cluster_max_freq(cluster));
}
- 6、cluster->max_power_cost:cluster的最大功耗 = voltage^2 * frequence
- 7、cluster->min_power_cost:cluster的最小功耗 = voltage^2 * frequence
static void sort_clusters(void)
{
for_each_sched_cluster(cluster) {
cluster->max_power_cost = power_cost(cluster_first_cpu(cluster),
max_task_load());
cluster->min_power_cost = power_cost(cluster_first_cpu(cluster),
0);
if (cluster->max_power_cost > tmp_max)
tmp_max = cluster->max_power_cost;
}
max_power_cost = tmp_max;
}
|→
unsigned int power_cost(int cpu, u64 demand)
{
int first, mid, last;
struct cpu_pwr_stats *per_cpu_info = get_cpu_pwr_stats();
struct cpu_pstate_pwr *costs;
struct freq_max_load *max_load;
int total_static_pwr_cost = 0;
struct rq *rq = cpu_rq(cpu);
unsigned int pc;
if (!per_cpu_info || !per_cpu_info[cpu].ptable)
/*
* When power aware scheduling is not in use, or CPU
* power data is not available, just use the CPU
* capacity as a rough stand-in for real CPU power
* numbers, assuming bigger CPUs are more power
* hungry.
*/
return cpu_max_possible_capacity(cpu);
rcu_read_lock();
max_load = rcu_dereference(per_cpu(freq_max_load, cpu));
if (!max_load) {
pc = cpu_max_possible_capacity(cpu);
goto unlock;
}
costs = per_cpu_info[cpu].ptable;
if (demand <= max_load->freqs[0].hdemand) {
pc = costs[0].power;
goto unlock;
} else if (demand > max_load->freqs[max_load->length - 1].hdemand) {
pc = costs[max_load->length - 1].power;
goto unlock;
}
first = 0;
last = max_load->length - 1;
mid = (last - first) >> 1;
while (1) {
if (demand <= max_load->freqs[mid].hdemand)
last = mid;
else
first = mid;
if (last - first == 1)
break;
mid = first + ((last - first) >> 1);
}
pc = costs[last].power;
unlock:
rcu_read_unlock();
if (idle_cpu(cpu) && rq->cstate) {
total_static_pwr_cost += rq->static_cpu_pwr_cost;
if (rq->cluster->dstate)
total_static_pwr_cost +=
rq->cluster->static_cluster_pwr_cost;
}
return pc + total_static_pwr_cost;
}
/* qualcom的power的计算公式 = voltage^2 * frequence */
static int msm_get_power_values(int cpu, struct cpu_static_info *sp)
{
int i = 0, j;
int ret = 0;
uint64_t power;
/* Calculate dynamic power spent for every frequency using formula:
* Power = V * V * f
* where V = voltage for frequency
* f = frequency
* */
sp->power = allocate_2d_array_uint32_t(sp->num_of_freqs);
if (IS_ERR_OR_NULL(sp->power))
return PTR_ERR(sp->power);
for (i = 0; i < TEMP_DATA_POINTS; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < sp->num_of_freqs; j++) {
power = sp->voltage[j] *
sp->table[j].frequency;
do_div(power, 1000);
do_div(power, 1000);
power *= sp->voltage[j];
do_div(power, 1000);
sp->power[i][j] = power;
}
}
return ret;
}
5.3.1.1、update_task_ravg()
walt关于进程的负载计算流程如下:
- 1、把时间分成一个个window窗口,累加时间时,需要综合efficiency和freq分量(也就是capacity):delta = delta_time * (curr_freq/max_possible_freq) * (cluster->efficiency/max_possible_efficiency);
static inline u64 scale_exec_time(u64 delta, struct rq *rq)
{
u32 freq;
/* curr_freq / max_possible_freq */
freq = cpu_cycles_to_freq(rq->cc.cycles, rq->cc.time);
delta = DIV64_U64_ROUNDUP(delta * freq, max_possible_freq);
/* exec_scale_factor = cluster->efficiency / max_possible_efficiency */
delta *= rq->cluster->exec_scale_factor;
delta >>= 10;
return delta;
}- 2、统计runnable状态的时间:account_busy_for_task_demand()屏蔽掉runnable以外的其他状态的时间统计;
static int account_busy_for_task_demand(struct task_struct *p, int event)
{
/*
* No need to bother updating task demand for exiting tasks
* or the idle task.
*/
/* (3.1.1) exit、idle任务不计入统计 */
if (exiting_task(p) || is_idle_task(p))
return 0;
/*
* When a task is waking up it is completing a segment of non-busy
* time. Likewise, if wait time is not treated as busy time, then
* when a task begins to run or is migrated, it is not running and
* is completing a segment of non-busy time.
*/
/* (3.1.2) 任务被wakeup,之前的等待时间不计入统计
SCHED_ACCOUNT_WAIT_TIME用来控制ruannable的等待时间是否计入统计,默认是计入的
*/
if (event == TASK_WAKE || (!SCHED_ACCOUNT_WAIT_TIME &&
(event == PICK_NEXT_TASK || event == TASK_MIGRATE)))
return 0;
return 1;
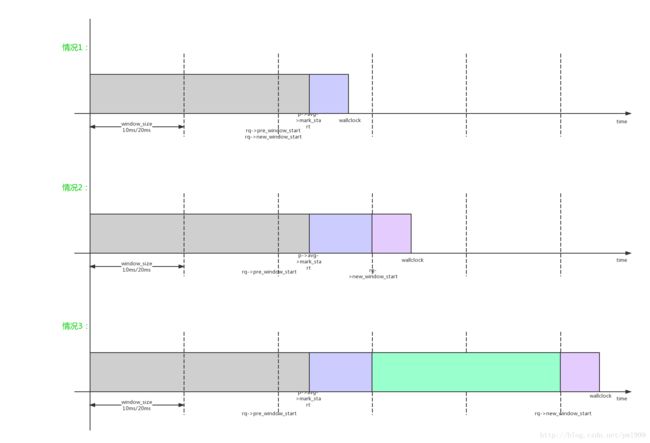
}- 3、在统计时间时,可能碰到的3种组合情况:
4、如果一个window还没有完成,会逐步累加时间到p->ravg.sum;如果一个window完成,存储最新window负载到p->ravg.sum_history[RAVG_HIST_SIZE_MAX]中,sum_history[]一共有5个槽位;系统根据sched_window_stats_policy选择策略(RECENT、MAX、AVG、MAX_RECENT_AVG),根据sum_history[]计算选择一个合适的值作为进程负载p->ravg.demand;同时根据sum_history[]的计算进程的负载预测p->ravg.pred_demand;

5、walt的task级别的负载是p->ravg.demand,cpu级别负载是rq->hmp_stats.cumulative_runnable_avg;
6、
具体的update_task_ravg()代码解析如下:
scheduler_tick() -> update_task_ravg()
↓
/* Reflect task activity on its demand and cpu's busy time statistics */
void update_task_ravg(struct task_struct *p, struct rq *rq, int event,
u64 wallclock, u64 irqtime)
{
u64 runtime;
if (!rq->window_start || sched_disable_window_stats ||
p->ravg.mark_start == wallclock)
return;
lockdep_assert_held(&rq->lock);
/* (1) 根据wallclock更新rq->window_start */
update_window_start(rq, wallclock);
if (!p->ravg.mark_start) {
update_task_cpu_cycles(p, cpu_of(rq));
goto done;
}
/* (2) 更新cycle、walltime的差值,用来计算cpu的当前freq */
update_task_rq_cpu_cycles(p, rq, event, wallclock, irqtime);
/* (3) 更新task的负载demand */
runtime = update_task_demand(p, rq, event, wallclock);
if (runtime)
update_task_burst(p, rq, event, runtime);
/* (4) 更新cpu的busy时间 */
update_cpu_busy_time(p, rq, event, wallclock, irqtime);
/* (5) 更新task的负载预测pred_demand */
update_task_pred_demand(rq, p, event);
done:
trace_sched_update_task_ravg(p, rq, event, wallclock, irqtime,
rq->cc.cycles, rq->cc.time,
p->grp ? &rq->grp_time : NULL);
/* (6) 更新task的时间更新点:p->ravg.mark_start */
p->ravg.mark_start = wallclock;
}
|→
static u64 update_task_demand(struct task_struct *p, struct rq *rq,
int event, u64 wallclock)
{
u64 mark_start = p->ravg.mark_start;
u64 delta, window_start = rq->window_start;
int new_window, nr_full_windows;
u32 window_size = sched_ravg_window;
u64 runtime;
new_window = mark_start < window_start;
/* (3.1) 这是一个关键点,非runnable状态的统计需要在这里异常返回 */
if (!account_busy_for_task_demand(p, event)) {
if (new_window)
/*
* If the time accounted isn't being accounted as
* busy time, and a new window started, only the
* previous window need be closed out with the
* pre-existing demand. Multiple windows may have
* elapsed, but since empty windows are dropped,
* it is not necessary to account those.
*/
update_history(rq, p, p->ravg.sum, 1, event);
return 0;
}
/* (3.2) 第一种情况:还在原窗口内,简单继续累加p->ravg.sum */
if (!new_window) {
/*
* The simple case - busy time contained within the existing
* window.
*/
return add_to_task_demand(rq, p, wallclock - mark_start);
}
/* (3.3) 第二、三种情况:原窗口已经填满 */
/*
* Busy time spans at least two windows. Temporarily rewind
* window_start to first window boundary after mark_start.
*/
delta = window_start - mark_start;
nr_full_windows = div64_u64(delta, window_size);
window_start -= (u64)nr_full_windows * (u64)window_size;
/* (3.4.1) 补全第一个窗口 */
/* Process (window_start - mark_start) first */
runtime = add_to_task_demand(rq, p, window_start - mark_start);
/* (3.4.2) 把第一个窗口更新到进程task负载history中,
更新p->ravg.demand、p->ravg.pred_demand
*/
/* Push new sample(s) into task's demand history */
update_history(rq, p, p->ravg.sum, 1, event);
/* (3.5) 如果中间有几个完整窗口,更新负载,更新history */
if (nr_full_windows) {
u64 scaled_window = scale_exec_time(window_size, rq);
update_history(rq, p, scaled_window, nr_full_windows, event);
runtime += nr_full_windows * scaled_window;
}
/* (3.6) 最后一个没有完成的窗口,只是简单累加时间,不更新history */
/*
* Roll window_start back to current to process any remainder
* in current window.
*/
window_start += (u64)nr_full_windows * (u64)window_size;
/* Process (wallclock - window_start) next */
mark_start = window_start;
runtime += add_to_task_demand(rq, p, wallclock - mark_start);
return runtime;
}
||→
static int account_busy_for_task_demand(struct task_struct *p, int event)
{
/*
* No need to bother updating task demand for exiting tasks
* or the idle task.
*/
/* (3.1.1) exit、idle任务不计入统计 */
if (exiting_task(p) || is_idle_task(p))
return 0;
/*
* When a task is waking up it is completing a segment of non-busy
* time. Likewise, if wait time is not treated as busy time, then
* when a task begins to run or is migrated, it is not running and
* is completing a segment of non-busy time.
*/
/* (3.1.2) 任务被wakeup,之前的等待时间不计入统计
SCHED_ACCOUNT_WAIT_TIME用来控制ruannable的等待时间是否计入统计,默认是计入的
*/
if (event == TASK_WAKE || (!SCHED_ACCOUNT_WAIT_TIME &&
(event == PICK_NEXT_TASK || event == TASK_MIGRATE)))
return 0;
return 1;
}
||→
static void add_to_task_demand(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p,
u64 delta)
{
/* (3.4.1) 累加窗口的时间值 */
delta = scale_exec_time(delta, rq);
p->ravg.sum += delta;
if (unlikely(p->ravg.sum > walt_ravg_window))
p->ravg.sum = walt_ravg_window;
}
static inline u64 scale_exec_time(u64 delta, struct rq *rq)
{
u32 freq;
/* curr_freq / max_possible_freq */
freq = cpu_cycles_to_freq(rq->cc.cycles, rq->cc.time);
delta = DIV64_U64_ROUNDUP(delta * freq, max_possible_freq);
/* exec_scale_factor = cluster->efficiency / max_possible_efficiency */
delta *= rq->cluster->exec_scale_factor;
delta >>= 10;
return delta;
}
||→
static void update_history(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p,
u32 runtime, int samples, int event)
{
u32 *hist = &p->ravg.sum_history[0];
int ridx, widx;
u32 max = 0, avg, demand, pred_demand;
u64 sum = 0;
/* (3.4.2.1) 不活跃的进程不进行更新 */
/* Ignore windows where task had no activity */
if (!runtime || is_idle_task(p) || exiting_task(p) || !samples)
goto done;
/* (3.4.2.2) 把新窗口的runtime推送到history stack中 */
/* Push new 'runtime' value onto stack */
widx = sched_ravg_hist_size - 1;
ridx = widx - samples;
for (; ridx >= 0; --widx, --ridx) {
hist[widx] = hist[ridx];
sum += hist[widx];
if (hist[widx] > max)
max = hist[widx];
}
for (widx = 0; widx < samples && widx < sched_ravg_hist_size; widx++) {
hist[widx] = runtime;
sum += hist[widx];
if (hist[widx] > max)
max = hist[widx];
}
p->ravg.sum = 0;
/* (3.4.2.3) 根据sched_window_stats_policy策略(RECENT、MAX、AVG、MAX_RECENT_AVG),
从sum_history[]中选择合适的值作为进程负载p->ravg.demand
*/
if (sched_window_stats_policy == WINDOW_STATS_RECENT) {
demand = runtime;
} else if (sched_window_stats_policy == WINDOW_STATS_MAX) {
demand = max;
} else {
avg = div64_u64(sum, sched_ravg_hist_size);
if (sched_window_stats_policy == WINDOW_STATS_AVG)
demand = avg;
else
demand = max(avg, runtime);
}
/* (3.4.2.4) 计算进程的预测负载 */
pred_demand = predict_and_update_buckets(rq, p, runtime);
/*
* A throttled deadline sched class task gets dequeued without
* changing p->on_rq. Since the dequeue decrements hmp stats
* avoid decrementing it here again.
*/
/* (3.4.2.5) 更新进程负载(p->ravg.demand)到cpu负载(rq->hmp_stats.cumulative_runnable_avg)中
cfs中p->sched_class->fixup_hmp_sched_stats对应函数fixup_hmp_sched_stats_fair()
*/
if (task_on_rq_queued(p) && (!task_has_dl_policy(p) ||
!p->dl.dl_throttled))
p->sched_class->fixup_hmp_sched_stats(rq, p, demand,
pred_demand);
p->ravg.demand = demand;
p->ravg.pred_demand = pred_demand;
done:
trace_sched_update_history(rq, p, runtime, samples, event);
}
|||→
static inline u32 predict_and_update_buckets(struct rq *rq,
struct task_struct *p, u32 runtime) {
int bidx;
u32 pred_demand;
/* (3.4.2.4.1) 把window负载转换成bucket index(最大10) */
bidx = busy_to_bucket(runtime);
/* (3.4.2.4.2) 根据index,找到历史曾经达到过的更大值,取历史的值作为预测值 */
pred_demand = get_pred_busy(rq, p, bidx, runtime);
/* (3.4.2.4.3) 对bucket[]中本次index权重进行增加,其他权重减少 */
bucket_increase(p->ravg.busy_buckets, bidx);
return pred_demand;
}
|||→
static void
fixup_hmp_sched_stats_fair(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p,
u32 new_task_load, u32 new_pred_demand)
{
/* (3.4.2.5.1) 计算task负载和预测的变化值delta */
s64 task_load_delta = (s64)new_task_load - task_load(p);
s64 pred_demand_delta = PRED_DEMAND_DELTA;
/* (3.4.2.5.2) 将进程级别的delta计入cpu级别的负载统计(rq->hmp_stats)中 */
fixup_cumulative_runnable_avg(&rq->hmp_stats, p, task_load_delta,
pred_demand_delta);
/* (3.4.2.5.3) 更新cpu级别big_task的数量 */
fixup_nr_big_tasks(&rq->hmp_stats, p, task_load_delta);
}
static inline void
fixup_cumulative_runnable_avg(struct hmp_sched_stats *stats,
struct task_struct *p, s64 task_load_delta,
s64 pred_demand_delta)
{
if (sched_disable_window_stats)
return;
stats->cumulative_runnable_avg += task_load_delta;
BUG_ON((s64)stats->cumulative_runnable_avg < 0);
stats->pred_demands_sum += pred_demand_delta;
BUG_ON((s64)stats->pred_demands_sum < 0);
}
void fixup_nr_big_tasks(struct hmp_sched_stats *stats,
struct task_struct *p, s64 delta)
{
u64 new_task_load;
u64 old_task_load;
if (sched_disable_window_stats)
return;
/* task_load按照capacity反比放大,让所有cpu处在同一级别 */
old_task_load = scale_load_to_cpu(task_load(p), task_cpu(p));
new_task_load = scale_load_to_cpu(delta + task_load(p), task_cpu(p));
/* 如果进程负载 > 最大负载 * 80% (sysctl_sched_upmigrate_pct)
该任务为big_task
*/
if (__is_big_task(p, old_task_load) && !__is_big_task(p, new_task_load))
stats->nr_big_tasks--;
else if (!__is_big_task(p, old_task_load) &&
__is_big_task(p, new_task_load))
stats->nr_big_tasks++;
BUG_ON(stats->nr_big_tasks < 0);
}
我们再来详细看看cpu级别的busy time计算:
static void update_cpu_busy_time(struct task_struct *p, struct rq *rq,
int event, u64 wallclock, u64 irqtime)
{
int new_window, full_window = 0;
int p_is_curr_task = (p == rq->curr);
u64 mark_start = p->ravg.mark_start;
u64 window_start = rq->window_start;
u32 window_size = sched_ravg_window;
u64 delta;
u64 *curr_runnable_sum = &rq->curr_runnable_sum;
u64 *prev_runnable_sum = &rq->prev_runnable_sum;
u64 *nt_curr_runnable_sum = &rq->nt_curr_runnable_sum;
u64 *nt_prev_runnable_sum = &rq->nt_prev_runnable_sum;
bool new_task;
struct related_thread_group *grp;
int cpu = rq->cpu;
u32 old_curr_window = p->ravg.curr_window;
new_window = mark_start < window_start;
if (new_window) {
full_window = (window_start - mark_start) >= window_size;
if (p->ravg.active_windows < USHRT_MAX)
p->ravg.active_windows++;
}
new_task = is_new_task(p);
/*
* Handle per-task window rollover. We don't care about the idle
* task or exiting tasks.
*/
/* (1) 如果有新window,滚动进程窗口:p->ravg.prev_window、p->ravg.curr_window */
if (!is_idle_task(p) && !exiting_task(p)) {
if (new_window)
rollover_task_window(p, full_window);
}
/* (2) 如果有新window且进程是rq的当前进程,
cpu级别的窗口滚动:rq->prev_runnable_sum、rq->curr_runnable_sum
cpu级别的进程统计窗口滚动:rq->top_tasks[prev_table]、rq->top_tasks[curr_table]
*/
if (p_is_curr_task && new_window) {
rollover_cpu_window(rq, full_window);
rollover_top_tasks(rq, full_window);
}
/* (3) 判断哪些情况可以统计进cpu time */
if (!account_busy_for_cpu_time(rq, p, irqtime, event))
goto done;
grp = p->grp;
if (grp && sched_freq_aggregate) {
struct group_cpu_time *cpu_time = &rq->grp_time;
curr_runnable_sum = &cpu_time->curr_runnable_sum;
prev_runnable_sum = &cpu_time->prev_runnable_sum;
nt_curr_runnable_sum = &cpu_time->nt_curr_runnable_sum;
nt_prev_runnable_sum = &cpu_time->nt_prev_runnable_sum;
}
/* (4) 如果时间没有达到新window,
在cpu级别的当前负载上累加:rq->curr_runnable_sum
在进程级别的基础上累加:p->ravg.curr_window
*/
if (!new_window) {
/*
* account_busy_for_cpu_time() = 1 so busy time needs
* to be accounted to the current window. No rollover
* since we didn't start a new window. An example of this is
* when a task starts execution and then sleeps within the
* same window.
*/
if (!irqtime || !is_idle_task(p) || cpu_is_waiting_on_io(rq))
delta = wallclock - mark_start;
else
delta = irqtime;
delta = scale_exec_time(delta, rq);
*curr_runnable_sum += delta;
if (new_task)
*nt_curr_runnable_sum += delta;
if (!is_idle_task(p) && !exiting_task(p)) {
p->ravg.curr_window += delta;
p->ravg.curr_window_cpu[cpu] += delta;
}
goto done;
}
/* (5) 如果时间达到新window,但是进程不是rq的当前进程
在进程级别的基础上累加:p->ravg.prev_window、p->ravg.curr_window
在cpu级别的当前负载上累加:rq->prev_runnable_sum、rq->curr_runnable_sum
*/
if (!p_is_curr_task) {
/*
* account_busy_for_cpu_time() = 1 so busy time needs
* to be accounted to the current window. A new window
* has also started, but p is not the current task, so the
* window is not rolled over - just split up and account
* as necessary into curr and prev. The window is only
* rolled over when a new window is processed for the current
* task.
*
* Irqtime can't be accounted by a task that isn't the
* currently running task.
*/
if (!full_window) {
/*
* A full window hasn't elapsed, account partial
* contribution to previous completed window.
*/
delta = scale_exec_time(window_start - mark_start, rq);
if (!exiting_task(p)) {
p->ravg.prev_window += delta;
p->ravg.prev_window_cpu[cpu] += delta;
}
} else {
/*
* Since at least one full window has elapsed,
* the contribution to the previous window is the
* full window (window_size).
*/
delta = scale_exec_time(window_size, rq);
if (!exiting_task(p)) {
p->ravg.prev_window = delta;
p->ravg.prev_window_cpu[cpu] = delta;
}
}
*prev_runnable_sum += delta;
if (new_task)
*nt_prev_runnable_sum += delta;
/* Account piece of busy time in the current window. */
delta = scale_exec_time(wallclock - window_start, rq);
*curr_runnable_sum += delta;
if (new_task)
*nt_curr_runnable_sum += delta;
if (!exiting_task(p)) {
p->ravg.curr_window = delta;
p->ravg.curr_window_cpu[cpu] = delta;
}
goto done;
}
/* (6) 如果时间达到新window,且进程是rq的当前进程
在进程级别的基础上累加:p->ravg.prev_window、p->ravg.curr_window
在cpu级别的当前负载上累加:rq->prev_runnable_sum、rq->curr_runnable_sum
*/
if (!irqtime || !is_idle_task(p) || cpu_is_waiting_on_io(rq)) {
/*
* account_busy_for_cpu_time() = 1 so busy time needs
* to be accounted to the current window. A new window
* has started and p is the current task so rollover is
* needed. If any of these three above conditions are true
* then this busy time can't be accounted as irqtime.
*
* Busy time for the idle task or exiting tasks need not
* be accounted.
*
* An example of this would be a task that starts execution
* and then sleeps once a new window has begun.
*/
if (!full_window) {
/*
* A full window hasn't elapsed, account partial
* contribution to previous completed window.
*/
delta = scale_exec_time(window_start - mark_start, rq);
if (!is_idle_task(p) && !exiting_task(p)) {
p->ravg.prev_window += delta;
p->ravg.prev_window_cpu[cpu] += delta;
}
} else {
/*
* Since at least one full window has elapsed,
* the contribution to the previous window is the
* full window (window_size).
*/
delta = scale_exec_time(window_size, rq);
if (!is_idle_task(p) && !exiting_task(p)) {
p->ravg.prev_window = delta;
p->ravg.prev_window_cpu[cpu] = delta;
}
}
/*
* Rollover is done here by overwriting the values in
* prev_runnable_sum and curr_runnable_sum.
*/
*prev_runnable_sum += delta;
if (new_task)
*nt_prev_runnable_sum += delta;
/* Account piece of busy time in the current window. */
delta = scale_exec_time(wallclock - window_start, rq);
*curr_runnable_sum += delta;
if (new_task)
*nt_curr_runnable_sum += delta;
if (!is_idle_task(p) && !exiting_task(p)) {
p->ravg.curr_window = delta;
p->ravg.curr_window_cpu[cpu] = delta;
}
goto done;
}
if (irqtime) {
/*
* account_busy_for_cpu_time() = 1 so busy time needs
* to be accounted to the current window. A new window
* has started and p is the current task so rollover is
* needed. The current task must be the idle task because
* irqtime is not accounted for any other task.
*
* Irqtime will be accounted each time we process IRQ activity
* after a period of idleness, so we know the IRQ busy time
* started at wallclock - irqtime.
*/
BUG_ON(!is_idle_task(p));
mark_start = wallclock - irqtime;
/*
* Roll window over. If IRQ busy time was just in the current
* window then that is all that need be accounted.
*/
if (mark_start > window_start) {
*curr_runnable_sum = scale_exec_time(irqtime, rq);
return;
}
/*
* The IRQ busy time spanned multiple windows. Process the
* busy time preceding the current window start first.
*/
delta = window_start - mark_start;
if (delta > window_size)
delta = window_size;
delta = scale_exec_time(delta, rq);
*prev_runnable_sum += delta;
/* Process the remaining IRQ busy time in the current window. */
delta = wallclock - window_start;
rq->curr_runnable_sum = scale_exec_time(delta, rq);
return;
}
done:
/* (7) 更新cpu上的top task */
if (!is_idle_task(p) && !exiting_task(p))
update_top_tasks(p, rq, old_curr_window,
new_window, full_window);
}
|→
static void update_top_tasks(struct task_struct *p, struct rq *rq,
u32 old_curr_window, int new_window, bool full_window)
{
u8 curr = rq->curr_table;
u8 prev = 1 - curr;
u8 *curr_table = rq->top_tasks[curr];
u8 *prev_table = rq->top_tasks[prev];
int old_index, new_index, update_index;
u32 curr_window = p->ravg.curr_window;
u32 prev_window = p->ravg.prev_window;
bool zero_index_update;
if (old_curr_window == curr_window && !new_window)
return;
/* (1) 把就进程p的"当前window负载"、"旧的当前window负载"转换成index(NUM_LOAD_INDICES=1000) */
old_index = load_to_index(old_curr_window);
new_index = load_to_index(curr_window);
/* (2) 如果没有新window
更新当前top表rq->top_tasks[curr][]中新旧index的计数
根据index的计数是否为0,更新rq->top_tasks_bitmap[curr] bitmap中对应index的值
*/
if (!new_window) {
zero_index_update = !old_curr_window && curr_window;
if (old_index != new_index || zero_index_update) {
if (old_curr_window)
curr_table[old_index] -= 1;
if (curr_window)
curr_table[new_index] += 1;
if (new_index > rq->curr_top)
rq->curr_top = new_index;
}
if (!curr_table[old_index])
__clear_bit(NUM_LOAD_INDICES - old_index - 1,
rq->top_tasks_bitmap[curr]);
if (curr_table[new_index] == 1)
__set_bit(NUM_LOAD_INDICES - new_index - 1,
rq->top_tasks_bitmap[curr]);
return;
}
/*
* The window has rolled over for this task. By the time we get
* here, curr/prev swaps would has already occurred. So we need
* to use prev_window for the new index.
*/
update_index = load_to_index(prev_window);
if (full_window) {
/*
* Two cases here. Either 'p' ran for the entire window or
* it didn't run at all. In either case there is no entry
* in the prev table. If 'p' ran the entire window, we just
* need to create a new entry in the prev table. In this case
* update_index will be correspond to sched_ravg_window
* so we can unconditionally update the top index.
*/
if (prev_window) {
prev_table[update_index] += 1;
rq->prev_top = update_index;
}
if (prev_table[update_index] == 1)
__set_bit(NUM_LOAD_INDICES - update_index - 1,
rq->top_tasks_bitmap[prev]);
} else {
zero_index_update = !old_curr_window && prev_window;
if (old_index != update_index || zero_index_update) {
if (old_curr_window)
prev_table[old_index] -= 1;
prev_table[update_index] += 1;
if (update_index > rq->prev_top)
rq->prev_top = update_index;
if (!prev_table[old_index])
__clear_bit(NUM_LOAD_INDICES - old_index - 1,
rq->top_tasks_bitmap[prev]);
if (prev_table[update_index] == 1)
__set_bit(NUM_LOAD_INDICES - update_index - 1,
rq->top_tasks_bitmap[prev]);
}
}
if (curr_window) {
curr_table[new_index] += 1;
if (new_index > rq->curr_top)
rq->curr_top = new_index;
if (curr_table[new_index] == 1)
__set_bit(NUM_LOAD_INDICES - new_index - 1,
rq->top_tasks_bitmap[curr]);
}
}
5.3.2、基于WALT的负载均衡
5.3.2.1、load_balance()
其他部分和主干内核算法一致,这里只标识出qualcom的HMP算法特有的部分。在负载均衡部分,walt用来找出cpu;但是在负载迁移时,计算负载还是使用pelt?
- 在find_busiest_queue()中:原本是找出cfs_rq->runnable_load_avg * capacity负载最大的cpu,qualcom HMP改为找出walt runnable负载(rq->hmp_stats.cumulative_runnable_avg)最重的cpu。
run_rebalance_domains() -> rebalance_domains() -> load_balance() -> find_busiest_queue() -> find_busiest_queue_hmp()
↓
static struct rq *find_busiest_queue_hmp(struct lb_env *env,
struct sched_group *group)
{
struct rq *busiest = NULL, *busiest_big = NULL;
u64 max_runnable_avg = 0, max_runnable_avg_big = 0;
int max_nr_big = 0, nr_big;
bool find_big = !!(env->flags & LBF_BIG_TASK_ACTIVE_BALANCE);
int i;
cpumask_t cpus;
cpumask_andnot(&cpus, sched_group_cpus(group), cpu_isolated_mask);
/* (1) 遍历sg中的cpu */
for_each_cpu(i, &cpus) {
struct rq *rq = cpu_rq(i);
u64 cumulative_runnable_avg =
rq->hmp_stats.cumulative_runnable_avg;
if (!cpumask_test_cpu(i, env->cpus))
continue;
/* (2) 考虑big_task,找出big_task最重的cpu */
if (find_big) {
nr_big = nr_big_tasks(rq);
if (nr_big > max_nr_big ||
(nr_big > 0 && nr_big == max_nr_big &&
cumulative_runnable_avg > max_runnable_avg_big)) {
max_runnable_avg_big = cumulative_runnable_avg;
busiest_big = rq;
max_nr_big = nr_big;
continue;
}
}
/* (3) 找出walt runnable负载(rq->hmp_stats.cumulative_runnable_avg)最重的cpu */
if (cumulative_runnable_avg > max_runnable_avg) {
max_runnable_avg = cumulative_runnable_avg;
busiest = rq;
}
}
if (busiest_big)
return busiest_big;
env->flags &= ~LBF_BIG_TASK_ACTIVE_BALANCE;
return busiest;
}
5.3.2.2、nohz_idle_balance()
- _nohz_kick_needed():
scheduler_tick() -> trigger_load_balance() -> nohz_kick_needed() -> _nohz_kick_needed() -> nohz_kick_needed_hmp()
↓
static inline int _nohz_kick_needed_hmp(struct rq *rq, int cpu, int *type)
{
struct sched_domain *sd;
int i;
if (rq->nr_running < 2)
return 0;
/* (1) 如果是SCHED_BOOST_ON_ALL,返回true */
if (!sysctl_sched_restrict_cluster_spill ||
sched_boost_policy() == SCHED_BOOST_ON_ALL)
return 1;
/* (2) 如果当前cpu是max cpu,返回true */
if (cpu_max_power_cost(cpu) == max_power_cost)
return 1;
rcu_read_lock();
sd = rcu_dereference_check_sched_domain(rq->sd);
if (!sd) {
rcu_read_unlock();
return 0;
}
for_each_cpu(i, sched_domain_span(sd)) {
if (cpu_load(i) < sched_spill_load &&
cpu_rq(i)->nr_running <
sysctl_sched_spill_nr_run) {
/* Change the kick type to limit to CPUs that
* are of equal or lower capacity.
*/
*type = NOHZ_KICK_RESTRICT;
break;
}
}
rcu_read_unlock();
return 1;
}
- find_new_hmp_ilb():原本是找出nohz.idle_cpus_mask中的第一个cpu作为ilb cpu,qualcom HMP改为尝试在nohz.idle_cpus_mask中找到一个max power小于当前cpu的作为ilb cpu。
scheduler_tick() -> trigger_load_balance() -> nohz_balancer_kick() -> find_new_ilb()
↓
static inline int find_new_hmp_ilb(int type)
{
int call_cpu = raw_smp_processor_id();
struct sched_domain *sd;
int ilb;
rcu_read_lock();
/* Pick an idle cpu "closest" to call_cpu */
for_each_domain(call_cpu, sd) {
for_each_cpu_and(ilb, nohz.idle_cpus_mask,
sched_domain_span(sd)) {
/* (1) 尝试找到一个max power小于当前power的cpu作为ilb cpu */
if (idle_cpu(ilb) && (type != NOHZ_KICK_RESTRICT ||
cpu_max_power_cost(ilb) <=
cpu_max_power_cost(call_cpu))) {
rcu_read_unlock();
reset_balance_interval(ilb);
return ilb;
}
}
}
rcu_read_unlock();
return nr_cpu_ids;
}5.3.2.3、select_task_rq_fair()
- select_task_rq_fair():使用qualcom自己的算法,综合capacity、power、idle给出一个best cpu。
select_task_rq_fair() -> select_best_cpu()
↓
/* return cheapest cpu that can fit this task */
static int select_best_cpu(struct task_struct *p, int target, int reason,
int sync)
{
struct sched_cluster *cluster, *pref_cluster = NULL;
struct cluster_cpu_stats stats;
struct related_thread_group *grp;
unsigned int sbc_flag = 0;
int cpu = raw_smp_processor_id();
bool special;
struct cpu_select_env env = {
.p = p,
.reason = reason,
.need_idle = wake_to_idle(p),
.need_waker_cluster = 0,
.sync = sync,
.prev_cpu = target,
.rtg = NULL,
.sbc_best_flag = 0,
.sbc_best_cluster_flag = 0,
.pack_task = false,
};
rcu_read_lock();
env.boost_policy = task_sched_boost(p) ?
sched_boost_policy() : SCHED_BOOST_NONE;
bitmap_copy(env.candidate_list, all_cluster_ids, NR_CPUS);
bitmap_zero(env.backup_list, NR_CPUS);
cpumask_and(&env.search_cpus, tsk_cpus_allowed(p), cpu_active_mask);
cpumask_andnot(&env.search_cpus, &env.search_cpus, cpu_isolated_mask);
init_cluster_cpu_stats(&stats);
special = env_has_special_flags(&env);
grp = task_related_thread_group(p);
if (grp && grp->preferred_cluster) {
pref_cluster = grp->preferred_cluster;
if (!cluster_allowed(&env, pref_cluster))
clear_bit(pref_cluster->id, env.candidate_list);
else
env.rtg = grp;
} else if (!special) {
cluster = cpu_rq(cpu)->cluster;
if (wake_to_waker_cluster(&env)) {
if (bias_to_waker_cpu(&env, cpu)) {
target = cpu;
sbc_flag = SBC_FLAG_WAKER_CLUSTER |
SBC_FLAG_WAKER_CPU;
goto out;
} else if (cluster_allowed(&env, cluster)) {
env.need_waker_cluster = 1;
bitmap_zero(env.candidate_list, NR_CPUS);
__set_bit(cluster->id, env.candidate_list);
env.sbc_best_cluster_flag =
SBC_FLAG_WAKER_CLUSTER;
}
} else if (bias_to_prev_cpu(&env, &stats)) {
sbc_flag = SBC_FLAG_PREV_CPU;
goto out;
}
}
if (!special && is_short_burst_task(p)) {
env.pack_task = true;
sbc_flag = SBC_FLAG_PACK_TASK;
}
retry:
/* (1) 从低到高找到一个power最低,且capacity能满足task_load的cluster */
cluster = select_least_power_cluster(&env);
if (!cluster)
goto out;
/*
* 'cluster' now points to the minimum power cluster which can satisfy
* task's perf goals. Walk down the cluster list starting with that
* cluster. For non-small tasks, skip clusters that don't have
* mostly_idle/idle cpus
*/
do {
/* (2) 全方位统计:capacity spare、cost、idle */
find_best_cpu_in_cluster(cluster, &env, &stats);
} while ((cluster = next_best_cluster(cluster, &env, &stats)));
/* (3) 从idle角度给出best cpu */
if (env.need_idle) {
if (stats.best_idle_cpu >= 0) {
target = stats.best_idle_cpu;
sbc_flag |= SBC_FLAG_IDLE_CSTATE;
} else if (stats.least_loaded_cpu >= 0) {
target = stats.least_loaded_cpu;
sbc_flag |= SBC_FLAG_IDLE_LEAST_LOADED;
}
/* (4) 从综合角度给出best cpu */
} else if (stats.best_cpu >= 0) {
if (stats.best_sibling_cpu >= 0 &&
stats.best_cpu != task_cpu(p) &&
stats.min_cost == stats.best_sibling_cpu_cost) {
stats.best_cpu = stats.best_sibling_cpu;
sbc_flag |= SBC_FLAG_BEST_SIBLING;
}
sbc_flag |= env.sbc_best_flag;
target = stats.best_cpu;
} else {
if (env.rtg && env.boost_policy == SCHED_BOOST_NONE) {
env.rtg = NULL;
goto retry;
}
/*
* With boost_policy == SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG, we reach here with
* backup_list = little cluster, candidate_list = none and
* stats->best_capacity_cpu points the best spare capacity
* CPU among the CPUs in the big cluster.
*/
if (env.boost_policy == SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG &&
stats.best_capacity_cpu >= 0)
sbc_flag |= SBC_FLAG_BOOST_CLUSTER;
else
find_backup_cluster(&env, &stats);
if (stats.best_capacity_cpu >= 0) {
target = stats.best_capacity_cpu;
sbc_flag |= SBC_FLAG_BEST_CAP_CPU;
}
}
p->last_cpu_selected_ts = sched_ktime_clock();
out:
sbc_flag |= env.sbc_best_cluster_flag;
rcu_read_unlock();
trace_sched_task_load(p, sched_boost_policy() && task_sched_boost(p),
env.reason, env.sync, env.need_idle, sbc_flag, target);
return target;
}5.3.2.4、Interaction Governor & sched_load
qualcom对interactive governor进行了改造,打造成了可以使用sched_load的interactive governor。
- 1、interactive governor注册回调函数,接收sched_load变化事件;
static ssize_t store_use_sched_load(
struct cpufreq_interactive_tunables *tunables,
const char *buf, size_t count)
{
int ret;
unsigned long val;
ret = kstrtoul(buf, 0, &val);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
if (tunables->use_sched_load == (bool) val)
return count;
tunables->use_sched_load = val;
if (val)
ret = cpufreq_interactive_enable_sched_input(tunables);
else
ret = cpufreq_interactive_disable_sched_input(tunables);
if (ret) {
tunables->use_sched_load = !val;
return ret;
}
return count;
}
|→
static int cpufreq_interactive_enable_sched_input(
struct cpufreq_interactive_tunables *tunables)
{
int rc = 0, j;
struct cpufreq_interactive_tunables *t;
mutex_lock(&sched_lock);
set_window_count++;
if (set_window_count > 1) {
for_each_possible_cpu(j) {
if (!per_cpu(polinfo, j))
continue;
t = per_cpu(polinfo, j)->cached_tunables;
if (t && t->use_sched_load) {
tunables->timer_rate = t->timer_rate;
tunables->io_is_busy = t->io_is_busy;
break;
}
}
} else {
/* (1) 设置walt窗口大小 */
rc = set_window_helper(tunables);
if (rc) {
pr_err("%s: Failed to set sched window\n", __func__);
set_window_count--;
goto out;
}
sched_set_io_is_busy(tunables->io_is_busy);
}
if (!tunables->use_migration_notif)
goto out;
migration_register_count++;
if (migration_register_count > 1)
goto out;
else
/* (2) 注册sched_load变化的回调函数 */
atomic_notifier_chain_register(&load_alert_notifier_head,
&load_notifier_block);
out:
mutex_unlock(&sched_lock);
return rc;
}
||→
static inline int set_window_helper(
struct cpufreq_interactive_tunables *tunables)
{
/* 设置默认窗口size为DEFAULT_TIMER_RATE(20ms) */
return sched_set_window(round_to_nw_start(get_jiffies_64(), tunables),
usecs_to_jiffies(tunables->timer_rate));
}
static struct notifier_block load_notifier_block = {
.notifier_call = load_change_callback,
};
- 2、sched_load的变化通过回调函数通知给Interaction Governor;
check_for_freq_change() -> load_alert_notifier_head -> load_change_callback()
↓
static int load_change_callback(struct notifier_block *nb, unsigned long val,
void *data)
{
unsigned long cpu = (unsigned long) data;
struct cpufreq_interactive_policyinfo *ppol = per_cpu(polinfo, cpu);
struct cpufreq_interactive_tunables *tunables;
unsigned long flags;
if (!ppol || ppol->reject_notification)
return 0;
if (!down_read_trylock(&ppol->enable_sem))
return 0;
if (!ppol->governor_enabled)
goto exit;
tunables = ppol->policy->governor_data;
if (!tunables->use_sched_load || !tunables->use_migration_notif)
goto exit;
spin_lock_irqsave(&ppol->target_freq_lock, flags);
ppol->notif_pending = true;
ppol->notif_cpu = cpu;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ppol->target_freq_lock, flags);
if (!hrtimer_is_queued(&ppol->notif_timer))
hrtimer_start(&ppol->notif_timer, ms_to_ktime(1),
HRTIMER_MODE_REL);
exit:
up_read(&ppol->enable_sem);
return 0;
}
- 3、除了事件通知,interactive governor还会在20ms timer中轮询sched_load的变化来决定是否需要调频。
static void cpufreq_interactive_timer(unsigned long data)
{
s64 now;
unsigned int delta_time;
u64 cputime_speedadj;
int cpu_load;
int pol_load = 0;
struct cpufreq_interactive_policyinfo *ppol = per_cpu(polinfo, data);
struct cpufreq_interactive_tunables *tunables =
ppol->policy->governor_data;
struct sched_load *sl = ppol->sl;
struct cpufreq_interactive_cpuinfo *pcpu;
unsigned int new_freq;
unsigned int prev_laf = 0, t_prevlaf;
unsigned int pred_laf = 0, t_predlaf = 0;
unsigned int prev_chfreq, pred_chfreq, chosen_freq;
unsigned int index;
unsigned long flags;
unsigned long max_cpu;
int cpu, i;
int new_load_pct = 0;
int prev_l, pred_l = 0;
struct cpufreq_govinfo govinfo;
bool skip_hispeed_logic, skip_min_sample_time;
bool jump_to_max_no_ts = false;
bool jump_to_max = false;
bool start_hyst = true;
if (!down_read_trylock(&ppol->enable_sem))
return;
if (!ppol->governor_enabled)
goto exit;
now = ktime_to_us(ktime_get());
spin_lock_irqsave(&ppol->target_freq_lock, flags);
spin_lock(&ppol->load_lock);
skip_hispeed_logic =
tunables->ignore_hispeed_on_notif && ppol->notif_pending;
skip_min_sample_time = tunables->fast_ramp_down && ppol->notif_pending;
ppol->notif_pending = false;
now = ktime_to_us(ktime_get());
ppol->last_evaluated_jiffy = get_jiffies_64();
/* (1) sched_load模式,查询最新的sched_load */
if (tunables->use_sched_load)
sched_get_cpus_busy(sl, ppol->policy->cpus);
max_cpu = cpumask_first(ppol->policy->cpus);
i = 0;
for_each_cpu(cpu, ppol->policy->cpus) {
pcpu = &per_cpu(cpuinfo, cpu);
/* (2) sched_load模式,使用sched_load来计算负载变化 */
if (tunables->use_sched_load) {
/* (2.1) 根据上个窗口负载,获得当前目标值 */
t_prevlaf = sl_busy_to_laf(ppol, sl[i].prev_load);
prev_l = t_prevlaf / ppol->target_freq;
/* (2.2) 根据上个窗口负载预测,获得当前的预测值 */
if (tunables->enable_prediction) {
t_predlaf = sl_busy_to_laf(ppol,
sl[i].predicted_load);
pred_l = t_predlaf / ppol->target_freq;
}
if (sl[i].prev_load)
new_load_pct = sl[i].new_task_load * 100 /
sl[i].prev_load;
else
new_load_pct = 0;
/* (3) 传统模式,使用time*freq的模式来计算负载变化 */
} else {
now = update_load(cpu);
delta_time = (unsigned int)
(now - pcpu->cputime_speedadj_timestamp);
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!delta_time))
continue;
cputime_speedadj = pcpu->cputime_speedadj;
do_div(cputime_speedadj, delta_time);
t_prevlaf = (unsigned int)cputime_speedadj * 100;
prev_l = t_prevlaf / ppol->target_freq;
}
/* find max of loadadjfreq inside policy */
if (t_prevlaf > prev_laf) {
prev_laf = t_prevlaf;
max_cpu = cpu;
}
pred_laf = max(t_predlaf, pred_laf);
cpu_load = max(prev_l, pred_l);
pol_load = max(pol_load, cpu_load);
trace_cpufreq_interactive_cpuload(cpu, cpu_load, new_load_pct,
prev_l, pred_l);
/* save loadadjfreq for notification */
pcpu->loadadjfreq = max(t_prevlaf, t_predlaf);
/* detect heavy new task and jump to policy->max */
if (prev_l >= tunables->go_hispeed_load &&
new_load_pct >= NEW_TASK_RATIO) {
skip_hispeed_logic = true;
jump_to_max = true;
}
i++;
}
spin_unlock(&ppol->load_lock);
tunables->boosted = tunables->boost_val || now < tunables->boostpulse_endtime;
/* (4) 取目标值和预测值中的较大值,作为调频目标 */
prev_chfreq = choose_freq(ppol, prev_laf);
pred_chfreq = choose_freq(ppol, pred_laf);
chosen_freq = max(prev_chfreq, pred_chfreq);
if (prev_chfreq < ppol->policy->max && pred_chfreq >= ppol->policy->max)
if (!jump_to_max)
jump_to_max_no_ts = true;
if (now - ppol->max_freq_hyst_start_time <
tunables->max_freq_hysteresis &&
pol_load >= tunables->go_hispeed_load &&
ppol->target_freq < ppol->policy->max) {
skip_hispeed_logic = true;
skip_min_sample_time = true;
if (!jump_to_max)
jump_to_max_no_ts = true;
}
new_freq = chosen_freq;
if (jump_to_max_no_ts || jump_to_max) {
new_freq = ppol->policy->cpuinfo.max_freq;
} else if (!skip_hispeed_logic) {
if (pol_load >= tunables->go_hispeed_load ||
tunables->boosted) {
if (ppol->target_freq < tunables->hispeed_freq)
new_freq = tunables->hispeed_freq;
else
new_freq = max(new_freq,
tunables->hispeed_freq);
}
}
if (now - ppol->max_freq_hyst_start_time <
tunables->max_freq_hysteresis) {
if (new_freq < ppol->policy->max &&
ppol->policy->max <= tunables->hispeed_freq)
start_hyst = false;
new_freq = max(tunables->hispeed_freq, new_freq);
}
if (!skip_hispeed_logic &&
ppol->target_freq >= tunables->hispeed_freq &&
new_freq > ppol->target_freq &&
now - ppol->hispeed_validate_time <
freq_to_above_hispeed_delay(tunables, ppol->target_freq)) {
trace_cpufreq_interactive_notyet(
max_cpu, pol_load, ppol->target_freq,
ppol->policy->cur, new_freq);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ppol->target_freq_lock, flags);
goto rearm;
}
ppol->hispeed_validate_time = now;
if (cpufreq_frequency_table_target(&ppol->p_nolim, ppol->freq_table,
new_freq, CPUFREQ_RELATION_L,
&index)) {
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ppol->target_freq_lock, flags);
goto rearm;
}
new_freq = ppol->freq_table[index].frequency;
/*
* Do not scale below floor_freq unless we have been at or above the
* floor frequency for the minimum sample time since last validated.
*/
if (!skip_min_sample_time && new_freq < ppol->floor_freq) {
if (now - ppol->floor_validate_time <
tunables->min_sample_time) {
trace_cpufreq_interactive_notyet(
max_cpu, pol_load, ppol->target_freq,
ppol->policy->cur, new_freq);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ppol->target_freq_lock, flags);
goto rearm;
}
}
/*
* Update the timestamp for checking whether speed has been held at
* or above the selected frequency for a minimum of min_sample_time,
* if not boosted to hispeed_freq. If boosted to hispeed_freq then we
* allow the speed to drop as soon as the boostpulse duration expires
* (or the indefinite boost is turned off). If policy->max is restored
* for max_freq_hysteresis, don't extend the timestamp. Otherwise, it
* could incorrectly extended the duration of max_freq_hysteresis by
* min_sample_time.
*/
if ((!tunables->boosted || new_freq > tunables->hispeed_freq)
&& !jump_to_max_no_ts) {
ppol->floor_freq = new_freq;
ppol->floor_validate_time = now;
}
if (start_hyst && new_freq >= ppol->policy->max && !jump_to_max_no_ts)
ppol->max_freq_hyst_start_time = now;
if (ppol->target_freq == new_freq &&
ppol->target_freq <= ppol->policy->cur) {
trace_cpufreq_interactive_already(
max_cpu, pol_load, ppol->target_freq,
ppol->policy->cur, new_freq);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ppol->target_freq_lock, flags);
goto rearm;
}
trace_cpufreq_interactive_target(max_cpu, pol_load, ppol->target_freq,
ppol->policy->cur, new_freq);
ppol->target_freq = new_freq;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ppol->target_freq_lock, flags);
spin_lock_irqsave(&speedchange_cpumask_lock, flags);
cpumask_set_cpu(max_cpu, &speedchange_cpumask);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&speedchange_cpumask_lock, flags);
wake_up_process_no_notif(speedchange_task);
rearm:
if (!timer_pending(&ppol->policy_timer))
cpufreq_interactive_timer_resched(data, false);
/*
* Send govinfo notification.
* Govinfo notification could potentially wake up another thread
* managed by its clients. Thread wakeups might trigger a load
* change callback that executes this function again. Therefore
* no spinlock could be held when sending the notification.
*/
for_each_cpu(i, ppol->policy->cpus) {
pcpu = &per_cpu(cpuinfo, i);
govinfo.cpu = i;
govinfo.load = pcpu->loadadjfreq / ppol->policy->max;
govinfo.sampling_rate_us = tunables->timer_rate;
atomic_notifier_call_chain(&cpufreq_govinfo_notifier_list,
CPUFREQ_LOAD_CHANGE, &govinfo);
}
exit:
up_read(&ppol->enable_sem);
return;
}
|→
void sched_get_cpus_busy(struct sched_load *busy,
const struct cpumask *query_cpus)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct rq *rq;
const int cpus = cpumask_weight(query_cpus);
u64 load[cpus], group_load[cpus];
u64 nload[cpus], ngload[cpus];
u64 pload[cpus];
unsigned int max_freq[cpus];
int notifier_sent = 0;
int early_detection[cpus];
int cpu, i = 0;
unsigned int window_size;
u64 max_prev_sum = 0;
int max_busy_cpu = cpumask_first(query_cpus);
u64 total_group_load = 0, total_ngload = 0;
bool aggregate_load = false;
struct sched_cluster *cluster = cpu_cluster(cpumask_first(query_cpus));
if (unlikely(cpus == 0))
return;
local_irq_save(flags);
/*
* This function could be called in timer context, and the
* current task may have been executing for a long time. Ensure
* that the window stats are current by doing an update.
*/
for_each_cpu(cpu, query_cpus)
raw_spin_lock_nested(&cpu_rq(cpu)->lock, cpu);
window_size = sched_ravg_window;
/*
* We don't really need the cluster lock for this entire for loop
* block. However, there is no advantage in optimizing this as rq
* locks are held regardless and would prevent migration anyways
*/
raw_spin_lock(&cluster->load_lock);
for_each_cpu(cpu, query_cpus) {
rq = cpu_rq(cpu);
update_task_ravg(rq->curr, rq, TASK_UPDATE, sched_ktime_clock(),
0);
account_load_subtractions(rq);
/* (1) 获取:
cpu上一个窗口的负载:rq->prev_runnable_sum
cpu上一个窗口的的新任务负载:rq->nt_prev_runnable_sum
cpu上一个窗口的负载预测:rq->hmp_stats.pred_demands_sum
*/
load[i] = rq->prev_runnable_sum;
nload[i] = rq->nt_prev_runnable_sum;
pload[i] = rq->hmp_stats.pred_demands_sum;
rq->old_estimated_time = pload[i];
if (load[i] > max_prev_sum) {
max_prev_sum = load[i];
max_busy_cpu = cpu;
}
/*
* sched_get_cpus_busy() is called for all CPUs in a
* frequency domain. So the notifier_sent flag per
* cluster works even when a frequency domain spans
* more than 1 cluster.
*/
if (rq->cluster->notifier_sent) {
notifier_sent = 1;
rq->cluster->notifier_sent = 0;
}
early_detection[i] = (rq->ed_task != NULL);
max_freq[i] = cpu_max_freq(cpu);
i++;
}
raw_spin_unlock(&cluster->load_lock);
group_load_in_freq_domain(
&cpu_rq(max_busy_cpu)->freq_domain_cpumask,
&total_group_load, &total_ngload);
aggregate_load = !!(total_group_load > sched_freq_aggregate_threshold);
i = 0;
for_each_cpu(cpu, query_cpus) {
group_load[i] = 0;
ngload[i] = 0;
if (early_detection[i])
goto skip_early;
rq = cpu_rq(cpu);
if (aggregate_load) {
if (cpu == max_busy_cpu) {
group_load[i] = total_group_load;
ngload[i] = total_ngload;
}
} else {
group_load[i] = rq->grp_time.prev_runnable_sum;
ngload[i] = rq->grp_time.nt_prev_runnable_sum;
}
load[i] += group_load[i];
nload[i] += ngload[i];
load[i] = freq_policy_load(rq, load[i]);
rq->old_busy_time = load[i];
/*
* Scale load in reference to cluster max_possible_freq.
*
* Note that scale_load_to_cpu() scales load in reference to
* the cluster max_freq.
*/
load[i] = scale_load_to_cpu(load[i], cpu);
nload[i] = scale_load_to_cpu(nload[i], cpu);
pload[i] = scale_load_to_cpu(pload[i], cpu);
skip_early:
i++;
}
for_each_cpu(cpu, query_cpus)
raw_spin_unlock(&(cpu_rq(cpu))->lock);
local_irq_restore(flags);
i = 0;
for_each_cpu(cpu, query_cpus) {
rq = cpu_rq(cpu);
if (early_detection[i]) {
busy[i].prev_load = div64_u64(sched_ravg_window,
NSEC_PER_USEC);
busy[i].new_task_load = 0;
busy[i].predicted_load = 0;
goto exit_early;
}
load[i] = scale_load_to_freq(load[i], max_freq[i],
cpu_max_possible_freq(cpu));
nload[i] = scale_load_to_freq(nload[i], max_freq[i],
cpu_max_possible_freq(cpu));
pload[i] = scale_load_to_freq(pload[i], max_freq[i],
rq->cluster->max_possible_freq);
/* (2) 负载经过转换后赋值给busy:
cpu上一个窗口的负载:busy[i].prev_load
cpu上一个窗口的的新任务负载:busy[i].new_task_load
cpu上一个窗口的负载预测:busy[i].predicted_load
*/
busy[i].prev_load = div64_u64(load[i], NSEC_PER_USEC);
busy[i].new_task_load = div64_u64(nload[i], NSEC_PER_USEC);
busy[i].predicted_load = div64_u64(pload[i], NSEC_PER_USEC);
exit_early:
trace_sched_get_busy(cpu, busy[i].prev_load,
busy[i].new_task_load,
busy[i].predicted_load,
early_detection[i],
aggregate_load &&
cpu == max_busy_cpu);
i++;
}
}